目录
- Bean生命周期概念
- Spring容器管理Bean的生命周期大致流程
- Spring源码,Bean的创建与初始化
- 实例1:测试Bean的初始化方法和销毁方法
- 实例2:测试Spring IoC初始化到Bean应用到容器销毁全过程
- Bean具体生命周期
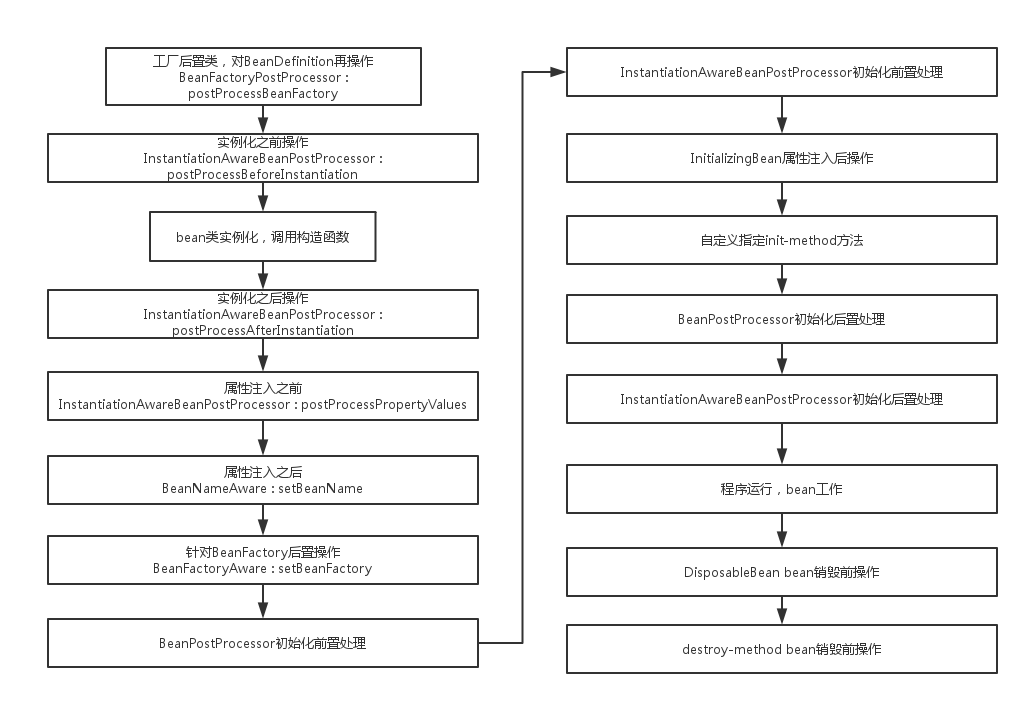
一.Bean生命周期
概述
我们知道一个对象的生命周期:创建(实例化-初始化)-使用-销毁,而在Spring中,Bean对象周期当然遵从这一过程,但是Spring提供了许多对外接口,允许开发者对三个过程(实例化、初始化、销毁)的前后做一些操作。
这里就实例化、初始化区别做一个说明,在Spring Bean中,实例化是为bean对象开辟空间(具体可以理解为构造函数的调用),初始化则是对属性的初始化,说的具体点,这里的属性初始化应该是属性的注入(构造函数也可以有属性的初始化语句,但不属于这一部分),属性注入是通过setter方法注入属性(不管是注解方式还是bean配置property属性方式,其实质都是通过属性的setter方法实现的)。
二.Spring容器管理Bean的生命周期大致流程
步骤:
- 容器初始化
- 通过构造器或工厂方法创建Bean
scope属性主要有两个singleton(单例)与prototype(多例模式),默认值为singleton。
Bean的创建时机主要由几个配置项共同来决定,包括:<bean id="person" class="com" scope="prototype"/>- scope属性,决定是Bean是单例模式(singleton)还是多例模式(prototype),默认为单例singleton;
- singleton:表示单例模式,这个很好理解,表示在容器中,只存在该Bean的一个实例,每次请求Bean时,返回的都是同一个。
- prototype:表示每次请求Bean时,都会新建一个Bean实例
- request:每次http请求都会创建一个bean,该作用域仅在基于web的Spring ApplicationContext情形下有效。
- session:在一个HTTP Session中,一个bean定义对应一个实例。该作用域仅在基于web的Spring ApplicationContext情形下有效。
- global-session:在一个全局的HTTP Session中,一个bean定义对应一个实例。该作用域仅在基于web的Spring ApplicationContext情形下有效。
- lazy-init属性,只对单例模式有效,决定是否延时加载,默认为false,表示在容器初始化时,就会生成单例
- lazy-init=false,表示容器在初始化时,就会创建单例Bean
- lazy-init=true,在初次getBean时,才会去创建Bean
- RequestMapping属性,这个注解MVC中才有,当有该属性时,lazy-init属性会失效(其实不是简单的冲突,而是RequestMapping会在另外的逻辑处理中生成单例);
- scope属性,决定是Bean是单例模式(singleton)还是多例模式(prototype),默认为单例singleton;
- 为Bean的属性设置值和对其他的Bean的应用(依赖的对象)
- 调用Bean的初始化方法,init-method=""
- Bean的使用
- 当容器关闭了,调用Bean的销毁方法,destroy-method=""
<bean id="person" class="com.Person" init-method="init" destroy-method="destroy">
三.Spring源码,Bean的创建与初始化
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory#doGetBean
protected <T> T doGetBean(
final String name, final Class<T> requiredType, final Object[] args, boolean typeCheckOnly)
throws BeansException {
...
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
...
}
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#createBean
/**
* Central method of this class: creates a bean instance,
* populates the bean instance, applies post-processors, etc.
* @see #doCreateBean
*/
@Override
protected Object createBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
//查找Bean相关的类
// Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point.
resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName);
// Prepare method overrides.
...
//检查重载(字面意思,非对象继承)方法是否存在
mbd.prepareMethodOverrides();
// Give BeanPostProcessors a chance to return a proxy instead of the target bean instance.
Object bean = resolveBeforeInstantiation(beanName, mbd);
...
//创建Bean
Object beanInstance = doCreateBean(beanName, mbd, args);
...
return beanInstance;
}
/**
* Actually create the specified bean. Pre-creation processing has already happened
* at this point, e.g. checking {@code postProcessBeforeInstantiation} callbacks.
* <p>Differentiates between default bean instantiation, use of a
* factory method, and autowiring a constructor.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param mbd the merged bean definition for the bean
* @param args arguments to use if creating a prototype using explicit arguments to a
* static factory method. This parameter must be {@code null} except in this case.
* @return a new instance of the bean
* @throws BeanCreationException if the bean could not be created
*/
//真正创建Bean的地方
protected Object doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final Object[] args) {
// Instantiate the bean.
...
//创建Bean实例,会调用构造函数
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
...
//进行属性设置
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
...
/*
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#initializeBean
初始化Bean,按顺序包括:
1.BeanNameAware,BeanClassLoaderAware,BeanFactoryAware的对应接口方法
2.BeanPostProcessor的预处理postProcessBeforeInitialization
3.InitializingBean接口的afterPropertiesSet
4.自定义的init-method方法
5.BeanPostProcessor的后处理postProcessAfterInitialization
*/
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
...
// Register bean as disposable.
//注册DisposableBean,只对singleton的Bean处理
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd);
return exposedObject;
}
四.实例1:测试Bean的初始化方法和销毁方法
1.目录
2.代码
Person.java
package com;
public class Person {
public Person() {
System.out.println("无参构造方法......");
}
public void init() {
System.out.println("初始化方法......");
}
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("销毁方法......");
}
private Integer id;
private String name;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + "]";
}
}
beans.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd">
<bean id="person" class="com.Person" init-method="init" destroy-method="destroy">
<property name="id" value="1"></property>
<property name="name" value="天明"></property>
</bean>
</beans>Test.java
package test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import com.Person;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext bf=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
Person per=(Person) bf.getBean("person");
System.out.println(per.getName());
//销毁bean
bf.close();
}
}
控制台打印结果:

五.实例2:测试Spring IoC初始化到Bean应用到容器销毁全过程
项目结构

Category.java
package com.yiguang.Spring.springTest.pojo;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactoryAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanNameAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
public class Category implements BeanNameAware,BeanFactoryAware,InitializingBean,DisposableBean{
private int id;
private String name;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Category() {
System.out.println("无参构造方法......");
}
public void init() {
System.out.println("初始化方法......");
}
public void destory() {
System.out.println("销毁方法......");
}
//BeanNameAware接口
public void setBeanName(String name) {
//属性注入后调用
System.out.println("6.setBeanName(BeanNameAware) 属性注入后调用, 此时name= " + name);
}
//BeanFactoryAware接口
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
//setBeanName 后调用
System.out.println("7.setBeanFactory(BeanFactory) setBeanName后调用");
}
//InitializingBean接口
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
//processBeforeInitialization(BeanPostProcessor)后调用
System.out.println("10.afterPropertiesSet(InitializingBean) processBeforeInitialization之后,配置的xml_init之前调用");
}
//DisposableBean
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("15.destroy(DisposableBean) 在processAfterInitialization之后,配置的xml_destroy之前调用");
}
}BeanFactoryPostProcessor.java
package com.yiguang.Spring.springTest.test;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanFactoryPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory;
public class BeanFactoryPostProcessorTest implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor{
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
//configurableListableBeanFactory.getBeanDefinition("Beans.xml");
System.out.println("1.postProcessBeanFactory(BeanFactoryPostProcessor) 工厂后处理器, ApplicationContext容器初始化中refresh()中调用");
}
}InitBeanPostProcessor.java
package com.yiguang.Spring.springTest.test;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
public class InitBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor{
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object o, String s) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("8.postProcessBeforeInitialization(BeanPostProcessor), bean = " + o.getClass());
return o;
}
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object o, String s) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("12.postProcessAfterInitialization(BeanPostProcessor), bean = " + o.getClass());
return o;
}
}InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.java
package com.yiguang.Spring.springTest.test;
import java.beans.PropertyDescriptor;
import java.util.Arrays;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.PropertyValues;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor;
public class InstanceBeanPostProcessor implements InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor{
public Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> aClass, String s) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("2.实例化bean之前调用,即调用bean类构造函数之前调用 " + aClass.getName());
/*try {
return Class.forName(""+aClass);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}*/
return null;//其实我不是很明白这里返回值得作用,之后可能会去深入理解
}
public boolean postProcessAfterInstantiation(Object o, String s) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("4.返回boolean,bean实例化后调用,并且返回false则不会注入属性");
return true;
}
public PropertyValues postProcessPropertyValues(PropertyValues propertyValues, PropertyDescriptor[] propertyDescriptors, Object o, String s) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("5.postProcessPropertyValues,在属性注入之前调用...... beanName = " + s + " 属性名集合 : " + Arrays.toString(propertyValues.getPropertyValues()));
//System.out.println("message = " + ((HelloWorld)o).getMessage()); 这里可以看到message还是null
return propertyValues;//这里要返回propertyValues,否则属性无法注入
}
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object o, String s) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("9.postProcessBeforeInitialization(InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) ");
return o;
}
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object o, String s) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("13.postProcessAfterInitialization(InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) ");
return o;
}
}
测试类Test
package com.yiguang.Spring.springTest.test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import com.yiguang.Spring.springTest.pojo.Category;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("Beans.xml");
Category category=(Category) context.getBean("c");
System.out.println(category.getName());
context.close();
}
}Spring Bean配置文件Beans.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd">
<bean name="c" class="com.yiguang.Spring.springTest.pojo.Category" scope="singleton" init-method="init" destroy-method="destory">
<property name="name" value="天明" />
</bean>
<bean class="com.yiguang.Spring.springTest.test.InitBeanPostProcessor" />
<bean class="com.yiguang.Spring.springTest.test.InstanceBeanPostProcessor" />
<bean class="com.yiguang.Spring.springTest.test.BeanFactoryPostProcessorTest" />
</beans>
执行结果:
























 1937
1937











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








