一、常识了解
1.GBK包含GB2312,即如果通过GB2312编码后可以通过GBK解码,反之可能不成立;
2.java.nio.charset.Charset.defaultCharset() 获得平台默认字符编码;
3.getBytes() 是通过平台默认字符集进行编码;
二、中文乱码出现
在学习任何一门技术时,经常会有初学者遇到中文乱码问题,比如MySQL,是因为在安装时没有设置;而在Servlet中,也会遇到中文乱码问题;
比如:
OutputStream out = response.getOutputStream();
out.write(String );
输出中文时可能会出现乱码;
比如:
- protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
- OutputStream out = response.getOutputStream();
- String data = "博客" ;
- out.write(data.getBytes("UTF-8" ));
- }
输出乱码的问题是程序用UTF-8编码,而浏览器用GB2312解码,因此会出现乱码;
Servlet乱码分为request乱码和response乱码;
三、response中文乱码
在网上很有效的解决方法是添加:
response.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
解决不了,后来又搜到一条解决方法是:
respnse.setHeader("content-type","text/html;charset=UTF-8");
两句都填上,后来终于解决了这个问题;
其实我们应该思考一下本质;
问题1:
我们这里先来说明一下错误的原因,下图是显示乱码的流程图:
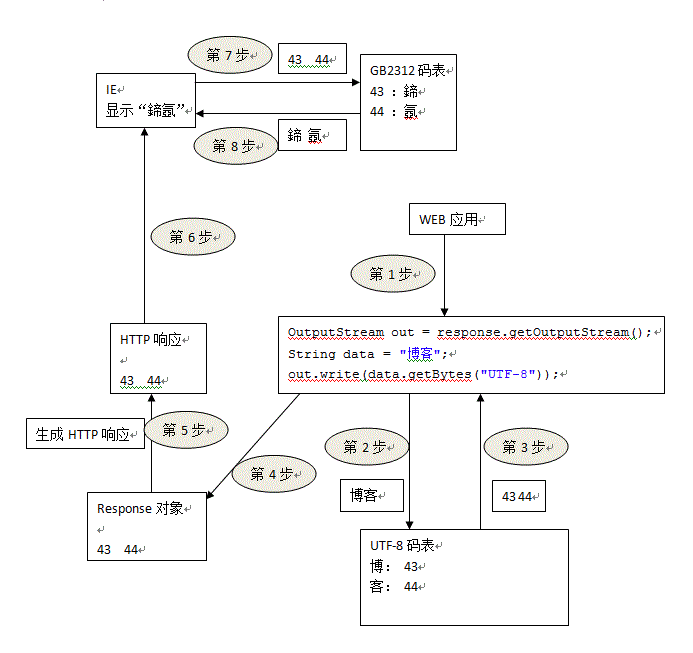
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8"); 目的是为了控制浏览器的行为,即控制浏览器用UTF-8进行解码;
response.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8"); 的目的是用于response.getWriter()输出的字符流的乱码问题,如果是response.getOutputStream()是不需要此种解决方案的; 因为这句话的意思是为了将response对象中的数据以UTF-8解码后发向浏览器;
解决方案流程图:
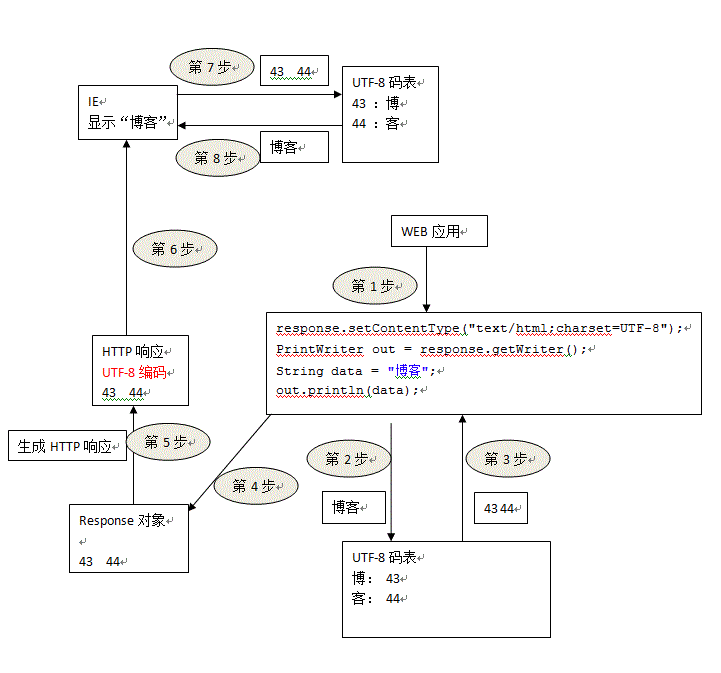
问题2
问题代码如下:
- protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
- PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
- String data = "博客" ;
- out.println(data);
- }
浏览器输出: ??
原因 :"博客"首先被封装在response对象中,因为IE和WEB服务器之间不能传输文本,然后就通过ISO-8859-1进行编码,但是ISO-8859-1中没有“博客”的编码,因此输出“??”表示没有编码;
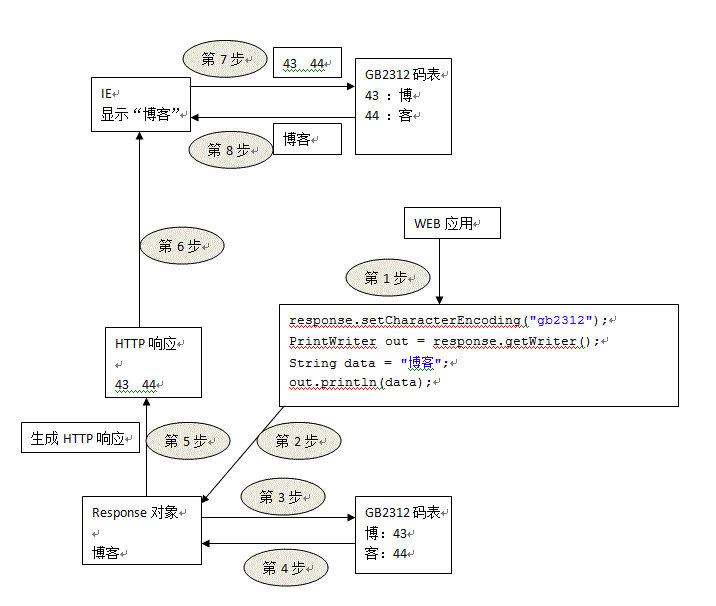
错误代码流程图:

而解决方案是:response.setCharacterEncoding("GB2312"); 设置response使用的码表
解决方案流程图:
补充:通过<meta>标签模拟response头;
<meta http-equiv="content-type" content="text/html"/> 等价于 response.setContentType("text/html");
四、request乱码问题
request请求分为post和get,对于不同的请求方式有不同的解决乱码的方案;
1.post请求乱码
错误原因:
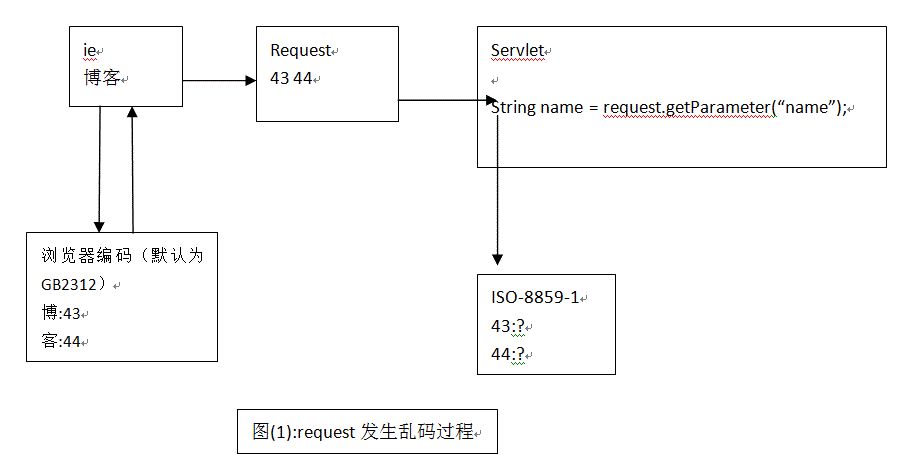
解决方案:
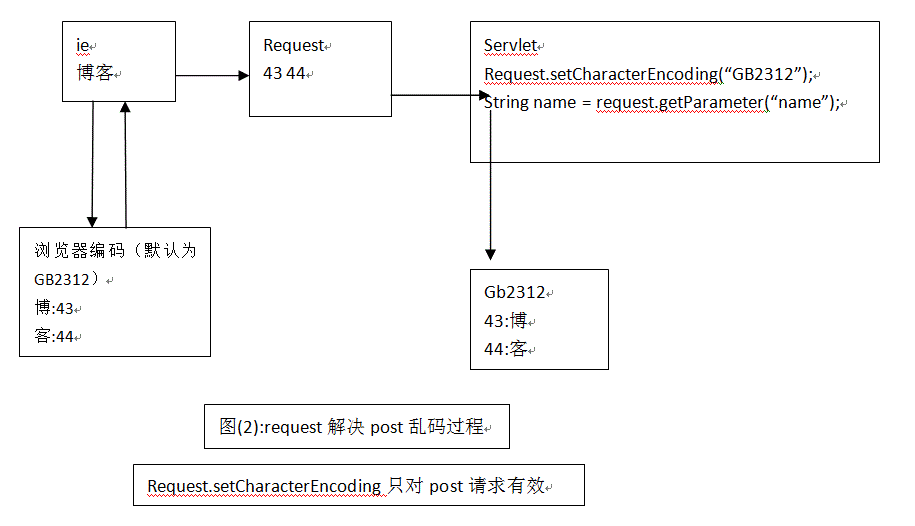
2.get请求乱码

























 1310
1310

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








