先来看如何使用,再跟踪源码
目录
Serializable 和 Externalizable接口
new ObjectOutputStream/ ObjectInputStream
ObjectOutputStream.writeObject(user) 序列化
new ObjectStreamClass(Class cl)
ObjectInputStream.readObject() 反序列化
测试代码
数组对象是否深拷贝
序列化和反序列化之后的两个对象是深拷贝,本例中user对象和内部的数组对象都是不同的
import java.io.Serializable;
public class User implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1101703620149581079L;
private long long1;
private int int2;
private String str1;
private String[] strArr = new String[5];
public User(long long1, int int2, String str1) {
this.long1 = long1;
this.int2 = int2;
this.str1 = str1;
}
public String toStirng() {
return "long1:" + long1 + ", int2: " + int2 + ", str1: " + str1 + ", strArr:" + strArr;
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
//序列化
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("object.out");
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(fos);
User user1 = new User(1234534l, 12, "111111");
System.out.println("序列化前对象值====" + user1.toStirng());
oos.writeObject(user1);
oos.flush();
oos.close();
//反序列化
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("object.out");
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(fis);
User user2 = (User) ois.readObject();
System.out.println("序列化后对象值====" + user2.toStirng());
}
}
serialVersionUID不一致
表示类版本,序列化时,将类中UID输出到文件中,反序列化时会检查文件中的UID和 当前类中的UID,不一致则会报错不兼容。测试把对象序列化后改动UID,再反序列化,如下报错
Exception in thread "main" java.io.InvalidClassException: com.example.demo.Serializable.User; local class incompatible: stream classdesc serialVersionUID = 1101703620149581079, local class serialVersionUID = 1101703620149581071
at java.io.ObjectStreamClass.initNonProxy(ObjectStreamClass.java:699)
at java.io.ObjectInputStream.readNonProxyDesc(ObjectInputStream.java:1885)
at java.io.ObjectInputStream.readClassDesc(ObjectInputStream.java:1751)
at java.io.ObjectInputStream.readOrdinaryObject(ObjectInputStream.java:2042)
at java.io.ObjectInputStream.readObject0(ObjectInputStream.java:1573)
at java.io.ObjectInputStream.readObject(ObjectInputStream.java:431)
at com.example.demo.Serializable.Test.main(Test.java:22)static变量是否序列化
public class User0 implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1101703620149581079L;
private long long1;
private int int2;
private String str1;
private static String static_str;
public User0(long long1, int int2, String str1, String static_str) {
this.long1 = long1;
this.int2 = int2;
this.str1 = str1;
this.static_str = static_str;
}
public void setStatic(String sta) {
static_str = sta;
}
public String toStirng() {
return "long1:" + long1 + ", int2: " + int2 + ", str1: " + str1 + ", static_str: " + static_str;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
//序列化
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("object.out");
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(fos);
User0 user1 = new User0(1234534l, 12, "111111", "2222222");
System.out.println("序列化前对象值====" + user1.toStirng());
oos.writeObject(user1);
oos.flush();
oos.close();
// 修改静态变量值
user1.setStatic("444444");
//反序列化
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("object.out");
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(fis);
User0 user2 = (User0) ois.readObject();
//反序列化的输出结果为:
System.out.println("序列化后对象值====" + user2.toStirng());
}
}可以看到,类变量和序列化无关

自定义序列化内容
上述代码将类中非static的对象都序列化到文件中,若想部分字段不参与序列化,或想自定义序列化方式,有三种方式
- transient关键字修饰成员变量,则此变量不参与序列化
- 实现Externalizable接口的writeExternal / readExternal方法,进行自定义
- 对象存在private void 的writeObject / readObject方法,进行自定义
transient变量
public class User1 implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1101703620149581079L;
private long long1;
private int int2;
private String str1;
private transient String tran_str;
public User1(long long1, int int2, String str1, String tran_str) {
this.long1 = long1;
this.int2 = int2;
this.str1 = str1;
this.tran_str = tran_str;
}
public String toStirng() {
return "long1:" + long1 + ", int2: " + int2 + ", str1: " + str1 + ", tran_str: " + tran_str + "";
}
} 看到transient修饰的String变量未被序列化,值为null
Serializable 和 Externalizable接口
序列化必须实现 java.io.Serializable 接口,实现Serializable接口没有需要实现的接口方法,但若对象未实现Serializable接口,序列化时将会报错如下
Exception in thread "main" java.io.NotSerializableException: com.example.demo.Serializable.User
at java.io.ObjectOutputStream.writeObject0(ObjectOutputStream.java:1184)
at java.io.ObjectOutputStream.writeObject(ObjectOutputStream.java:348)
at com.example.demo.Serializable.Test.main(Test.java:12)实现了Serializable接口的类的父类必须存在无参构造器,否则将会报错如下图,本例中User.java无父类,但是其实父类为Object.java, Object存在无参构造所以不会报错。

Externalizable接口实现了Serializable,并定义了两个方法,如下
import java.io.ObjectOutput;
import java.io.ObjectInput;
public interface Externalizable extends java.io.Serializable {
void writeExternal(ObjectOutput out) throws IOException;
void readExternal(ObjectInput in) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException;
}
实现Externalizable方法,可以进行自定义需要序列化的字段和序列化方式,代码中将部分字段 还有 transient变量序列化
public class User2 implements Externalizable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1101703620149581079L;
private long long1;
private int int2;
private String str1;
private transient String tran_str;
/* public User2() {
}*/
public User2(long long1, int int2, String str1, String tran_str) {
this.long1 = long1;
this.int2 = int2;
this.str1 = str1;
this.tran_str = tran_str;
}
@Override
public void writeExternal(ObjectOutput out) throws IOException {
out.writeObject(str1);
out.writeObject(tran_str);
}
@Override
public void readExternal(ObjectInput in) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
this.str1 = (String) in.readObject();
this.tran_str = (String) in.readObject();
}
public String toStirng() {
return "long1:" + long1 + ", int2: " + int2 + ", str1: " + str1 + ", tran_str: " + tran_str + "";
}
}运行发现报错如下,原因是实现了Externalizable接口的类必须存在无参构造
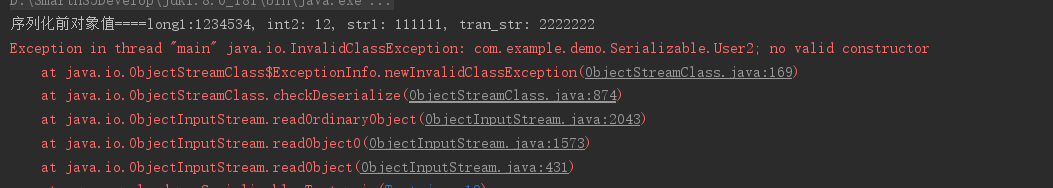
删除上边代码的注释再次运行,看到只有自定义的字段被序列化了,transient也不例外
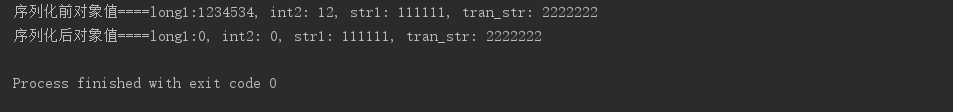
writeObject / readObject
和Externalizable接口类似,不实现任何接口,在类中声明如下两个方法,即可实现自定义
private void writeObject(ObjectOutputStream out);
private void readObject(ObjectInputStream in);
public class User3 implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1101703620149581079L;
private long long1;
private int int2;
private String str1;
private transient String tran_str;
public User3(long long1, int int2, String str1, String tran_str) {
this.long1 = long1;
this.int2 = int2;
this.str1 = str1;
this.tran_str = tran_str;
}
private void writeObject(ObjectOutputStream out) throws IOException {
// out.writeObject(str1);
// out.writeObject("tututututu");
// out.writeObject(tran_str);
out.writeObject("1234234322");
out.writeObject("999999999999");
}
private void readObject(ObjectInputStream in) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
this.str1 = (String) in.readObject();
this.tran_str = (String) in.readObject();
}
public String toStirng() {
return "long1:" + long1 + ", int2: " + int2 + ", str1: " + str1 + ", tran_str: " + tran_str + "";
}
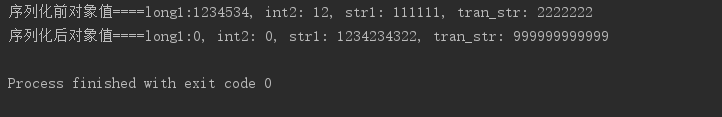
}
writeReplace
类中实现private Object writeReplace()方法,即可在序列化时,由方法返回的对象替换当前对象进行序列化
public class User4 implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1101703620149581071L;
private long long1;
private int int2;
private String str1;
private String[] strArr = new String[5];
public User4(long long1, int int2, String str1) {
this.long1 = long1;
this.int2 = int2;
this.str1 = str1;
}
private Object writeReplace() {
return "fdsfsdfsdfs";
}
public String toStirng() {
return "long1:" + long1 + ", int2: " + int2 + ", str1: " + str1 + ", strArr:" + strArr;
}
}
readResolve
类似writeReplace,类中实现private Object readResolve()方法,即ObjectInputStream.readObject()方法直接返回readResolve()方法返回的对象。可以用于防止单例模式被破坏,下边细讲
private Object readResolve() {
return "fdsfsdfsdfs";
}
源码跟踪
new ObjectOutputStream/ ObjectInputStream
public ObjectOutputStream(OutputStream out) throws IOException {
verifySubclass();
// 序列化数据流
bout = new BlockDataOutputStream(out);
// 缓存由本ObjectOutputStream序列化过的对象,如果非首次序列化,获取缓存索引值
handles = new HandleTable(10, (float) 3.00);
// 上文提到的writeReplace方式,缓存替换和被替换对象
subs = new ReplaceTable(10, (float) 3.00);
enableOverride = false;
// 写 流的头数据
writeStreamHeader();
bout.setBlockDataMode(true);
if (extendedDebugInfo) {
debugInfoStack = new DebugTraceInfoStack();
} else {
debugInfoStack = null;
}
}
public ObjectInputStream(InputStream in) throws IOException {
verifySubclass();
// 序列化数据流
bin = new BlockDataInputStream(in);
// 对象缓存
handles = new HandleTable(10);
vlist = new ValidationList();
serialFilter = ObjectInputFilter.Config.getSerialFilter();
enableOverride = false;
// 读流的头数据
readStreamHeader();
bin.setBlockDataMode(true);
}可以看到,序列化和反序列化在 new ObjectOutputStream/ ObjectInputStream时就会写入和读取对象序列化数据头,再类中搜索了一下,没有发现其他地方调用writeStreamHeader或readStreamHeader, 那么就意味着,ObjectOutputStream/ ObjectInputStream对象 序列化和反序列化是一一对应的。要是每次序列化writeObject写入数据,使用不同的ObjectInputStream来读取,会报错,来测试一下。
简单的客户端和服务器端socket通信代码
public class server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(8080);
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
// ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(socket.getInputStream());
while(true) {
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(socket.getInputStream());
Object o = ois.readObject();
System.out.println(o);
}
}
}
public class client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
Socket socket = new Socket("localhost", 8080);
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(socket.getOutputStream());
while (true) {
//ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(socket.getOutputStream());
oos.writeObject("sadadasd");
oos.flush();
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
}
}
}ObjectOutputStream/ ObjectInputStream一个在循环里,一个在循环外,即client用一个oos来写数据流,server端用多个ois来读,报错如下
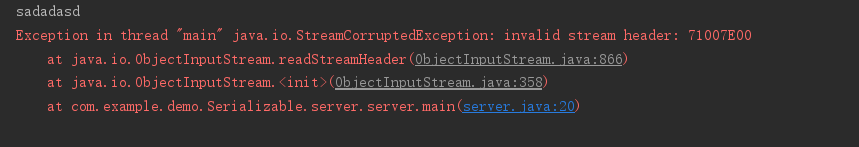
上述代码应该是oos和ois要么都在循环里,要么都在循环外,一一对应
ObjectOutputStream.writeObject(user) 序列化
writeObject0()方法三部分
一、缓存查找是否已经处理过此对象 或对象为Class或ObjectStreamClass对象描述类,进行特殊处理
二、产生class对象的描述对象ObjectStreamClass,判断是否需要替换对象(writeReplace)
三、进行一般对象的处理,递归处理该对象
public final void writeObject(Object obj) throws IOException {
if (enableOverride) {// enableOverride 为 false
writeObjectOverride(obj);
return;
}
try {
writeObject0(obj, false);
} catch (IOException ex) {
if (depth == 0) {
writeFatalException(ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
private void writeObject0(Object obj, boolean unshared)
throws IOException
{
boolean oldMode = bout.setBlockDataMode(false);
depth++;
try {
// handle previously written and non-replaceable objects
// 第一部分:处理已经处理过的对象(从缓存查找并处理)、和处理不可被替换的对象
int h;
if ((obj = subs.lookup(obj)) == null) {
writeNull();
return;
} else if (!unshared && (h = handles.lookup(obj)) != -1) {
writeHandle(h);
return;
} else if (obj instanceof Class) {
writeClass((Class) obj, unshared);
return;
} else if (obj instanceof ObjectStreamClass) {
writeClassDesc((ObjectStreamClass) obj, unshared);
return;
}
// 第二部分:检查该对象是否需要被替换,本文提到的writeReplace
Object orig = obj;// 保存源对象引用
Class<?> cl = obj.getClass();// 保存源对象的class对象引用
// 这个对象是class的序列化描述对象,内部保存元数据比如:类有哪些字段,有哪些方法,是否有writeObject等方法等等
ObjectStreamClass desc;
for (;;) {
// REMIND: skip this check for strings/arrays?
Class<?> repCl;
// 根据class对象生成ObjectStreamClass描述对象
desc = ObjectStreamClass.lookup(cl, true);
// 1、该对象如果不存在writeReplace方法
// 2、或者调用了writeReplace方法返回的对象为null
// 3、或者调用writeReplace方法返回的对象是同类的对象
// 那么使用刚才的ObjectStreamClass描述对象,否则需要根据替换对象的class重新产生ObjectStreamClass
if (!desc.hasWriteReplaceMethod() ||
(obj = desc.invokeWriteReplace(obj)) == null ||
(repCl = obj.getClass()) == cl)
{
break;
}
// 替换class对象,再循环查找新的对象是否存在writeReplace,重新产生ObjectStreamClass描述对象
cl = repCl;
}
if (enableReplace) {
Object rep = replaceObject(obj);
if (rep != obj && rep != null) {
cl = rep.getClass();
desc = ObjectStreamClass.lookup(cl, true);
}
obj = rep;
}
// if object replaced, run through original checks a second time
// 此时obj != orig,意味着对象已经被writeReplace替换了,重新走一遍 第一部分的处理
if (obj != orig) {
// subs中保存源对象和替换对象的对应关系,缓存,之后对相同对象的处理就直接查缓存
subs.assign(orig, obj);
if (obj == null) {
writeNull();
return;
} else if (!unshared && (h = handles.lookup(obj)) != -1) {
writeHandle(h);
return;
} else if (obj instanceof Class) {
writeClass((Class) obj, unshared);
return;
} else if (obj instanceof ObjectStreamClass) {
writeClassDesc((ObjectStreamClass) obj, unshared);
return;
}
}
// 剩余的对象,string array 枚举,实现了Serializable的对象的对应处理
// 对其他没有实现Serializable的对象报错NotSerializableException
if (obj instanceof String) {
writeString((String) obj, unshared);
} else if (cl.isArray()) {
writeArray(obj, desc, unshared);
} else if (obj instanceof Enum) {
writeEnum((Enum<?>) obj, desc, unshared);
} else if (obj instanceof Serializable) {
writeOrdinaryObject(obj, desc, unshared);
} else {
if (extendedDebugInfo) {
throw new NotSerializableException(
cl.getName() + "\n" + debugInfoStack.toString());
} else {
throw new NotSerializableException(cl.getName());
}
}
} finally {
depth--;
bout.setBlockDataMode(oldMode);
}
}new ObjectStreamClass(Class<?> cl)
产生class对象的序列化描述对象ObjectStreamClass
private ObjectStreamClass(final Class<?> cl) {
this.cl = cl;
// 类名
name = cl.getName();
// 是否JDK代理产生的代理对象(继承Proxy类)
isProxy = Proxy.isProxyClass(cl);
// 是否是枚举类
isEnum = Enum.class.isAssignableFrom(cl);
// 是否实现了Serializable接口
serializable = Serializable.class.isAssignableFrom(cl);
// 是否实现了Externalizable接口
externalizable = Externalizable.class.isAssignableFrom(cl);
// 若存在超类,产生超类的描述对象ObjectStreamClass
Class<?> superCl = cl.getSuperclass();
superDesc = (superCl != null) ? lookup(superCl, false) : null;
localDesc = this;
if (serializable) {
// 若实现了Serializable接口,判断可序列化字段等
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Void>() {
public Void run() {
// 若是枚举类,只序列化枚举对象名即可,不需序列化字段,serialVersionUID默认0
if (isEnum) {
suid = Long.valueOf(0);
fields = NO_FIELDS;
return null;
}
// 数组对象没有字段需要序列化,后续会循环数组对内部对象序列化
if (cl.isArray()) {
fields = NO_FIELDS;
return null;
}
// 获取serialVersionUID
suid = getDeclaredSUID(cl);
try {
// 获取可序列化的字段,获取所有字段,排除static和transient所修饰的
fields = getSerialFields(cl);
// 计算各字段序列化顺序,得到各字段的序列化偏移量
// 反序列化时,根据这个偏移量来从流中获取某一段的字节并设置为对应的属性值
computeFieldOffsets();
} catch (InvalidClassException e) {
serializeEx = deserializeEx =
new ExceptionInfo(e.classname, e.getMessage());
fields = NO_FIELDS;
}
if (externalizable) {
// 若实现了Externalizable ,获取无参构造器
cons = getExternalizableConstructor(cl);
} else {
// 获取序列化对象父类的无参构造器
cons = getSerializableConstructor(cl);
// 自定义的序列化方法writeObject/readObject,readObjectNoData
writeObjectMethod = getPrivateMethod(cl, "writeObject",
new Class<?>[] { ObjectOutputStream.class },
Void.TYPE);
readObjectMethod = getPrivateMethod(cl, "readObject",
new Class<?>[] { ObjectInputStream.class },
Void.TYPE);
readObjectNoDataMethod = getPrivateMethod(
cl, "readObjectNoData", null, Void.TYPE);
hasWriteObjectData = (writeObjectMethod != null);
}
// 这不知道
domains = getProtectionDomains(cons, cl);
// 上边提到过的替换对象相关的两个方法
writeReplaceMethod = getInheritableMethod(
cl, "writeReplace", null, Object.class);
readResolveMethod = getInheritableMethod(
cl, "readResolve", null, Object.class);
return null;
}
});
} else {
suid = Long.valueOf(0);
fields = NO_FIELDS;
}
try {
// 各字段Field的引用,似乎是用来反序列化时设置字段的值
fieldRefl = getReflector(fields, this);
} catch (InvalidClassException ex) {
// field mismatches impossible when matching local fields vs. self
throw new InternalError(ex);
}
if (deserializeEx == null) {
if (isEnum) {
deserializeEx = new ExceptionInfo(name, "enum type");
} else if (cons == null) {
deserializeEx = new ExceptionInfo(name, "no valid constructor");
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < fields.length; i++) {
if (fields[i].getField() == null) {
defaultSerializeEx = new ExceptionInfo(
name, "unmatched serializable field(s) declared");
}
}
// 初始化 ObjectStreamClass完毕
initialized = true;
}writeArray()
先看个简单的数组对象序列化方法,内部判断数组存的是基本数据类型还是引用类型,基本数据类型直接写字节数据,引用类型则需递归调用writeObject0方法序列化
private void writeArray(Object array,
ObjectStreamClass desc,
boolean unshared)
throws IOException
{
// 流中写入数组对象的描述类信息desc
bout.writeByte(TC_ARRAY);
writeClassDesc(desc, false);
// 写入缓存
handles.assign(unshared ? null : array);
// 如果数组对象中存得是基本数据类型,写入int long等数据
Class<?> ccl = desc.forClass().getComponentType();
if (ccl.isPrimitive()) {
if (ccl == Integer.TYPE) {
int[] ia = (int[]) array;
bout.writeInt(ia.length);
bout.writeInts(ia, 0, ia.length);
} else if (ccl == Byte.TYPE) {
byte[] ba = (byte[]) array;
bout.writeInt(ba.length);
bout.write(ba, 0, ba.length, true);
} else if (ccl == Long.TYPE) {
long[] ja = (long[]) array;
bout.writeInt(ja.length);
bout.writeLongs(ja, 0, ja.length);
} else if (ccl == Float.TYPE) {
float[] fa = (float[]) array;
bout.writeInt(fa.length);
bout.writeFloats(fa, 0, fa.length);
} else if (ccl == Double.TYPE) {
double[] da = (double[]) array;
bout.writeInt(da.length);
bout.writeDoubles(da, 0, da.length);
} else if (ccl == Short.TYPE) {
short[] sa = (short[]) array;
bout.writeInt(sa.length);
bout.writeShorts(sa, 0, sa.length);
} else if (ccl == Character.TYPE) {
char[] ca = (char[]) array;
bout.writeInt(ca.length);
bout.writeChars(ca, 0, ca.length);
} else if (ccl == Boolean.TYPE) {
boolean[] za = (boolean[]) array;
bout.writeInt(za.length);
bout.writeBooleans(za, 0, za.length);
} else {
throw new InternalError();
}
} else {
// 是引用对象数组
Object[] objs = (Object[]) array;
int len = objs.length;
bout.writeInt(len);
if (extendedDebugInfo) {
debugInfoStack.push(
"array (class \"" + array.getClass().getName() +
"\", size: " + len + ")");
}
try {
// 循环数组,递归调用writeObject0 序列化
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
if (extendedDebugInfo) {
debugInfoStack.push(
"element of array (index: " + i + ")");
}
try {
writeObject0(objs[i], false);
} finally {
if (extendedDebugInfo) {
debugInfoStack.pop();
}
}
}
} finally {
if (extendedDebugInfo) {
debugInfoStack.pop();
}
}
}
}writeOrdinaryObject
对实现了Serializable接口的类进行序列化的方法
private void writeOrdinaryObject(Object obj,
ObjectStreamClass desc,
boolean unshared)
throws IOException
{
try {
desc.checkSerialize();
// 写入Object类型标识,接着写入class描述对象ObjectStreamClass
bout.writeByte(TC_OBJECT);
writeClassDesc(desc, false);
// 写入缓存
handles.assign(unshared ? null : obj);
if (desc.isExternalizable() && !desc.isProxy()) {
// 如果实现的是Externalizable接口,调用接口方法进行序列化
writeExternalData((Externalizable) obj);
} else {
// 一般走这
writeSerialData(obj, desc);
}
} finally {
if (extendedDebugInfo) {
debugInfoStack.pop();
}
}
}
java.io.ObjectOutputStream#writeExternalData
private void writeExternalData(Externalizable obj) throws IOException {
// 删除了部分
bout.setBlockDataMode(true);
obj.writeExternal(this);
bout.setBlockDataMode(false);
bout.writeByte(TC_ENDBLOCKDATA);
}java.io.ObjectOutputStream#writeSerialData
if...else...两块,如果实现了writeObject方法,调用writeObject写数据,否则默认操作
private void writeSerialData(Object obj, ObjectStreamClass desc)
throws IOException
{
ObjectStreamClass.ClassDataSlot[] slots = desc.getClassDataLayout();
for (int i = 0; i < slots.length; i++) {
ObjectStreamClass slotDesc = slots[i].desc;
if (slotDesc.hasWriteObjectMethod()) {
PutFieldImpl oldPut = curPut;
curPut = null;
SerialCallbackContext oldContext = curContext;
try {
curContext = new SerialCallbackContext(obj, slotDesc);
bout.setBlockDataMode(true);
slotDesc.invokeWriteObject(obj, this);
bout.setBlockDataMode(false);
bout.writeByte(TC_ENDBLOCKDATA);
} finally {
curContext.setUsed();
curContext = oldContext;
if (extendedDebugInfo) {
debugInfoStack.pop();
}
}
curPut = oldPut;
} else {
defaultWriteFields(obj, slotDesc);
}
}
}
private void defaultWriteFields(Object obj, ObjectStreamClass desc)
throws IOException
{
Class<?> cl = desc.forClass();
if (cl != null && obj != null && !cl.isInstance(obj)) {
throw new ClassCastException();
}
desc.checkDefaultSerialize();
// 获取基本数据类型共占用多少字节大小
int primDataSize = desc.getPrimDataSize();
if (primVals == null || primVals.length < primDataSize) {
primVals = new byte[primDataSize];
}
// 根据描述对象 将基本数据类型按 顺序写入btye数组中
// 顺序在new ObjectStreamClass().computeFieldOffsets() 计算;
desc.getPrimFieldValues(obj, primVals);
// 将字节数组写入流
bout.write(primVals, 0, primDataSize, false);
// 再序列化引用类型
// 获取对象中需要序列化的字段数
ObjectStreamField[] fields = desc.getFields(false);
// 声明一个对象数组,大小为引用类型字段数
Object[] objVals = new Object[desc.getNumObjFields()];
// numPrimFields 为基本数据类型字段数(总-引用类型数)
int numPrimFields = fields.length - objVals.length;
// 获取对象的引用类型字段值
desc.getObjFieldValues(obj, objVals);
for (int i = 0; i < objVals.length; i++) {
try {
// 递归调用writeObject0方法序列化
writeObject0(objVals[i],
fields[numPrimFields + i].isUnshared());
} finally {
if (extendedDebugInfo) {
debugInfoStack.pop();
}
}
}
}ObjectInputStream.readObject() 反序列化
序列化时,每次会先写入当前对象的类型(一个字节),其次写入该对象的描述ObjectStreamClass类,再写入对象的各字段数据,反序列化时反向来一遍,读类型、读class描述类、再根据描述类按顺序读取各个字段值
下边的分支,本文只看Object类型
private Object readObject0(boolean unshared) throws IOException {
// 搂一眼第一个字节,即对象的类型,是字符串还是数组还是对象
byte tc;
while ((tc = bin.peekByte()) == TC_RESET) {
bin.readByte();
handleReset();
}
depth++;
totalObjectRefs++;
try {
// 根据第一个字节是什么,来判断走哪个处理分支
switch (tc) {
case TC_NULL:
return readNull();
case TC_REFERENCE:
return readHandle(unshared);
case TC_CLASS:
return readClass(unshared);
case TC_CLASSDESC:
case TC_PROXYCLASSDESC:
return readClassDesc(unshared);
case TC_STRING:
case TC_LONGSTRING:
return checkResolve(readString(unshared));
case TC_ARRAY:
return checkResolve(readArray(unshared));
case TC_ENUM:
return checkResolve(readEnum(unshared));
case TC_OBJECT:
return checkResolve(readOrdinaryObject(unshared));
case TC_EXCEPTION:
IOException ex = readFatalException();
throw new WriteAbortedException("writing aborted", ex);
case TC_BLOCKDATA:
case TC_BLOCKDATALONG:
if (oldMode) {
bin.setBlockDataMode(true);
bin.peek(); // force header read
throw new OptionalDataException(
bin.currentBlockRemaining());
} else {
throw new StreamCorruptedException(
"unexpected block data");
}
case TC_ENDBLOCKDATA:
if (oldMode) {
throw new OptionalDataException(true);
} else {
throw new StreamCorruptedException(
"unexpected end of block data");
}
default:
throw new StreamCorruptedException(
String.format("invalid type code: %02X", tc));
}
} finally {
depth--;
bin.setBlockDataMode(oldMode);
}
} private Object readOrdinaryObject(boolean unshared)
throws IOException
{
// 第一个字节,须为Object类型
if (bin.readByte() != TC_OBJECT) {
throw new InternalError();
}
// 读ObjectStreamClass 类
ObjectStreamClass desc = readClassDesc(false);
desc.checkDeserialize();
Class<?> cl = desc.forClass();
if (cl == String.class || cl == Class.class
|| cl == ObjectStreamClass.class) {
throw new InvalidClassException("invalid class descriptor");
}
// 用解析出的无参构造函数,new一个空对象
Object obj;
try {
obj = desc.isInstantiable() ? desc.newInstance() : null;
} catch (Exception ex) {
throw (IOException) new InvalidClassException(
desc.forClass().getName(),
"unable to create instance").initCause(ex);
}
// 缓存
passHandle = handles.assign(unshared ? unsharedMarker : obj);
ClassNotFoundException resolveEx = desc.getResolveException();
if (resolveEx != null) {
handles.markException(passHandle, resolveEx);
}
// 根据实现的接口,走不同的解析路子
if (desc.isExternalizable()) {
// 自定义实现的readExternal方法读取数据流
readExternalData((Externalizable) obj, desc);
} else {
// 若有readObject方法,使用此方法读取
// 若没有,看下文
readSerialData(obj, desc);
}
handles.finish(passHandle);
// 判断是否存在readResolve方法,如果有,调用并替换对象,return
if (obj != null &&
handles.lookupException(passHandle) == null &&
desc.hasReadResolveMethod())
{
Object rep = desc.invokeReadResolve(obj);
if (unshared && rep.getClass().isArray()) {
rep = cloneArray(rep);
}
if (rep != obj) {
// Filter the replacement object
if (rep != null) {
if (rep.getClass().isArray()) {
filterCheck(rep.getClass(), Array.getLength(rep));
} else {
filterCheck(rep.getClass(), -1);
}
}
handles.setObject(passHandle, obj = rep);
}
}
return obj;
}默认的读取对象规则
private void defaultReadFields(Object obj, ObjectStreamClass desc)
throws IOException
{
Class<?> cl = desc.forClass();
if (cl != null && obj != null && !cl.isInstance(obj)) {
throw new ClassCastException();
}
// 从ObjectStreamClass 对象获取基本数据类型大小
int primDataSize = desc.getPrimDataSize();
if (primVals == null || primVals.length < primDataSize) {
primVals = new byte[primDataSize];
}
// 读取相应大小的字节到数组中
bin.readFully(primVals, 0, primDataSize, false);
if (obj != null) {
// 按顺序设置到对象属性中
desc.setPrimFieldValues(obj, primVals);
}
// 获取引用类型的属性,递归readObject0方法
int objHandle = passHandle;
ObjectStreamField[] fields = desc.getFields(false);
Object[] objVals = new Object[desc.getNumObjFields()];
int numPrimFields = fields.length - objVals.length;
for (int i = 0; i < objVals.length; i++) {
ObjectStreamField f = fields[numPrimFields + i];
objVals[i] = readObject0(f.isUnshared());
if (f.getField() != null) {
handles.markDependency(objHandle, passHandle);
}
}
// 设置引用类型的值
if (obj != null) {
desc.setObjFieldValues(obj, objVals);
}
passHandle = objHandle;
}序列化破坏单例模式的解决方案
利用readResolve方法替换序列化对象的操作,实现readResolve方法,返回单例对象,代码示例如下
public class Singleton2 implements Serializable{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 2855907098089861400L;
private static Singleton2 instance = new Singleton2();
private Singleton2() {}
private Object readResolve() {
return instance;
}
public static Singleton2 getInstance() {
return instance;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("instance.out");
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(fos);
Singleton2 instance = Singleton2.getInstance();
oos.writeObject(instance);
oos.flush();
oos.close();
//反序列化
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("instance.out");
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(fis);
Object obj = ois.readObject();
Singleton2 instance2 = (Singleton2) obj;
System.out.println(instance == instance2);
}
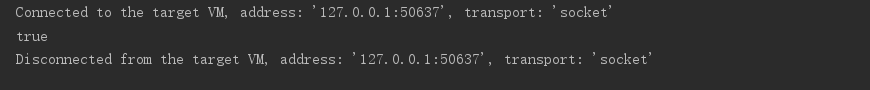
}执行为true,表示为同对象
























 3139
3139











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








