原型模式中主要用到Cloneable这个接口,来实现浅拷贝,下面是具体内容:
原型模式的适用场合:
1、实际项目中很少单独出现,一般与工厂模式一起出现,通过clone创建对象,并由工厂方法提供给调用者使用;
2、如果这个类的初始化非常复杂,需要消耗较多的资源(数据,硬件资源);
3、资源优化、性能和安全有要求的场景;
4、通过new创建对象比较繁琐或者需要访问权限;
5;多人访问一个对象,多个调用者都需要修改其值,使用原型模式拷贝多个对象提供给调用者使用
优点:提高性能,逃避构造器的约束
缺点:
1、必须实现Cloneable接口;
2、实现克隆时,必须对该类的功能进行全盘考虑,尤其是已有的类,或者是该类不支持串行化的间接对象,或者引用含有循环结构的时候
代码实现:
1:创建一个实现Cloneable接口的抽象类
package prototype_pattern;
public abstract class Shape implements Cloneable {
private String id;
protected String type;
abstract void draw();
public String getType(){
return type;
}
public String getId(){
return id;
}
public void setId(String id){
this.id=id;
}
public Object clone(){
Object clone=null;
try{
clone=super.clone();
}catch(CloneNotSupportedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return clone;
}
}2、创建扩展上面抽象类的实体类:Rectangle.java Circle.java Square.java
package prototype_pattern;
public class Rectangle extends Shape {
public Rectangle(){
type="Rectangle";
}
void draw(){
System.out.println("Rectangle");
}
}
package prototype_pattern;
public class Circle extends Shape{
void draw(){
System.out.println("Circle");
}
public Circle(){
type="Circle";
}
}
package prototype_pattern;
public class Square extends Shape {
void draw(){
System.out.println("Square");
}
public Square(){
type="Circle";
super.setId("2");
}
}3:创建一个类,从数据库中获取实体类,并将它们保存在hashtable中
package prototype_pattern;
import java.util.Hashtable;
public class ShapeClone {
private static Hashtable <String,Shape> shapeMap = new Hashtable();
public static Shape getShape(String shapeId){
Shape cacheShape = shapeMap.get(shapeId);
return (Shape)cacheShape.clone();
}
public static void loadCache(){
Circle circle= new Circle();
circle.setId("1");
shapeMap.put(circle.getId(), circle);
Square square= new Square();
square.setId("2");
shapeMap.put(square.getId(), square);
Rectangle rectangle=new Rectangle();
rectangle.setId("3");
shapeMap.put(rectangle.getId(), rectangle);
}
}4.测试demo
package prototype_pattern;
public class PrototypePatternDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ShapeClone.loadCache();
Shape cloneShape = ShapeClone.getShape("1");
System.out.println("Shape:"+cloneShape.getType());
Shape cloneShape1 = ShapeClone.getShape("2");
System.out.println("Shape:"+cloneShape1.getType());
Shape cloneShape2= ShapeClone.getShape("3");
System.out.println("Shape:"+cloneShape2.getType());
}
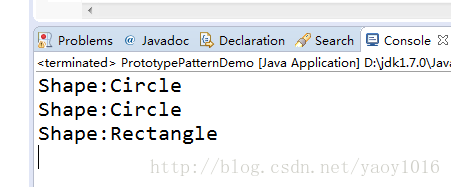
}5:运行结果
备注:
常说的浅拷贝:实现Cloneable接口,重写clone();
深拷贝:实现Serializable接口,读取二进制流






















 4740
4740

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








