使用Trie树解决数字位操作问题。
Trie树
Trie树可以将keys/numbers/strings等信息保存在树中。
Trie树由一系列结点组成,每个结点存储一个字符/位。从而我们可以插入新的strings/numbers。
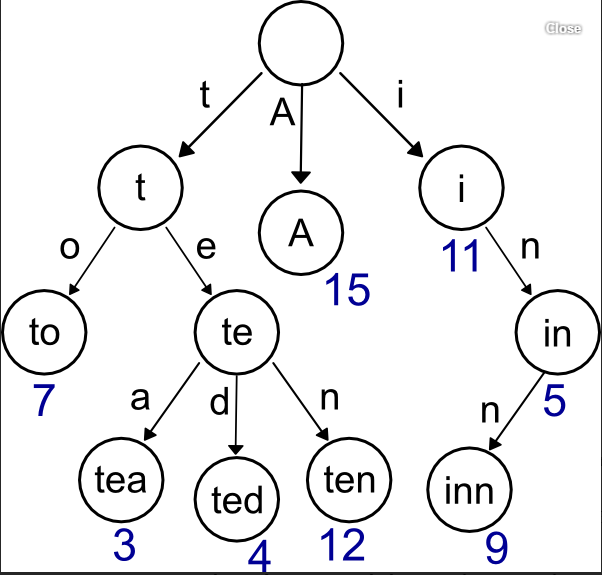
以trie树存储strings为例:
但现在我们要用trie树解决数字问题,特别是二进制位。问题如下:
Problem1: Given an array of integers, we have to find two elements whose XOR is maximum.
Solution:
假设有一种数据结构可以满足两种查询操作:
+1.插入一个数值X
+2.给定Y,找到目前已经插入的所有数据中与Y相异或(XOR)结果的最大值
如果有这样的数据结构,那就依次插入数据,查询最大值,从而获得最终的最大值。
trie树就是我们将要使用的数据结构。
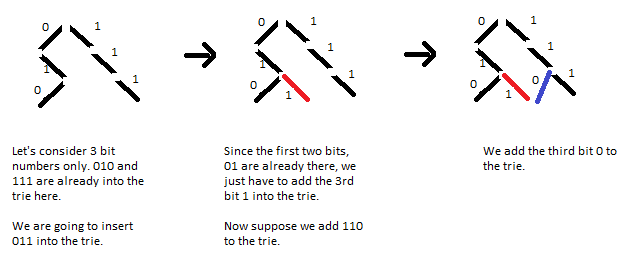
首先,看看如何在trie树中插入元素。
所以,只需要记录数字需要插入的路径,不必管已经存在的路径。
插入长度为N的key的时间复杂度O(N),O(N)就是log2(MAX),M








 本文介绍了如何使用Trie树解决数字位操作问题,包括找到两个元素的最大异或值、子数组最大异或和以及满足特定XOR条件的子数组数量。通过插入和查询操作,利用Trie树的特性,可以高效地处理这些问题。
本文介绍了如何使用Trie树解决数字位操作问题,包括找到两个元素的最大异或值、子数组最大异或和以及满足特定XOR条件的子数组数量。通过插入和查询操作,利用Trie树的特性,可以高效地处理这些问题。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章


















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








