2.3.1 class selector
用法1:
为了配合class selector的使用,文档要有相应的标识。
<p
class="warning">When handling plutonium, care must be taken to avoid
the formation of a critical mass.</p>
<p>With plutonium, <span
class="warning">the possibility of implosion is
very real, and must be avoided at all costs</span>. This can be accomplished
by keeping the various masses separate.</p>
为了配合不同元素中的warning,css定义为:
*.warning {font-weight: bold;}
可简写为:
.warning {font-weight: bold;}
用法2:
class selector通过直接引用一个元素的class属性中的值来产生作用。通常,引用之前有一个点号“.”,该点号表明这是一个class selector。该点号将class selector和与其他可以组合在一起的东西分割开来,比如element selector。下例:
p.warning {font-weight: bold;}
意为:该selector与任何具有class属性的p元素相匹配。
用法3:
将class selector和针对特定元素的class selector混合使用。例如
.warning {font-style: italic;}
span.warning {font-weight: bold;}
意为:除了span,所有的warining将设为italic。
2.3.1.1 multiple classes
一个元素可以指定一个class来确定其显示方式,也可以指定多个class。如下:
<p class="urgent warning">When handling plutonium, care must be taken to avoid the formation of a critical mass.</p>
上例中的p指定了两个class。下面的css片断可以适用:
.warning.urgent {background: silver;}
上面的css片断指定了warning和urgent两个class,实际是指定了一个class组合。任何元素的属性class中出现了warning和urgent的,不论顺序都有效,即出现的
class都在组合中。
但是如果在class属性值的列表中,出现的多个class不属于任何以定义的一个组合时,
错误。但是允许只出现某个组合中的所有class中的部分class。
2.3.2 id selectors
id selectors类型class selectors,区别在于:
id selector中以“#”代替“.”
id selector根据元素中的id属性来过滤。
一个例子:
*#lead-para {font-weight: bold;}
类似于:
*.lead-para {font-weight: bold;}
因此可以简写为:
#lead-para {font-weight: bold;}
一个例子:
<p id="lead-para">This paragraph will be boldfaced.</p>
<p>This paragraph will NOT be bold.</p>
2.3.3 class selector和id selector之间的选取
1
class可以在任意数目的elements中使用。
Id在一个html文档中只能使用一次。即如果一个element使用了某id,在该文档中其
他element就不能使用该id了。
但是,对很多浏览器而言,如果html文档违反上述规定却是可以容忍的,依然正确显
示。然而带来的问题是跟DOM相关的操作就会出错。比如getElementById认为文档中只有一个element的id是给定值。
2
id selectors不能像class selectors那样具有组合的形式。
3
在纯语法的角度来看,dot-class的形式(如,“.warning”),xml文档不识别。而hash-ID的形式可以被任意文档html,svg,mathml,xml识别。
4
当用来决定某个给定的element使用的style的时候,id比class显得更重量级heavier weight。
另外,class和id selector是大小写敏感的。
2.4 attribute selectors
从class和id selectors的使用中可以看到,我们是通过具有某个值的属性来选择元素的。上面所谈到的class和id selectors只对html,svg,mathml适用,然而在其他标记语言mackup language中可能是不适用的。Css2对此情况,引入attribute selectors。Attribute selectors基于属性和属性的值来选择元素。一共有四类attribute selectors。
但是attribute selectors不被ie6/win支持,被opera和gecko支持。Ie7也似乎不支持。
2.4.1 简单属性选择
如果想根据属性来选择元素,而不关注属性的值,就可以使用simple attribute selector。
如,
h1[class] {color: silver;}
定义了所有具有class属性的h1元素的style,不论其class的具体取值。
So given the following markup:
<h1 class="hoopla">Hello</h1>
<h1 class="severe">Serenity</h1>
<h1 class="fancy">Fooling</h1>
又,
*[title] {font-weight: bold;}
所有具体title属性的所有元素的style。
又,多选的情况
a[href][title] {font-weight: bold;}
同时具体href和title属性的a元素的style。
2.4.2 基于具体属性值的选择
选择具有某特定取值的某属性的元素,如
a[href="http://www.css-discuss.org/about.html"] {font-weight: bold;}
同样存在多选,
a[href="http://www.w3.org/"][title="W3C Home"] {font-size: 200%;}
2.4.3 基于部分属性值的选择
上一节根据属性值选择时,对属性值的使用是完全匹配的策略,为了实现部分匹配的策略,如下:
p[class~="warning"] {font-weight: bold;}
部分匹配的意思是包含,不存在以warning开头或结尾的匹配方式。
2.4.4 特定属性选择
*[lang|="en"] {color: white;}
任何等于en或以en-开头的lang属性值对于的element的style。
如果存在一组列相关的属性值,就将其定义为xxx-?的形式,xxx是固定的,?用来区别各个不同的属性。
比如定义一组图片的名字为pic-1.jpg,pic-2.jpg。那么img[src|="pic"]就可以用来选出这组图片中的所有图片。
2.5 使用文档结构
css之所以很强大是因为它利用html文档的结构来决定文档中的元素的style。这不是css利用html文档的唯一方式。为了理解这一点,先来看看html文档的结构。
2.5.1 理解父子关系parent-child relationship
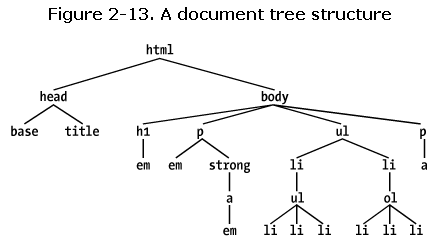
先看一段html
<html>
<head>
<base href="http://www.meerkat.web/">
<title>Meerkat Central</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Meerkat <em>Central</em></h1>
<p>
Welcome to Meerkat <em>Central</em>, the <strong>best meerkat web site
on <a href="inet.html">the <em>entire</em> Internet</a></strong>!</p>
<ul>
<li>We offer:
<ul>
<li><strong>Detailed information</strong> on how to adopt a meerkat</li>
<li>Tips for living with a meerkat</li>
<li><em>Fun</em> things to do with a meerkat, including:
<ol>
<li>Playing fetch</li>
<li>Digging for food</li>
<li>Hide and seek</li>
</ol>
</li>
</ul>
</li>
<li>...and so much more!</li>
</ul>
<p>
Questions? <a href="mailto:suricate@meerkat.web">Contact us!</a>
</p>
</body>
</html>
css所表现出来的强大是基于元素的父子关系的。Html文档的元素是等级式的
hierarchy,可以用树的结构来表示。父子关系就是祖先和后代关系的特例。
2.5.2 descendant selectors
descendant selector利用了html模型的树型关系,可以找到某元素的特定后代元素。如,
h1 em {color: gray;}
做为h1元素的后代的所有em元素。
2.5.3 选择子元素
如果只选择子元素,使用“>”如下:
h1 > strong {color: red;}
一个复杂的,结合class selector的例子:
table.summary
td
>
p
class属性为summary的table元素的后代中的p元素,且p元素的父元素是td。
2.5.4 选择临近的兄弟元素
利用+,如:
h1 + p {margin-top: 0;}
紧跟h1的元素,并且是p的兄弟元素。
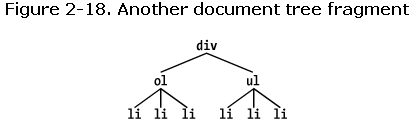
li+li只能选中ol下面第二,三个li,ul下面第二,三个li。如下:

ol+ul{}可以选出ul下所有三个li。
W3c的定义:
Adjacent sibling selectors have the following syntax: E1 + E2, where E2 is the subject of the selector. The selector matches if E1 and E2 share the same parent in the document tree and E1 immediately precedes E2.
选择紧贴在对象E1之后的所有E2对象。E2和E1对象在文档目录结构树(DOM)中有共同的父对象。























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








