操作系统中运行的一个进程具有三个状态:
(1) 就绪态(Ready):此时进程获得了除过CPU资源外的所有资源,只要获得了处理机,便会立即执行;
(2)执行态(Running):此时程序已经获得了处理机,程序正在运行的状态;
(3)阻塞态(Blocked):正在运行的进程由于等待某一个资源而无法继续运行,此时放弃处理机而进入的状态。
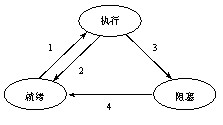
上图提供了三种状态之间的转换过程:
(1) 就绪态---> 执行态:获得了处理机,程序开始执行
(2) 执行态---> 就绪态:时间片用完,程序进入就绪态
(3) 执行态---> 阻塞态:由于等待某种资源而不得不处于阻塞态
(4) 阻塞态---> 就绪态:获取了等待的资源
一个进程在运行期间可以不断地处于就绪态和执行态,也可能处于阻塞态!






















 8146
8146

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








