c++String类详细介绍
write in front
作者:@ 不进大厂不改名
专栏:@ c++
作者简介:大一学生 希望能向其他大佬和同学学习!
本篇博客简介:讲述了c++中为什么要引入String类,以及String类的优点。
本章目标
1.String类的引入
2.String类的用法
3.熟练使用String类
学习并理解String类
1.String类的引入
为什么学习string类?
C语言中的字符串
C语言中,字符串是以’\0’结尾的一些字符的集合,为了操作方便,C标准库中提供了一些str系列的库函数,但是这些库函数与字符串是分离开的,不太符合OOP(指的是面向对象的编程)的思想,而且底层空间需要用户自己管理,稍不留神可能还会越界访问。
c++标准库中的String类
- 字符串是表示字符序列的类
- 标准的字符串类提供了对此类对象的支持,其接口类似于标准字符容器的接口,但添加了专门用于操作单字节字符字符串的设计特性。
- string类是使用char(即作为它的字符类型),使用它的默认char_traits和分配器类型(关于模板的更多信息,请参阅basic_string)。
- string类是basic_string模板类的一个实例,它使用char来实例化basic_string模板类,并用char_traits和allocator作为basic_string的默认参数.
- 注意,这个类独立于所使用的编码来处理字节:如果用来处理多字节或变长字符(如UTF-8)的序列,这个类的所有成员(如长度或大小)以及它的迭代器,将仍然按照字节(而不是实际编码的字符)来操作。
省流:
1. string是表示字符串的字符串类
2. 该类的接口与常规容器的接口基本相同,再添加了一些专门用来操作string的常规操作。
3. string在底层实际是:basic_string模板类的别,typedefbasic_string<char, char_traits, allocator>string;
4.不能操作多字节或者变长字符的序列。
下面我们将介绍String类常用的接口函数,这里就先一一列出了,等到后面一一介绍
2.String类的读写
访问方式:
1.下标访问
使用operator[]实现数组下标的访问
在这之前我们先初始化一个String类,看看它的长度
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1("hello world");
cout<< s1.size()<< endl;
return 0;
}
这一行代码的意思是创建一个string类并初始化赋值为hello world,这里的s1.size()是字符串长度(等价于s1.legth())。
我们开始用下标开始访问:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1("hello world");
//cout<< s1.size()<< endl;
for (int i = 0; i < s1.size(); i++)
{
cout << s1[i]<< ' ';
}
return 0;
}
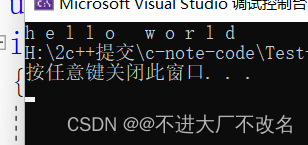
这里其实上等价于
cout << s1.operator[](i) << ' ';
2.使用at访问
cout << s1.at(i) << ' ';
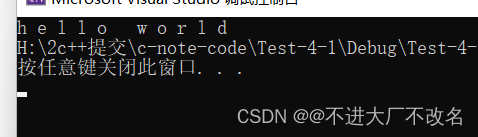
两种访问方式的区别
唯一的区别就是报错的时候
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1("hello world");
//cout<< s1.size()<< endl;
for (int i = 0; i < s1.size(); i++)
{
cout << s1.operator[](12) << ' ';
}
for (int i = 0; i < s1.size(); i++)
{
cout << s1.at(12) << ' ';
}
return 0;
}
下标访问报断言错误
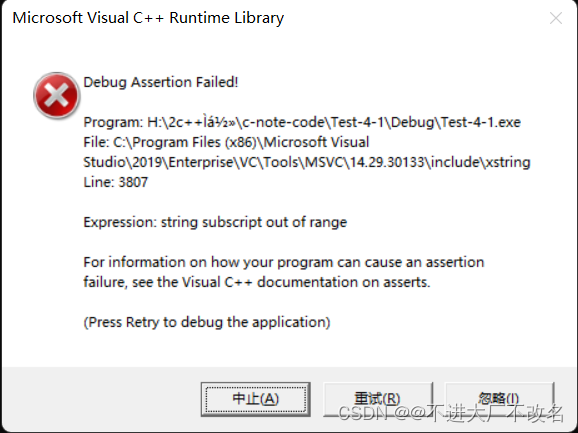
at访问抛出异常

迭代器读写
正向迭代器
语法:
string::iterator it=s.begin();
解析:这里先写个string类名后面跟上iterator(迭代器)后再跟一个it等于然后写上对象的begin()或者end()
我们先把它当作是指针处理就行:
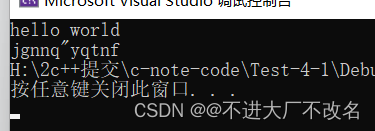
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1("hello world");
string::iterator it = s1.begin();
while (it != s1.end())
{
cout << *it;
it++;
}
cout << endl;
it = s1.begin();
while (it != s1.end())
{
*it += 2;
cout << *it;
it++;
}
return 0;
}
当然我们也可以对它进行修改
反向迭代器
语法:
string::reverse_iterator it=s1.rbegin();

我们发现是不是要使用迭代器很麻烦,这时候我们就应该想到之前学到的一个关键字auto是不是专门来解决这种问题的,所以上面的代码可以改为
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1("hello world");
auto it = s1.rbegin();
while (it != s1.rend())
{
cout << *it;
it++;
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
这里就可以学到一点我们可用学到的知识简化我们的工作,这也是创新的作用,让我们使用的东西越来越简单。
const正向迭代器
相比于一般的迭代器,就是权限缩小不能修改,只能读
这里就直接给代码了:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1("hello world");
string::const_iterator it = s1.begin();
while (it != s1.end())
{
cout << *it;
it++;
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
这样就不能修改了,如果发生修改,那肯定就会报错的
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1("hello world");
string::const_iterator it = s1.begin();
while (it != s1.end())
{
*it++;
cout << *it;
it++;
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
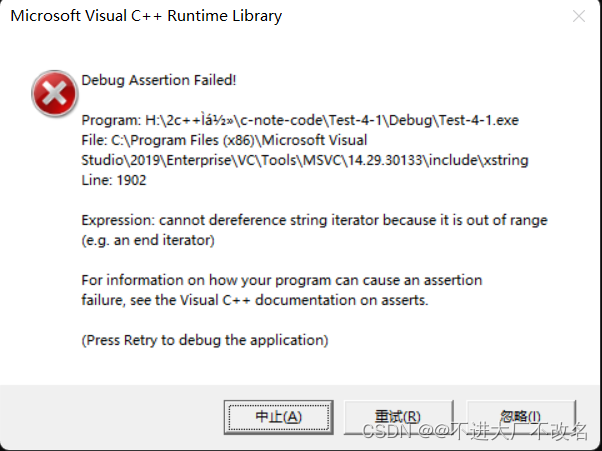
const反向迭代器
这个和正向的差不多,就不多介绍了
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1("hello world");
string::const_reverse_iterator it = s1.rbegin();
while (it != s1.rend())
{
cout << *it;
it++;
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
3.String类的构造函数
string类对象的常见构造函数
| 函数名称 | 功能说明 |
|---|---|
| string()重点 | -----构造空string类对象,即空字符 |
| string(const char* s) (重点) | 用C-string来构造string类对象 |
| string(size_t n, char c) | string类对象中包含n个字符c |
| string(const string&s) (重点) | 拷贝构造函数 |
在这里只讲解三个重点构造函数
无参构造
string s;
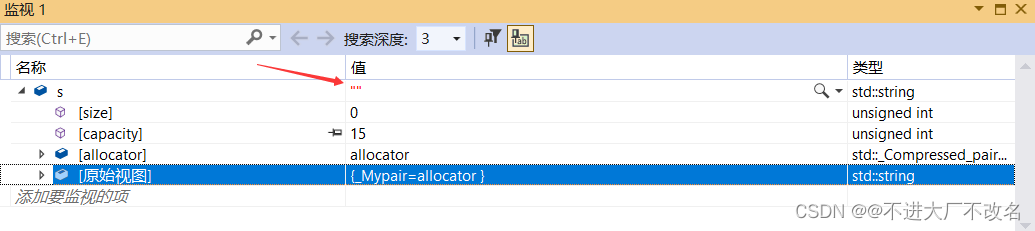
这就是一个空字符了。
有参构造
string s("hello world");
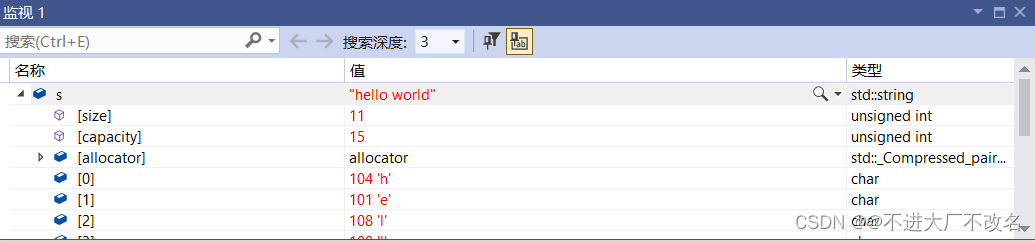
这里发现字符串的长度变成11,然后字符串里的内容变成了hello world.
拷贝构造
string s("hello world");
string s1(s);
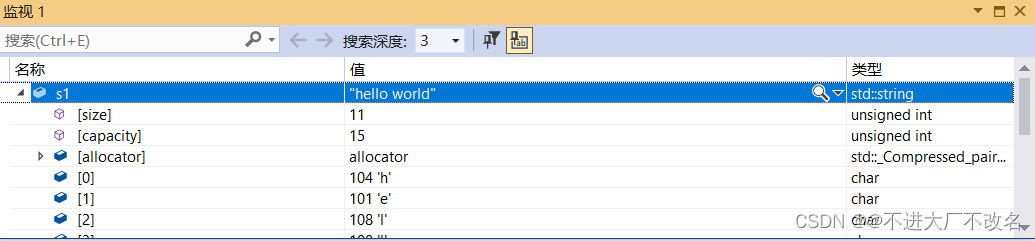
s1也变成了hello world
4.String类容量接口函数
| 函数名称 | 功能说明 |
|---|---|
| size(重点) | 返回字符串有效字符长度 |
| length | 返回字符串有效字符长度 |
| capacity | 返回空间总大小 |
| empty | (重点) 检测字符串释放为空串,是返回true,否则返回false |
| clear | (重点) 清空有效字符 |
| reserve | (重点) 为字符串预留空间 |
| resize | (重点) 将有效字符的个数该成n个,多出的空间用字符c填充 |
这里也向上面那样我们挑重点的介绍
size
计算字符串长度
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s("hello world");
cout<<s.size();
return 0;
}
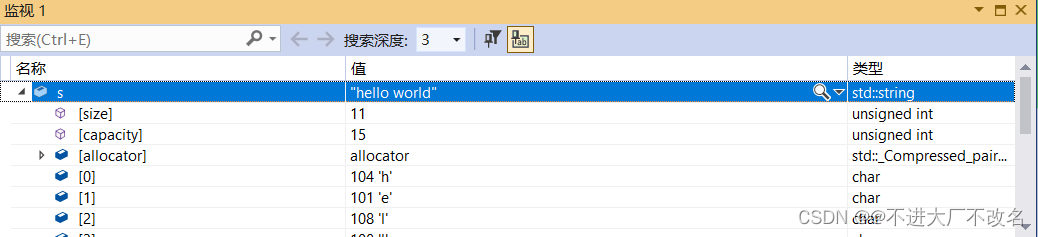
我们可以发现输出的是11,我们发现这是把debug的值返回
empty
判断是否为空
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s("hello world");
string s1;
cout << s.empty()<<endl;
cout << s1.empty()<<endl;
return 0;
}

clear
清空字符串,可以用empty进行检测
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s("hello world");
s.clear();
cout << s.empty()<<endl;
return 0;
}
reserve
这个函数用于预先开辟空间,因为每当字符串长度大于容量时就会扩容。所以如果我们知道所需要的空间大小是多少就可以使用这个函数了。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s("hello world");
s.reserve(1000);
return 0;
}
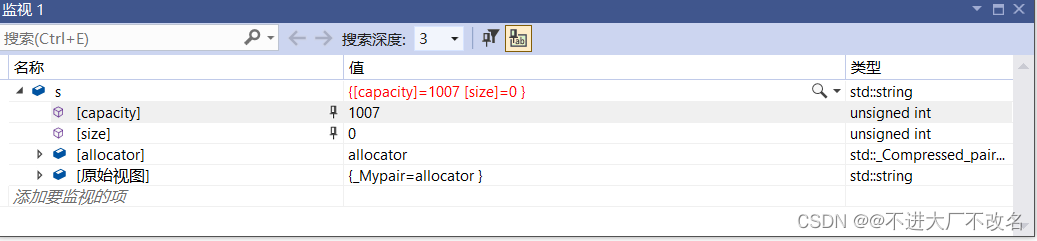
我们发现空间变成了1007(因为是按照1.5倍开辟空间的)
resize
使用它可以改变size的大小,如果我们size的大小大于字符串本身大小,size后面就会以‘\0结尾’。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s("hello world");
s.resize(50);
return 0;
}
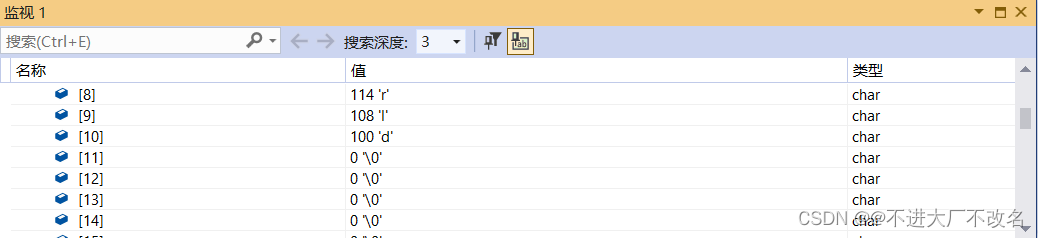
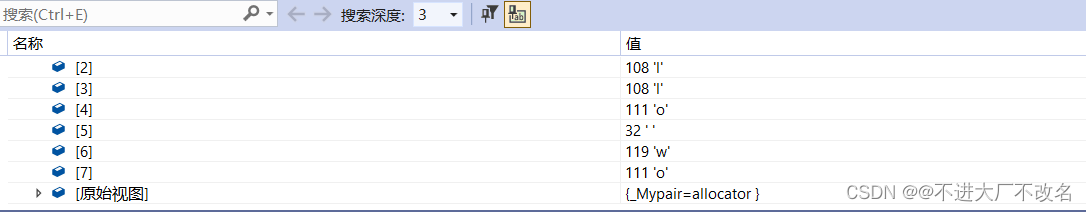
假如resize的大小小于字符串的大小,那么后面的字符就被截断了。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s("hello world");
s.resize(8);
return 0;
}
5.String类对象修改接口
| 函数名称 | 功能说明 |
|---|---|
| push_back | 在字符串后尾插字符c |
| append | 在字符串后追加一个字符串 |
| operator+= (重点) | 在字符串后追加字符串str |
| insert | 在pos位置插入 |
| erase | 在pos位置删除 |
| assign | 对原有字符串清空后赋值 |
| replace | 替换 |
push_back和attend很简单就理解一下就行了。(这里不给予代码和演示)
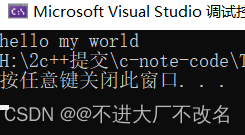
+=
在后面最佳字符串
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s("hello world");
s += "xxxx";
cout << s;
return 0;
}

replace
替换
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1("hello the world");
string s2("the");
string key("my");
int pos = s1.find(s2);
s1.replace(pos, s2.size(), key);
cout << s1;
return 0;
}
intsert(不太常用)
插入
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string str = "hello world";
string str2 = "the";
string str3 = "it is so sad now";
//s.insert(pos,n,b) 在字符串s的pos位置的后面插入n个字符b
str.insert(6, 4, 'b'); // str = "hello bbbbworld"
cout << str<<endl;
//s.insert(pos,str) 在字符串s的pos位置后面插入字符串str
str.insert(6, str2); // str = "hello theworld"
cout <<str<<endl;
//s.insert(pos,str,a,n) 在字符串s的pos位置插入字符串str中位置a到后面的n个字符
str.insert(6, str3, 6,10); // str = "hello so sad nowworld"
cout << str << endl;
//s.insert(pos,cstr,n) 在字符串s的pos位置插入字符数组cstr从开始到后面的n个字符
str.insert(6, str3, 9); // str = "hello sad nowworld"
cout << str << endl;
return 0;
}
assign
这里我们可以将这个操作符理解成清空赋值
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cstddef>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1 = "hello world";
string s2 = "welcome to my world";
s1.assign("hello");
cout << s1 << endl;
s1.assign(s2);
cout << s1 << endl;
s1.assign(s2, 5, 5);
cout << s1 << endl;
return 0;
}
erase
它同样也有三种使用方法(删除)
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cstddef>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1 = "hello world";
string s2 = "welcome to my world";
s1.erase();
cout << s1 << endl;
s1 = "hello world";
s1.erase(0, 3);
cout << s1 << endl;
s1 = "hello world";
s1.erase(3);
cout << s1 << endl;
return 0;
}
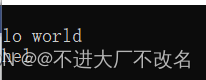
reverse
我们这里可以将整个字符串反转
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cstddef>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1 = "hello world";
string s2 = "welcome to my world";
reverse(s1.begin(), s1.end());
cout << s1 << endl;
return 0;
}

6.String类字符串运算的接口
| 函数名称 | 功能说明 |
|---|---|
| c_str(重点) | 返回C格式字符串 |
| find + npos(重点) | 从字符串pos位置开始往后找字符c,返回该字符在字符串中的位置 |
| rfind | 从字符串pos位置开始往前找字符c,返回该字符在字符串中的位置 |
| getline | (重点)获取一行字符串 |
c_str
使用这个函数的时候返回的是一个字符串
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s("hello world");
cout << s.c_str();
return 0;
}
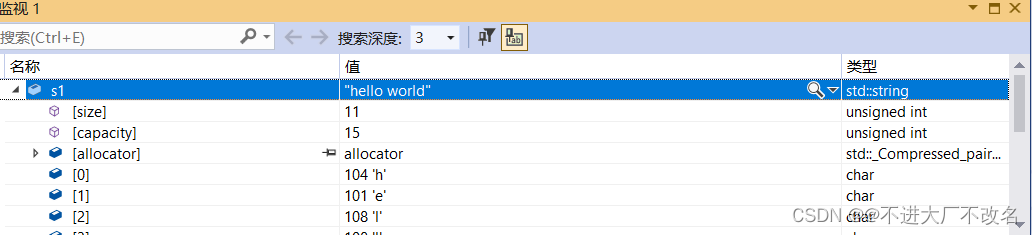
发现这里的两个类型明显不同
一个是string对象
一个是空符指针(也就是字符串)
find
这里的find有四种用法
第一种 (最常用)
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cstddef>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1 = "hello the world";
string key = "the";
int pos = s1.find(key);
cout << pos << endl;
return 0;
}
这里的"the"第一次是在第6个位置出现,所以pos是6
如果查找一个不存在的字符呢?
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cstddef>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1 = "hello the world";
string key = "the";
//int pos = s1.find(key);
int pos1 = s1.find('wl');
cout << pos1 << endl;
return 0;
}

实际上是找最后一个字符的位置(如果找不到就返回-1)
假如我们要从某个位置找到某个位置呢?
只要在后面加上范围就行
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cstddef>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1 = "hello the world";
string key = "the";
//int pos = s1.find(key);
int pos1 = s1.find(key,7);
cout << pos1 << endl;
return 0;
}
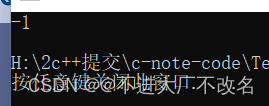
最后一种不常用
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cstddef>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1 = "hello the world";
//string key = "the";
//int pos = s1.find(key);
int pos1 = s1.find("the", 0, 2);
cout << pos1 << endl;
return 0;
}
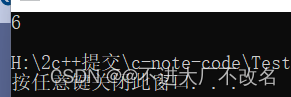
查找"the"从0这个位置开始,查找这个字符串的2个字符(“th”)
substr
得到pos位置后面n个字符组成的字符串
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cstddef>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1 = "hello the world";
string s2 = s1.substr(5);//第五个往后的字符串
string s3 = s1.substr();//全部字符串
string s4 = s1.substr(5, 2);//第五个后面2个
cout << s2 << endl;
cout << s3 << endl;
cout << s4 << endl;
return 0;
}
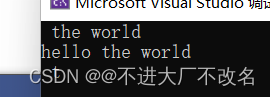
getline
得到一整行的数
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cstddef>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1 = "hello the world";
getline(cin, s1);
cout << s1;
return 0;
}
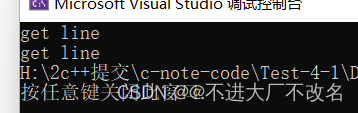
7.String类的运用
题目一
https://baidu.com/string/find
我们如果得到上面的字符串
要我们获得上面的三个部分
1.前面的https
2.域名
3.地址
首先先看怎么解决第一个问题
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s("https://baidu.com/string/find");
int pos = s.find(":");
string s1 = s.substr(0, pos);
cout << s1;
return 0;
}
首先我们先找到:,然后获得从第一个字符到冒号前的字符就可以
接下来解决第二个问题
int pos1 = s.find('/', pos + 3);
string s2 = s.substr(pos + 3, pos1 - pos - 3);
cout <<s2;
我们找到第三个‘/’既可以确定范围了,因此要跳过前两个‘/’,在计算域名的字符串的长度就可以了
最后解决第三个问题
string s3 = s.substr(pos1 + 1);
cout << s3;
直接从pos2的后一个位置开始就行
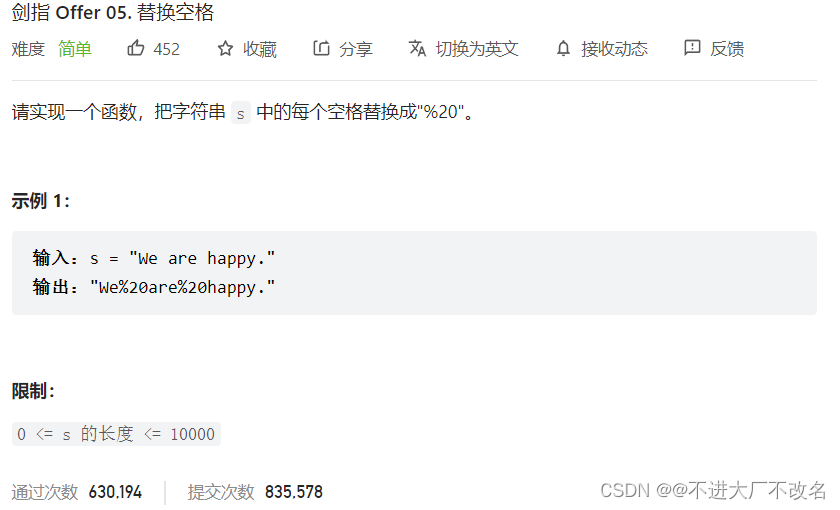
题目二
class Solution {
public:
string replaceSpace(string s) {
int pos=s.find(' ');
while(pos!=-1)
{
s.replace(pos,1,"%20");
pos=s.find(' ');
}
return s;
}
};
题目三
字符串最后一个单词的长度
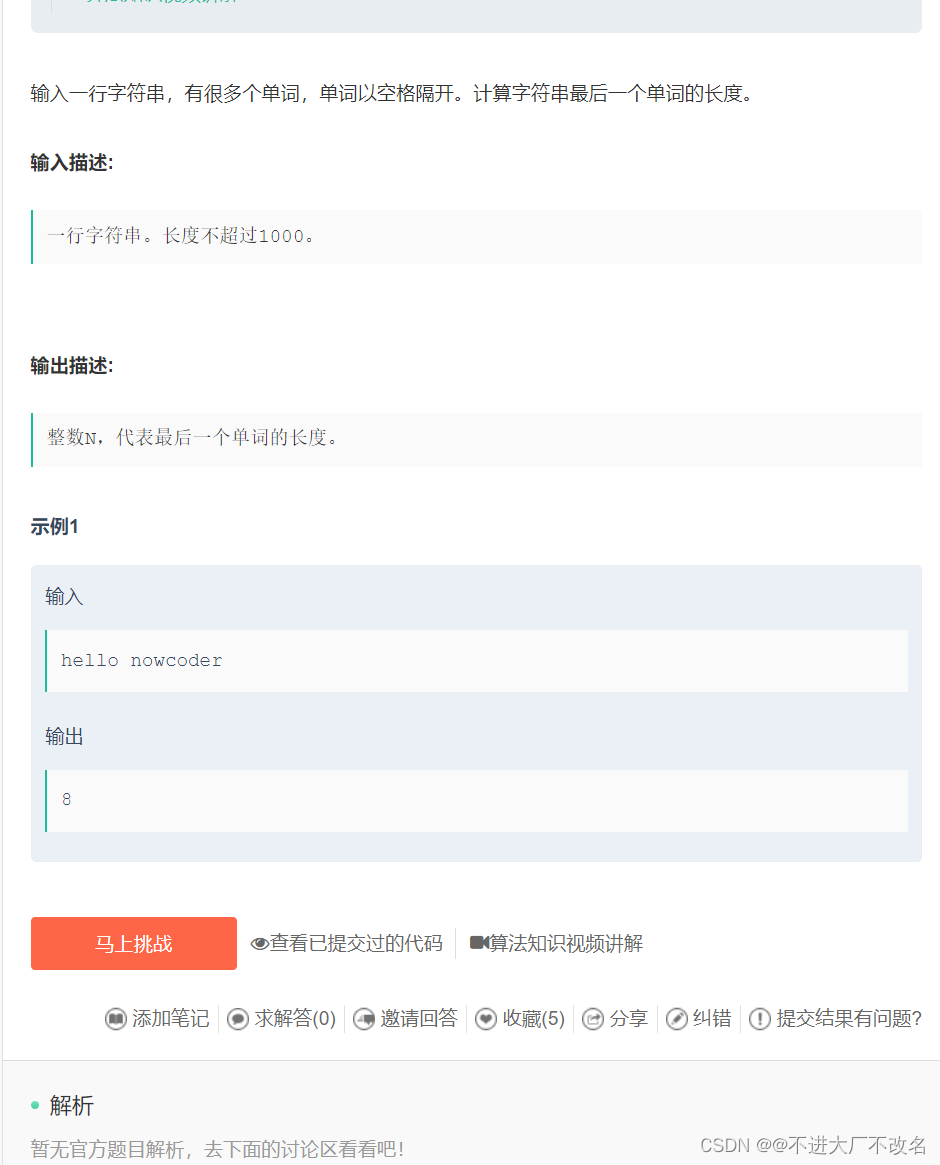
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string s;
getline(cin,s);
int pos=s.rfind(' ');
string s1=s.substr(pos+1);
cout<<s1.size();
}
我们发现学习做上面的题是不是变得很简单了(在使用了string类后),这就是我们学习STL的原因。






















 2535
2535











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








