目录
3. 在Fragment所依赖的 Activity中的activity.xml文件中调用
4.之后再创建三个Fragment,并且在他们的.xml文件上设置背景颜色
CardView
1. CardView的基本使用
CardView是用于实现卡片式布局效果的重要控件,实际上也是一个frameLayout,
只是额外提供了圆角和 阴影,看上去有立体效果。
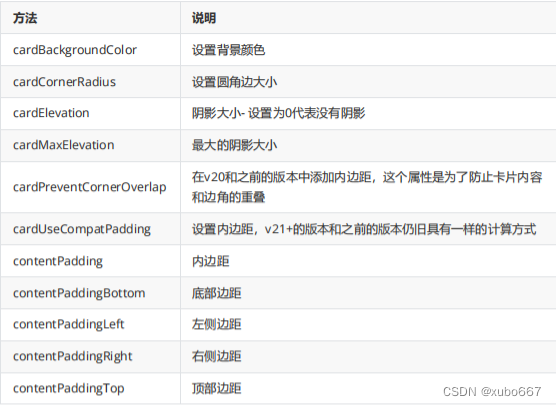
2.CardView常见的使用方法以及其说明
3.CardView与RecycleView的结合使用
1.主布局文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity3"
android:padding="5dp">
<androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView
android:id="@+id/rv_news"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
/>
</LinearLayout>2.子布局文件
这里运用到了CardView
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.cardview.widget.CardView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="150dp"
app:cardCornerRadius="4dp"
app:cardElevation="6dp"
android:layout_marginTop="5dp"
android:padding="5dp">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="150dp"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:padding="5dp">
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/iv_img"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="140dp"
app:srcCompat="@mipmap/touxiang1" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_name"
android:layout_marginStart="8dp"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_vertical"
android:text="TextView" />
</LinearLayout>
</androidx.cardview.widget.CardView>3.实体类
public class News {
private int imgID;
private String name;
public News(int imgID,String name){
this.name=name;
this.imgID=imgID;
}
public int getImgID() {
return imgID;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}4.适配器
public class NewsAdapter extends RecyclerView.Adapter<NewsAdapter.ViewHolder> {
List<News> list;
public NewsAdapter(List<News> list){
this.list=list;
}
@NonNull
@Override
public ViewHolder onCreateViewHolder(@NonNull ViewGroup parent, int viewType) {
View view= LayoutInflater.from(parent.getContext()).inflate(R.layout.news_item,parent,false);
ViewHolder viewHolder=new ViewHolder(view);
return viewHolder;
}
@Override
public void onBindViewHolder(@NonNull ViewHolder holder, int position) {
News news=list.get(position);
holder.iv_img.setImageResource(news.getImgID());
holder.tv_name.setText(news.getName());
}
@Override
public int getItemCount() {
return list.size();
}
public class ViewHolder extends RecyclerView.ViewHolder {
ImageView iv_img;
TextView tv_name;
public ViewHolder(@NonNull View itemView) {
super(itemView);
iv_img=itemView.findViewById(R.id.iv_img);
tv_name=itemView.findViewById(R.id.tv_name);
}
}
}5.在主活动中使用
public class MainActivity3 extends AppCompatActivity {
public String[] names={"你","好","啊","你","好","啊"};
public int[] imgs={R.mipmap.touxiang1,R.mipmap.touxiang2,
R.mipmap.touxiang3,R.mipmap.touxiang1,R.mipmap.touxiang2,R.mipmap.touxiang3,};
RecyclerView rv_news;
List<News> list=new ArrayList<>();
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main3);
rv_news=findViewById(R.id.rv_news);
initData();
NewsAdapter newsAdapter=new NewsAdapter(list);
LinearLayoutManager layoutManager=new LinearLayoutManager(this);
rv_news.setLayoutManager(layoutManager);
rv_news.setAdapter(newsAdapter);
}
private void initData() {
for (int i=0;i<names.length;i++){
News news=new News(imgs[i],names[i]);
list.add(news);
}
}
}Fragment
1.Fragment的简介
Fragment








 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章















 48
48











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








