前言:
The colon is one of the most useful operators in MATLAB®. It can create vectors, subscript arrays, and specify for iterations.
冒号在Matlab中主要应用向量和数组下标和for迭代等,在做下标表述的时候,比较晦涩难懂难懂有必要单独讨论一下:
1 表达式:
x = j:k x = j:i:k A(:,n) A(m,:) A(:) A(j:k)
1.1 x = j:k 【默认间隔1,j为第一维度,k为第二维度】
creates a unit-spaced vector
xwith elements[j,j+1,j+2,...,j+m]wherem = fix(k-j). Ifjandkare both integers, then this is simply[j,j+1,...,k].创建一个具备j到j+m的单位间隔向量,每个元素默认增加的步长为1.
【案,默认间隔增加的步长为1,这时候】
【例1】创建一个单位间隔向量:
x = 1:10
x = 1×10
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
>> y=7:14
y =
7 8 9 10 11 12 13 141.2 x = j:i:k 创建指定间隔的向量
x = j:i:kcreates a regularly-spaced vectorxusingias the increment between elements. The vector elements are roughly equal to[j,j+i,j+2*i,...,j+m*i]wherem = fix((k-j)/i). However, ifiis not an integer, then floating point arithmetic plays a role in determining whethercolonincludes the endpointkin the vector, sincekmight not be exactly equal toj+m*i. If you specify nonscalar arrays, then MATLAB interpretsj:i:kasj(1):i(1):k(1).创建一个普通间隔的向量,将i作为元素增加的步长。
【例2】创建一个指定间隔的向量:这个例子里面步长为0.1,这样0开始计算后,正好是有
Create vectors that increment or decrement by a specified value.
Create a vector whose elements increment by 0.1.
>> x = 0:0.1:1
x =
列 1 至 6
0 0.1000 0.2000 0.3000 0.4000 0.5000
列 7 至 11
0.6000 0.7000 0.8000 0.9000 1.0000有约束条件:
Output Arguments
collapse all
x— Regularly-spaced vector
row vectorRegularly-spaced vector, returned as a row vector. If
j > k, thenx = j:kis an empty matrix. More generally, the syntaxx = j:i:kreturns an empty matrix when:
i,j, orkis an empty input
i == 0
i > 0andj > k
i < 0andj < k
1.3 A(:,n), A(m,:), A(:), and A(j:k) common indexing expressions 数组的一般标号表达式
A(:,n),A(m,:),A(:), andA(j:k)are common indexing expressions for a matrixAthat contain a colon. When you use a colon as a subscript in an indexing expression, such asA(:,n), it acts as shorthand to include all subscripts in a particular array dimension. It is also common to create a vector with a colon for the purposes of indexing, such asA(j:k). Some indexing expressions combine both uses of the colon, as inA(:,j:k).一般标号表达式,冒号有点像通配符:
先生成一个3by3的矩阵,
A = magic(3)
A = 3×3
8 1 6
3 5 7
4 9 2
A(:,n)is thenth column of matrixA.【第n列所有元素】A(1,:) ans = 1×3 8 1 6>> A(2,:) ans = 3 5 7
A(m,:)is themth row of matrixA.-【第m行的所有元素】>> A(:,1) ans = 8 3 4>> A(:,2) ans = 1 5 9
A(:,:,p)is thepth page of three-dimensional arrayA.【一个page的数据】>> B = randn(4,3,2) B(:,:,1) = -0.1924 -1.4224 1.4193 0.8886 0.4882 0.2916 -0.7648 -0.1774 0.1978 -1.4023 -0.1961 1.5877
A(:)reshapes all elements ofAinto a single column vector. This has no effect ifAis already a column vector.【把二维数组的列合并成1列,降维了】>> A(:) ans = 8 3 4 1 5 9 6 7 2注意,3维数组这个操做不行。
A(:,:)reshapes all elements ofAinto a two-dimensional matrix. This has no effect ifAis already a matrix or vector. 【把刚才的一维的又搞成2维的了】>> A(:,:) ans = 8 1 6 3 5 7 4 9 2
A(j:k)uses the vectorj:kto index intoAand is therefore equivalent to the vector[A(j), A(j+1), ..., A(k)].按照从左到右,从上到下的顺序,将A从元素j到元素k,提取出来,并合成一个向量。
>> A(2:3) ans = 3 4>> A(1:3) ans = 8 3 4
A(:,j:k)includes all subscripts in the first dimension but uses the vectorj:kto index in the second dimension. This returns a matrix with columns[A(:,j), A(:,j+1), ..., A(:,k)].这个就组合的意思:这里坐标的参数是向量的第一维度,右边的参数是向量的第二维度:
于是如果A=
>> A(:,:) ans = 8 1 6 3 5 7 4 9 2那么, 1到2列的选择为
>> A(:,1:2) ans = 8 1 3 5 4 91到3列的选择为:
>> A(:,1:3) ans = 8 1 6 3 5 7 4 9 2
3 实例举例和分析:
构建一个4阶的幻方备用:
>> A = magic(4) A = 16 2 3 13 5 11 10 8 9 7 6 12 4 14 15 1再构造一个8阶的幻方备用:
>> B = magic(8) B = 64 2 3 61 60 6 7 57 9 55 54 12 13 51 50 16 17 47 46 20 21 43 42 24 40 26 27 37 36 30 31 33 32 34 35 29 28 38 39 25 41 23 22 44 45 19 18 48 49 15 14 52 53 11 10 56 8 58 59 5 4 62 63 1
3.1 从某个指定行按照指定的顺序摘取数据:
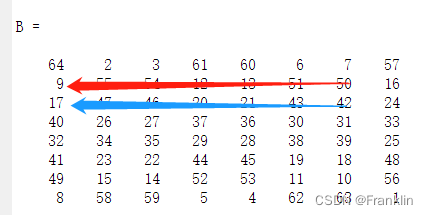
【例1】从幻方B,的第2,3行,从第7列到第1列,倒序或者说减序(-1)摘取数据
>> B(2:3,7:-1:1)
ans =
50 51 13 12 54 55 9
42 43 21 20 46 47 17【案,表征如下】
【例二】幻方A,从第3到4行,2到4列,正序摘取数据,默认为1,所以,可以不写,
>> A(3:4,2:4)
ans =
7 6 12
14 15 1 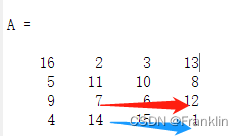
【例3】引用最后一列元素
>> A(:,end)
ans =
13
8
12
1【例四】引用第3行,导数第2个数据
>> B(3,end - 1)
ans =
42 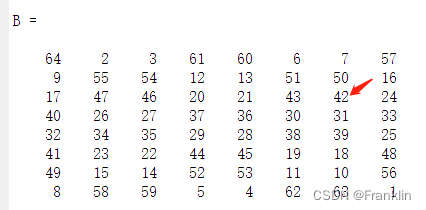
3.2 复杂的数据重组:
继续使用,上一小结生成的幻方矩阵做例子:
例五,摘取不确定的行和列,可以重复,并把他们重新组织起来。
本例,将B的第1,3行的,第2,3列组织起来,注意,第3行,和第2列,第3列都取了2次
>> B([1 3 3],[2 2 3 3])
ans =
2 2 3 3
47 47 46 46
47 47 46 463.3 冒号的通配符例子:
例6,我们用:做通配符,将一个3x3的矩阵拓展为 3x3x3x2的四维度的矩阵
>> C(:,:,1,2)=[1 2 3;4 5 6;7 8 9]
C(:,:,1,1) =
0 0 0
0 0 0
0 0 0
C(:,:,1,2) =
1 2 3
4 5 6
7 8 9【案,通配符这里占据了第1,2向量维度,我们只给出了一个3x3的矩阵,其他的矩阵自动赋值为0,这里我们定义了维度3by1&维度4by2的一个值,系统自动将3by1的赋值为0】
>> C(:,:,2,2)=[9 8 1;6 5 4;3 2 1]
C(:,:,1,1) =
0 0 0
0 0 0
0 0 0
C(:,:,2,1) =
0 0 0
0 0 0
0 0 0
C(:,:,1,2) =
1 2 3
4 5 6
7 8 9
C(:,:,2,2) =
9 8 1
6 5 4
3 2 1【案,我们继续赋值维度3by2&维度4by2的值,系统自动赋值其他】
>> C(:,:,3,2)=[5 5 5;5 5 5;5 5 5]
C(:,:,1,1) =
0 0 0
0 0 0
0 0 0
C(:,:,2,1) =
0 0 0
0 0 0
0 0 0
C(:,:,3,1) =
0 0 0
0 0 0
0 0 0
C(:,:,1,2) =
1 2 3
4 5 6
7 8 9
C(:,:,2,2) =
9 8 1
6 5 4
3 2 1
C(:,:,3,2) =
5 5 5
5 5 5
5 5 5【同理,构造了整个矩阵】
2 相关名称参考:
2.1 unit-spaced vector 【单位间隔向量 】
注意这个和Unit vect不太一样,是单位间隔向量。
参考:
Vector creation, array subscripting, and for-loop iteration - MATLAB colon : (mathworks.com)








 本文详细介绍了MATLAB中冒号运算符的使用,包括创建单位间隔和指定间隔的向量,以及在数组索引中的应用,如提取矩阵的行、列和子集。通过实例展示了如何利用冒号进行数据的选取和重组,对于理解MATLAB编程具有指导意义。
本文详细介绍了MATLAB中冒号运算符的使用,包括创建单位间隔和指定间隔的向量,以及在数组索引中的应用,如提取矩阵的行、列和子集。通过实例展示了如何利用冒号进行数据的选取和重组,对于理解MATLAB编程具有指导意义。



















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










