1.内部类
1.1静态内部类
静态内部类:需要+static进行修饰的内部类
使用特点: 在静态内部类中,不能使用外部类的成员属性
class Outter{
private static int a = 1;
private int b = 2;
public static class Inner{
public void test() {
System.out.println(a);
//System.out.println(b); //加载时机问题
}
}
}
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//调用静态内部类方式1:
Outter.Inner inner = new Outter.Inner();
inner.test();
//直接new一个静态内部类方式2:
Inner inner2 = new Inner();
}
}
1.2局部内部类
局部内部类:在外部类的方法中定义的一个类; 外界是不能调用的
不能在局部内部类中加权限修饰--例如:public权限
局部内部类,只能在方法内部去调用它
class Outter{
private String name="乔乔";
public void show() {
final String name2 = "小乔"; //在局部内部类中如果使用了外部类的局部变量,则会默认+final
class Inner{
private String name = "小禾乔";
public void test(){
System.out.println("局部内部类的方法--"+name); //小禾乔
System.out.println(Outter.this.name); //乔乔
System.out.println(name2); //小乔
}
}
new Inner().test(); //在外部类方法中才能调局部内部类
}
}
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Outter().show();
}
}
1.3匿名内部类(重点)
匿名内部类:本质就是多态,只要能用上之前的抽象类或接口实现多态,则肯定能用匿名内部类
1.3.1直接赋值的匿名内部类
======================直接赋值的匿名内部类=====================
//案例:喷火娃具备喷火的能力
//分析:
//类 Person Fireable接口
//方法: 重写fire fire
interface Fireable{
void fire();
}
class Person implements Fireable{
@Override
public void fire() {
System.out.println("喷火娃在喷火...");
}
}
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//---接口实现多态---
Fireable fireable = new Person();
fireable.fire();
//----匿名内部类----
Fireable fireable2 = new Fireable() {
@Override
public void fire() {
System.out.println("匿名内部类在喷火...");
}
};
fireable2.fire();
}
}
1.3.2传参形式的匿名内部类
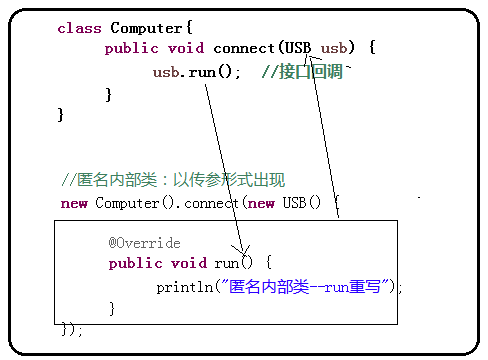
//匿名内部类以传参形式出现:
//案例:电脑连接usb的鼠标
//匿名内部类与接口实现多态的应用场景:
//当项目中需要多次实例化对象---接口实现多态
//当进行简单测试或实例化一次对象时---匿名内部类
interface USB{
void run();
}
class Mouse implements USB{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("鼠标正在运转..");
}
}
class Computer{
public void connect(USB usb) {
usb.run(); //接口回调
}
}
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//接口以传参形式实现多态
new Computer().connect(new Mouse());
//匿名内部类:以传参形式出现
new Computer().connect(new USB() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("匿名内部类,以传参方式出现---run重写");
}
});
}
}
1.3.3匿名内部类扩展案例
======================匿名内部类扩展案例=====================
/**
匿名内部类的扩展应用:
案例: 使用工具类,测试一段代码执行的时间,要求使用匿名内部内方式进行接口回调
提示:
测试时间的方法:System.currentTimeMillis()
分析:
接口: ITest 标准:codeTest
工具类: Tool 静态方法: getTime;
好处:使用匿名内部类后,使得程序的扩展性,维护性,复用性更强
说明:在后续的过滤器,拦截器,spring内部源码都有匿名内部类的思想
*/
interface ITest{
void codeTest();
}
class Tool{
public static long getTime(ITest test) {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
test.codeTest(); //接口回调
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
return end-start;
}
}
public class Test3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
//执行的代码
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(end-start);
*/
long timer = Tool.getTime(new ITest() {
@Override
public void codeTest() {
//放测试代码的区域
String s = "";
for(int i=0;i<10000;i++) {
s+=i;
}
}
});
System.out.println(timer);
}
}
2.Object类
2.1Object基本操作
Object类:老祖宗类,所有类直接或间接继承Object
Object类中的方法是所有类都具有的方法---继承性Object中的多态使用:
1.直接Object引用子类对象
2.Object引用传参方式接收对象
3.Object以返回值方式接收对象
class Son{
}
public class BasicTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Object obj1 = new Son(); //多态核心--父类引用直接指向子类对象
test(new Son());
Object obj3 = getSon(); //以返回值方式实现多态
}
private static Object getSon() {
return new Son();
}
private static void test(Object obj) { //Object以传参方式实现多态
}
}
2.2Object的getClass方法
//getClass方法: 获取Object类的类对象
class Person{
}
public class ClassTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Class class1 = new Object().getClass(); //获取Object的类对象
Class class2 = new Object().getClass();
//获取类对象,只要调用对象所在类是同一个类,那么类对象就是同一个
System.out.println(class1==class2); //true---反射机制
Class class3 = new Person().getClass();
Class class4 = new Person().getClass();
System.out.println(class3==class4); //true--两个都是Person类的对象,所以类对象一致
}
}
2.3Object的hashCode方法(重点)
Object的hashCode:每个不同对象都会得到一个唯一的hash值(整数值)
应用场景:new不同对象,根据相同属性设置,决定hashCode一致
//案例: 获取自定义对象的hashCode
//目的: 属性一致,则hash值相同,如何做?
//解决方案---重写,父类的方法不适用我,我需要重写
class Student{
String name;
public Student(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public int hashCode(){
//重写后,将调用Object的hashCode转为了调用String类型的hashCode
return name.hashCode(); //返回属性的hashCode
}
}
public class HashCodeTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(new Object().hashCode()); //不同对象,两个打印的hashCode不同
System.out.println(new Object().hashCode());
System.out.println(new Student("乔乔").hashCode());
System.out.println(new Student("乔乔").hashCode());
}
}
2.4toString方法(重点)
Object的toString:用于打印类名@hash值
应用场景:toString一般用于打印自身对象,返回属性值的打印
处理方案:重写自定义类的toString方法
class Teacher{
private String name;
public Teacher(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override //重写Object的toString方法,返回属性值
public String toString() {
return name;
}
}
public class ToStringTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Object obj = new Object();
System.out.println(obj.toString()); //java.lang.Object@15db9742
Teacher teacher = new Teacher("qiaoqiao");
System.out.println(teacher.toString());
//简化版打印对象:
System.out.println(teacher);
}
}
2.5equals方法(重点)
Object的equals方法:
比较两个对象是同一个对象,返回结果才为true, 等价于‘==’
//案例:自定义对象比较相等
//应用场景: 往往属性值一致,则认为是同一个对象
//问题: 传入相同属性名,但是调的依然是Object的equals方法,还是比较地址
//解决方案: 重写equals,按自己方式比较属性值
class Star{
private String name;
public Star(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (obj instanceof Star) {
Star star = (Star) obj;
//转为了属性String的equals的调用,String的equals方法就是比较内容的
return this.name.equals(star.name);
}else {
return false;
}
}
}
public class EqualsTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Object object = new Object();
System.out.println(object.equals(object)); //true
System.out.println(object==object); //true
Star star = new Star("qiaoqiao");
System.out.println(star.equals(new Star("qiaoqiao"))); //true
System.out.println(star.equals("qiaoqiao")); //false
}
}
2.6finalize方法
当程序中出现垃圾对象时,jvm可以通过gc(垃圾回收器),将垃圾对象进行回收
垃圾对象:就是new出来的对象,没有人使用
两种垃圾回收方式:
1.自动回收:当程序内存耗尽时,jvm会一次性将垃圾对象回收
2.手动回收:调用System.gc(),通知jvm需要进行垃圾回收了(调用finalize方法),一般都会延时回收
class Woman{
private String name;
public Woman(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override //通过jvm需要回收垃圾的触发
protected void finalize() throws Throwable {
System.out.println(name+"已经被回收了");
}
}
public class FinalizeTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Woman woman = new Woman("刘亦菲"); //new的对象有人用
new Woman("凤姐"); //new的对象没人用--垃圾对象
System.gc(); //手动通知回收垃圾
}
}
3.包装类
java语言特性: 面向对象
为了承诺java中一切皆为对象,八大基本类型需要有对应的包装类的类型,
包装类是一个引用类型,具备了面向对象的特点
int--->Integer
char-->Character
其余只需首字母大写就变成了包装类
3.1装箱与拆箱
//基本类型与包装类的转换
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//------装箱:基本类型转包装类-------
int a = 3;
Integer integer = new Integer(a); //构造器方式
integer = Integer.valueOf(a); //静态方法方式
System.out.println(integer); //Integer重写了toString
//-------拆箱:包装类转基本类型--------
a = integer.intValue();
System.out.println(a);
//---------自动装箱------------
Integer integer2 = a;
int b = integer2; //自动拆箱
//注意:自动装箱和拆箱的本质依然需要通过手动装箱和拆箱,只不过系统帮我们做了
//查看反编译工具
//其他类型与数字字符串的操作
//1.其他类型转字符串
String s = integer2+"";
//2.字符串转基本类型
int c = Integer.parseInt(s);
double d = Double.parseDouble(s);
//3.字符串转包装类型
Integer integer3 = new Integer(s);
}
}
3.2包装类的用法
//包装类的用法
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer integer = new Integer(10);
Integer integer2 = new Integer(10);
System.out.println(integer==integer2); //false 比较地址
//valueOf:传入的参数为-128~127之间,那么预先给定了空间;所以每次传的值一致,则是同一个地址
Integer integer3 = Integer.valueOf(10);
Integer integer4 = Integer.valueOf(10);
System.out.println(integer3==integer4); //true
Integer integer5 = Integer.valueOf(300);
Integer integer6 = Integer.valueOf(300);
System.out.println(integer5==integer6); //false
}
}
4.String类(重点)
4.1String的创建
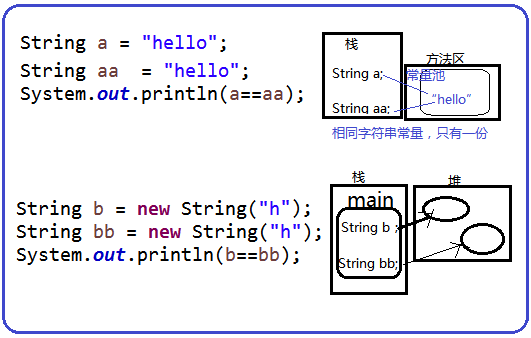
//字符串类的创建:
public class CreateTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String a = "hello"; //直接赋值创建对象
String aa = "hello";
System.out.println(a==aa); //true
String b = new String("hello");
String bb = new String("hello");
System.out.println(b==bb); //false
//一般比较字符串相同,使用equals--比较内容
System.out.println(b.equals(bb)); //true
}
}
4.2String的常用方法
//String类: 不可变字符串
//不可变字符串:调用任何方法,不会改变原对象的值
public class MethodTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String a = "hello";
System.out.println(a.charAt(0)); //获取该下标的字符,下标从0开始
String b = a.concat("world"); //字符串拼接--helloworld
System.out.println(b); //hello
System.out.println(a.contains("hel")); //是否包含子串
char[] c = a.toCharArray(); //将字符串转字符数组返回
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(c));
System.out.println(a.length()); //求长度
System.out.println(a.indexOf("ll")); //根据传入的子串,得到下标
System.out.println(a.toUpperCase()); //小写转大写
System.out.println(a.startsWith("h")); //true
System.out.println(a.startsWith("hello")); //true
System.out.println(" h e ".trim()); //去除左右空格
String d = "窗外的麻雀,在电线杆上多嘴";
//replace:完全匹配的替换
System.out.println(d.replace("麻雀", "xx")); //
//replaceAll:正则表达式替换,可以完全匹配也可以按规则;
//例如: 手机号替换;规则:1开头,长度11,必须都数字 dd13833388833ff
System.out.println(d.replaceAll("麻雀", "xx")); //
String[] dd = d.split(","); //按某个字符串进行分割,返回字符串数组
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(dd));
System.out.println(a.substring(1)); //从下标1开始提取子串到最后
System.out.println(a.subSequence(1, 3)); //包括起始下标,不包括终止下标
}
}
4.3可变字符串(重点)
可变字符串(StringBuffer、StringBuilder)
调用任何方法,可以改变原对象的值
有了不可变字符串,为什么需要可变字符串? 提升性能StringBuffer、StringBuilder区别(扩展先了解)
在使用上都是一样的,只是StringBuffer加了锁,更安全,性能低;
StringBuilder没加锁,不安全,性能高
应用场景:
在单线程(一条执行通道)中倾向用StringBuilder,性能更好,因为不存在不安全的情况
在多线程中倾向用StringBuffer,考虑安全为主
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//可变字符串的创建
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("hello");
//StringBuilder sb2 = "dd"; //注意:不能直接赋值字符串
sb.append("world"); //字符串追加
System.out.println(sb);
//StringBuilder与String性能PK---通过反编译工具查看
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
//String a = "";
for(int i=0;i<10000;i++) {
//a += i;
sb.append(i);
}
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis()-start);
System.out.println(sb.toString()); //转字符串返回
//System.out.println(sb.reverse()); //字符串反转
System.out.println(sb.delete(3, 6)); //删除指定起始下标和终止下标字符串,不包括终止下标
}
}
5.BigDecimal与BigInteger
5.1BigDecimal
BigDecimal:用于存储比double更精确的值
public class BigDecimailTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double a = 0.1;
double b = 0.09;
System.out.println(a-b);
BigDecimal big1 = new BigDecimal("0.1");
BigDecimal big2 = new BigDecimal("0.09");
System.out.println(big1.subtract(big2)); //减法
System.out.println(big1.add(big2)); //加法
System.out.println(big1.multiply(big2)); //乘法
//1.1111111111111
//注意:除法有除不尽的情况,一定后面再加2个参数; 1.保留几位 2.取值模式
//除法取值模式:有向上取,向下取,四舍五入
System.out.println(big1.divide(big2, 2, BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP)); //除法
}
}
5.2BigInteger
BigInteger比int存储的值更大
public class BigIntegerTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(Integer.MAX_VALUE); //2147483647
System.out.println(Integer.MAX_VALUE+1); //-2147483648
BigInteger big1 = new BigInteger(Integer.MAX_VALUE+"");//21474836471
BigInteger big2 = new BigInteger("1");
System.out.println(big1.add(big2)); //2147483648
}
}
6.Math与Random
6.1Math类
Math类: 数据的工具类 ,里面提供了很多数学计算方面的静态方法
public class MathTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(Math.ceil(1.2)); //2.0 向上取整
System.out.println(Math.ceil(1.8)); //2.0
System.out.println(Math.floor(1.2)); //1.0 向下取整
System.out.println(Math.floor(1.8)); //1.0
System.out.println(Math.round(1.2)); //1 四舍五入
System.out.println(Math.round(1.8)); //2
//Math.random()---0.0~1.0之间,不包括1.0
//案例:随机出来75~100的数
int num =(int)(Math.random()*26)+75;
System.out.println(num);
}
}
6.2Random类
Random类: 专业求随机数的类
public class RandomTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Random random = new Random(); //真随机
//Random random = new Random(2); //伪随机
//根据传入参数进行随机:例如 5--0到4之间随机
for(int i=0;i<5;i++) {
System.out.print(random.nextInt(5)+"\t");
}
//案例:随机出来75~100的数
int num = random.nextInt(26)+75;
System.out.println(num);
}
}
7.日期类
7.1Date类
Date类: 日期类
打印日期为格林威治时间格式
public class DateTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Date date = new Date();
System.out.println(date);
System.out.println(date.getTime());
//Date date2 = new Date(1000); //从1970年开始+1秒
Date date2 = new Date(date.getTime());
System.out.println(date2);
}
}
7.2日历类
日历类: abstract抽象类 用于求时间的类
public class CalendarTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
//System.out.println(Calendar.YEAR); //2021?
System.out.println(calendar.get(Calendar.YEAR)); //2021
System.out.println(calendar.get(Calendar.MONTH)+1); //10 0~11代表月份
System.out.println(calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH)); //27
calendar.set(calendar.YEAR, 2000); //设置年份
System.out.println(calendar.get(Calendar.YEAR)); //2000
calendar.add(Calendar.YEAR, 20); //给年份增加数量
System.out.println(calendar.get(Calendar.YEAR)); //2020
}
}
7.3日期格式类
SimpleDateFormat:带格式的日期类---配合Date使用
public class SimpleDateFormatTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {
//实例化日期格式类,传入日期格式
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
//传入Date--->转字符串输出
System.out.println(sdf.format(new Date()));
String strDate = "2009-08-09 08:10:08";
//传入字符串-->根据日期格式返回Date对象
Date date = sdf.parse(strDate);
System.out.println(date);
}
}
8.System类
System类: 系统类,用于进行系统操作的工具类---静态方法
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//System.exit(0); //退出
int[] a = {1,3,5};
int[] b = new int[a.length+3]; //扩容输入
System.arraycopy(a, 0, b, 0, a.length);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(b));
//获取系统的属性对象:键值对形式出现的
Properties properties = System.getProperties();
System.out.println(properties); //{key=value,key2=value,,,}
System.out.println("========================");
//可以根据key获取value,key往往为已知且是字符串形式
System.out.println(properties.getProperty("sun.boot.library.path"));
}
}
9.例题
/**
* 1.编写程序检查“hello” 是否包含e
* */
public class Work01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String a = "hello";
if(a.contains("e")) {
System.out.println("包含e");
}else {
System.out.println("不包含e");
}
}
}/**
* 2、编写程序去除“ ha he ”的前后空格
* */
public class Work02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = " ha he ";
System.out.println(s.trim());
}
}/**
* 3、编写程序将 “hello” 全部变为大写,并输出到屏幕,截取子串”LLO” 并输出到屏幕
* */
public class Work03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "hello";
String result1 = s.toUpperCase();
String result2 = result1.substring(2);
System.out.println(result1);
System.out.println(result2);
}
}/**
* 4、String s = "富家不用买良田,书中自有千钟粟, 安居不用架高堂,书中自有黄金屋, 出门莫恨无人随,书中车马多如簇,娶妻莫恨无良媒,书中自有颜如玉,男儿欲遂平生志,五经勤向窗前读"
请输出分段输出诗句
* */
public class Work04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "富家不用买良田,书中自有千钟粟,安居不用架高堂,书中自有黄金屋,出门莫恨无人随,书中车马多如簇,娶妻莫恨无良媒,书中自有颜如玉,男儿欲遂平生志,五经勤向窗前读";
for(String result:s.split(",")) {
System.out.println(result);
}
}
}/**
* 5、倒叙输出字符串“abcdefg”
* */
public class Work05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "abcdefg";
StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer(s);
System.out.println(stringBuffer.reverse());
}
}import java.math.BigDecimal;
/**
* 6、使用BigDecimal做加、减、乘、除计算
* */
public class Work06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BigDecimal a = new BigDecimal("3.3");
BigDecimal b = new BigDecimal("6.6");
System.out.println(a.add(b));//加法
System.out.println(a.subtract(b));//减法
System.out.println(a.multiply(b));//乘法
System.out.println(a.divide(b));//除法
}
}import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* 7、输入一个字符串,输入要查找,查找特定字符出现的次数
* */
public class Work07 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入一个字符串:");
String str = input.next();
int l = str.length();
System.out.println("输入您要查找的字符:");
String s = input.next();
if(str.contains(s)) {
str = str.replaceAll(s, "");
System.out.println("您查找的字符出现"+(l-str.length())+"次");
}else {
System.out.println("您查找的字符没有出现!");
}
}
}
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* 8、编写Emp类,属性:name、age、sex、account、pwd,编写注册验证方法,
* account及pwd不能小于6位,用户名不能有特殊符号(@、#、$、%)
* */
class Emp{
private String name;
private int age;
private String sex;
private String account;
private String pwd;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public String getAccount() {
return account;
}
public void setAccount(String account) {
this.account = account;
}
public String getPwd() {
return pwd;
}
public void setPwd(String pwd) {
this.pwd = pwd;
}
public Emp(String name, int age, String sex, String account, String pwd) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.sex = sex;
this.account = account;
this.pwd = pwd;
}
@Override
public String toString(){
return "Emp [姓名:" + name + ", 性别:" + sex + ", 年龄:" + age + ", 账户:" + account + ", 密码:" + pwd + "]";
}
}
public class Work08 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入用户账号:");
String account = input.next();
System.out.println("请输入用户密码:");
String pwd = input.next();
System.out.println("请输入姓名:");
String name = input.next();
System.out.println("请输入年龄:");
int age = input.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入性别:");
String sex = input.next();
//创建emp对象
Emp emp = new Emp(name,age,sex,account,pwd);
if(show(emp)) {
System.out.println("注册成功!"+emp);
}else {
System.out.println("注册有误!");
}
}
public static boolean show(Emp e) {
//判断用户密码长度不能小于6
if(e.getAccount().trim().length()>=6 && e.getPwd().trim().length()>=6) {
String[] s = {"@","#","$","%"};//特殊符号数组
for(String string:s) {//遍历特殊符号数组
if(e.getAccount().contains(string)) {
System.out.println("用户账号或者密码不能含有特殊符号!");
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
System.out.println("用户密码不能少于6位");
return false;
}
}



















 956
956











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








