目录
一、Glide几个基本概念
-
Model
表示数据的来源;加载图片的时候需要告诉Glide从哪获取这个图片,可以是url类型、本地文件类型、资源ID类型。不管什么类型,Glide都将其称为Model。 -
Data
从数据源中获取到model之后,把它加工成原始数据,一般就是InputStream输入流,Glide把 它们称之为Data。负责从数据源中获取原始数据的功能角色称之为ModelLoader。 -
Resource
负责将得到的原始数据进行解码,比如将InputStream解码成bitmap,而解码之后的资源称之为Resource。而负责解码的功能角色称之为Decoder。 -
TransformedResource
把Resouce进行变换,比如图片要进行裁剪,调用fitcenter、centerCrop等等方法转换,在Glide方法中采用Resource Transform功能来进行转换,而转换后的资源就称之为TransformedResource。 -
TranscodedResource
转码,Glide不仅能加载静态图之外,还能加载Gif动态图,但是解码之后的bitmap和gif drawable其实类型都是统一的,为了逻辑方便处理,Glide会把bitmap转换成GlideBitmapDrawable,这样类型就统一了,负责转码的角色称为Transcode,而转码之后的角色称为TranscodedResource -
Target
最终将图片显示到目标上,比如ImageView上,这时候Glide就会将要显示的目标封装成Target。

二、Glide基本使用和参数说明:
Glide.with(getApplicationContext()) //指定Context
.load(url) //指定图片的URL
.placeholder(R.mipmap.ic_launcher) //指定图片未成功加载前显示的图片
.error(R.mipmap.ic_launcher) //指定图片加载失败显示的图片
.override(300, 300) //指定图片的尺寸
.fitCenter() //指定图片缩放类型
.centerCrop() //指定图片缩放类型
.skipMemoryCache(true) //跳过内存缓存,默认为false
.crossFade(1000) //设置渐变式显示的时间
.diskCacheStrategy(DiskCacheStrategy.NONE) //表示不缓存任何内容,跳过磁盘缓存
.diskCacheStrategy(DiskCacheStrategy.DATA) //表示只缓存原始图片,即只缓存原来的全分辨率的图片
.diskCacheStrategy(DiskCacheStrategy.RESOURCE) //表示只缓存转换后的图片
.diskCacheStrategy(DiskCacheStrategy.ALL) //表示即缓存原始图片,也缓存转换过后的图片
.diskCacheStrategy(DiskCacheStrategy.AUTOMATIC) //表示让Glide根据图片资源智能地选择使用哪一种缓存策略(默认选项)
.priority(Priority.HIGH) //指定优先级,Glide将会用他们作为一个准则,并尽可能的处理这些请求,但是它不一定能百分之百保证所有的图片都按照你优先级来加载
.into(imageView); //指定显示图片的ImageView
1. with流程解析
with流程时序图:

(1) 生命周期的作用域(Application、Activity、Fragment)
这里笼统将作用域划为:
- 第一种为Application作用域,它的生命周期是全局的,不创建空白Fragment绑定Activity/Fragment
- 第二种非Application作用域(Activity/Fragment),专门创建一个空白Fragment绑定Activity/Fragment
Glide.java
/**
* Begin a load with Glide by passing in a context.
*
* <p> Any requests started using a context will only have the application level options applied
* and will not be started or stopped based on lifecycle events. In general, loads should be
* started at the level the result will be used in. If the resource will be used in a view in a
* child fragment, the load should be started with {@link #with(android.app.Fragment)}} using that
* child fragment. Similarly, if the resource will be used in a view in the parent fragment, the
* load should be started with {@link #with(android.app.Fragment)} using the parent fragment. In
* the same vein, if the resource will be used in a view in an activity, the load should be
* started with {@link #with(android.app.Activity)}}. </p>
*
* <p> This method is appropriate for resources that will be used outside of the normal fragment
* or activity lifecycle (For example in services, or for notification thumbnails). </p>
*
* @param context Any context, will not be retained.
* @return A RequestManager for the top level application that can be used to start a load.
* @see #with(android.app.Activity)
* @see #with(android.app.Fragment)
* @see #with(android.support.v4.app.Fragment)
* @see #with(android.support.v4.app.FragmentActivity)
*/
@NonNull
public static RequestManager with(@NonNull Context context) {
return getRetriever(context).get(context);
}
/**
* Begin a load with Glide that will be tied to the given {@link android.app.Activity}'s lifecycle
* and that uses the given {@link Activity}'s default options.
*
* @param activity The activity to use.
* @return A RequestManager for the given activity that can be used to start a load.
*/
@NonNull
public static RequestManager with(@NonNull Activity activity) {
return getRetriever(activity).get(activity);
}
/**
* Begin a load with Glide that will tied to the give
* {@link android.support.v4.app.FragmentActivity}'s lifecycle and that uses the given
* {@link android.support.v4.app.FragmentActivity}'s default options.
*
* @param activity The activity to use.
* @return A RequestManager for the given FragmentActivity that can be used to start a load.
*/
@NonNull
public static RequestManager with(@NonNull FragmentActivity activity) {
return getRetriever(activity).get(activity);
}
/**
* Begin a load with Glide that will be tied to the given
* {@link android.support.v4.app.Fragment}'s lifecycle and that uses the given
* {@link android.support.v4.app.Fragment}'s default options.
*
* @param fragment The fragment to use.
* @return A RequestManager for the given Fragment that can be used to start a load.
*/
@NonNull
public static RequestManager with(@NonNull Fragment fragment) {
return getRetriever(fragment.getActivity()).get(fragment);
}
/**
* Begin a load with Glide that will be tied to the given {@link android.app.Fragment}'s lifecycle
* and that uses the given {@link android.app.Fragment}'s default options.
*
* @param fragment The fragment to use.
* @return A RequestManager for the given Fragment that can be used to start a load.
* @deprecated Prefer support Fragments and {@link #with(Fragment)} instead,
* {@link android.app.Fragment} will be deprecated. See
* https://github.com/android/android-ktx/pull/161#issuecomment-363270555.
*/
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
@Deprecated
@NonNull
public static RequestManager with(@NonNull android.app.Fragment fragment) {
return getRetriever(fragment.getActivity()).get(fragment);
}
/**
* Begin a load with Glide that will be tied to the lifecycle of the {@link Fragment},
* {@link android.app.Fragment}, or {@link Activity} that contains the View.
*
* <p>A {@link Fragment} or {@link android.app.Fragment} is assumed to contain a View if the View
* is a child of the View returned by the {@link Fragment#getView()}} method.
*
* <p>This method will not work if the View is not attached. Prefer the Activity and Fragment
* variants unless you're loading in a View subclass.
*
* <p>This method may be inefficient aways and is definitely inefficient for large hierarchies.
* Consider memoizing the result after the View is attached or again, prefer the Activity and
* Fragment variants whenever possible.
*
* <p>When used in Applications that use the non-support {@link android.app.Fragment} classes,
* calling this method will produce noisy logs from {@link android.app.FragmentManager}. Consider
* avoiding entirely or using the {@link Fragment}s from the support library instead.
*
* <p>If the support {@link FragmentActivity} class is used, this method will only attempt to
* discover support {@link Fragment}s. Any non-support {@link android.app.Fragment}s attached
* to the {@link FragmentActivity} will be ignored.
*
* @param view The view to search for a containing Fragment or Activity from.
* @return A RequestManager that can be used to start a load.
*/
@NonNull
public static RequestManager with(@NonNull View view) {
return getRetriever(view.getContext()).get(view);
}
with()方法参数可以为Context、Activity、FragmentActivity、Fragment、View。with设计了这么多重装方法就是为了可以灵活根据当前的上下文和组件进行不同图片的操作选择。将图片加载的过程与组件的生命周期进行挂钩。
下面以参数为FragmentActivity进行流程阐述:
Glide.java
@NonNull
public static RequestManager with(@NonNull FragmentActivity activity) {
return getRetriever(activity).get(activity);
}
getRetriever(activity)是获取RequestManagerRetriever对象
RequestManagerRetriever.java
@NonNull
public RequestManager get(@NonNull FragmentActivity activity) {
if (Util.isOnBackgroundThread()) { // ①
return get(activity.getApplicationContext());
} else { // ②
assertNotDestroyed(activity);
FragmentManager fm = activity.getSupportFragmentManager();
return supportFragmentGet(activity, fm, /*parentHint=*/ null, isActivityVisible(activity));
}
}
如果当前是后台线程(即子线程)就走流程①,否则走流程②。
- 流程①最后是通过getApplicationManager(context)语句DCL单例模式来获取RequestManager对象。
- 流程②
SupportRequestManagerFragment 是一种没有UI界面的fragment
glide添加一种没有界面的fragment到Activity或fragment上,通过这种没有界面SupportRequestManagerFragment 的这个fragment来监听activity或fragment的生命周期,因为glide是无法监听activity的生命周期,从而来完成绑定activity的生命周期,来去选择完成图片加载操作的过程。
这里参数为context的get()方法需要注意下:
RequestManagerRetriever.java
@NonNull
public RequestManager get(@NonNull Context context) {
if (context == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("You cannot start a load on a null Context");
} else if (Util.isOnMainThread() && !(context instanceof Application)) {
// FragmentActivity
if (context instanceof FragmentActivity) {
return get((FragmentActivity) context);
// Activity
} else if (context instanceof Activity) {
return get((Activity) context);
} else if (context instanceof ContextWrapper
// Only unwrap a ContextWrapper if the baseContext has a non-null application context.
// Context#createPackageContext may return a Context without an Application instance,
// in which case a ContextWrapper may be used to attach one.
&& ((ContextWrapper) context).getBaseContext().getApplicationContext() != null) {
return get(((ContextWrapper) context).getBaseContext()); // 递归再次查找
}
}
// Application 若上面的判定都不满足,就会执行下面的这句代码,会调用到Application作用域处理区域
return getApplicationManager(context);
}
RequestManagerRetriever.java
@NonNull
private RequestManager getApplicationManager(@NonNull Context context) {
// Either an application context or we're on a background thread.
if (applicationManager == null) {
synchronized (this) {
if (applicationManager == null) {
// Normally pause/resume is taken care of by the fragment we add to the fragment or
// activity. However, in this case since the manager attached to the application will not
// receive lifecycle events, we must force the manager to start resumed using
// ApplicationLifecycle.
// TODO(b/27524013): Factor out this Glide.get() call.
Glide glide = Glide.get(context.getApplicationContext());
applicationManager =
factory.build(
glide,
new ApplicationLifecycle(), //调用是Application作用域对应的生命周期
new EmptyRequestManagerTreeNode(),
context.getApplicationContext());
}
}
}
return applicationManager;
}
除了子线程会走Application作用域,主线程with()传的参数是SeviceContext和ApplicationContext也会走到Application作用域,不会创建一个空白的Fragment去监听,对应的是ApplicationLifecycle生命周期;其他的都是走非Application作用域,会创建一个空白的Fragment去监听Activity/Fragment/FragmentActivity,对应的是ActivityFragmentLifecycle生命周期。
(2)生命周期的绑定
通过RequestManager就可以控制整个界面生命周期的监听,用于监听整个组件的生命周期,根据这个生命周期来做图片的相应操作。
RequestManagerFragment 与 RequestManager是一 一对应的
下面的supportFragmentGet()方法必须在主线程执行,因为子线程不可能调用到这里来
RequestManagerRetriever.java
@NonNull
private RequestManager supportFragmentGet(
@NonNull Context context,
@NonNull FragmentManager fm,
@Nullable Fragment parentHint,
boolean isParentVisible) {
// 1.从FragmentManager 中获取 SupportRequestManagerFragment
SupportRequestManagerFragment current =
getSupportRequestManagerFragment(fm, parentHint, isParentVisible);
// 2.从该Fragment中获取RequestManager
RequestManager requestManager = current.getRequestManager();
// 3.首次获取,则实例化 RequestManager
if (requestManager == null) {
// TODO(b/27524013): Factor out this Glide.get() call.
// 3.1 实例化
Glide glide = Glide.get(context);
requestManager =
factory.build(
glide, current.getGlideLifecycle(), current.getRequestManagerTreeNode(), context);
// 3.2 设置 Fragment 对应的 RequestManager
// 将SupportRequestManagerFragment这个空界面的fragment与RequestManager图片加载进行绑定,目的就是为了将监听activity生命周期的来管理整个图片加载
current.setRequestManager(requestManager);
}
return requestManager;
}
Activity和Fragment都会调用supportFragmentGet()来获得RequestManager
getSupportRequestManagerFragment()函数分析:
RequestManagerRetriever.java
// pendingRequestManagerFragments用于【记录保存】 FragmentManager--RequestManagerFragment 的映射关系
@VisibleForTesting
final Map<android.app.FragmentManager, RequestManagerFragment> pendingRequestManagerFragments =
new HashMap<>();
// pendingSupportRequestManagerFragments 用于【记录保存】 FragmentManager--SupportRequestManagerFragment 的映射关系
@VisibleForTesting
final Map<FragmentManager, SupportRequestManagerFragment> pendingSupportRequestManagerFragments =
new HashMap<>();
// 从 FragmentManager 中获取 SupportRequestManagerFragment
@NonNull
private SupportRequestManagerFragment getSupportRequestManagerFragment(
@NonNull final FragmentManager fm, @Nullable Fragment parentHint, boolean isParentVisible) {
// 1.1 尝试获取 FRAGMENT_TAG 对应的 Fragment
SupportRequestManagerFragment current =
(SupportRequestManagerFragment) fm.findFragmentByTag(FRAGMENT_TAG);
if (current == null) {
// 1.2 尝试从临时记录中获取 Fragment
current = pendingSupportRequestManagerFragments.get(fm);
// 1.3 实例化 Fragment
if (current == null) {
// 1.3.1 创建对象
current = new SupportRequestManagerFragment();
current.setParentFragmentHint(parentHint);
// 1.3.2 如果父层可见,则调用 onStart() 生命周期
if (isParentVisible) {
current.getGlideLifecycle().onStart();
}
// 1.3.3 临时记录映射关系
pendingSupportRequestManagerFragments.put(fm, current);
// 1.3.4 提交 Fragment 事务
fm.beginTransaction().add(current, FRAGMENT_TAG).commitAllowingStateLoss();
// 1.3.5 post 一个消息
handler.obtainMessage(ID_REMOVE_SUPPORT_FRAGMENT_MANAGER, fm).sendToTarget();
}
}
return current;
}
post 一个消息分析:
RequestManagerRetriever.java
@Override
public boolean handleMessage(Message message) {
boolean handled = true;
Object removed = null;
Object key = null;
switch (message.what) {
case ID_REMOVE_FRAGMENT_MANAGER:
android.app.FragmentManager fm = (android.app.FragmentManager) message.obj;
key = fm;
removed = pendingRequestManagerFragments.remove(fm);
break;
case ID_REMOVE_SUPPORT_FRAGMENT_MANAGER:
// 移除临时记录中的映射关系
FragmentManager supportFm = (FragmentManager) message.obj;
key = supportFm;
removed = pendingSupportRequestManagerFragments.remove(supportFm);
break;
default:
handled = false;
break;
}
if (handled && removed == null && Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.WARN)) {
Log.w(TAG, "Failed to remove expected request manager fragment, manager: " + key);
}
return handled;
}
上面supportFragmentGet()之后的流程重点关心下面三点:
- 从FragmentManager 中获取SupportRequestManagerFragment;
- 从该Fragment中获取RequestManager;
- 首次获取,则实例化RequestManager,后续从同一个SupportRequestManagerFragment中都获取的是这个RequestManager;
整个的关键核心在getSupportRequestManagerFragment函数:
第一步:尝试获取FRAGMENT_TAG对应的Fragment
第二步:尝试从临时记录中获取Fragment
第三步:实例化Fragment
- 1)创建对象
- 2)如果父层可见,则调用onStart()生命周期
- 3)临时记录映射关系
- 4)提交Fragment事务
- 5)post一个消息
- 6)移除临时记录中的映射关系
在提交Fragment事务之前,为什么需要先保存记录?
就是为了避免SupportRequestManagerFragment 在一个作用域中重复创建。因为commitAllowingStateLoss()是将事务post到消息队列中的,也就是说,事务是异步处理的,而不是同步处理的,假如没有临时保存记录,一旦在事务异步等待执行时调用了Glide.with(…),就会在该作用域中重复创建Fragment。
(3)生命周期的监听机制
从上面我们已经明白框架为每个Activity 和 Fragment作用域创建了一个无UI的Fragment,现在我们来分析Glide如何监听这个无界面Fragment的生命周期的。
SupportRequestManagerFragemt.java
private final ActivityFragmentLifecycle lifecycle;
public SupportRequestManagerFragment() {
this(new ActivityFragmentLifecycle());
}
@VisibleForTesting
@SuppressLint("ValidFragment")
public SupportRequestManagerFragment(@NonNull ActivityFragmentLifecycle lifecycle) {
this.lifecycle = lifecycle;
}
@NonNull
ActivityFragmentLifecycle getGlideLifecycle() {
return lifecycle;
}
@Override
public void onStart() {
super.onStart();
lifecycle.onStart();
}
@Override
public void onStop() {
super.onStop();
lifecycle.onStop();
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
lifecycle.onDestroy();
unregisterFragmentWithRoot();
}
在执行supportFragmentGet()方法体中会进行RequestManager实例化操作。
RequestManagerRetriever.java
// 实例化 RequestManager
Glide glide = Glide.get(context);
requestManager =
factory.build(
glide, current.getGlideLifecycle(), current.getRequestManagerTreeNode(), context);
RequestManagerRetriever.java
// RequestManager工厂接口
public interface RequestManagerFactory {
@NonNull
RequestManager build(
@NonNull Glide glide,
@NonNull Lifecycle lifecycle,
@NonNull RequestManagerTreeNode requestManagerTreeNode,
@NonNull Context context);
}
// 默认 RequestManager 工厂接口实现类
private static final RequestManagerFactory DEFAULT_FACTORY =
new RequestManagerFactory() {
@NonNull
@Override
public RequestManager build(
@NonNull Glide glide,
@NonNull Lifecycle lifecycle,
@NonNull RequestManagerTreeNode requestManagerTreeNode,
@NonNull Context context) {
return new RequestManager(glide, lifecycle, requestManagerTreeNode, context);
}
};
RequestManager.java
public RequestManager(
@NonNull Glide glide,
@NonNull Lifecycle lifecycle,
@NonNull RequestManagerTreeNode treeNode,
@NonNull Context context) {
this(
glide,
lifecycle,
treeNode,
new RequestTracker(),
glide.getConnectivityMonitorFactory(),
context);
}
// Our usage is safe here.
@SuppressWarnings("PMD.ConstructorCallsOverridableMethod")
RequestManager(
Glide glide,
Lifecycle lifecycle,
RequestManagerTreeNode treeNode,
RequestTracker requestTracker,
ConnectivityMonitorFactory factory,
Context context) {
this.glide = glide;
this.lifecycle = lifecycle;
this.treeNode = treeNode;
this.requestTracker = requestTracker;
this.context = context;
connectivityMonitor =
factory.build(
context.getApplicationContext(),
new RequestManagerConnectivityListener(requestTracker));
// If we're the application level request manager, we may be created on a background thread.
// In that case we cannot risk synchronously pausing or resuming requests, so we hack around the
// issue by delaying adding ourselves as a lifecycle listener by posting to the main thread.
// This should be entirely safe.
if (Util.isOnBackgroundThread()) {
mainHandler.post(addSelfToLifecycle);
} else {
lifecycle.addListener(this); // 添加监听
}
lifecycle.addListener(connectivityMonitor);
defaultRequestListeners =
new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>(glide.getGlideContext().getDefaultRequestListeners());
setRequestOptions(glide.getGlideContext().getDefaultRequestOptions());
glide.registerRequestManager(this);
}
@Override
public synchronized void onDestroy() {
targetTracker.onDestroy();
for (Target<?> target : targetTracker.getAll()) {
clear(target);
}
targetTracker.clear();
requestTracker.clearRequests();
lifecycle.removeListener(this); // 移除监听
lifecycle.removeListener(connectivityMonitor);
mainHandler.removeCallbacks(addSelfToLifecycle);
glide.unregisterRequestManager(this);
}
从上面代码可以看到,实例化RequestManagr时需要应给Lifecycle对象,这个对象是在无界面Fragment中创建的,当Fragment的生命周期变化时,就是通过这个Lifecycle对象将事件分发到RequestManager。
(4) 生命周期的回调
RequestManager收到生命周期回调后的处理:
LifecycleListener.java
public interface LifecycleListener {
/**
* Callback for when {@link android.app.Fragment#onStart()}} or {@link
* android.app.Activity#onStart()} is called.
*/
void onStart();
/**
* Callback for when {@link android.app.Fragment#onStop()}} or {@link
* android.app.Activity#onStop()}} is called.
*/
void onStop();
/**
* Callback for when {@link android.app.Fragment#onDestroy()}} or {@link
* android.app.Activity#onDestroy()} is called.
*/
void onDestroy();
}
回调相关的源码分析:
- Activity/Fragment 不可见时暂停请求
onStop()调用函数 - Activity/Fragment 可见时恢复请求
onStart()调用函数 - Activity/Fragment 销毁时销毁请求
onDestroy()调用函数
RequestManager.java
public class RequestManager
implements ComponentCallbacks2, LifecycleListener, ModelTypes<RequestBuilder<Drawable>> {
private final RequestTracker requestTracker;
// onStart()时恢复任务(页面可见)
@Override
public synchronized void onStart() {
resumeRequests();
targetTracker.onStart();
}
// onStop()时暂停任务(页面不可见)
@Override
public synchronized void onStop() {
pauseRequests();
targetTracker.onStop();
}
// onDestroy()时销毁任务(页面销毁)
@Override
public synchronized void onDestroy() {
targetTracker.onDestroy();
for (Target<?> target : targetTracker.getAll()) {
clear(target);
}
targetTracker.clear();
requestTracker.clearRequests();
lifecycle.removeListener(this);
lifecycle.removeListener(connectivityMonitor);
mainHandler.removeCallbacks(addSelfToLifecycle);
glide.unregisterRequestManager(this);
}
public synchronized void resumeRequests() {
requestTracker.resumeRequests();
}
public synchronized void pauseRequests() {
requestTracker.pauseRequests();
}
}
Glide生命周期大致描述:
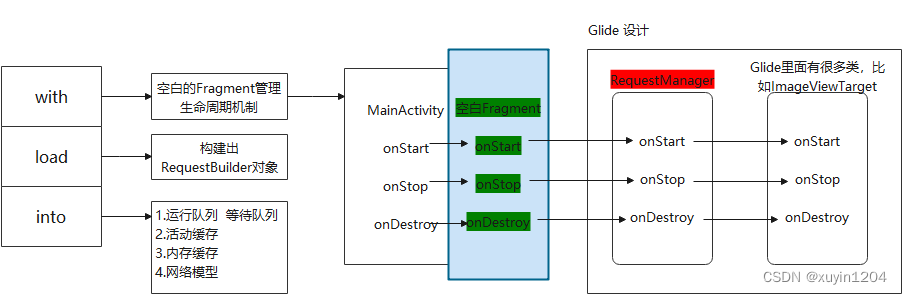
生命周期机制:
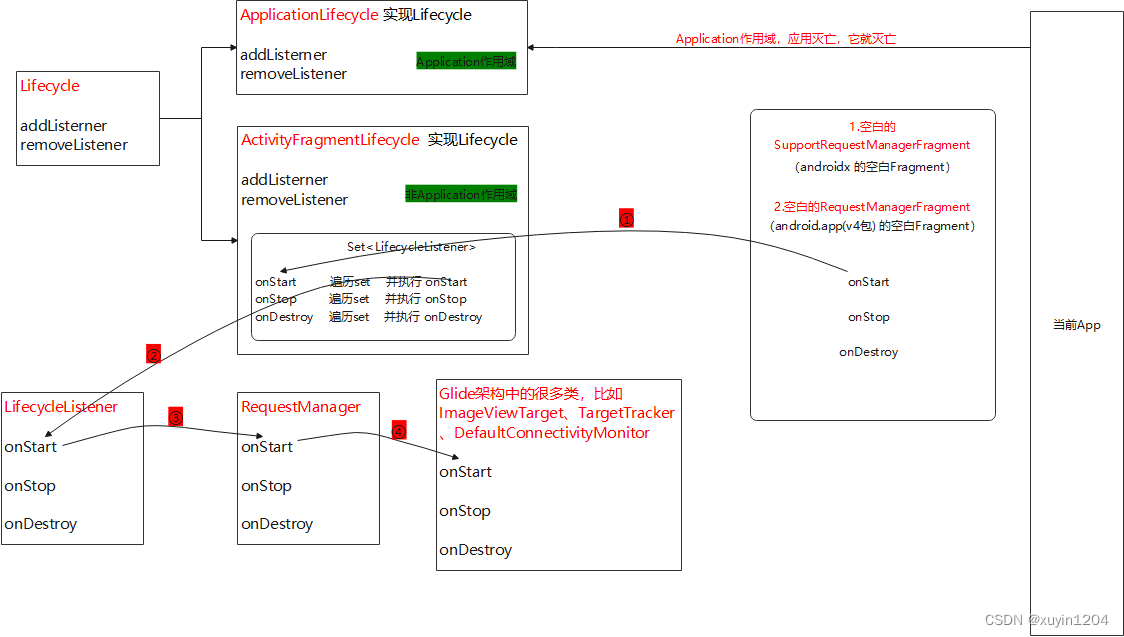
其中,ImageViewTarget、TargetTracker的onStart()是通过RequestManager的onStart()方法中加载的,而DefaultConnectivityMonitor实现ConnectivityMonitor接口,ConnectivityMonitor接口继承LifecycleListener接口,是通过lifecycle.addListener(connectivityMonitor);方式来注册,然后遍历set集合的onStart时候会调用到LifecycleListener的onStart(),从而加载到DefaultConnectivityMonitor的onStart()方法。
with方法流程总结: 主要是为了获取RequestManager对象,该对象是用于管理请求;通过RequestManagerRetriever生产RequestManager这个类来处理的;由于glide绑定了组件的生命周期,这样可以根据不同的生命周期来进行相应的处理。
2. load流程解析
load流程时序图:

glide支持多种图片的来源,包含url、本地文件、资源ID等等,从而会重写不同参数类型的load()方法。
ModelTypes.java
interface ModelTypes<T> {
@NonNull
@CheckResult
T load(@Nullable Bitmap bitmap);
@NonNull
@CheckResult
T load(@Nullable Drawable drawable);
@NonNull
@CheckResult
T load(@Nullable String string);
@NonNull
@CheckResult
T load(@Nullable Uri uri);
@NonNull
@CheckResult
T load(@Nullable File file);
@NonNull
@CheckResult
T load(@RawRes @DrawableRes @Nullable Integer resourceId);
@Deprecated
@CheckResult
T load(@Nullable URL url);
@NonNull
@CheckResult
T load(@Nullable byte[] model);
@NonNull
@CheckResult
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T load(@Nullable Object model);
}
RequestManager.java
@Override
public RequestBuilder<Drawable> load(@Nullable String string) {
return asDrawable().load(string);
}
RequestBuilder.java
@NonNull
@Override
@CheckResult
public RequestBuilder<TranscodeType> load(@Nullable String string) {
return loadGeneric(string);
}
RequestBuilder.java
@NonNull
private RequestBuilder<TranscodeType> loadGeneric(@Nullable Object model) {
this.model = model;
isModelSet = true;
return this;
}
load总结: 其实也就是一些初始化的创建工作,最后获取RequestBuilder。
3. init流程解析
init流程时序图:

/**
* Sets the {@link ImageView} the resource will be loaded into, cancels any existing loads into
* the view, and frees any resources Glide may have previously loaded into the view so they may be
* reused.
*
* @see RequestManager#clear(Target)
*
* @param view The view to cancel previous loads for and load the new resource into.
* @return The
* {@link com.bumptech.glide.request.target.Target} used to wrap the given {@link ImageView}.
*/
@NonNull
public ViewTarget<ImageView, TranscodeType> into(@NonNull ImageView view) {
Util.assertMainThread();
Preconditions.checkNotNull(view);
BaseRequestOptions<?> requestOptions = this;
if (!requestOptions.isTransformationSet()
&& requestOptions.isTransformationAllowed()
&& view.getScaleType() != null) {
// Clone in this method so that if we use this RequestBuilder to load into a View and then
// into a different target, we don't retain the transformation applied based on the previous
// View's scale type.
switch (view.getScaleType()) {
case CENTER_CROP:
requestOptions = requestOptions.clone().optionalCenterCrop();
break;
case CENTER_INSIDE:
requestOptions = requestOptions.clone().optionalCenterInside();
break;
case FIT_CENTER:
case FIT_START:
case FIT_END:
requestOptions = requestOptions.clone().optionalFitCenter();
break;
case FIT_XY:
requestOptions = requestOptions.clone().optionalCenterInside();
break;
case CENTER:
case MATRIX:
default:
// Do nothing.
}
}
return into(
glideContext.buildImageViewTarget(view, transcodeClass),
/*targetListener=*/ null,
requestOptions,
Executors.mainThreadExecutor());
}
Util.assertMainThread(); 这个语句就可以确定into方法必须要在主线程中进行操作,
glideContext.buildImageViewTarget(view, transcodeClass)就是为了构建一个target对象
public <Z> ViewTarget<ImageView, Z> buildTarget(@NonNull ImageView view,
@NonNull Class<Z> clazz) {
if (Bitmap.class.equals(clazz)) {
return (ViewTarget<ImageView, Z>) new BitmapImageViewTarget(view);
} else if (Drawable.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz)) {
return (ViewTarget<ImageView, Z>) new DrawableImageViewTarget(view);
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Unhandled class: " + clazz + ", try .as*(Class).transcode(ResourceTranscoder)");
}
}
into操作主要就是图片加载,
- 首先会对操作是否在主线程中进行判断,
- 之后创建所需要的target
private <Y extends Target<TranscodeType>> Y into(
@NonNull Y target,
@Nullable RequestListener<TranscodeType> targetListener,
BaseRequestOptions<?> options,
Executor callbackExecutor) {
Preconditions.checkNotNull(target);
if (!isModelSet) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("You must call #load() before calling #into()");
}
Request request = buildRequest(target, targetListener, options, callbackExecutor);
Request previous = target.getRequest();
if (request.isEquivalentTo(previous)
&& !isSkipMemoryCacheWithCompletePreviousRequest(options, previous)) {
request.recycle();
// If the request is completed, beginning again will ensure the result is re-delivered,
// triggering RequestListeners and Targets. If the request is failed, beginning again will
// restart the request, giving it another chance to complete. If the request is already
// running, we can let it continue running without interruption.
if (!Preconditions.checkNotNull(previous).isRunning()) {
// Use the previous request rather than the new one to allow for optimizations like skipping
// setting placeholders, tracking and un-tracking Targets, and obtaining View dimensions
// that are done in the individual Request.
previous.begin();
}
return target;
}
requestManager.clear(target);
target.setRequest(request); //设置tag,将tag与图片request进行绑定,防止图片错位
requestManager.track(target, request);
return target;
}
RequestManager.java
synchronized void track(@NonNull Target<?> target, @NonNull Request request) {
targetTracker.track(target);
requestTracker.runRequest(request);
}
RequestTracker.java
/**
* Starts tracking the given request.
*/
public void runRequest(@NonNull Request request) {
requests.add(request);
if (!isPaused) {
request.begin();
} else {
request.clear();
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.VERBOSE)) {
Log.v(TAG, "Paused, delaying request");
}
pendingRequests.add(request);
}
}
SingleRequest.java
@Override
public synchronized void begin() {
assertNotCallingCallbacks();
stateVerifier.throwIfRecycled();
startTime = LogTime.getLogTime();
if (model == null) {
if (Util.isValidDimensions(overrideWidth, overrideHeight)) {
width = overrideWidth;
height = overrideHeight;
}
// Only log at more verbose log levels if the user has set a fallback drawable, because
// fallback Drawables indicate the user expects null models occasionally.
int logLevel = getFallbackDrawable() == null ? Log.WARN : Log.DEBUG;
onLoadFailed(new GlideException("Received null model"), logLevel);
return;
}
if (status == Status.RUNNING) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot restart a running request");
}
// If we're restarted after we're complete (usually via something like a notifyDataSetChanged
// that starts an identical request into the same Target or View), we can simply use the
// resource and size we retrieved the last time around and skip obtaining a new size, starting a
// new load etc. This does mean that users who want to restart a load because they expect that
// the view size has changed will need to explicitly clear the View or Target before starting
// the new load.
if (status == Status.COMPLETE) {
onResourceReady(resource, DataSource.MEMORY_CACHE);
return;
}
// Restarts for requests that are neither complete nor running can be treated as new requests
// and can run again from the beginning.
status = Status.WAITING_FOR_SIZE;
if (Util.isValidDimensions(overrideWidth, overrideHeight)) {
onSizeReady(overrideWidth, overrideHeight);
} else {
target.getSize(this);
}
if ((status == Status.RUNNING || status == Status.WAITING_FOR_SIZE)
&& canNotifyStatusChanged()) {
target.onLoadStarted(getPlaceholderDrawable());
}
if (IS_VERBOSE_LOGGABLE) {
logV("finished run method in " + LogTime.getElapsedMillis(startTime));
}
}
SingleRequest.java
/**
* A callback method that should never be invoked directly.
*/
@Override
public synchronized void onSizeReady(int width, int height) {
stateVerifier.throwIfRecycled();
if (IS_VERBOSE_LOGGABLE) {
logV("Got onSizeReady in " + LogTime.getElapsedMillis(startTime));
}
if (status != Status.WAITING_FOR_SIZE) {
return;
}
status = Status.RUNNING;
float sizeMultiplier = requestOptions.getSizeMultiplier();
this.width = maybeApplySizeMultiplier(width, sizeMultiplier);
this.height = maybeApplySizeMultiplier(height, sizeMultiplier);
if (IS_VERBOSE_LOGGABLE) {
logV("finished setup for calling load in " + LogTime.getElapsedMillis(startTime));
}
loadStatus =
engine.load(
glideContext,
model,
requestOptions.getSignature(),
this.width,
this.height,
requestOptions.getResourceClass(),
transcodeClass,
priority,
requestOptions.getDiskCacheStrategy(),
requestOptions.getTransformations(),
requestOptions.isTransformationRequired(),
requestOptions.isScaleOnlyOrNoTransform(),
requestOptions.getOptions(),
requestOptions.isMemoryCacheable(),
requestOptions.getUseUnlimitedSourceGeneratorsPool(),
requestOptions.getUseAnimationPool(),
requestOptions.getOnlyRetrieveFromCache(),
this,
callbackExecutor);
// This is a hack that's only useful for testing right now where loads complete synchronously
// even though under any executor running on any thread but the main thread, the load would
// have completed asynchronously.
if (status != Status.RUNNING) {
loadStatus = null;
}
if (IS_VERBOSE_LOGGABLE) {
logV("finished onSizeReady in " + LogTime.getElapsedMillis(startTime));
}
}
Engine.java
/**
* Starts a load for the given arguments.
*
* <p>Must be called on the main thread.
*
* <p>The flow for any request is as follows:
*
* <ul>
* <li>Check the current set of actively used resources, return the active resource if present,
* and move any newly inactive resources into the memory cache.
* <li>Check the memory cache and provide the cached resource if present.
* <li>Check the current set of in progress loads and add the cb to the in progress load if one
* is present.
* <li>Start a new load.
* </ul>
*
* <p>Active resources are those that have been provided to at least one request and have not yet
* been released. Once all consumers of a resource have released that resource, the resource then
* goes to cache. If the resource is ever returned to a new consumer from cache, it is re-added to
* the active resources. If the resource is evicted from the cache, its resources are recycled and
* re-used if possible and the resource is discarded. There is no strict requirement that
* consumers release their resources so active resources are held weakly.
*
* @param width The target width in pixels of the desired resource.
* @param height The target height in pixels of the desired resource.
* @param cb The callback that will be called when the load completes.
*/
public synchronized <R> LoadStatus load(
GlideContext glideContext,
Object model,
Key signature,
int width,
int height,
Class<?> resourceClass,
Class<R> transcodeClass,
Priority priority,
DiskCacheStrategy diskCacheStrategy,
Map<Class<?>, Transformation<?>> transformations,
boolean isTransformationRequired,
boolean isScaleOnlyOrNoTransform,
Options options,
boolean isMemoryCacheable,
boolean useUnlimitedSourceExecutorPool,
boolean useAnimationPool,
boolean onlyRetrieveFromCache,
ResourceCallback cb,
Executor callbackExecutor) {
long startTime = VERBOSE_IS_LOGGABLE ? LogTime.getLogTime() : 0;
EngineKey key = keyFactory.buildKey(model, signature, width, height, transformations,
resourceClass, transcodeClass, options);
EngineResource<?> active = loadFromActiveResources(key, isMemoryCacheable); //活动缓存
if (active != null) {
cb.onResourceReady(active, DataSource.MEMORY_CACHE);
if (VERBOSE_IS_LOGGABLE) {
logWithTimeAndKey("Loaded resource from active resources", startTime, key);
}
return null;
}
EngineResource<?> cached = loadFromCache(key, isMemoryCacheable); //内存缓存
if (cached != null) {
cb.onResourceReady(cached, DataSource.MEMORY_CACHE);
if (VERBOSE_IS_LOGGABLE) {
logWithTimeAndKey("Loaded resource from cache", startTime, key);
}
return null;
}
EngineJob<?> current = jobs.get(key, onlyRetrieveFromCache);
if (current != null) {
current.addCallback(cb, callbackExecutor);
if (VERBOSE_IS_LOGGABLE) {
logWithTimeAndKey("Added to existing load", startTime, key);
}
return new LoadStatus(cb, current);
}
EngineJob<R> engineJob =
engineJobFactory.build(
key,
isMemoryCacheable,
useUnlimitedSourceExecutorPool,
useAnimationPool,
onlyRetrieveFromCache);
DecodeJob<R> decodeJob =
decodeJobFactory.build(
glideContext,
model,
key,
signature,
width,
height,
resourceClass,
transcodeClass,
priority,
diskCacheStrategy,
transformations,
isTransformationRequired,
isScaleOnlyOrNoTransform,
onlyRetrieveFromCache,
options,
engineJob);
jobs.put(key, engineJob);
engineJob.addCallback(cb, callbackExecutor);
engineJob.start(decodeJob);
if (VERBOSE_IS_LOGGABLE) {
logWithTimeAndKey("Started new load", startTime, key);
}
return new LoadStatus(cb, engineJob);
}
























 1713
1713











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








