欢迎关注[【youcans的AGI学习笔记】](https://blog.csdn.net/youcans/category_12244543.html)原创作品
【微软:多模态基础模型】(1)从专家到通用助手
【微软:多模态基础模型】(2)视觉理解
【微软:多模态基础模型】(3)视觉生成
【微软:多模态基础模型】(4)统一视觉模型
【微软:多模态基础模型】(5)多模态大模型
【微软:多模态基础模型】(6)多模态代理
【微软:多模态基础模型】(6)多模态代理:与LLM一起链接工具
Multimodal Foundation Models: From Specialists to General-Purpose Assistants
2023 年 6 月,微软在 CVPR2023 发表论文「 多模态基础模型:从专家到通用助手 」(Multimodal Foundation Models: From Specialists to General-Purpose Assistants) 。本文全面综述了多模态基础模型的分类和演化,这些模型展示了视觉和视觉语言能力,并重点关注了从专家向通用助手的过渡。
论文下载地址:
https://arxiv.org/abs/2309.10020
https://ar5iv.labs.arxiv.org/html/2309.10020
6. 多模态代理:与LLM一起链接工具
Chapter 6:Large Multimodal Models: Training with LLM

大型语言模型(LLM)(Chowdhery等,2022;OpenAI,2023a)已经展示了在各个领域接受通用的用户提示的有趣特性,并可以使用少量示例进行使用上下文学习以快速适应新场景。受到这些强大功能的启发,研究人员正在探索一种新的建模范式,,从解决有限、预定义问题的独立模型转变为将多个工具或专家与LLM协同链接以解决复杂、开放的问题。与第5章中介绍的不同,这种系统可以在没有任何训练的情况下构建,只需使用几个演示示例来教LLM生成对现有工具的正确调用。
在本章中,我们回顾了关于将不同的多模态专家与LLM链接以解决复杂的多模态理解问题的快速发展文献,这被称为多模态代理。我们从第6.1节开始概述了这种建模范式的演变,重点介绍了传统方法与新的通过LLM链接工具的建模范式之间的差异。第6.2节概括了多模态代理的概况。第6.3节以示例性的多模态代理 MM-REACT(Yang等,2023)为中心,全面回顾了如何构建多模态代理,它在多模态理解方面的新兴能力,以及如何轻松扩展以包括最新和最强大的 LLM 和潜在的数百万工具。最后,在第6.4节,我们以关于高级主题的讨论结束本章,例如如何改进/评估多模态代理,以及多模态代理驱动的多种应用。
6.1 概览
我们首先回顾了建模范式的演变,从特定任务的模型到最近的大型多模态模型,这些模型都需要数据管理和模型训练。然后,我们介绍了将工具与LLM链接起来的新建模范式,这可能不需要任何训练,而是直接利用预训练的 LLM 和通过开源平台或 API 广泛可用的现有工具。

图6.1 建模范式的演化
建模范式的演变。
如图6.1所示,我们正在见证从特定任务模型向跨语言、视觉和多模式研究的通用助手的过渡。
我们从针对特定任务的模型开始,这些模型是在小规模、有良好标注的数据上训练的。这导致了为每个任务甚至每个数据集专门设计的模型(Anderson等,2018;Li等,2019a;Yu等,2019)。
然后,我们过渡到预训练模型阶段,预训练-微调范式在NLP和视觉语言(VL)研究中得到了广泛采用。在预训练期间,模型可以利用大规模的、从网络抓取的噪声数据,例如数百万到数十亿的图像文本对(Chen等人,2020d;Wang等人,2022a),或数十亿的文本标记(Devlin 等,2019;Liu 等,2019)。然而,它仍然主要是针对特定任务的微调,需要与训练特定任务模型中使用的数据类似的小规模、注释良好的数据。这种范式催生了许多著名的模型,如NLP中的BERT(Devlin等,2019)、RoBERTa(Liu等人,2018)和VL中的UNITER(Chen等人,2020d)、OSCAR(Li等,2020b)。这些早期的VL基础模型被认为是大规模的(用1000万图像-文本对训练),但从今天的视角来看,它们可能是中等甚至小型模型(数十亿对)。
如今,我们正在进入一个通用建模的新时代,预训练已进一步扩展到数万亿个文本标记(Gao等,2023b,)。对于下游应用,这些通用模型已经显示出强大的性能,只需在少数演示示例上进行上下文的少量学习,甚至可以在零样本评估。这些模型就是我们现在所说的大型语言/多模态模型,包括GPT家族(OpenAI,2022;OpenAI,2023a)、PaLM家族(Chowdhery等,2022;Driess 等,2023)、LLaMa(Touvron 等,2023)和Flamingo(Alayrac等,2022)。
基于通用模型,第5章中介绍的构建指令遵循模型的流程类似于预训练-微调范式。例如,Alpaca(Taori等,2023)是基于预训练的 LLaMa(Touvron等,2023)构建的,然后在小规模的指导性调整数据上进行微调。类似地,对于指导性的 VL 模型(例如LLaVA(Li等,2023e),引入了额外的图像文本对齐预训练阶段,首先将视觉表示与冻结的LLM对齐,然后进行视觉指令微调。
新的建模范式:使用LLM链接工具。
LLM(Brown等,2020;Chowdhery等,2022;OpenAI,2023a)已经展示出了用极少的示例或文本指令来应对新任务的杰出能力,显示了它们有望成为许多应用的通用基础。尽管它们多才多艺且令人印象深刻,但它们在基本功能方面也面临挑战,如数学推理和信息检索。此外,不仅仅是LLM,现在大规模模型的一个基本限制是它们只代表了它们训练数据中描述的世界,随着时间的推移,这些数据将不可避免地变得过时。定期使用最新信息重新训练模型根本不可行。
与此同时,许多具有现实影响的任务无法仅仅由LLM来轻松解决。例如,访问最新信息和进行计算可以通过现有工具来完成(例如搜索引擎或计算器)。因此,最近的语言建模研究探索了一种新的建模范式,通过提供外部NLP工具(Nakano等,2021;Huang等,2022b;Ahn等,2022)来补充LLM,包括计算器、搜索引擎、翻译系统、日历,甚至是其他模型上的API调用。
上述研究主要集中在单一的模态,即语言,其中工具的输出以文本格式呈现,因此可以自然地作为附加知识输入到LLM中。然而,我们生活在一个多模态的世界中,一个真正智能的代理应该能够进行高级多模态推理和操作。如何通过工具使用使LLM具备多模态信号的感知能力,是本章其余部分的重点。
6.2 多模态代理
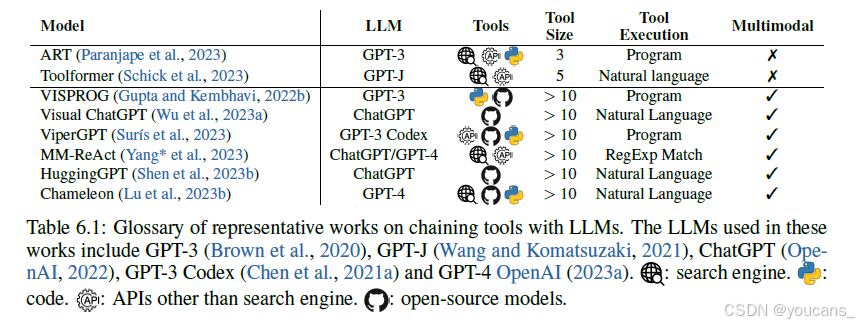
关于使用视觉专家的工具构建多模式代理,有几项具有代表性的工作,包括VISPROG(Gupta,2022b)、Visual ChatGPT(Wu等,2023a)和 MM ReAct(Yang等,2023)。VISPROG是第一个使用编程语言将不同的视觉工具与LLM链接起来的工作。Visual ChatGPT通过结合ChatGPT(OpenAI,2022)和各种图像生成工具,实现了基于对话的图像编辑。MM ReAct表明,当与各种先进的视觉专家协作时,ChatGPT 可以执行复杂的多模态操作和推理。图6.2显示了 2022年11月18日至2023年7月26日期间多模态代理领域的快速发展的文献。其中,我们在表6.1 中列出了更多的一些多模态代理,以及NLP领域的两篇代表性作品。

图6.2:从2022年11月18日到2023年7月26日的多模式代理的激增。
表6.1:LLM 链式工具代表性作品汇总表。这些工作中使用的 LLM 包括GPT-3(Brown等,2020)、GPT-J(Wang,2021)、ChatGPT(OpenAI,2022)、GPT-3 Codex(Chen等,2021a)和 GPT-4 OpenAI,2023a。
典型的多模态代理框架的概述如图6.3所示。用户直接与工具分配器交互,工具分配器充当代理的大脑。在当前的文献中,工具分配器通常是LLM。为了实现用户的目标,LLM将概述使用单个工具或将多个工具协同工作所需的所有步骤。随后,它将从所有候选工具中检索所需工具,并可能执行多轮工具以满足人类的需求。最后,收集工具的执行结果作为 LLM 的输入,以生成对用户的响应。接下来,我们将介绍多模态代理的三个关键组件。。

图6.3 多模态代理框架概览
-
工具。
工具是LLM可调用的外部模块,用于获取模型权重中缺少的额外信息,包括开源模型、公共/私有API 或代码解释器。由于LLM只接受语言输入,因此必须包含可以处理多模态输入的工具,来构建多模式代理。 -
规划。
在规划过程中,LLM将用户请求分解为更小的、可管理的子问题,并概述了一个逐步解决方案,每个解决方案都涉及调用外部工具。有两种方法可以教LLM进行规划。一种是在上下文中用所有候选工具的少数示例来提示LLM。这种方法可以直接扩展通用模型,但受到上下文长度的限制。另一种方法依赖于大量标注数据来微调 LLM,这很可能会损害模型的鲁棒性和通用性。 -
执行。
生成的计划进一步转化为对所需工具的可执行调用,可以通过正则表达式来匹配(Yang 等,2023)来完成;或直接提示LLM生成可执行程序(Surıs等,2023);或通过提供自然语言说明和一些调用示例来利用 LLM 的上下文少量示例学习能力,以描述每个模块的角色(Lu等,2023年)。执行结果反馈给LLM,以生成对用户的响应。
6.3 案例学习:MM-REACT
我们以MM-REACT(Yang*等人,2023年)作为案例研究,展示如何构建多模态代理,以及它在多模态理解方面的新兴能力,以及如何轻松扩展以包括最新和最强大的LLM 和潜在的数百万个工具。
6.3.1 系统设计
MM ReAct设计了一个由众多多模态工具组成的系统范式。在Yang等人(2023)的研究中,这些工具被称为专家。在本章中,我们统一称为为工具。使用ChatGPT(OpenAI,,2022)进行多模态推理和动作。通过用各种多模式工具增强纯语言的ChatGPT,MM ReAct支持多种模式的输入和输出,包括文本、图像和视频,如图6.4所示。

图6.4:MM-REACT的输入和输出(Yang 等,2023)
图6.5显示了MM ReAct的系统设计。MM ReAct中探索的多模态工具主要是计算机视觉模型,它们以图像为输入,从不同的角度解释图像内容。例如,图像字幕模型生成自然描述,OCR模型提取图像中的场景文本,名人识别模型识别名人姓名,对象检测模型提取具有边界框位置的突出对象。诸如ChatGPT之类的LLM充当代理的大脑,它根据输入图像和用户意图计划使用哪些工具以及以什么顺序使用。下来,通过图6.5中的示例,我们将揭示MM-REACT在幕后的规划和执行过程。
-
用户提示:
由于ChatGPT只接受语言输入,为了使图像作为输入生效,我们只需使用文件路径作为ChatGPT的输入。文件路径充当占位符,允许ChatGPT将其视为黑匣子,并在规划阶段后向不同的工具寻求帮助。除了输入图像,用户还可以以文本格式提供意图(例如,有关输入图像的问题)。当用户没有提供文本输入时,目标是获得关于图像的一般理解。 -
规划:
在接收到输入图像和用户提示后,ChatGPT规划要使用哪些工具。受到REACT(Yao等人,2022年)的启发,MM-REACT指示ChatGPT在需要特定工具时以特定的关键词回应,例如“助手,图像中有哪些物体?<文件路径>”(即图6.5中的操作请求)。在实践中,可以通过简单地字符串匹配ChatGPT响应中的关键词“助手”来判断是否需要多模态工具。
MM ReAct 鼓励 ChatGPT展示思维(推理)过程,以突出为什么需要外部工具,这在NLP研究中已被证明是有益的(Yao等,2022c)。此外,为了生成对每个工具的正确调用,在提示ChatGPT时,会添加指令和上下文示例作为前缀。每个工具都用模型名称、其功能的一般描述、输入数据格式和输出信息进行描述。在描述了每个工具之后,还包括了一些上下文对话示例,以提高性能。

图6.5 MM-REACT的系统设计
-
执行:
根据ChatGPT的行动请求,可以通过正则表达式匹配来解析工具名称和文件路径,然后用于调用工具(执行操作)。
以图6.5所示的示例为例,在收到输入图像后,ChatGPT首先调用一系列工具来获得有关图像的一般理解。所调用的工具包括图像字幕,用于对图像进行整体描述;密集字幕,用于获取有关图像中物体的区域级更详细的描述;对象标记,用于获取图像中物体的标签;人脸检测,用于获取物体标签中提到的两张脸的框坐标。工具的输出(即观察)被序列化为文本,并反馈给ChatGPT。
将观察结果与聊天历史相结合,ChatGPT可以进一步调用其他专家或将最终答案返回给用户。在这个具体的例子中,ChatGPT对图像中检测到的两张脸进行第二轮思考-行动-观察,并调用名人识别来获取这两个人的名字。 -
响应生成:
当ChatGPT决定不需要外部工具时,它会考虑所有收集到的观察结果,并将它们总结为对用户的响应。例如,在图6.5中所示的示例中,响应是:“这张图像包含两位名人,科比·布莱恩特和保罗·皮尔斯。他们都是篮球运动员。”
如果用户继续与MM-REACT互动,它会重复上述过程,但在规划所需工具时会考虑所有观察结果和聊天历史。例如,如果用户接着问:“左边的球员在他的职业生涯中赢得了多少个总冠军戒指”,这个信息既不包含在现有的观察中,也不在聊天历史中,但ChatGPT 有边界框以确定谁在左边,还知道球员的名字。它计划调用 Bing 搜索来找到正确答案,这应该是5个。
6.3.2 能力
图6.6显示了 MM-REACT 演示的代表性功能和应用场景,包括涉及数学和文本的视觉内容推理、理解视觉条件笑话/表情包、空间/坐标理解、视觉规划和预测、多图像推理、多跳文档理解、开放世界概念理解、视频分析和总结。
此外,我们在图6.7中展示了 MM-REACT 对多图像推理的完整响应示例,这可能不容易通过第5章中的视觉指令调整来实现。有关 MM-REACT 所有新功能的更全面的例子,建议读者参考原始论文。
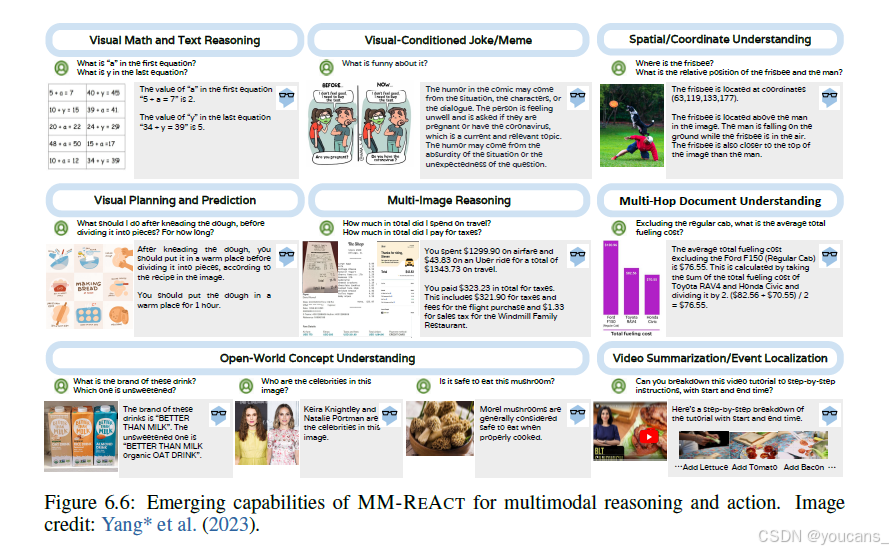
图6.6:MM-REACT涌现的多模态推理和行动能力。

图6.7:MM-REACT的能力和应用场景示例:多图像推理。
6.3.3 可扩展性
使用工具链构建多模态代理的一个有利特性是,系统可以从两个方面轻松扩展和增强。一种方法是升级系统的核心部分,即LLM,另一种方法是扩展外部工具的数量。
升级LLM:
MM-REACT的系统设计允许升级系统的核心部分,即LLM,以适应更新和更强大的模型,而无需重新训练。我们在图6.8中展示了一个示例,将ChatGPT升级为仅支持语言的GPT-4,这将提高MM-REACT的性能,潜在地达到多模态GPT-4的性能水平。

图6.8:多模态代理的可扩展性:升级LLM。
即插即用(添加更多工具):
现有的多模态代理通过即插即用机制集成各种工具,允许在无需训练的情况下添加更多工具。这个方向的一项突出工作是HuggingGPT(Shen等,2023b),它提出利用 Huggingface 托管的所有开源模型。Chameleon(Lu等,2023b)不仅包括Huggingface 模型,还包括来自 GitHub、Bing搜索API 和 Python编译器的开源模型。RestGPT(Song等,2023)提出了一个多层次在线规划框架,有效地处理了将LLM与100多个RESTful API 集成的实际挑战。然而,如果将这一框架扩展到成千上万甚至百万种工具方面,仍然具有挑战性,这是 TaskMatrix.AI(Liang 等,2023b)展示的潜在未来。
此外,人们可以利用SAM(Kirillov等,2023)作为一个工具,允许多模态代理以文本之外的更多方式与人类互动。回顾一下 MM-REACT,用户意图都是通过用户的自然语言查询来获得的。在InternGPT(Liu等,2023l)中,通过将SAM工具与 GPT连接起来,可以以更多的方式与系统互动,例如通过点击、涂鸦和绘制边界框。这些额外的互动在某种程度上模仿了我们人类在进行对话时的手指指点动作。
6.4 前沿话题
在本节中,我们将讨论更前沿的主题并探讨潜在的未来方向。
6.4.1 与第5章使用LLM进行训练的比较
我们已经探讨了基于LLM构建高级多模态系统的两个方向。关键区别在于,本章中的多模态代理利用LLM的高级规划能力来分配各种多模态工具,而第5章中使用LLM进行多模态模型训练仅仅是为了在多模态输入条件下生成文本。
然而,这两种方法都具有各自的优点和缺点。一方面,指令微调允许建立一个端到端模型,直接解释多模态输入中的丰富语义,但需要数据管理和训练,因此计算成本更高。然而,有限的指令微调数据可能会限制其在某些场景下的能力,比如 OCR。另一方面,通过将LLM与大量现成的模型/API/代码解释器连接起来作为工具,可以无需任何训练构建一个多模态代理,并利用上下文中的少量示例来教 LLM 进行规划。然而,由于没有训练,系统可能无法调用正确的工具。此外,弱领域专家可能会产生嘈杂的输出,可能会让LLM在规划或推理中感到困惑,从而导致性能不佳。
尽管这两种方法有明显的差异,但我们设想有一种中间的可能性,融合两种范式的优势,并提出以下问题。既然我们有像 LLaVA(Liu等,2023c)这样的开源LMM,是否可以将 LLM 替换为 LLaVA 作为工具分配器?如果可以,那么工具需要具备什么能力?指令微调可以解决什么问题?这些都是值得在不久的将来探索的有趣方向。
6.4.2 提升多模态代理
现有的多模式代理主要依赖于上下文中的少数示例来教授LLM规划,这可能不可靠,导致工具使用不准确。为了提高规划的准确性,已经提出了几项工作,我们将其分为以下三类。
通过代码生成来构建工具。
大多数现有的多模态代理使用自然语言提示LLM进行规划,以确定使用哪个工具。研究人员(Gupta,2023;Surıs等,2023)还探索使用编程语言进行更精确的执行。可视化编程(Gupta,2023)是这个方向的一项突出工作,它利用GPT-3(Brown等,2020)的上下文学习能力,从自然语言指令生成类似 Python 的模块化程序,用于组合视觉任务。ViperGPT(Surıs等,2023)指示 GPT-3 Codex(Chen等人,2021a)生成Python代码,为单轮查询应答编写多模式工具的组合。然而,由于代码仍然是由LLM生成的,因此工具使用不准确的问题仍然存在。
提高工具使用准确性:自我评估。
最近的工作 AssistGPT(Gao等,2023a)试图通过自我评估来提高工具使用的准确性。它在系统中增加了一轮检查和学习循环。当一轮计划和执行阶段完成时,系统会检查结果,并确定调用工具的推理路径是否成功,如果成功,将其保存为上下文示例,以便在未来的回合中更准确地教授LLM如何调用工具。
提高工具使用准确性:指令微调。
另一种提高工具使用准确性的方法是将系统与指令微调结合起来(Patil等,2023;Yang等,2023c)。可以通过自我指导生成一组指令-API对的数据集,以调整较小的LLM(例如,Vicuna-7B(Vicuna,2023))。
使用LMM作为工具分配器?
此外,随着LMM的发展,我们设想LLM可以被LMM取代,作为系统中的工具分配器,以实现更高级的应用场景。如果工具分配器可以接受多模态输入,则不需要将工具的输出统一为文本序列,从而使工具分配器与多模态工具之间的互动更加自然,特别是那些产生多模态输出的工具。例如,可以想象使用多模态GPT-4(OpenAI,2023a)来协调各种图像或视频生成工具,通过提供故事情节草图和主要角色的视觉示例,制作一部短片。
6.4.3 多模态代理的多样化应用
通过组合来自特定领域的工具,这种新的系统范例还可以支持各种特定领域的应用。
Yu等(2023b)将LLM与图像合成工具以及对象级/像素级的图像理解工具组合,构建了一个数据合成流水线,为合成图像提供多样化的注释。Instruct2Act(Huang等,2023c)将LLM与机器人执行器相结合,以实现基于多模态指令的机器人动作。当将一组音频模型与LLM连接时,AudioGPT(Huang等,2023a)可以理解和生成语音、音乐、声音和说话。类似地,WavJourney(Liu等,2023i)进一步支持包括语音、音乐和音效在内的叙述性音频创作。通过跟踪、字幕和音频理解模型,ChatVideo(Wang等,2023c)使ChatGPT能够理解多通道视频。其他应用场景包括 3D 场景生成(Lin等,2023;Feng 等,2023)、医学图像理解(Liu,2023;Sun 等,2023c)和视觉语言导航(Zhou等人,2023b)。
6.4.4 多模态代理的评估
使用多模态工具
尽管我们已经看到了多模态代理支持的新场景的定性示例,但目前尚不清楚这些代理在工具使用的准确性方面的表现如何。API-Bank(Li 等,2023k)是系统评估工具增强型LLM的性能的一个起点。
新兴能力。
现有的视觉语言基准主要关注感兴趣的特定能力,如视觉识别(Antol等,2015)、图像描述(Chen等,2015;Agrawal等,2019),以及其他专门能力,如场景文本理解(Sidorov等,2020;Gurari等,2018)、常识推理(Zellers等,2019)、外部知识(Schwenk等,2022)。大型多模态模型和多模态代理展示的有趣能力未被现有基准所检验,例如解决写在黑板上的数学问题,对新闻图像中的事件和名人进行推理,或解释视觉笑话。此外,这些系统产生的冗长的对话式输出对今天的评估指标提出了挑战。研究人员(Fu等,2023;Liu等,2023j)已经开始设计全面的评估样本,以促进对LMM的评估。为了测试多模态系统的综合能力,MM-Vet(Yu等,2023d)定义了6个核心的视觉语言能力,并检查了从能力组合中得出的16个感兴趣能力的集成(图6.10)。此外,为了适应开放式自由文本输出,MM-Vet提出了一种基于LLM的评估器,以实现对不同问题类型和答案样式进行评估。

图 6.9: 评估基准示例,侧重于工具使用的准确性。

图 6.10: 评估基准示例,侧重于新兴能力。MM-Vet关注不同核心视觉语言能力的集成,包括识别、OCR、知识、语言生成、空间感知和数学。
6.4.5 工具创建
想象一下,如果我们面临一个全新的情景,没有强大的工具可供使用,我们是否可以根据用户的需求即时创建一个工具?在自然语言处理领域,CREATOR(Qian等,2023)提出通过编写数学推理的Python代码来创建工具,而不是调用数学求解器API,如Wolfram Alpha。Cai等(2023)进一步探讨了LLM的能力来创建工具,并进行了两种LLM的实验,一个作为工具制造者,另一个作为工具使用者,共同解决复杂任务,如安排会议。在多模态代理方面,挑战在于如何创建一个可以处理多模态输入的工具。可以借鉴 ViperGPT(Surıs等,2023)的方法,指示 LLM生成利用预先存在的 Python包(如OpenCV)的 Python程序。AutoML GPT(Zhang 等,2023j)设想可以利用LLM来自动化模型训练流程。开发新颖的多模态深度学习工具,以更有效地满足用户的需求。
想象一下,如果我们有一个全新的场景,没有一个强大的工具可以使用。我们能否根据用户的需求即时创建一个工具?在NLP中,CREATOR(Qian et al.,2023)建议通过编写用于数学推理的python代码来创建工具,而不是调用Wolfram Alpha等数学求解器API。Cai等人(2023)进一步探索了LLM制造工具的能力,并尝试了两种LLM,一种作为工具制造商,另一种是工具用户,以协作解决复杂的任务,例如安排会议。就多模式代理而言,挑战在于如何创建一个可以处理多模式输入的工具。可以遵循ViperGPT(Surís等人,2023)来指示LLM利用Open CV等预先存在的python包生成python程序。AutoML GPT(Zhang等人,2023j)设想可以利用LLM来自动化模型训练管道。开发新的多模式深度学习工具,来更有效地满足用户的需求,可能是具有潜力的。
6.4.6 检索增强型多模态代理
在实际应用中,大量信息存储在数据库中,用户需求可能需要准确检索这些信息。同时,将所有世界知识编码到预训练模型的权重中是不可行的,特别是当涉及到长尾概念和快速发展的数据时。
在自然语言处理领域,一些工作通过结构化语言和关系表示编码的外部数据对LLM进行增强(Peters等,2019;Guu等,2020;Lewis 等,2020)。在给定输入文本的情况下,这些检索增强模型利用检索器从外部存储器中检索相关文档,并使用生成器在检索到的文档的情况下生成预测。
受自然语言处理领域中检索增强模型的启发,最近的一些工作利用视觉和/或文本知识来改进视觉任务,如图像分类(Long等,2022)、图像描述(Yang等,2023a)、问答(Wu等,2021;Marino等,2021;Yang等,2022d;Chen等,2022e)、图像生成(Blattmann等,2022;Sheynin等,2022;Chen等,2022f;Zhou等,2022c),以及同时进行多模态任务(Yasunaga等,2022)。RAC(Long等,2022)通过从预编码的图像和文本组成的非参数性存储器中检索来改进长尾分类。K-LITE(Shen等,2022a)通过检索自然语言编码的外部知识来增强文本提示。REACT(Liu等,2023d)从图像文本的数十亿对知识中检索,旨在提高核心视觉问题的任务转移性能。其中,RA-CM3(Yasunaga等,2022)构建了第一个具有多模态检索器的检索增强型LMM,以检索多模态文档,并具有可以生成文本和图像的检索增强生成器。LLM的链接工具与检索增强方法有着密切的联系,因为两者都利用外部知识为核心模型提供额外的信息。在多模态模式下,图像本身可以用作查询以获取外部知识,可以从知识库检索,也可以从另一个预训练的视觉专家模型中提取。
7. 结论和研究趋势
Chapter 7:Conclusions and Research Trends

多模态基础模型引起了计算机视觉和多模态视觉语言研究领域学者的极大兴趣。尽管当前的研究主题、方法和手段一直在不断发展,包括图像自我监督学习、语言图像对比学习、文本到图像生成、统一视觉建模以及大规模语言和视觉助手,但它们都集中在一个共同的总体目标上:创建通用型模型和系统,能够理解人类的意图,并轻松执行真实场景下各种不同的视觉和视觉-语言任务。在本章中,我们简要总结了所回顾的内容,并深入探讨了该领域的主要研究趋势。
7.1 总结和结论
本文综述了多模态基础模型研究前沿的最新进展,分为以下两类。
-
特定用途的多模态基础模型:
在计算机视觉领域有各种不同的问题需要解决。为了为通用视觉助手的引入奠定全面的基础,我们在预训练时代讨论了许多研究论文。在这一时期的主要范式是在大量与问题相关的数据上进行预训练,然后以零样本或少样本迁移到同一类型问题的实际场景中。具体而言,我们提出了两个主题:
(1) 第2章的视觉理解:个体多模态基础模型已经发展,以在图像、区域和像素级别前瞻性地分析视觉数据的内容。带有语言增强的视觉模型是一种流行的家族,为最近真实场景视觉理解任务的成功做出了贡献。
(2) 第3章的视觉生成:文本到图像生成模型为图像合成奠定了基础,成功地扩展到更细粒度的用户可控性和自定义性。大量与问题相关的数据的可用性和创建在使这些多模态基础模型成为可能方面发挥了关键作用。 -
通用型助手:
我们回顾了最近出现的关于构建通用型助手的文献,这些助手通常具有统一的网络架构、统一的输入输出数据格式和便于与人类进行交互的通用接口。受到NLP中LLM(例如ChatGPT/GPT-4)在各种语言任务中的成功启发,计算机视觉研究人员探索了各种解决方案来为视觉任务提供类似的通用型助手。根据LLM在方法论中的应用方式,现有研究可以分为三个主题:
(1) 第4章的统一视觉模型:借鉴LLM中的统一建模精神,构建了不同级别和不同任务的统一视觉模型。
(2) 第5章的LLM训练:从预训练的LLM开始,将视觉数据连接到LLM以进行端到端训练。
(3) 第6章的LLM链接:通过冻结LLM,现有的视觉专家可以通过LMM工程完成特定的视觉任务。
这些模型之间的比较总结在表7.1中。

表7.1:本文涵盖的不同多模态基础模型家族的比较。
7.2 朝着构建通用型人工智能代理迈进
在每章的末尾,我们讨论了各个主题的未来趋势。本文的组织结构旨在展示从专门的多模态基础模型向通用视觉助手的过渡。尽管现有的视觉助手如 Flamingo(Alayrac等,2022)和多模态GPT-4(OpenAI,2023b)已经非常强大,但与构建通用多模态AI代理的宏伟愿景相比,还处于初步阶段。接下来,我们将重点介绍朝着实现这一目标的一些研究趋势。
多模态通用型代理。
这与构建一个单一的通用型代理的宏伟目标相一致,该代理与人类一样,通过融合语言、视觉、言语和行动等多个渠道与世界进行交互。从这个角度来看,多模态基础模型的概念本身就变得有些模糊。相反,代理的关键组成部分,在于感知和合成视觉信号。例如,Gato(Reed等,2022)和PaLM-E(Driess等,2023)使用一组模型权重执行各种语言、多模态和控制任务,其中视觉感知是理解环境的关键组成部分。这还对统一视觉和多模态建模的有效和可扩展的预训练目标提出了挑战。
与人类意图的对齐。
人工智能对齐研究侧重于引导人工智能系统朝着人类预期的目标、价值观或伦理准则前进。当人工智能系统有效地促进了期望的目标时,被认为是对齐的。尽管语言已经展示出了在表达人类意图方面的普遍性,但它并不总是最佳选择。正如SAM(Kirillov等,2023)和 ControlNet/GLIGEN(Zhang,2023;Li等,2023n)所展示的,人类意图可以更精确、更方便地以视觉提示的形式表示,例如关键点、边界框和草图绘制,用于视觉理解和生成任务。构建配备这种多模态人机交互界面的基础模型是解锁新的使用场景的关键一步,其中人类意图在视觉上得到最好的表现。例如,场景内元素的空间排列,以及视觉艺术品的艺术风格和视觉吸引力。
规划、记忆和工具使用。
Weng(2023)强调可以构建一个由LLM驱动的自主代理系统,其中LLM充当代理的大脑,并辅以几个关键组件:规划、记忆和工具的使用。按照这一框架,我们可以预见多模态基础模型在这个人工智能代理系统中的角色。
-
规划。
为了在现实场景中完成复杂任务,代理应该能够将大任务分解成较小、可管理的子目标,从而高效地处理复杂任务。在理想情况下,人工智能代理具备自我改进的能力,对之前的行为进行自我评估和反省,使其能够从错误中学习,并增强其后续努力的方法,最终带来更好的结果。视觉模态是表示环境状态的常用通道。为了便于规划,它在提高当前视觉理解模型感知更细粒度的视觉细节和更长序列视频的能力方面提出了挑战。 -
记忆。
对于短期记忆,上下文学习(或提示工程)被用作模型的短期记忆来学习。交错的多模式提示可以使新的场景能够阐明人类的意图。对于长期记忆,它提供了代理在延长的会话中回忆外部知识的能力,这可以通过从多模态向量空间中快速检索来实现(Liu等,2023d)。在建模方面,基础模型需要学习新技能,以有效地利用这两种类型的记忆。 -
工具使用。
代理学习利用来自基础模型权重缺失的知识的外部API。在多种情景中需要新的能力来处理视觉模态。例如,基于输入的视觉信号和指令,模型决定和规划是否需要特定的外部API来完成目标,例如检测/分割/OCR/专家生成器的代码执行。
多模态基础模型领域正在快速发展,新的方向和方法经常涌现。本文没有涵盖许多重要的研究主题,主要是因为每日都有新的研究创新。我们对多模态基础模型的未来充满乐观,不仅因为我们相信,通过追随LLM的道路,可以在不久的将来实现各个领域的可预见的令人兴奋的研究创新和想法,还因为将计算机视觉与更广泛的人工智能社区联系起来,构建通用型人工智能代理将显著推动人类的日常生活。
致谢
本书主要基于我们关于视觉基础模型的CVPR 2023教程。许多人支持我们,并为这本书的写作提供了宝贵的反馈。我们感谢所有为相关论文做出贡献的作者,这使得本教程和本书成为可能。我们还感谢《Foundations and Trends® in Computer Graphics and Vision》杂志的编辑 Mark de Jongh,他启发并鼓励我们写这本关于多模态基础模型的书。
参考文献
References
sta, (2022)(2022).Stable diffusion.https://github.com/CompVis/stable-diffusion.
Agarwal et al., (2023)Agarwal, A., Karanam, S., Joseph, K., Saxena, A., Goswami, K., and Srinivasan, B. V. (2023).A-star: Test-time attention segregation and retention for text-to-image synthesis.arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.14544.
Agrawal et al., (2019)Agrawal, H., Desai, K., Wang, Y., Chen, X., Jain, R., Johnson, M., Batra, D., Parikh, D., Lee, S., and Anderson, P. (2019).nocaps: novel object captioning at scale.In ICCV.
Ahn et al., (2022)Ahn, M., Brohan, A., Brown, N., Chebotar, Y., Cortes, O., David, B., Finn, C., Gopalakrishnan, K., Hausman, K., Herzog, A., et al. (2022).Do as i can, not as i say: Grounding language in robotic affordances.arXiv preprint arXiv:2204.01691.
Alayrac et al., (2022)Alayrac, J.-B., Donahue, J., Luc, P., Miech, A., Barr, I., Hasson, Y., Lenc, K., Mensch, A., Millican, K., Reynolds, M., et al. (2022).Flamingo: a visual language model for few-shot learning.arXiv preprint arXiv:2204.14198.
Allahyari et al., (2017)Allahyari, M., Pouriyeh, S., Assefi, M., Safaei, S., Trippe, E. D., Gutierrez, J. B., and Kochut, K. (2017).Text summarization techniques: a brief survey.arXiv preprint arXiv:1707.02268.
Amrani et al., (2022)Amrani, E., Karlinsky, L., and Bronstein, A. (2022).Self-supervised classification network.In ECCV.
Anderson et al., (2018)Anderson, P., He, X., Buehler, C., Teney, D., Johnson, M., Gould, S., and Zhang, L. (2018).Bottom-up and top-down attention for image captioning and visual question answering.In CVPR.
Antol et al., (2015)Antol, S., Agrawal, A., Lu, J., Mitchell, M., Batra, D., Zitnick, C. L., and Parikh, D. (2015).Vqa: Visual question answering.In ICCV.
Arora et al., (2019)Arora, S., Khandeparkar, H., Khodak, M., Plevrakis, O., and Saunshi, N. (2019).A theoretical analysis of contrastive unsupervised representation learning.arXiv preprint arXiv:1902.09229.
Assran et al., (2022)Assran, M., Caron, M., Misra, I., Bojanowski, P., Bordes, F., Vincent, P., Joulin, A., Rabbat, M., and Ballas, N. (2022).Masked siamese networks for label-efficient learning.In ECCV.
(12)Avrahami, O., Aberman, K., Fried, O., Cohen-Or, D., and Lischinski, D. (2023a).Break-a-scene: Extracting multiple concepts from a single image.arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.16311.
(13)Avrahami, O., Fried, O., and Lischinski, D. (2022a).Blended latent diffusion.arXiv preprint arXiv:2206.02779.
(14)Avrahami, O., Hayes, T., Gafni, O., Gupta, S., Taigman, Y., Parikh, D., Lischinski, D., Fried, O., and Yin, X. (2023b).Spatext: Spatio-textual representation for controllable image generation.In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 18370–18380.
(15)Avrahami, O., Lischinski, D., and Fried, O. (2022b).Blended diffusion for text-driven editing of natural images.In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 18208–18218.
Awadalla et al., (2023)Awadalla, A., Gao, I., Gardner, J., Hessel, J., Hanafy, Y., Zhu, W., Marathe, K., Bitton, Y., Gadre, S., Jitsev, J., Kornblith, S., Koh, P. W., Ilharco, G., Wortsman, M., and Schmidt, L. (2023).Openflamingo.
Awais et al., (2023)Awais, M., Naseer, M., Khan, S., Anwer, R. M., Cholakkal, H., Shah, M., Yang, M.-H., and Khan, F. S. (2023).Foundational models defining a new era in vision: A survey and outlook.arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.13721.
Bachman et al., (2019)Bachman, P., Hjelm, R. D., and Buchwalter, W. (2019).Learning representations by maximizing mutual information across views.NeurIPS.
Baevski et al., (2022)Baevski, A., Hsu, W.-N., Xu, Q., Babu, A., Gu, J., and Auli, M. (2022).Data2vec: A general framework for self-supervised learning in speech, vision and language.In ICML.
Bahdanau et al., (2015)Bahdanau, D., Cho, K., and Bengio, Y. (2015).Neural machine translation by jointly learning to align and translate.In ICLR.
(21)Bai, J., Bai, S., Yang, S., Wang, S., Tan, S., Wang, P., Lin, J., Zhou, C., and Zhou, J. (2023a).Qwen-vl: A frontier large vision-language model with versatile abilities.arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.12966.
(22)Bai, S., Yang, S., Bai, J., Wang, P., Zhang, X., Lin, J., Wang, X., Zhou, C., and Zhou, J. (2023b).Touchstone: Evaluating vision-language models by language models.
Balaji et al., (2022)Balaji, Y., Nah, S., Huang, X., Vahdat, A., Song, J., Kreis, K., Aittala, M., Aila, T., Laine, S., Catanzaro, B., et al. (2022).ediffi: Text-to-image diffusion models with an ensemble of expert denoisers.arXiv preprint arXiv:2211.01324.
Balažević et al., (2023)Balažević, I., Steiner, D., Parthasarathy, N., Arandjelović, R., and Hénaff, O. J. (2023).Towards in-context scene understanding.arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.01667.
Bansal et al., (2023)Bansal, A., Chu, H.-M., Schwarzschild, A., Sengupta, S., Goldblum, M., Geiping, J., and Goldstein, T. (2023).Universal guidance for diffusion models.In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 843–852.
Bansal et al., (2018)Bansal, A., Sikka, K., Sharma, G., Chellappa, R., and Divakaran, A. (2018).Zero-shot object detection.In Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV), pages 384–400.
Bao et al., (2022)Bao, H., Dong, L., and Wei, F. (2022).BEiT: Bert pre-training of image transformers.In ICLR.
Bar et al., (2022)Bar, A., Gandelsman, Y., Darrell, T., Globerson, A., and Efros, A. (2022).Visual prompting via image inpainting.Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 35:25005–25017.
Bardes et al., (2021)Bardes, A., Ponce, J., and LeCun, Y. (2021).Vicreg: Variance-invariance-covariance regularization for self-supervised learning.arXiv preprint arXiv:2105.04906.
Berant et al., (2013)Berant, J., Chou, A., Frostig, R., and Liang, P. (2013).Semantic parsing on freebase from question-answer pairs.In Proceedings of the 2013 conference on empirical methods in natural language processing, pages 1533–1544.
Bitton et al., (2023)Bitton, Y., Bansal, H., Hessel, J., Shao, R., Zhu, W., Awadalla, A., Gardner, J., Taori, R., and Schimdt, L. (2023).Visit-bench: A benchmark for vision-language instruction following inspired by real-world use.
Black et al., (2023)Black, K., Janner, M., Du, Y., Kostrikov, I., and Levine, S. (2023).Training diffusion models with reinforcement learning.arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.13301.
Blattmann et al., (2022)Blattmann, A., Rombach, R., Oktay, K., and Ommer, B. (2022).Retrieval-augmented diffusion models.arXiv preprint arXiv:2204.11824.
Bolya et al., (2019)Bolya, D., Zhou, C., Xiao, F., and Lee, Y. J. (2019).Yolact: Real-time instance segmentation.In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pages 9157–9166.
Bommasani et al., (2021)Bommasani, R., Hudson, D. A., Adeli, E., Altman, R., Arora, S., von Arx, S., Bernstein, M. S., Bohg, J., Bosselut, A., Brunskill, E., et al. (2021).On the opportunities and risks of foundation models.arXiv preprint arXiv:2108.07258.
Brooks et al., (2023)Brooks, T., Holynski, A., and Efros, A. A. (2023).Instructpix2pix: Learning to follow image editing instructions.In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 18392–18402.
Brown et al., (2020)Brown, T. B., Mann, B., Ryder, N., Subbiah, M., Kaplan, J., Dhariwal, P., Neelakantan, A., Shyam, P., Sastry, G., Askell, A., et al. (2020).Language models are few-shot learners.In NeuIPS.
Bubeck et al., (2023)Bubeck, S., Chandrasekaran, V., Eldan, R., Gehrke, J., Horvitz, E., Kamar, E., Lee, P., Lee, Y. T., Li, Y., Lundberg, S., et al. (2023).Sparks of artificial general intelligence: Early experiments with gpt-4.arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.12712.
Byeon et al., (2022)Byeon, M., Park, B., Kim, H., Lee, S., Baek, W., and Kim, S. (2022).Coyo-700m: Image-text pair dataset.https://github.com/kakaobrain/coyo-dataset.
Cai et al., (2023)Cai, T., Wang, X., Ma, T., Chen, X., and Zhou, D. (2023).Large language models as tool makers.arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.17126.
Cai et al., (2022)Cai, Z., Kwon, G., Ravichandran, A., Bas, E., Tu, Z., Bhotika, R., and Soatto, S. (2022).X-detr: A versatile architecture for instance-wise vision-language tasks.In ECCV.
Cao et al., (2023)Cao, L., Zhang, B., Chen, C., Yang, Y., Du, X., Zhang, W., Lu, Z., and Zheng, Y. (2023).Less is more: Removing text-regions improves clip training efficiency and robustness.arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.05095.
Carion et al., (2020)Carion, N., Massa, F., Synnaeve, G., Usunier, N., Kirillov, A., and Zagoruyko, S. (2020).End-to-end object detection with transformers.In ECCV.
Caron et al., (2018)Caron, M., Bojanowski, P., Joulin, A., and Douze, M. (2018).Deep clustering for unsupervised learning of visual features.In ECCV.
Caron et al., (2020)Caron, M., Misra, I., Mairal, J., Goyal, P., Bojanowski, P., and Joulin, A. (2020).Unsupervised learning of visual features by contrasting cluster assignments.NeurIPS.
Caron et al., (2021)Caron, M., Touvron, H., Misra, I., Jégou, H., Mairal, J., Bojanowski, P., and Joulin, A. (2021).Emerging properties in self-supervised vision transformers.In ICCV.
Castrejon et al., (2017)Castrejon, L., Kundu, K., Urtasun, R., and Fidler, S. (2017).Annotating object instances with a polygon-rnn.In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pages 5230–5238.
Chang et al., (2023)Chang, H., Zhang, H., Barber, J., Maschinot, A., Lezama, J., Jiang, L., Yang, M.-H., Murphy, K., Freeman, W. T., Rubinstein, M., et al. (2023).Muse: Text-to-image generation via masked generative transformers.arXiv preprint arXiv:2301.00704.
Chang et al., (2022)Chang, H., Zhang, H., Jiang, L., Liu, C., and Freeman, W. T. (2022).Maskgit: Masked generative image transformer.In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 11315–11325.
Changpinyo et al., (2021)Changpinyo, S., Sharma, P., Ding, N., and Soricut, R. (2021).Conceptual 12m: Pushing web-scale image-text pre-training to recognize long-tail visual concepts.In CVPR.
Chefer et al., (2023)Chefer, H., Alaluf, Y., Vinker, Y., Wolf, L., and Cohen-Or, D. (2023).Attend-and-excite: Attention-based semantic guidance for text-to-image diffusion models.arXiv preprint arXiv:2301.13826.
(52)Chen, C., Zhang, B., Cao, L., Shen, J., Gunter, T., Jose, A. M., Toshev, A., Shlens, J., Pang, R., and Yang, Y. (2023a).Stair: Learning sparse text and image representation in grounded tokens.arXiv preprint arXiv:2301.13081.
(53)Chen, D., Liu, J., Dai, W., and Wang, B. (2023b).Visual instruction tuning with polite flamingo.arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.01003.
(54)Chen, F., Han, M., Zhao, H., Zhang, Q., Shi, J., Xu, S., and Xu, B. (2023c).X-llm: Bootstrapping advanced large language models by treating multi-modalities as foreign languages.arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.04160.
(55)Chen, F., Zhang, D., Han, M., Chen, X., Shi, J., Xu, S., and Xu, B. (2022a).Vlp: A survey on vision-language pre-training.arXiv preprint arXiv:2202.09061.
(56)Chen, K., Zhang, Z., Zeng, W., Zhang, R., Zhu, F., and Zhao, R. (2023d).Shikra: Unleashing multimodal llm’s referential dialogue magic.arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.15195.
Chen et al., (2019)Chen, L., Zhai, M., He, J., and Mori, G. (2019).Object grounding via iterative context reasoning.In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, pages 0–0.
Chen et al., (2017)Chen, L.-C., Papandreou, G., Schroff, F., and Adam, H. (2017).Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation.arXiv preprint arXiv:1706.05587.
(59)Chen, M., Laina, I., and Vedaldi, A. (2023e).Training-free layout control with cross-attention guidance.arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.03373.
(60)Chen, M., Tworek, J., Jun, H., Yuan, Q., Pinto, H. P. d. O., Kaplan, J., Edwards, H., Burda, Y., Joseph, N., Brockman, G., et al. (2021a).Evaluating large language models trained on code.arXiv preprint arXiv:2107.03374.
(61)Chen, Q., Chen, X., Zeng, G., and Wang, J. (2022b).Group detr: Fast training convergence with decoupled one-to-many label assignment.arXiv preprint arXiv:2207.13085.
(62)Chen, T., Kornblith, S., Norouzi, M., and Hinton, G. (2020a).A simple framework for contrastive learning of visual representations.In ICML.
(63)Chen, T., Kornblith, S., Swersky, K., Norouzi, M., and Hinton, G. E. (2020b).Big self-supervised models are strong semi-supervised learners.NeurIPS.
(64)Chen, T., Saxena, S., Li, L., Fleet, D. J., and Hinton, G. (2022c).Pix2seq: A language modeling framework for object detection.In ICLR.
(65)Chen, T., Saxena, S., Li, L., Lin, T.-Y., Fleet, D. J., and Hinton, G. (2022d).A unified sequence interface for vision tasks.arXiv preprint arXiv:2206.07669.
(66)Chen, W., Hu, H., Chen, X., Verga, P., and Cohen, W. W. (2022e).Murag: Multimodal retrieval-augmented generator for open question answering over images and text.arXiv preprint arXiv:2210.02928.
(67)Chen, W., Hu, H., Li, Y., Rui, N., Jia, X., Chang, M.-W., and Cohen, W. W. (2023f).Subject-driven text-to-image generation via apprenticeship learning.arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.00186.
(68)Chen, W., Hu, H., Saharia, C., and Cohen, W. W. (2022f).Re-imagen: Retrieval-augmented text-to-image generator.arXiv preprint arXiv:2209.14491.
(69)Chen, X., Ding, M., Wang, X., Xin, Y., Mo, S., Wang, Y., Han, S., Luo, P., Zeng, G., and Wang, J. (2022g).Context autoencoder for self-supervised representation learning.arXiv preprint arXiv:2202.03026.
(70)Chen, X., Djolonga, J., Padlewski, P., Mustafa, B., Changpinyo, S., Wu, J., Ruiz, C. R., Goodman, S., Wang, X., Tay, Y., et al. (2023g).Pali-x: On scaling up a multilingual vision and language model.arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.18565.
(71)Chen, X., Fan, H., Girshick, R., and He, K. (2020c).Improved baselines with momentum contrastive learning.arXiv preprint arXiv:2003.04297.
Chen et al., (2015)Chen, X., Fang, H., Lin, T., Vedantam, R., Gupta, S., Dollár, P., and Zitnick, C. L. (2015).Microsoft COCO captions: Data collection and evaluation server.arXiv preprint arXiv:1504.00325.
Chen and He, (2021)Chen, X. and He, K. (2021).Exploring simple siamese representation learning.In CVPR.
(74)Chen, X., Wang, X., Changpinyo, S., Piergiovanni, A., Padlewski, P., Salz, D., Goodman, S., Grycner, A., Mustafa, B., Beyer, L., et al. (2022h).Pali: A jointly-scaled multilingual language-image model.arXiv preprint arXiv:2209.06794.
(75)Chen, X., Xie, S., and He, K. (2021b).An empirical study of training self-supervised vision transformers.In ICCV.
(76)Chen, X., Zhao, Z., Yu, F., Zhang, Y., and Duan, M. (2021c).Conditional diffusion for interactive segmentation.In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pages 7345–7354.
(77)Chen, X., Zhao, Z., Zhang, Y., Duan, M., Qi, D., and Zhao, H. (2022i).Focalclick: Towards practical interactive image segmentation.In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 1300–1309.
(78)Chen, Y.-C., Li, L., Yu, L., El Kholy, A., Ahmed, F., Gan, Z., Cheng, Y., and Liu, J. (2020d).UNITER: Universal image-text representation learning.In ECCV.
(79)Chen, Z., Duan, Y., Wang, W., He, J., Lu, T., Dai, J., and Qiao, Y. (2022j).Vision transformer adapter for dense predictions.arXiv preprint arXiv:2205.08534.
Cheng et al., (2022)Cheng, B., Misra, I., Schwing, A. G., Kirillov, A., and Girdhar, R. (2022).Masked-attention mask transformer for universal image segmentation.In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 1290–1299.
Cherti et al., (2023)Cherti, M., Beaumont, R., Wightman, R., Wortsman, M., Ilharco, G., Gordon, C., Schuhmann, C., Schmidt, L., and Jitsev, J. (2023).Reproducible scaling laws for contrastive language-image learning.In CVPR.
Cho et al., (2021)Cho, J., Lei, J., Tan, H., and Bansal, M. (2021).Unifying vision-and-language tasks via text generation.In ICML.
Cho et al., (2023)Cho, J., Li, L., Yang, Z., Gan, Z., Wang, L., and Bansal, M. (2023).Diagnostic benchmark and iterative inpainting for layout-guided image generation.arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.06671.
Chowdhery et al., (2022)Chowdhery, A., Narang, S., Devlin, J., Bosma, M., Mishra, G., Roberts, A., Barham, P., Chung, H. W., Sutton, C., Gehrmann, S., et al. (2022).Palm: Scaling language modeling with pathways.arXiv preprint arXiv:2204.02311.
Computer, (2023)Computer, T. (2023).Redpajama-data: An open source recipe to reproduce llama training dataset.
Crawshaw, (2020)Crawshaw, M. (2020).Multi-task learning with deep neural networks: A survey.arXiv preprint arXiv:2009.09796.
Creswell et al., (2018)Creswell, A., White, T., Dumoulin, V., Arulkumaran, K., Sengupta, B., and Bharath, A. A. (2018).Generative adversarial networks: An overview.IEEE signal processing magazine, 35(1):53–65.
(88)Dai, H., Ma, C., Liu, Z., Li, Y., Shu, P., Wei, X., Zhao, L., Wu, Z., Zhu, D., Liu, W., et al. (2023a).Samaug: Point prompt augmentation for segment anything model.arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.01187.
(89)Dai, W., Li, J., Li, D., Tiong, A. M. H., Zhao, J., Wang, W., Li, B., Fung, P., and Hoi, S. (2023b).Instructblip: Towards general-purpose vision-language models with instruction tuning.arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.06500.
Dai et al., (2021)Dai, X., Chen, Y., Xiao, B., Chen, D., Liu, M., Yuan, L., and Zhang, L. (2021).Dynamic head: Unifying object detection heads with attentions.In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pages 7373–7382.
Datta et al., (2008)Datta, R., Joshi, D., Li, J., and Wang, J. Z. (2008).Image retrieval: Ideas, influences, and trends of the new age.ACM Computing Surveys (Csur), 40(2):1–60.
Deng et al., (2018)Deng, C., Wu, Q., Wu, Q., Hu, F., Lyu, F., and Tan, M. (2018).Visual grounding via accumulated attention.In CVPR.
Deng et al., (2009)Deng, J., Dong, W., Socher, R., Li, L.-J., Li, K., and Fei-Fei, L. (2009).Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical image database.In CVPR.
Desai and Johnson, (2021)Desai, K. and Johnson, J. (2021).Virtex: Learning visual representations from textual annotations.In CVPR.
Desai et al., (2021)Desai, K., Kaul, G., Aysola, Z., and Johnson, J. (2021).Redcaps: Web-curated image-text data created by the people, for the people.In NeurIPS, Track on Datasets and Benchmarks.
Dettmers et al., (2023)Dettmers, T., Pagnoni, A., Holtzman, A., and Zettlemoyer, L. (2023).Qlora: Efficient finetuning of quantized llms.arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.14314.
Devlin et al., (2019)Devlin, J., Chang, M.-W., Lee, K., and Toutanova, K. (2019).Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding.In NAACL.
Dhariwal and Nichol, (2021)Dhariwal, P. and Nichol, A. (2021).Diffusion models beat gans on image synthesis.In NeurIPS.
(99)Ding, J., Xue, N., Xia, G.-S., and Dai, D. (2022a).Decoupling zero-shot semantic segmentation.
(100)Ding, Z., Wang, J., and Tu, Z. (2022b).Open-vocabulary panoptic segmentation with maskclip.arXiv preprint arXiv:2208.08984.
Dong et al., (2021)Dong, B., Zeng, F., Wang, T., Zhang, X., and Wei, Y. (2021).Solq: Segmenting objects by learning queries.Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 34:21898–21909.
Dong et al., (2022)Dong, X., Bao, J., Zhang, T., Chen, D., Zhang, W., Yuan, L., Chen, D., Wen, F., and Yu, N. (2022).Bootstrapped masked autoencoders for vision bert pretraining.In ECCV.
Dong et al., (2023)Dong, X., Bao, J., Zhang, T., Chen, D., Zhang, W., Yuan, L., Chen, D., Wen, F., Yu, N., and Guo, B. (2023).Peco: Perceptual codebook for bert pre-training of vision transformers.In AAAI.
Dosovitskiy et al., (2021)Dosovitskiy, A., Beyer, L., Kolesnikov, A., Weissenborn, D., Zhai, X., Unterthiner, T., Dehghani, M., Minderer, M., Heigold, G., Gelly, S., et al. (2021).An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale.In ICLR.
(105)Dou, Z.-Y., Kamath, A., Gan, Z., Zhang, P., Wang, J., Li, L., Liu, Z., Liu, C., LeCun, Y., Peng, N., Gao, J., and Wang, L. (2022a).Coarse-to-fine vision-language pre-training with fusion in the backbone.In NeurIPS.
(106)Dou, Z.-Y., Xu, Y., Gan, Z., Wang, J., Wang, S., Wang, L., Zhu, C., Liu, Z., Zeng, M., et al. (2022b).An empirical study of training end-to-end vision-and-language transformers.In CVPR.
Driess et al., (2023)Driess, D., Xia, F., Sajjadi, M. S., Lynch, C., Chowdhery, A., Ichter, B., Wahid, A., Tompson, J., Vuong, Q., Yu, T., et al. (2023).PaLM-E: An embodied multimodal language model.arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.03378.
Du et al., (2022)Du, Y., Liu, Z., Li, J., and Zhao, W. X. (2022).A survey of vision-language pre-trained models.In IJCAI survey track.
El-Nouby et al., (2021)El-Nouby, A., Izacard, G., Touvron, H., Laptev, I., Jegou, H., and Grave, E. (2021).Are large-scale datasets necessary for self-supervised pre-training?arXiv preprint arXiv:2112.10740.
Elharrouss et al., (2020)Elharrouss, O., Almaadeed, N., Al-Maadeed, S., and Akbari, Y. (2020).Image inpainting: A review.Neural Processing Letters, 51:2007–2028.
Ermolov et al., (2021)Ermolov, A., Siarohin, A., Sangineto, E., and Sebe, N. (2021).Whitening for self-supervised representation learning.In ICML.
Esser et al., (2021)Esser, P., Rombach, R., and Ommer, B. (2021).Taming transformers for high-resolution image synthesis.In CVPR.
Everingham and Winn, (2011)Everingham, M. and Winn, J. (2011).The pascal visual object classes challenge 2012 (voc2012) development kit.Pattern Analysis, Statistical Modelling and Computational Learning, Tech. Rep, 8(5).
(114)Fan, L., Krishnan, D., Isola, P., Katabi, D., and Tian, Y. (2023a).Improving clip training with language rewrites.arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.20088.
(115)Fan, Y., Watkins, O., Du, Y., Liu, H., Ryu, M., Boutilier, C., Abbeel, P., Ghavamzadeh, M., Lee, K., and Lee, K. (2023b).Dpok: Reinforcement learning for fine-tuning text-to-image diffusion models.arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.16381.
Fang et al., (2023)Fang, Y., Wang, W., Xie, B., Sun, Q., Wu, L., Wang, X., Huang, T., Wang, X., and Cao, Y. (2023).Eva: Exploring the limits of masked visual representation learning at scale.In CVPR.
Fang et al., (2022)Fang, Z., Wang, J., Hu, X., Liang, L., Gan, Z., Wang, L., Yang, Y., and Liu, Z. (2022).Injecting semantic concepts into end-to-end image captioning.In CVPR.
Feichtenhofer et al., (2022)Feichtenhofer, C., Li, Y., He, K., et al. (2022).Masked autoencoders as spatiotemporal learners.NeurIPS.
(119)Feng, C., Zhong, Y., Jie, Z., Chu, X., Ren, H., Wei, X., Xie, W., and Ma, L. (2022a).Promptdet: Towards open-vocabulary detection using uncurated images.In European Conference on Computer Vision, pages 701–717. Springer.
(120)Feng, W., He, X., Fu, T.-J., Jampani, V., Akula, A. R., Narayana, P., Basu, S., Wang, X. E., and Wang, W. Y. (2022b).Training-free structured diffusion guidance for compositional text-to-image synthesis.In The Eleventh International Conference on Learning Representations.
Feng et al., (2023)Feng, W., Zhu, W., Fu, T.-j., Jampani, V., Akula, A., He, X., Basu, S., Wang, X. E., and Wang, W. Y. (2023).Layoutgpt: Compositional visual planning and generation with large language models.arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.15393.
Frome et al., (2013)Frome, A., Corrado, G. S., Shlens, J., Bengio, S., Dean, J., Ranzato, M., and Mikolov, T. (2013).Devise: A deep visual-semantic embedding model.In NeurIPS.
Fu et al., (2023)Fu, C., Chen, P., Shen, Y., Qin, Y., Zhang, M., Lin, X., Qiu, Z., Lin, W., Yang, J., Zheng, X., et al. (2023).Mme: A comprehensive evaluation benchmark for multimodal large language models.arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.13394.
Gadre et al., (2023)Gadre, S. Y., Ilharco, G., Fang, A., Hayase, J., Smyrnis, G., Nguyen, T., Marten, R., Wortsman, M., Ghosh, D., Zhang, J., et al. (2023).Datacomp: In search of the next generation of multimodal datasets.arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.14108.
Gafni et al., (2022)Gafni, O., Polyak, A., Ashual, O., Sheynin, S., Parikh, D., and Taigman, Y. (2022).Make-a-scene: Scene-based text-to-image generation with human priors.arXiv preprint arXiv:2203.13131.
Gal et al., (2022)Gal, R., Alaluf, Y., Atzmon, Y., Patashnik, O., Bermano, A. H., Chechik, G., and Cohen-Or, D. (2022).An image is worth one word: Personalizing text-to-image generation using textual inversion.arXiv preprint arXiv:2208.01618.
Gan et al., (2020)Gan, Z., Chen, Y.-C., Li, L., Zhu, C., Cheng, Y., and Liu, J. (2020).Large-scale adversarial training for vision-and-language representation learning.In NeurIPS.
Gan et al., (2022)Gan, Z., Li, L., Li, C., Wang, L., Liu, Z., Gao, J., et al. (2022).Vision-language pre-training: Basics, recent advances, and future trends.Foundations and Trends® in Computer Graphics and Vision.
(129)Gao, D., Ji, L., Zhou, L., Lin, K. Q., Chen, J., Fan, Z., and Shou, M. Z. (2023a).Assistgpt: A general multi-modal assistant that can plan, execute, inspect, and learn.arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.08640.
(130)Gao, P., Han, J., Zhang, R., Lin, Z., Geng, S., Zhou, A., Zhang, W., Lu, P., He, C., Yue, X., et al. (2023b).Llama-adapter v2: Parameter-efficient visual instruction model.arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.15010.
Gao et al., (2022)Gao, P., Ma, T., Li, H., Lin, Z., Dai, J., and Qiao, Y. (2022).Convmae: Masked convolution meets masked autoencoders.arXiv preprint arXiv:2205.03892.
Ge et al., (2023)Ge, Y., Ge, Y., Zeng, Z., Wang, X., and Shan, Y. (2023).Planting a seed of vision in large language model.arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.08041.
Geng and Liu, (2023)Geng, X. and Liu, H. (2023).Openllama: An open reproduction of llama.
Geng et al., (2023)Geng, Z., Yang, B., Hang, T., Li, C., Gu, S., Zhang, T., Bao, J., Zhang, Z., Hu, H., Chen, D., et al. (2023).Instructdiffusion: A generalist modeling interface for vision tasks.arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.03895.
(135)Ghiasi, G., Gu, X., Cui, Y., and Lin, T.-Y. (2022a).Open-vocabulary image segmentation.In ECCV.
(136)Ghiasi, G., Gu, X., Cui, Y., and Lin, T.-Y. (2022b).Scaling open-vocabulary image segmentation with image-level labels.In European Conference on Computer Vision, pages 540–557. Springer.
Girdhar et al., (2023)Girdhar, R., El-Nouby, A., Liu, Z., Singh, M., Alwala, K. V., Joulin, A., and Misra, I. (2023).Imagebind: One embedding space to bind them all.In CVPR.
Girshick, (2015)Girshick, R. (2015).Fast r-cnn.In ICCV.
Girshick et al., (2015)Girshick, R., Donahue, J., Darrell, T., and Malik, J. (2015).Region-based convolutional networks for accurate object detection and segmentation.IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence, 38(1):142–158.
Gong et al., (2023)Gong, T., Lyu, C., Zhang, S., Wang, Y., Zheng, M., Zhao, Q., Liu, K., Zhang, W., Luo, P., and Chen, K. (2023).Multimodal-gpt: A vision and language model for dialogue with humans.arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.04790.
Goodfellow et al., (2020)Goodfellow, I., Pouget-Abadie, J., Mirza, M., Xu, B., Warde-Farley, D., Ozair, S., Courville, A., and Bengio, Y. (2020).Generative adversarial networks.Communications of the ACM.
Grill et al., (2020)Grill, J.-B., Strub, F., Altché, F., Tallec, C., Richemond, P., Buchatskaya, E., Doersch, C., Avila Pires, B., Guo, Z., Gheshlaghi Azar, M., et al. (2020).Bootstrap your own latent-a new approach to self-supervised learning.NeurIPS.
Gu et al., (2023)Gu, X., Cui, Y., Huang, J., Rashwan, A., Yang, X., Zhou, X., Ghiasi, G., Kuo, W., Chen, H., Chen, L.-C., et al. (2023).Dataseg: Taming a universal multi-dataset multi-task segmentation model.arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.01736.
Gu et al., (2021)Gu, X., Lin, T.-Y., Kuo, W., and Cui, Y. (2021).Open-vocabulary object detection via vision and language knowledge distillation.arXiv preprint arXiv:2104.13921.
Gu et al., (2022)Gu, X., Lin, T.-Y., Kuo, W., and Cui, Y. (2022).Open-vocabulary object detection via vision and language knowledge distillation.In ICLR.
Gudibande et al., (2023)Gudibande, A., Wallace, E., Snell, C., Geng, X., Liu, H., Abbeel, P., Levine, S., and Song, D. (2023).The false promise of imitating proprietary llms.arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.15717.
Gunjal et al., (2023)Gunjal, A., Yin, J., and Bas, E. (2023).Detecting and preventing hallucinations in large vision language models.arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.06394.
(148)Gupta, T., Kamath, A., Kembhavi, A., and Hoiem, D. (2022a).Towards general purpose vision systems: An end-to-end task-agnostic vision-language architecture.In CVPR.
(149)Gupta, T., Kamath, A., Kembhavi, A., and Hoiem, D. (2022b).Towards general purpose vision systems: An end-to-end task-agnostic vision-language architecture.In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pages 16399–16409.
(150)Gupta, T. and Kembhavi, A. (2022a).Visual programming: Compositional visual reasoning without training.arXiv preprint arXiv:2211.11559.
(151)Gupta, T. and Kembhavi, A. (2022b).Visual programming: Compositional visual reasoning without training.ArXiv, abs/2211.11559.
Gupta and Kembhavi, (2023)Gupta, T. and Kembhavi, A. (2023).Visual programming: Compositional visual reasoning without training.In CVPR.
(153)Gupta, T., Marten, R., Kembhavi, A., and Hoiem, D. (2022c).Grit: General robust image task benchmark.arXiv preprint arXiv:2204.13653.
Gurari et al., (2018)Gurari, D., Li, Q., Stangl, A. J., Guo, A., Lin, C., Grauman, K., Luo, J., and Bigham, J. P. (2018).Vizwiz grand challenge: Answering visual questions from blind people.In CVPR.
Gutmann and Hyvärinen, (2010)Gutmann, M. and Hyvärinen, A. (2010).Noise-contrastive estimation: A new estimation principle for unnormalized statistical models.In AISTATS.
Guu et al., (2020)Guu, K., Lee, K., Tung, Z., Pasupat, P., and Chang, M.-W. (2020).Realm: Retrieval-augmented language model pre-training.arXiv preprint arXiv:2002.08909.
Hafiz and Bhat, (2020)Hafiz, A. M. and Bhat, G. M. (2020).A survey on instance segmentation: state of the art.International journal of multimedia information retrieval.
Harley et al., (2022)Harley, A. W., Fang, Z., and Fragkiadaki, K. (2022).Particle video revisited: Tracking through occlusions using point trajectories.In European Conference on Computer Vision, pages 59–75. Springer.
(159)He, K., Chen, X., Xie, S., Li, Y., Dollár, P., and Girshick, R. (2022a).Masked autoencoders are scalable vision learners.In CVPR.
He et al., (2020)He, K., Fan, H., Wu, Y., Xie, S., and Girshick, R. (2020).Momentum contrast for unsupervised visual representation learning.In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pages 9729–9738.
He et al., (2017)He, K., Gkioxari, G., Dollár, P., and Girshick, R. (2017).Mask r-cnn.In ICCV.
He et al., (2010)He, K., Sun, J., and Tang, X. (2010).Single image haze removal using dark channel prior.IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence, 33(12):2341–2353.
He et al., (2016)He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., and Sun, J. (2016).Deep residual learning for image recognition.In CVPR.
He et al., (2021)He, P., Liu, X., Gao, J., and Chen, W. (2021).DeBERTa: Decoding-enhanced bert with disentangled attention.In ICLR.
(165)He, R., Sun, S., Yu, X., Xue, C., Zhang, W., Torr, P., Bai, S., and Qi, X. (2022b).Is synthetic data from generative models ready for image recognition?arXiv preprint arXiv:2210.07574.
Henaff, (2020)Henaff, O. (2020).Data-efficient image recognition with contrastive predictive coding.In ICML.
Hertz et al., (2022)Hertz, A., Mokady, R., Tenenbaum, J., Aberman, K., Pritch, Y., and Cohen-or, D. (2022).Prompt-to-prompt image editing with cross-attention control.In The Eleventh International Conference on Learning Representations.
Hjelm et al., (2018)Hjelm, R. D., Fedorov, A., Lavoie-Marchildon, S., Grewal, K., Bachman, P., Trischler, A., and Bengio, Y. (2018).Learning deep representations by mutual information estimation and maximization.arXiv preprint arXiv:1808.06670.
Ho et al., (2022)Ho, J., Chan, W., Saharia, C., Whang, J., Gao, R., Gritsenko, A., Kingma, D. P., Poole, B., Norouzi, M., Fleet, D. J., et al. (2022).Imagen video: High definition video generation with diffusion models.arXiv preprint arXiv:2210.02303.
Ho et al., (2020)Ho, J., Jain, A., and Abbeel, P. (2020).Denoising diffusion probabilistic models.In NeurIPS.
Hoffmann et al., (2022)Hoffmann, J., Borgeaud, S., Mensch, A., Buchatskaya, E., Cai, T., Rutherford, E., Casas, D. d. L., Hendricks, L. A., Welbl, J., Clark, A., et al. (2022).Training compute-optimal large language models.arXiv preprint arXiv:2203.15556.
Hong et al., (2023)Hong, Y., Zhen, H., Chen, P., Zheng, S., Du, Y., Chen, Z., and Gan, C. (2023).3d-llm: Injecting the 3d world into large language models.arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.12981.
Hu et al., (2021)Hu, E. J., Shen, Y., Wallis, P., Allen-Zhu, Z., Li, Y., Wang, S., Wang, L., and Chen, W. (2021).Lora: Low-rank adaptation of large language models.arXiv preprint arXiv:2106.09685.
Hu et al., (2016)Hu, R., Rohrbach, M., and Darrell, T. (2016).Segmentation from natural language expressions.In European Conference on Computer Vision, pages 108–124. Springer.
(175)Hu, R. and Singh, A. (2021a).Unit: Multimodal multitask learning with a unified transformer.In ICCV.
(176)Hu, R. and Singh, A. (2021b).Unit: Multimodal multitask learning with a unified transformer.In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pages 1439–1449.
Hu et al., (2023)Hu, W., Xu, Y., Li, Y., Li, W., Chen, Z., and Tu, Z. (2023).Bliva: A simple multimodal llm for better handling of text-rich visual questions.arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.09936.
(178)Huang, L., You, S., Zheng, M., Wang, F., Qian, C., and Yamasaki, T. (2022a).Green hierarchical vision transformer for masked image modeling.NeurIPS.
(179)Huang, R., Li, M., Yang, D., Shi, J., Chang, X., Ye, Z., Wu, Y., Hong, Z., Huang, J., Liu, J., et al. (2023a).Audiogpt: Understanding and generating speech, music, sound, and talking head.arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.12995.
(180)Huang, S., Dong, L., Wang, W., Hao, Y., Singhal, S., Ma, S., Lv, T., Cui, L., Mohammed, O. K., Liu, Q., et al. (2023b).Language is not all you need: Aligning perception with language models.arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.14045.
(181)Huang, S., Jiang, Z., Dong, H., Qiao, Y., Gao, P., and Li, H. (2023c).Instruct2act: Mapping multi-modality instructions to robotic actions with large language model.arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.11176.
(182)Huang, W., Abbeel, P., Pathak, D., and Mordatch, I. (2022b).Language models as zero-shot planners: Extracting actionable knowledge for embodied agents.In International Conference on Machine Learning, pages 9118–9147. PMLR.
(183)Huang, Y., Meng, Z., Liu, F., Su, Y., Collier, N., and Lu, Y. (2023d).Sparkles: Unlocking chats across multiple images for multimodal instruction-following models.arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.16463.
Huang et al., (2021)Huang, Z., Zeng, Z., Huang, Y., Liu, B., Fu, D., and Fu, J. (2021).Seeing out of the box: End-to-end pre-training for vision-language representation learning.In CVPR.
Huang et al., (2020)Huang, Z., Zeng, Z., Liu, B., Fu, D., and Fu, J. (2020).Pixel-BERT: Aligning image pixels with text by deep multi-modal transformers.arXiv preprint arXiv:2004.00849.
Huynh et al., (2022)Huynh, D., Kuen, J., Lin, Z., Gu, J., and Elhamifar, E. (2022).Open-vocabulary instance segmentation via robust cross-modal pseudo-labeling.In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 7020–7031.
Ilharco et al., (2021)Ilharco, G., Wortsman, M., Wightman, R., Gordon, C., Carlini, N., Taori, R., Dave, A., Shankar, V., Namkoong, H., Miller, J., Hajishirzi, H., Farhadi, A., and Schmidt, L. (2021).Openclip.If you use this software, please cite it as below.
Jain et al., (2023)Jain, J., Li, J., Chiu, M. T., Hassani, A., Orlov, N., and Shi, H. (2023).Oneformer: One transformer to rule universal image segmentation.In CVPR.
Jaiswal et al., (2020)Jaiswal, A., Babu, A. R., Zadeh, M. Z., Banerjee, D., and Makedon, F. (2020).A survey on contrastive self-supervised learning.Technologies.
Jerripothula et al., (2016)Jerripothula, K. R., Cai, J., and Yuan, J. (2016).Image co-segmentation via saliency co-fusion.IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 18(9):1896–1909.
Jia et al., (2021)Jia, C., Yang, Y., Xia, Y., Chen, Y.-T., Parekh, Z., Pham, H., Le, Q. V., Sung, Y., Li, Z., and Duerig, T. (2021).Scaling up visual and vision-language representation learning with noisy text supervision.In ICML.
Jing and Tian, (2020)Jing, L. and Tian, Y. (2020).Self-supervised visual feature learning with deep neural networks: A survey.IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence.
Joulin et al., (2010)Joulin, A., Bach, F., and Ponce, J. (2010).Discriminative clustering for image co-segmentation.In 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 1943–1950. IEEE.
Kamath et al., (2021)Kamath, A., Singh, M., LeCun, Y., Synnaeve, G., Misra, I., and Carion, N. (2021).Mdetr-modulated detection for end-to-end multi-modal understanding.In ICCV.
Kang et al., (2023)Kang, M., Zhu, J.-Y., Zhang, R., Park, J., Shechtman, E., Paris, S., and Park, T. (2023).Scaling up gans for text-to-image synthesis.In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 10124–10134.
Kaplan et al., (2020)Kaplan, J., McCandlish, S., Henighan, T., Brown, T. B., Chess, B., Child, R., Gray, S., Radford, A., Wu, J., and Amodei, D. (2020).Scaling laws for neural language models.arXiv preprint arXiv:2001.08361.
Kawar et al., (2023)Kawar, B., Zada, S., Lang, O., Tov, O., Chang, H., Dekel, T., Mosseri, I., and Irani, M. (2023).Imagic: Text-based real image editing with diffusion models.In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 6007–6017.
Kazemzadeh et al., (2014)Kazemzadeh, S., Ordonez, V., Matten, M., and Berg, T. (2014).Referitgame: Referring to objects in photographs of natural scenes.In EMNLP.
Kim et al., (2021)Kim, W., Son, B., and Kim, I. (2021).ViLT: Vision-and-language transformer without convolution or region supervision.In ICML.
Kingma and Welling, (2013)Kingma, D. P. and Welling, M. (2013).Auto-encoding variational bayes.arXiv preprint arXiv:1312.6114.
Kirillov et al., (2019)Kirillov, A., He, K., Girshick, R., Rother, C., and Dollár, P. (2019).Panoptic segmentation.In CVPR.
Kirillov et al., (2023)Kirillov, A., Mintun, E., Ravi, N., Mao, H., Rolland, C., Gustafson, L., Xiao, T., Whitehead, S., Berg, A. C., Lo, W.-Y., et al. (2023).Segment anything.arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.02643.
Koh et al., (2023)Koh, J. Y., Fried, D., and Salakhutdinov, R. (2023).Generating images with multimodal language models.arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.17216.
Kojima et al., (2022)Kojima, T., Gu, S. S., Reid, M., Matsuo, Y., and Iwasawa, Y. (2022).Large language models are zero-shot reasoners.arXiv preprint arXiv:2205.11916.
Kokkinos, (2017)Kokkinos, I. (2017).Ubernet: Training a universal convolutional neural network for low-, mid-, and high-level vision using diverse datasets and limited memory.In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pages 6129–6138.
Kolesnikov et al., (2020)Kolesnikov, A., Beyer, L., Zhai, X., Puigcerver, J., Yung, J., Gelly, S., and Houlsby, N. (2020).Big transfer (bit): General visual representation learning.In ECCV.
Kolesnikov et al., (2022)Kolesnikov, A., Pinto, A. S., Beyer, L., Zhai, X., Harmsen, J., and Houlsby, N. (2022).Uvim: A unified modeling approach for vision with learned guiding codes.arXiv preprint arXiv:2205.10337.
Krizhevsky et al., (2012)Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., and Hinton, G. E. (2012).Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks.In NeurIPS.
Kumari et al., (2023)Kumari, N., Zhang, B., Zhang, R., Shechtman, E., and Zhu, J.-Y. (2023).Multi-concept customization of text-to-image diffusion.In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 1931–1941.
Kuo et al., (2022)Kuo, W., Bertsch, F., Li, W., Piergiovanni, A., Saffar, M., and Angelova, A. (2022).Findit: Generalized localization with natural language queries.In ECCV.
Lai et al., (2023)Lai, X., Tian, Z., Chen, Y., Li, Y., Yuan, Y., Liu, S., and Jia, J. (2023).Lisa: Reasoning segmentation via large language model.arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.00692.
Lamb et al., (2016)Lamb, A., Dumoulin, V., and Courville, A. (2016).Discriminative regularization for generative models.arXiv preprint arXiv:1602.03220.
Lambert et al., (2020)Lambert, J., Liu, Z., Sener, O., Hays, J., and Koltun, V. (2020).Mseg: A composite dataset for multi-domain semantic segmentation.In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pages 2879–2888.
Larsen et al., (2016)Larsen, A. B. L., Sønderby, S. K., Larochelle, H., and Winther, O. (2016).Autoencoding beyond pixels using a learned similarity metric.In International conference on machine learning, pages 1558–1566. PMLR.
Laurençon et al., (2023)Laurençon, H., Saulnier, L., Tronchon, L., Bekman, S., Singh, A., Lozhkov, A., Wang, T., Karamcheti, S., Rush, A. M., Kiela, D., et al. (2023).Obelisc: An open web-scale filtered dataset of interleaved image-text documents.arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.16527.
Lewis et al., (2020)Lewis, P., Perez, E., Piktus, A., Petroni, F., Karpukhin, V., Goyal, N., Küttler, H., Lewis, M., Yih, W.-t., Rocktäschel, T., et al. (2020).Retrieval-augmented generation for knowledge-intensive nlp tasks.In NeurIPS.
(217)Li, B., Liu, H., Chen, L., Lee, Y. J., Li, C., and Liu, Z. (2023a).Benchmarking and analyzing generative data for visual recognition.arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.13697.
(218)Li, B., Wang, R., Wang, G., Ge, Y., Ge, Y., and Shan, Y. (2023b).Seed-bench: Benchmarking multimodal llms with generative comprehension.arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.16125.
(219)Li, B., Weinberger, K. Q., Belongie, S., Koltun, V., and Ranftl, R. (2022a).Language-driven semantic segmentation.In ICLR.
(220)Li, B., Zhang, Y., Chen, L., Wang, J., Pu, F., Yang, J., Li, C., and Liu, Z. (2023c).Mimic-it: Multi-modal in-context instruction tuning.arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.05425.
(221)Li, B., Zhang, Y., Chen, L., Wang, J., Yang, J., and Liu, Z. (2023d).Otter: A multi-modal model with in-context instruction tuning.arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.03726.
(222)Li, C., Liu, H., Li, L. H., Zhang, P., Aneja, J., Yang, J., Jin, P., Lee, Y. J., Hu, H., Liu, Z., et al. (2022b).Elevater: A benchmark and toolkit for evaluating language-augmented visual models.In NeurIPS, Track on Datasets and Benchmarks.
(223)Li, C., Wong, C., Zhang, S., Usuyama, N., Liu, H., Yang, J., Naumann, T., Poon, H., and Gao, J. (2023e).Llava-med: Training a large language-and-vision assistant for biomedicine in one day.arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.00890.
(224)Li, C., Yang, J., Zhang, P., Gao, M., Xiao, B., Dai, X., Yuan, L., and Gao, J. (2021a).Efficient self-supervised vision transformers for representation learning.arXiv preprint arXiv:2106.09785.
(225)Li, F., Zhang, H., Sun, P., Zou, X., Liu, S., Yang, J., Li, C., Zhang, L., and Gao, J. (2023f).Semantic-sam: Segment and recognize anything at any granularity.arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.04767.
(226)Li, F., Zhang, H., Zhang, Y.-F., Liu, S., Guo, J., Ni, L. M., Zhang, P., and Zhang, L. (2022c).Vision-language intelligence: Tasks, representation learning, and large models.arXiv preprint arXiv:2203.01922.
(227)Li, G., Duan, N., Fang, Y., Gong, M., and Jiang, D. (2020a).Unicoder-vl: A universal encoder for vision and language by cross-modal pre-training.In AAAI.
(228)Li, H., Zhu, J., Jiang, X., Zhu, X., Li, H., Yuan, C., Wang, X., Qiao, Y., Wang, X., Wang, W., et al. (2023g).Uni-perceiver v2: A generalist model for large-scale vision and vision-language tasks.In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 2691–2700.
(229)Li, J., Li, D., Savarese, S., and Hoi, S. (2023h).Blip-2: Bootstrapping language-image pre-training with frozen image encoders and large language models.arXiv preprint arXiv:2301.12597.
(230)Li, J., Li, D., Xiong, C., and Hoi, S. (2022d).Blip: Bootstrapping language-image pre-training for unified vision-language understanding and generation.In ICML.
(231)Li, J., Selvaraju, R. R., Gotmare, A. D., Joty, S., Xiong, C., and Hoi, S. (2021b).Align before fuse: Vision and language representation learning with momentum distillation.In NeurIPS.
(232)Li, K., He, Y., Wang, Y., Li, Y., Wang, W., Luo, P., Wang, Y., Wang, L., and Qiao, Y. (2023i).Videochat: Chat-centric video understanding.arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.06355.
(233)Li, L., Gan, Z., Cheng, Y., and Liu, J. (2019a).Relation-aware graph attention network for visual question answering.In ICCV.
(234)Li, L., Yin, Y., Li, S., Chen, L., Wang, P., Ren, S., Li, M., Yang, Y., Xu, J., Sun, X., et al. (2023j).M3it: A large-scale dataset towards multi-modal multilingual instruction tuning.arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.04387.
(235)Li, L. H., Yatskar, M., Yin, D., Hsieh, C.-J., and Chang, K.-W. (2019b).VisualBERT: A simple and performant baseline for vision and language.arXiv preprint arXiv:1908.03557.
(236)Li, L. H., Zhang, P., Zhang, H., Yang, J., Li, C., Zhong, Y., Wang, L., Yuan, L., Zhang, L., Hwang, J.-N., et al. (2022e).Grounded language-image pre-training.CVPR.
(237)Li, L. H., Zhang, P., Zhang, H., Yang, J., Li, C., Zhong, Y., Wang, L., Yuan, L., Zhang, L., Hwang, J.-N., et al. (2022f).Grounded language-image pre-training.In CVPR.
(238)Li, M., Song, F., Yu, B., Yu, H., Li, Z., Huang, F., and Li, Y. (2023k).Api-bank: A benchmark for tool-augmented llms.arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.08244.
Li and Tajbakhsh, (2023)Li, S. and Tajbakhsh, N. (2023).Scigraphqa: A large-scale synthetic multi-turn question-answering dataset for scientific graphs.arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.03349.
(240)Li, X., Yin, X., Li, C., Zhang, P., Hu, X., Zhang, L., Wang, L., Hu, H., Dong, L., Wei, F., Choi, Y., and Gao, J. (2020b).Oscar: Object-semantics aligned pre-training for vision-language tasks.In ECCV.
Li and Liang, (2021)Li, X. L. and Liang, P. (2021).Prefix-tuning: Optimizing continuous prompts for generation.arXiv preprint arXiv:2101.00190.
(242)Li, Y., Du, Y., Zhou, K., Wang, J., Zhao, W. X., and Wen, J.-R. (2023l).Evaluating object hallucination in large vision-language models.arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.10355.
(243)Li, Y., Fan, H., Hu, R., Feichtenhofer, C., and He, K. (2023m).Scaling language-image pre-training via masking.In CVPR.
(244)Li, Y., Liang, F., Zhao, L., Cui, Y., Ouyang, W., Shao, J., Yu, F., and Yan, J. (2022g).Supervision exists everywhere: A data efficient contrastive language-image pre-training paradigm.In ICLR.
(245)Li, Y., Liu, H., Wu, Q., Mu, F., Yang, J., Gao, J., Li, C., and Lee, Y. J. (2023n).Gligen: Open-set grounded text-to-image generation.In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 22511–22521.
(246)Li, Y., Zhang, C., Yu, G., Wang, Z., Fu, B., Lin, G., Shen, C., Chen, L., and Wei, Y. (2023o).Stablellava: Enhanced visual instruction tuning with synthesized image-dialogue data.arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.10253.
(247)Liang, F., Wu, B., Dai, X., Li, K., Zhao, Y., Zhang, H., Zhang, P., Vajda, P., and Marculescu, D. (2023a).Open-vocabulary semantic segmentation with mask-adapted clip.In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 7061–7070.
(248)Liang, Y., Wu, C., Song, T., Wu, W., Xia, Y., Liu, Y., Ou, Y., Lu, S., Ji, L., Mao, S., et al. (2023b).Taskmatrix. ai: Completing tasks by connecting foundation models with millions of apis.arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.16434.
Lin et al., (2017)Lin, T.-Y., Goyal, P., Girshick, R., He, K., and Dollár, P. (2017).Focal loss for dense object detection.In Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pages 2980–2988.
Lin et al., (2014)Lin, T.-Y., Maire, M., Belongie, S., Hays, J., Perona, P., Ramanan, D., Dollár, P., and Zitnick, C. L. (2014).Microsoft coco: Common objects in context.In ECCV.
Lin et al., (2023)Lin, Y., Wu, H., Wang, R., Lu, H., Lin, X., Xiong, H., and Wang, L. (2023).Towards language-guided interactive 3d generation: Llms as layout interpreter with generative feedback.arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.15808.
Liu et al., (2017)Liu, C., Lin, Z., Shen, X., Yang, J., Lu, X., and Yuille, A. (2017).Recurrent multimodal interaction for referring image segmentation.In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pages 1271–1280.
(253)Liu, F., Lin, K., Li, L., Wang, J., Yacoob, Y., and Wang, L. (2023a).Aligning large multi-modal model with robust instruction tuning.arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.14565.
(254)Liu, H., Jiang, X., Li, X., Guo, A., Hu, Y., Jiang, D., and Ren, B. (2023b).The devil is in the frequency: Geminated gestalt autoencoder for self-supervised visual pre-training.In AAAI.
(255)Liu, H., Li, C., Wu, Q., and Lee, Y. J. (2023c).Visual instruction tuning.arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.08485.
(256)Liu, H., Son, K., Yang, J., Liu, C., Gao, J., Lee, Y. J., and Li, C. (2023d).Learning customized visual models with retrieval-augmented knowledge.In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.
(257)Liu, J., Ding, H., Cai, Z., Zhang, Y., Satzoda, R. K., Mahadevan, V., and Manmatha, R. (2023e).Polyformer: Referring image segmentation as sequential polygon generation.
(258)Liu, N., Li, S., Du, Y., Torralba, A., and Tenenbaum, J. B. (2022a).Compositional visual generation with composable diffusion models.In European Conference on Computer Vision, pages 423–439. Springer.
(259)Liu, S., Fan, L., Johns, E., Yu, Z., Xiao, C., and Anandkumar, A. (2023f).Prismer: A vision-language model with an ensemble of experts.
(260)Liu, S., Ye, J., and Wang, X. (2023g).Any-to-any style transfer.arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.09728.
(261)Liu, S., Zeng, Z., Ren, T., Li, F., Zhang, H., Yang, J., Li, C., Yang, J., Su, H., Zhu, J., et al. (2023h).Grounding dino: Marrying dino with grounded pre-training for open-set object detection.arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.05499.
Liu et al., (2016)Liu, W., Anguelov, D., Erhan, D., Szegedy, C., Reed, S., Fu, C.-Y., and Berg, A. C. (2016).Ssd: Single shot multibox detector.In Computer Vision–ECCV 2016: 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, October 11–14, 2016, Proceedings, Part I 14, pages 21–37. Springer.
Liu and Zuo, (2023)Liu, W. and Zuo, Y. (2023).Stone needle: A general multimodal large-scale model framework towards healthcare.arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.16034.
(264)Liu, X., Zhu, Z., Liu, H., Yuan, Y., Cui, M., Huang, Q., Liang, J., Cao, Y., Kong, Q., Plumbley, M. D., et al. (2023i).Wavjourney: Compositional audio creation with large language models.arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.14335.
(265)Liu, Y., Duan, H., Zhang, Y., Li, B., Zhang, S., Zhao, W., Yuan, Y., Wang, J., He, C., Liu, Z., et al. (2023j).Mmbench: Is your multi-modal model an all-around player?arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.06281.
(266)Liu, Y., Li, Z., Li, H., Yu, W., Huang, M., Peng, D., Liu, M., Chen, M., Li, C., Jin, L., et al. (2023k).On the hidden mystery of ocr in large multimodal models.arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.07895.
Liu et al., (2019)Liu, Y., Ott, M., Goyal, N., Du, J., Joshi, M., Chen, D., Levy, O., Lewis, M., Zettlemoyer, L., and Stoyanov, V. (2019).Roberta: A robustly optimized bert pretraining approach.arXiv preprint arXiv:1907.11692.
(268)Liu, Z., He, Y., Wang, W., Wang, W., Wang, Y., Chen, S., Zhang, Q., Yang, Y., Li, Q., Yu, J., et al. (2023l).Internchat: Solving vision-centric tasks by interacting with chatbots beyond language.arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.05662.
Liu et al., (2021)Liu, Z., Lin, Y., Cao, Y., Hu, H., Wei, Y., Zhang, Z., Lin, S., and Guo, B. (2021).Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows.In ICCV.
(270)Liu, Z., Mao, H., Wu, C.-Y., Feichtenhofer, C., Darrell, T., and Xie, S. (2022b).A convnet for the 2020s.In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pages 11976–11986.
Long et al., (2022)Long, A., Yin, W., Ajanthan, T., Nguyen, V., Purkait, P., Garg, R., Blair, A., Shen, C., and van den Hengel, A. (2022).Retrieval augmented classification for long-tail visual recognition.In CVPR.
Long et al., (2015)Long, J., Shelhamer, E., and Darrell, T. (2015).Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation.In CVPR.
(273)Lu, C.-Z., Jin, X., Hou, Q., Liew, J. H., Cheng, M.-M., and Feng, J. (2023a).Delving deeper into data scaling in masked image modeling.arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.15248.
Lu et al., (2019)Lu, J., Batra, D., Parikh, D., and Lee, S. (2019).Vilbert: Pretraining task-agnostic visiolinguistic representations for vision-and-language tasks.In NeurIPS.
(275)Lu, J., Clark, C., Zellers, R., Mottaghi, R., and Kembhavi, A. (2022a).Unified-io: A unified model for vision, language, and multi-modal tasks.arXiv preprint arXiv:2206.08916.
Lu et al., (2020)Lu, J., Goswami, V., Rohrbach, M., Parikh, D., and Lee, S. (2020).12-in-1: Multi-task vision and language representation learning.In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pages 10437–10446.
(277)Lu, P., Mishra, S., Xia, T., Qiu, L., Chang, K.-W., Zhu, S.-C., Tafjord, O., Clark, P., and Kalyan, A. (2022b).Learn to explain: Multimodal reasoning via thought chains for science question answering.Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems.
(278)Lu, P., Peng, B., Cheng, H., Galley, M., Chang, K.-W., Wu, Y. N., Zhu, S.-C., and Gao, J. (2023b).Chameleon: Plug-and-play compositional reasoning with large language models.arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.09842.
(279)Lu, Q., Kuen, J., Tiancheng, S., Jiuxiang, G., Weidong, G., Jiaya, J., Zhe, L., and Ming-Hsuan, Y. (2023c).High-quality entity segmentation.In ICCV.
(280)Lu, Y., Li, C., Liu, H., Yang, J., Gao, J., and Shen, Y. (2023d).An empirical study of scaling instruction-tuned large multimodal models.arXiv preprint.
Lüddecke and Ecker, (2022)Lüddecke, T. and Ecker, A. (2022).Image segmentation using text and image prompts.In CVPR.
(282)Luo, G., Zhou, Y., Ren, T., Chen, S., Sun, X., and Ji, R. (2023a).Cheap and quick: Efficient vision-language instruction tuning for large language models.arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.15023.
(283)Luo, H., Bao, J., Wu, Y., He, X., and Li, T. (2023b).Segclip: Patch aggregation with learnable centers for open-vocabulary semantic segmentation.In International Conference on Machine Learning, pages 23033–23044. PMLR.
(284)Luo, R., Zhao, Z., Yang, M., Dong, J., Qiu, M., Lu, P., Wang, T., and Wei, Z. (2023c).Valley: Video assistant with large language model enhanced ability.arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.07207.
Luo et al., (2021)Luo, W., Xing, J., Milan, A., Zhang, X., Liu, W., and Kim, T.-K. (2021).Multiple object tracking: A literature review.Artificial intelligence, 293:103448.
Ma and Wang, (2023)Ma, J. and Wang, B. (2023).Segment anything in medical images.arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.12306.
Ma et al., (2023)Ma, Z., Hong, X., and Shangguan, Q. (2023).Can sam count anything? an empirical study on sam counting.arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.10817.
Mao et al., (2016)Mao, J., Huang, J., Toshev, A., Camburu, O., Yuille, A. L., and Murphy, K. (2016).Generation and comprehension of unambiguous object descriptions.In CVPR.
Margffoy-Tuay et al., (2018)Margffoy-Tuay, E., Pérez, J. C., Botero, E., and Arbeláez, P. (2018).Dynamic multimodal instance segmentation guided by natural language queries.In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pages 630–645.
Marino et al., (2021)Marino, K., Chen, X., Parikh, D., Gupta, A., and Rohrbach, M. (2021).Krisp: Integrating implicit and symbolic knowledge for open-domain knowledge-based vqa.In CVPR.
Mazumder et al., (2022)Mazumder, M., Banbury, C., Yao, X., Karlaš, B., Rojas, W. G., Diamos, S., Diamos, G., He, L., Kiela, D., Jurado, D., et al. (2022).Dataperf: Benchmarks for data-centric ai development.arXiv preprint arXiv:2207.10062.
McGuinness and O’connor, (2010)McGuinness, K. and O’connor, N. E. (2010).A comparative evaluation of interactive segmentation algorithms.Pattern Recognition, 43(2):434–444.
Meng et al., (2021)Meng, C., He, Y., Song, Y., Song, J., Wu, J., Zhu, J.-Y., and Ermon, S. (2021).Sdedit: Guided image synthesis and editing with stochastic differential equations.In International Conference on Learning Representations.
Mertan et al., (2022)Mertan, A., Duff, D. J., and Unal, G. (2022).Single image depth estimation: An overview.Digital Signal Processing, 123:103441.
Miech et al., (2019)Miech, A., Zhukov, D., Alayrac, J.-B., Tapaswi, M., Laptev, I., and Sivic, J. (2019).Howto100m: Learning a text-video embedding by watching hundred million narrated video clips.In ICCV.
Mikolov et al., (2013)Mikolov, T., Chen, K., Corrado, G., and Dean, J. (2013).Efficient estimation of word representations in vector space.arXiv preprint arXiv:1301.3781.
Minderer et al., (2022)Minderer, M., Gritsenko, A., Stone, A., Neumann, M., Weissenborn, D., Dosovitskiy, A., Mahendran, A., Arnab, A., Dehghani, M., Shen, Z., Wang, X., Zhai, X., Kipf, T., and Houlsby, N. (2022).Simple open-vocabulary object detection with vision transformers.
Misra and Maaten, (2020)Misra, I. and Maaten, L. v. d. (2020).Self-supervised learning of pretext-invariant representations.In CVPR.
Misra et al., (2016)Misra, I., Shrivastava, A., Gupta, A., and Hebert, M. (2016).Cross-stitch networks for multi-task learning.In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pages 3994–4003.
Monajatipoor et al., (2023)Monajatipoor, M., Li, L. H., Rouhsedaghat, M., Yang, L. F., and Chang, K.-W. (2023).Metavl: Transferring in-context learning ability from language models to vision-language models.arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.01311.
Moor et al., (2023)Moor, M., Huang, Q., Wu, S., Yasunaga, M., Zakka, C., Dalmia, Y., Reis, E. P., Rajpurkar, P., and Leskovec, J. (2023).Med-flamingo: a multimodal medical few-shot learner.arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.15189.
Mortensen and Barrett, (1998)Mortensen, E. N. and Barrett, W. A. (1998).Interactive segmentation with intelligent scissors.Graphical models and image processing, 60(5):349–384.
Mottaghi et al., (2014)Mottaghi, R., Chen, X., Liu, X., Cho, N.-G., Lee, S.-W., Fidler, S., Urtasun, R., and Yuille, A. (2014).The role of context for object detection and semantic segmentation in the wild.In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pages 891–898.
Mou et al., (2023)Mou, C., Wang, X., Xie, L., Zhang, J., Qi, Z., Shan, Y., and Qie, X. (2023).T2i-adapter: Learning adapters to dig out more controllable ability for text-to-image diffusion models.arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.08453.
Mu et al., (2021)Mu, N., Kirillov, A., Wagner, D., and Xie, S. (2021).Slip: Self-supervision meets language-image pre-training.arXiv preprint arXiv:2112.12750.
Mu et al., (2023)Mu, Y., Zhang, Q., Hu, M., Wang, W., Ding, M., Jin, J., Wang, B., Dai, J., Qiao, Y., and Luo, P. (2023).Embodiedgpt: Vision-language pre-training via embodied chain of thought.arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.15021.
Musgrave et al., (2020)Musgrave, K., Belongie, S., and Lim, S.-N. (2020).A metric learning reality check.In ECCV.
Nagaraja et al., (2016)Nagaraja, V. K., Morariu, V. I., and Davis, L. S. (2016).Modeling context between objects for referring expression understanding.In ECCV.
Nakano et al., (2021)Nakano, R., Hilton, J., Balaji, S., Wu, J., Ouyang, L., Kim, C., Hesse, C., Jain, S., Kosaraju, V., Saunders, W., et al. (2021).Webgpt: Browser-assisted question-answering with human feedback.arXiv preprint arXiv:2112.09332.
Nguyen et al., (2022)Nguyen, T., Ilharco, G., Wortsman, M., Oh, S., and Schmidt, L. (2022).Quality not quantity: On the interaction between dataset design and robustness of clip.NeurIPS.
Ning et al., (2023)Ning, J., Li, C., Zhang, Z., Geng, Z., Dai, Q., He, K., and Hu, H. (2023).All in tokens: Unifying output space of visual tasks via soft token.arXiv preprint arXiv:2301.02229.
Oord et al., (2018)Oord, A. v. d., Li, Y., and Vinyals, O. (2018).Representation learning with contrastive predictive coding.arXiv preprint arXiv:1807.03748.
Oord et al., (2017)Oord, A. v. d., Vinyals, O., and Kavukcuoglu, K. (2017).Neural discrete representation learning.arXiv preprint arXiv:1711.00937.
OpenAI, (2022)OpenAI (2022).ChatGPT.https://openai.com/blog/chatgpt/.
(315)OpenAI (2023a).GPT-4 technical report.https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.08774.
(316)OpenAI (2023b).Gpt-4 technical report.
Oquab et al., (2023)Oquab, M., Darcet, T., Moutakanni, T., Vo, H., Szafraniec, M., Khalidov, V., Fernandez, P., Haziza, D., Massa, F., El-Nouby, A., et al. (2023).Dinov2: Learning robust visual features without supervision.arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.07193.
Ordonez et al., (2011)Ordonez, V., Kulkarni, G., and Berg, T. (2011).Im2text: Describing images using 1 million captioned photographs.In NeurIPS.
Ouyang et al., (2022)Ouyang, L., Wu, J., Jiang, X., Almeida, D., Wainwright, C., Mishkin, P., Zhang, C., Agarwal, S., Slama, K., Ray, A., et al. (2022).Training language models to follow instructions with human feedback.Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 35:27730–27744.
Ozbulak et al., (2023)Ozbulak, U., Lee, H. J., Boga, B., Anzaku, E. T., Park, H., Van Messem, A., De Neve, W., and Vankerschaver, J. (2023).Know your self-supervised learning: A survey on image-based generative and discriminative training.arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.13689.
Paranjape et al., (2023)Paranjape, B., Lundberg, S., Singh, S., Hajishirzi, H., Zettlemoyer, L., and Ribeiro, M. T. (2023).Art: Automatic multi-step reasoning and tool-use for large language models.arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.09014.
Patil et al., (2023)Patil, S. G., Zhang, T., Wang, X., and Gonzalez, J. E. (2023).Gorilla: Large language model connected with massive apis.arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.15334.
Penedo et al., (2023)Penedo, G., Malartic, Q., Hesslow, D., Cojocaru, R., Cappelli, A., Alobeidli, H., Pannier, B., Almazrouei, E., and Launay, J. (2023).The RefinedWeb dataset for Falcon LLM: outperforming curated corpora with web data, and web data only.arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.01116.
(324)Peng, B., Li, C., He, P., Galley, M., and Gao, J. (2023a).Instruction tuning with GPT-4.arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.03277.
(325)Peng, Z., Dong, L., Bao, H., Ye, Q., and Wei, F. (2022a).Beit v2: Masked image modeling with vector-quantized visual tokenizers.arXiv preprint arXiv:2208.06366.
(326)Peng, Z., Dong, L., Bao, H., Ye, Q., and Wei, F. (2022b).A unified view of masked image modeling.arXiv preprint arXiv:2210.10615.
(327)Peng, Z., Wang, W., Dong, L., Hao, Y., Huang, S., Ma, S., and Wei, F. (2023b).Kosmos-2: Grounding multimodal large language models to the world.arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.14824.
Peters et al., (2019)Peters, M. E., Neumann, M., Logan IV, R. L., Schwartz, R., Joshi, V., Singh, S., and Smith, N. A. (2019).Knowledge enhanced contextual word representations.arXiv preprint arXiv:1909.04164.
Pham et al., (2021)Pham, H., Dai, Z., Ghiasi, G., Liu, H., Yu, A. W., Luong, M.-T., Tan, M., and Le, Q. V. (2021).Combined scaling for zero-shot transfer learning.arXiv preprint arXiv:2111.10050.
Pi et al., (2023)Pi, R., Gao, J., Diao, S., Pan, R., Dong, H., Zhang, J., Yao, L., Han, J., Xu, H., and Zhang, L. K. T. (2023).Detgpt: Detect what you need via reasoning.arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.14167.
Plummer et al., (2015)Plummer, B. A., Wang, L., Cervantes, C. M., Caicedo, J. C., Hockenmaier, J., and Lazebnik, S. (2015).Flickr30k entities: Collecting region-to-phrase correspondences for richer image-to-sentence models.In ICCV.
Pont-Tuset et al., (2020)Pont-Tuset, J., Uijlings, J., Changpinyo, S., Soricut, R., and Ferrari, V. (2020).Connecting vision and language with localized narratives.In ECCV.
Qian et al., (2023)Qian, C., Han, C., Fung, Y. R., Qin, Y., Liu, Z., and Ji, H. (2023).Creator: Disentangling abstract and concrete reasonings of large language models through tool creation.arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.14318.
Qian et al., (2022)Qian, R., Li, Y., Xu, Z., Yang, M.-H., Belongie, S., and Cui, Y. (2022).Multimodal open-vocabulary video classification via pre-trained vision and language models.arXiv preprint arXiv:2207.07646.
(335)Qin, C., Zhang, S., Yu, N., Feng, Y., Yang, X., Zhou, Y., Wang, H., Niebles, J. C., Xiong, C., Savarese, S., et al. (2023a).Unicontrol: A unified diffusion model for controllable visual generation in the wild.arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.11147.
(336)Qin, J., Wu, J., Yan, P., Li, M., Yuxi, R., Xiao, X., Wang, Y., Wang, R., Wen, S., Pan, X., and Wang, X. (2023b).Freeseg: Unified, universal and open-vocabulary image segmentation.
Radford et al., (2021)Radford, A., Kim, J. W., Hallacy, C., Ramesh, A., Goh, G., Agarwal, S., Sastry, G., Askell, A., Mishkin, P., Clark, J., et al. (2021).Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision.In ICML.
Radford et al., (2019)Radford, A., Wu, J., Child, R., Luan, D., Amodei, D., Sutskever, I., et al. (2019).Language models are unsupervised multitask learners.OpenAI blog.
Raffel et al., (2020)Raffel, C., Shazeer, N., Roberts, A., Lee, K., Narang, S., Matena, M., Zhou, Y., Li, W., and Liu, P. J. (2020).Exploring the limits of transfer learning with a unified text-to-text transformer.JMLR.
Rahman et al., (2020)Rahman, S., Khan, S., and Barnes, N. (2020).Improved visual-semantic alignment for zero-shot object detection.In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, volume 34, pages 11932–11939.
Rajič et al., (2023)Rajič, F., Ke, L., Tai, Y.-W., Tang, C.-K., Danelljan, M., and Yu, F. (2023).Segment anything meets point tracking.arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.01197.
Ramesh et al., (2022)Ramesh, A., Dhariwal, P., Nichol, A., Chu, C., and Chen, M. (2022).Hierarchical text-conditional image generation with clip latents.arXiv preprint arXiv:2204.06125.
(343)Ramesh, A., Pavlov, M., Goh, G., Gray, S., Voss, C., Radford, A., Chen, M., and Sutskever, I. (2021a).Zero-Shot Text-to-Image Generation.In ICML.
(344)Ramesh, A., Pavlov, M., Goh, G., Gray, S., Voss, C., Radford, A., Chen, M., and Sutskever, I. (2021b).Zero-shot text-to-image generation.In International Conference on Machine Learning, pages 8821–8831. PMLR.
Rao et al., (2022)Rao, Y., Zhao, W., Chen, G., Tang, Y., Zhu, Z., Huang, G., Zhou, J., and Lu, J. (2022).Denseclip: Language-guided dense prediction with context-aware prompting.In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 18082–18091.
Razavi et al., (2019)Razavi, A., Van den Oord, A., and Vinyals, O. (2019).Generating diverse high-fidelity images with vq-vae-2.In NeurIPS.
Redmon et al., (2016)Redmon, J., Divvala, S., Girshick, R., and Farhadi, A. (2016).You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection.In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pages 779–788.
Reed et al., (2022)Reed, S., Zolna, K., Parisotto, E., Colmenarejo, S. G., Novikov, A., Barth-Maron, G., Gimenez, M., Sulsky, Y., Kay, J., Springenberg, J. T., et al. (2022).A generalist agent.arXiv preprint arXiv:2205.06175.
Ren et al., (2015)Ren, S., He, K., Girshick, R., and Sun, J. (2015).Faster r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks.In NeurIPS.
Ridnik et al., (2021)Ridnik, T., Ben-Baruch, E., Noy, A., and Zelnik-Manor, L. (2021).Imagenet-21k pretraining for the masses.arXiv preprint arXiv:2104.10972.
Rombach et al., (2021)Rombach, R., Blattmann, A., Lorenz, D., Esser, P., and Ommer, B. (2021).High-resolution image synthesis with latent diffusion models.
Rombach et al., (2022)Rombach, R., Blattmann, A., Lorenz, D., Esser, P., and Ommer, B. (2022).High-resolution image synthesis with latent diffusion models.In CVPR.
Ronneberger et al., (2015)Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., and Brox, T. (2015).U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation.In Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, October 5-9, 2015, Proceedings, Part III 18, pages 234–241. Springer.
Roy et al., (2023)Roy, S., Wald, T., Koehler, G., Rokuss, M. R., Disch, N., Holzschuh, J., Zimmerer, D., and Maier-Hein, K. H. (2023).Sam. md: Zero-shot medical image segmentation capabilities of the segment anything model.arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.05396.
Ruan and Jin, (2022)Ruan, L. and Jin, Q. (2022).Survey: Transformer based video-language pre-training.AI Open.
Ruiz et al., (2023)Ruiz, N., Li, Y., Jampani, V., Pritch, Y., Rubinstein, M., and Aberman, K. (2023).Dreambooth: Fine tuning text-to-image diffusion models for subject-driven generation.In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 22500–22510.
Russakovsky et al., (2015)Russakovsky, O., Deng, J., Su, H., Krause, J., Satheesh, S., Ma, S., Huang, Z., Karpathy, A., Khosla, A., Bernstein, M., et al. (2015).Imagenet large scale visual recognition challenge.IJCV.
Saharia et al., (2022)Saharia, C., Chan, W., Saxena, S., Li, L., Whang, J., Denton, E., Ghasemipour, S. K. S., Ayan, B. K., Mahdavi, S. S., Lopes, R. G., et al. (2022).Photorealistic text-to-image diffusion models with deep language understanding.arXiv preprint arXiv:2205.11487.
Sariyildiz et al., (2020)Sariyildiz, M. B., Perez, J., and Larlus, D. (2020).Learning visual representations with caption annotations.In ECCV.
Schick et al., (2023)Schick, T., Dwivedi-Yu, J., Dessì, R., Raileanu, R., Lomeli, M., Zettlemoyer, L., Cancedda, N., and Scialom, T. (2023).Toolformer: Language models can teach themselves to use tools.arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.04761.
Schuhmann et al., (2022)Schuhmann, C., Beaumont, R., Vencu, R., Gordon, C., Wightman, R., Cherti, M., Coombes, T., Katta, A., Mullis, C., Wortsman, M., et al. (2022).Laion-5b: An open large-scale dataset for training next generation image-text models.NeurIPS.
Schuhmann et al., (2021)Schuhmann, C., Vencu, R., Beaumont, R., Kaczmarczyk, R., Mullis, C., Katta, A., Coombes, T., Jitsev, J., and Komatsuzaki, A. (2021).Laion-400m: Open dataset of clip-filtered 400 million image-text pairs.arXiv preprint arXiv:2111.02114.
Schwenk et al., (2022)Schwenk, D., Khandelwal, A., Clark, C., Marino, K., and Mottaghi, R. (2022).A-okvqa: A benchmark for visual question answering using world knowledge.arXiv preprint arXiv:2206.01718.
Sennrich et al., (2016)Sennrich, R., Haddow, B., and Birch, A. (2016).Neural machine translation of rare words with subword units.In ACL.
Shao et al., (2019)Shao, S., Li, Z., Zhang, T., Peng, C., Yu, G., Zhang, X., Li, J., and Sun, J. (2019).Objects365: A large-scale, high-quality dataset for object detection.In ICCV.
Shao et al., (2023)Shao, W., Hu, Y., Gao, P., Lei, M., Zhang, K., Meng, F., Xu, P., Huang, S., Li, H., Qiao, Y., et al. (2023).Tiny lvlm-ehub: Early multimodal experiments with bard.arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.03729.
ShareGPT, (2023)ShareGPT (2023).https://sharegpt.com/.
Sharma et al., (2018)Sharma, P., Ding, N., Goodman, S., and Soricut, R. (2018).Conceptual captions: A cleaned, hypernymed, image alt-text dataset for automatic image captioning.In ACL.
(369)Shen, Q., Yang, X., and Wang, X. (2023a).Anything-3d: Towards single-view anything reconstruction in the wild.arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.10261.
(370)Shen, S., Li, C., Hu, X., Xie, Y., Yang, J., Zhang, P., Rohrbach, A., Gan, Z., Wang, L., Yuan, L., et al. (2022a).K-lite: Learning transferable visual models with external knowledge.In NeurIPS.
(371)Shen, S., Li, L. H., Tan, H., Bansal, M., Rohrbach, A., Chang, K.-W., Yao, Z., and Keutzer, K. (2022b).How much can clip benefit vision-and-language tasks?In ICLR.
(372)Shen, Y., Song, K., Tan, X., Li, D., Lu, W., and Zhuang, Y. (2023b).Hugginggpt: Solving ai tasks with chatgpt and its friends in huggingface.arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.17580.
Sheynin et al., (2022)Sheynin, S., Ashual, O., Polyak, A., Singer, U., Gafni, O., Nachmani, E., and Taigman, Y. (2022).Knn-diffusion: Image generation via large-scale retrieval.arXiv preprint arXiv:2204.02849.
(374)Shi, J., Xiong, W., Lin, Z., and Jung, H. J. (2023a).Instantbooth: Personalized text-to-image generation without test-time finetuning.arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.03411.
(375)Shi, P., Qiu, J., Abaxi, S. M. D., Wei, H., Lo, F. P.-W., and Yuan, W. (2023b).Generalist vision foundation models for medical imaging: A case study of segment anything model on zero-shot medical segmentation.Diagnostics.
Shin et al., (2020)Shin, T., Razeghi, Y., Logan IV, R. L., Wallace, E., and Singh, S. (2020).Autoprompt: Eliciting knowledge from language models with automatically generated prompts.arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.15980.
Sidorov et al., (2020)Sidorov, O., Hu, R., Rohrbach, M., and Singh, A. (2020).Textcaps: a dataset for image captioning with reading comprehension.In ECCV.
Silberman et al., (2012)Silberman, N., Hoiem, D., Kohli, P., and Fergus, R. (2012).Indoor segmentation and support inference from rgbd images.In Computer Vision–ECCV 2012: 12th European Conference on Computer Vision, Florence, Italy, October 7-13, 2012, Proceedings, Part V 12, pages 746–760. Springer.
Singer et al., (2022)Singer, U., Polyak, A., Hayes, T., Yin, X., An, J., Zhang, S., Hu, Q., Yang, H., Ashual, O., Gafni, O., et al. (2022).Make-a-video: Text-to-video generation without text-video data.arXiv preprint arXiv:2209.14792.
(380)Singh, A., Hu, R., Goswami, V., Couairon, G., Galuba, W., Rohrbach, M., and Kiela, D. (2022a).Flava: A foundational language and vision alignment model.In CVPR.
Singh et al., (2023)Singh, M., Duval, Q., Alwala, K. V., Fan, H., Aggarwal, V., Adcock, A., Joulin, A., Dollár, P., Feichtenhofer, C., Girshick, R., et al. (2023).The effectiveness of mae pre-pretraining for billion-scale pretraining.arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.13496.
(382)Singh, M., Gustafson, L., Adcock, A., de Freitas Reis, V., Gedik, B., Kosaraju, R. P., Mahajan, D., Girshick, R., Dollár, P., and Van Der Maaten, L. (2022b).Revisiting weakly supervised pre-training of visual perception models.In CVPR.
Sohl-Dickstein et al., (2015)Sohl-Dickstein, J., Weiss, E., Maheswaranathan, N., and Ganguli, S. (2015).Deep unsupervised learning using nonequilibrium thermodynamics.In International conference on machine learning, pages 2256–2265. PMLR.
Song and Ermon, (2020)Song, Y. and Ermon, S. (2020).Improved techniques for training score-based generative models.Advances in neural information processing systems, 33:12438–12448.
Song et al., (2023)Song, Y., Xiong, W., Zhu, D., Li, C., Wang, K., Tian, Y., and Li, S. (2023).Restgpt: Connecting large language models with real-world applications via restful apis.arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.06624.
Srinivasan et al., (2021)Srinivasan, K., Raman, K., Chen, J., Bendersky, M., and Najork, M. (2021).Wit: Wikipedia-based image text dataset for multimodal multilingual machine learning.arXiv preprint arXiv:2103.01913.
Su et al., (2019)Su, W., Zhu, X., Cao, Y., Li, B., Lu, L., Wei, F., and Dai, J. (2019).VL-BERT: Pre-training of generic visual-linguistic representations.In ICLR.
Su et al., (2023)Su, Y., Lan, T., Li, H., Xu, J., Wang, Y., and Cai, D. (2023).Pandagpt: One model to instruction-follow them all.arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.16355.
Sun et al., (2017)Sun, C., Shrivastava, A., Singh, S., and Gupta, A. (2017).Revisiting unreasonable effectiveness of data in deep learning era.In ICCV.
(390)Sun, Q., Yu, Q., Cui, Y., Zhang, F., Zhang, X., Wang, Y., Gao, H., Liu, J., Huang, T., and Wang, X. (2023a).Generative pretraining in multimodality.arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.05222.
(391)Sun, Y., Yang, Y., Peng, H., Shen, Y., Yang, Y., Hu, H., Qiu, L., and Koike, H. (2023b).Imagebrush: Learning visual in-context instructions for exemplar-based image manipulation.arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.00906.
(392)Sun, Y., Zhu, C., Zheng, S., Zhang, K., Shui, Z., Yu, X., Zhao, Y., Li, H., Zhang, Y., Zhao, R., et al. (2023c).Pathasst: Redefining pathology through generative foundation ai assistant for pathology.arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.15072.
Surís et al., (2023)Surís, D., Menon, S., and Vondrick, C. (2023).Vipergpt: Visual inference via python execution for reasoning.arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.08128.
Tan and Bansal, (2019)Tan, H. and Bansal, M. (2019).LXMERT: Learning cross-modality encoder representations from transformers.In EMNLP.
(395)Tang, L., Xiao, H., and Li, B. (2023a).Can sam segment anything? when sam meets camouflaged object detection.arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.04709.
(396)Tang, Z., Yang, Z., Zhu, C., Zeng, M., and Bansal, M. (2023b).Any-to-any generation via composable diffusion.
Tao et al., (2023)Tao, C., Zhu, X., Su, W., Huang, G., Li, B., Zhou, J., Qiao, Y., Wang, X., and Dai, J. (2023).Siamese image modeling for self-supervised vision representation learning.In CVPR.
Taori et al., (2023)Taori, R., Gulrajani, I., Zhang, T., Dubois, Y., Li, X., Guestrin, C., Liang, P., and Hashimoto, T. B. (2023).Stanford alpaca: An instruction-following llama model.https://github.com/tatsu-lab/stanford_alpaca.
Team, (2023)Team, M. N. (2023).Introducing mpt-7b: A new standard for open-source, ly usable llms.Accessed: 2023-03-28.
Thomee et al., (2016)Thomee, B., Shamma, D. A., Friedland, G., Elizalde, B., Ni, K., Poland, D., Borth, D., and Li, L.-J. (2016).Yfcc100m: The new data in multimedia research.Communications of the ACM.
(401)Tian, Y., Krishnan, D., and Isola, P. (2020a).Contrastive multiview coding.In ECCV.
(402)Tian, Z., Shen, C., and Chen, H. (2020b).Conditional convolutions for instance segmentation.In Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, August 23–28, 2020, Proceedings, Part I 16, pages 282–298. Springer.
Tong et al., (2022)Tong, Z., Song, Y., Wang, J., and Wang, L. (2022).Videomae: Masked autoencoders are data-efficient learners for self-supervised video pre-training.NeurIPS.
Touvron et al., (2021)Touvron, H., Cord, M., Douze, M., Massa, F., Sablayrolles, A., and Jégou, H. (2021).Training data-efficient image transformers & distillation through attention.In ICML.
Touvron et al., (2023)Touvron, H., Lavril, T., Izacard, G., Martinet, X., Lachaux, M.-A., Lacroix, T., Rozière, B., Goyal, N., Hambro, E., Azhar, F., et al. (2023).Llama: Open and efficient foundation language models.arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.13971.
Tschannen et al., (2023)Tschannen, M., Kumar, M., Steiner, A., Zhai, X., Houlsby, N., and Beyer, L. (2023).Image captioners are scalable vision learners too.arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.07915.
Tu et al., (2023)Tu, T., Azizi, S., Driess, D., Schaekermann, M., Amin, M., Chang, P.-C., Carroll, A., Lau, C., Tanno, R., Ktena, I., et al. (2023).Towards generalist biomedical ai.arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.14334.
Vahdat and Kautz, (2020)Vahdat, A. and Kautz, J. (2020).Nvae: A deep hierarchical variational autoencoder.
van den Oord et al., (2017)van den Oord, A., Vinyals, O., and Kavukcuoglu, K. (2017).Neural discrete representation learning.In NeurIPS.
Vaswani et al., (2017)Vaswani, A., Shazeer, N., Parmar, N., Uszkoreit, J., Jones, L., Gomez, A. N., Kaiser, Ł., and Polosukhin, I. (2017).Attention is all you need.In NeurIPS.
Vicuna, (2023)Vicuna (2023).Vicuna: An open-source chatbot impressing GPT-4 with 90%* chatgpt quality.https://vicuna.lmsys.org/.
Vinyals et al., (2015)Vinyals, O., Toshev, A., Bengio, S., and Erhan, D. (2015).Show and tell: A neural image caption generator.In CVPR.
Vinyals et al., (2016)Vinyals, O., Toshev, A., Bengio, S., and Erhan, D. (2016).Show and tell: Lessons learned from the 2015 mscoco image captioning challenge.IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence, 39(4):652–663.
Viola and Jones, (2001)Viola, P. and Jones, M. (2001).Rapid object detection using a boosted cascade of simple features.In Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. CVPR 2001, volume 1, pages I–I. Ieee.
Wang and Komatsuzaki, (2021)Wang, B. and Komatsuzaki, A. (2021).GPT-J-6B: A 6 Billion Parameter Autoregressive Language Model.https://github.com/kingoflolz/mesh-transformer-jax.
(416)Wang, B., Wu, F., Han, X., Peng, J., Zhong, H., Zhang, P., Dong, X., Li, W., Li, W., Wang, J., et al. (2023a).Vigc: Visual instruction generation and correction.arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.12714.
(417)Wang, F., Kong, T., Zhang, R., Liu, H., and Li, H. (2023b).Self-supervised learning by estimating twin class distribution.TIP.
Wang et al., (2018)Wang, H., Wang, Y., Zhou, Z., Ji, X., Li, Z., Gong, D., Zhou, J., and Liu, W. (2018).Cosface: Large margin cosine loss for deep face recognition.CVPR.
(419)Wang, H., Zhu, Y., Adam, H., Yuille, A., and Chen, L.-C. (2021a).Max-deeplab: End-to-end panoptic segmentation with mask transformers.In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 5463–5474.
(420)Wang, J., Chen, D., Luo, C., Dai, X., Yuan, L., Wu, Z., and Jiang, Y.-G. (2023c).Chatvideo: A tracklet-centric multimodal and versatile video understanding system.arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.14407.
(421)Wang, J., Yang, Z., Hu, X., Li, L., Lin, K., Gan, Z., Liu, Z., Liu, C., and Wang, L. (2022a).Git: A generative image-to-text transformer for vision and language.arXiv preprint arXiv:2205.14100.
(422)Wang, J., Zhou, Y., Xu, G., Shi, P., Zhao, C., Xu, H., Ye, Q., Yan, M., Zhang, J., Zhu, J., et al. (2023d).Evaluation and analysis of hallucination in large vision-language models.arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.15126.
(423)Wang, L., Huang, B., Zhao, Z., Tong, Z., He, Y., Wang, Y., Wang, Y., and Qiao, Y. (2023e).Videomae v2: Scaling video masked autoencoders with dual masking.In CVPR.
(424)Wang, P., Yang, A., Men, R., Lin, J., Bai, S., Li, Z., Ma, J., Zhou, C., Zhou, J., and Yang, H. (2022b).Ofa: Unifying architectures, tasks, and modalities through a simple sequence-to-sequence learning framework.In ICML.
(425)Wang, R., Chen, D., Wu, Z., Chen, Y., Dai, X., Liu, M., Jiang, Y.-G., Zhou, L., and Yuan, L. (2022c).Bevt: Bert pretraining of video transformers.In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pages 14733–14743.
(426)Wang, T., Li, L., Lin, K., Lin, C.-C., Yang, Z., Zhang, H., Liu, Z., and Wang, L. (2023f).Disco: Disentangled control for referring human dance generation in real world.arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.00040.
(427)Wang, T., Zhang, J., Fei, J., Ge, Y., Zheng, H., Tang, Y., Li, Z., Gao, M., Zhao, S., Shan, Y., et al. (2023g).Caption anything: Interactive image description with diverse multimodal controls.arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.02677.
(428)Wang, W., Bao, H., Dong, L., Bjorck, J., Peng, Z., Liu, Q., Aggarwal, K., Mohammed, O. K., Singhal, S., Som, S., and Wei, F. (2022d).Image as a foreign language: Beit pretraining for all vision and vision-language tasks.arXiv preprint arXiv:2208.10442.
(429)Wang, W., Bao, H., Dong, L., and Wei, F. (2021b).Vlmo: Unified vision-language pre-training with mixture-of-modality-experts.arXiv preprint arXiv:2111.02358.
(430)Wang, W., Chen, Z., Chen, X., Wu, J., Zhu, X., Zeng, G., Luo, P., Lu, T., Zhou, J., Qiao, Y., et al. (2023h).VisionLLM: Large language model is also an open-ended decoder for vision-centric tasks.arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.11175.
(431)Wang, X., Wang, W., Cao, Y., Shen, C., and Huang, T. (2023i).Images speak in images: A generalist painter for in-context visual learning.In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 6830–6839.
(432)Wang, X., Zhang, X., Cao, Y., Wang, W., Shen, C., and Huang, T. (2023j).Seggpt: Segmenting everything in context.arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.03284.
(433)Wang, Y., Ivison, H., Dasigi, P., Hessel, J., Khot, T., Chandu, K. R., Wadden, D., MacMillan, K., Smith, N. A., Beltagy, I., et al. (2023k).How far can camels go? exploring the state of instruction tuning on open resources.arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.04751.
(434)Wang, Y., Kordi, Y., Mishra, S., Liu, A., Smith, N. A., Khashabi, D., and Hajishirzi, H. (2022e).Self-instruct: Aligning language model with self generated instructions.arXiv preprint arXiv:2212.10560.
(435)Wang, Y., Mishra, S., Alipoormolabashi, P., Kordi, Y., Mirzaei, A., Arunkumar, A., Ashok, A., Dhanasekaran, A. S., Naik, A., Stap, D., et al. (2022f).Benchmarking generalization via in-context instructions on 1,600+ language tasks.arXiv preprint arXiv:2204.07705.
Wang et al., (2020)Wang, Z., Chen, J., and Hoi, S. C. (2020).Deep learning for image super-resolution: A survey.IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence, 43(10):3365–3387.
(437)Wang, Z., Huang, H., Zhao, Y., Zhang, Z., and Zhao, Z. (2023l).Chat-3d: Data-efficiently tuning large language model for universal dialogue of 3d scenes.arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.08769.
(438)Wang, Z., Jiang, Y., Lu, Y., Shen, Y., He, P., Chen, W., Wang, Z., and Zhou, M. (2023m).In-context learning unlocked for diffusion models.
(439)Wang, Z., Yu, J., Yu, A. W., Dai, Z., Tsvetkov, Y., and Cao, Y. (2022g).Simvlm: Simple visual language model pretraining with weak supervision.In ICLR.
Weers et al., (2023)Weers, F., Shankar, V., Katharopoulos, A., Yang, Y., and Gunter, T. (2023).Masked autoencoding does not help natural language supervision at scale.In CVPR.
Wei et al., (2021)Wei, C., Fan, H., Xie, S., Wu, C.-Y., Yuille, A., and Feichtenhofer, C. (2021).Masked feature prediction for self-supervised visual pre-training.In CVPR.
(442)Wei, J., Wang, X., Schuurmans, D., Bosma, M., Chi, E., Le, Q., and Zhou, D. (2022a).Chain of thought prompting elicits reasoning in large language models.arXiv preprint arXiv:2201.11903.
(443)Wei, L., Xie, L., Zhou, W., Li, H., and Tian, Q. (2022b).Mvp: Multimodality-guided visual pre-training.In ECCV.
Wei et al., (2023)Wei, Y., Zhang, Y., Ji, Z., Bai, J., Zhang, L., and Zuo, W. (2023).Elite: Encoding visual concepts into textual embeddings for customized text-to-image generation.arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.13848.
Weng, (2023)Weng, L. (2023).Llm-powered autonomous agents.lilianweng.github.io.
(446)Wu, C., Yin, S., Qi, W., Wang, X., Tang, Z., and Duan, N. (2023a).Visual chatgpt: Talking, drawing and editing with visual foundation models.arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.04671.
(447)Wu, C., Zhang, X., Zhang, Y., Wang, Y., and Xie, W. (2023b).Towards generalist foundation model for radiology.arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.02463.
(448)Wu, J., Jiang, Y., Sun, P., Yuan, Z., and Luo, P. (2022a).Language as queries for referring video object segmentation.In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 4974–4984.
Wu et al., (2021)Wu, J., Lu, J., Sabharwal, A., and Mottaghi, R. (2021).Multi-modal answer validation for knowledge-based VQA.arXiv preprint arXiv:2103.12248.
(450)Wu, J., Wang, J., Yang, Z., Gan, Z., Liu, Z., Yuan, J., and Wang, L. (2022b).Grit: A generative region-to-text transformer for object understanding.arXiv preprint arXiv:2212.00280.
(451)Wu, S., Fei, H., Qu, L., Ji, W., and Chua, T.-S. (2023c).Next-gpt: Any-to-any multimodal llm.CoRR, abs/2309.05519.
(452)Wu, W., Timofeev, A., Chen, C., Zhang, B., Duan, K., Liu, S., Zheng, Y., Shlens, J., Du, X., Gan, Z., et al. (2023d).Mofi: Learning image representations from noisy entity annotated images.arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.07952.
Wu et al., (2013)Wu, Y., Lim, J., and Yang, M.-H. (2013).Online object tracking: A benchmark.In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pages 2411–2418.
Wu et al., (2018)Wu, Z., Xiong, Y., Yu, S. X., and Lin, D. (2018).Unsupervised feature learning via non-parametric instance discrimination.In CVPR.
Xian et al., (2018)Xian, Y., Lampert, C. H., Schiele, B., and Akata, Z. (2018).Zero-shot learning—a comprehensive evaluation of the good, the bad and the ugly.TPAMI.
Xiao et al., (2023)Xiao, Z., Chen, Y., Zhang, L., Yao, J., Wu, Z., Yu, X., Pan, Y., Zhao, L., Ma, C., Liu, X., et al. (2023).Instruction-vit: Multi-modal prompts for instruction learning in vit.arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.00201.
(457)Xie, D., Wang, R., Ma, J., Chen, C., Lu, H., Yang, D., Shi, F., and Lin, X. (2023a).Edit everything: A text-guided generative system for images editing.arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.14006.
(458)Xie, X., Fu, L., Zhang, Z., Wang, Z., and Bai, X. (2022a).Toward understanding wordart: Corner-guided transformer for scene text recognition.
Xie et al., (2021)Xie, Z., Lin, Y., Yao, Z., Zhang, Z., Dai, Q., Cao, Y., and Hu, H. (2021).Self-supervised learning with swin transformers.arXiv preprint arXiv:2105.04553.
(460)Xie, Z., Zhang, Z., Cao, Y., Lin, Y., Bao, J., Yao, Z., Dai, Q., and Hu, H. (2022b).Simmim: A simple framework for masked image modeling.In CVPR.
(461)Xie, Z., Zhang, Z., Cao, Y., Lin, Y., Wei, Y., Dai, Q., and Hu, H. (2023b).On data scaling in masked image modeling.In CVPR.
Xu et al., (2018)Xu, D., Ouyang, W., Wang, X., and Sebe, N. (2018).Pad-net: Multi-tasks guided prediction-and-distillation network for simultaneous depth estimation and scene parsing.In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 675–684.
Xu et al., (2021)Xu, H., Yan, M., Li, C., Bi, B., Huang, S., Xiao, W., and Huang, F. (2021).E2e-vlp: End-to-end vision-language pre-training enhanced by visual learning.
(464)Xu, J., De Mello, S., Liu, S., Byeon, W., Breuel, T., Kautz, J., and Wang, X. (2022a).Groupvit: Semantic segmentation emerges from text supervision.In CVPR.
(465)Xu, J., Liu, S., Vahdat, A., Byeon, W., Wang, X., and De Mello, S. (2023a).Open-vocabulary panoptic segmentation with text-to-image diffusion models.In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 2955–2966.
(466)Xu, P., Shao, W., Zhang, K., Gao, P., Liu, S., Lei, M., Meng, F., Huang, S., Qiao, Y., and Luo, P. (2023b).Lvlm-ehub: A comprehensive evaluation benchmark for large vision-language models.arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.09265.
(467)Xu, R., Wang, X., Wang, T., Chen, Y., Pang, J., and Lin, D. (2023c).Pointllm: Empowering large language models to understand point clouds.arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.16911.
(468)Xu, Z., Shen, Y., and Huang, L. (2022b).Multiinstruct: Improving multi-modal zero-shot learning via instruction tuning.arXiv preprint arXiv:2212.10773.
Yan et al., (2023)Yan, B., Jiang, Y., Wu, J., Wang, D., Luo, P., Yuan, Z., and Lu, H. (2023).Universal instance perception as object discovery and retrieval.In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 15325–15336.
(470)Yang, B., Gu, S., Zhang, B., Zhang, T., Chen, X., Sun, X., Chen, D., and Wen, F. (2023a).Paint by example: Exemplar-based image editing with diffusion models.In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 18381–18391.
(471)Yang, J., Gao, M., Li, Z., Gao, S., Wang, F., and Zheng, F. (2023b).Track anything: Segment anything meets videos.arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.11968.
(472)Yang, J., Li, C., Zhang, P., Xiao, B., Liu, C., Yuan, L., and Gao, J. (2022a).Unified contrastive learning in image-text-label space.In CVPR.
(473)Yang, J., Li, C., Zhang, P., Xiao, B., Yuan, L., Liu, C., and Gao, J. (2022b).Unicl: Unified contrastive learning in image-text-label space.In CVPR.
(474)Yang, R., Song, L., Li, Y., Zhao, S., Ge, Y., Li, X., and Shan, Y. (2023c).Gpt4tools: Teaching large language model to use tools via self-instruction.arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.18752.
Yang et al., (2021)Yang, Z., Gan, Z., Wang, J., Hu, X., Ahmed, F., Liu, Z., Lu, Y., and Wang, L. (2021).Crossing the format boundary of text and boxes: Towards unified vision-language modeling.arXiv preprint arXiv:2111.12085.
(476)Yang, Z., Gan, Z., Wang, J., Hu, X., Ahmed, F., Liu, Z., Lu, Y., and Wang, L. (2022c).Unitab: Unifying text and box outputs for grounded vision-language modeling.In European Conference on Computer Vision, pages 521–539. Springer.
(477)Yang, Z., Gan, Z., Wang, J., Hu, X., Lu, Y., Liu, Z., and Wang, L. (2022d).An empirical study of gpt-3 for few-shot knowledge-based vqa.In AAAI.
Yang* et al., (2023)Yang*, Z., Li*, L., Wang*, J., Lin*, K., Azarnasab*, E., Ahmed*, F., Liu, Z., Liu, C., Zeng, M., and Wang, L. (2023).Mm-react: Prompting chatgpt for multimodal reasoning and action.
(479)Yang, Z., Ping, W., Liu, Z., Korthikanti, V., Nie, W., Huang, D.-A., Fan, L., Yu, Z., Lan, S., Li, B., et al. (2023a).Re-vilm: Retrieval-augmented visual language model for zero and few-shot image captioning.arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.04858.
(480)Yang, Z., Wang, J., Gan, Z., Li, L., Lin, K., Wu, C., Duan, N., Liu, Z., Liu, C., Zeng, M., et al. (2023b).Reco: Region-controlled text-to-image generation.In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 14246–14255.
(481)Yang, Z., Wang, J., Tang, Y., Chen, K., Zhao, H., and Torr, P. H. (2022e).Lavt: Language-aware vision transformer for referring image segmentation.In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 18155–18165.
Yao et al., (2023)Yao, L., Han, J., Liang, X., Xu, D., Zhang, W., Li, Z., and Xu, H. (2023).Detclipv2: Scalable open-vocabulary object detection pre-training via word-region alignment.In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 23497–23506.
(483)Yao, L., Han, J., Wen, Y., Liang, X., Xu, D., Zhang, W., Li, Z., Xu, C., and Xu, H. (2022a).Detclip: Dictionary-enriched visual-concept paralleled pre-training for open-world detection.arXiv preprint arXiv:2209.09407.
(484)Yao, L., Huang, R., Hou, L., Lu, G., Niu, M., Xu, H., Liang, X., Li, Z., Jiang, X., and Xu, C. (2022b).Filip: Fine-grained interactive language-image pre-training.In ICLR.
(485)Yao, S., Zhao, J., Yu, D., Du, N., Shafran, I., Narasimhan, K., and Cao, Y. (2022c).React: Synergizing reasoning and acting in language models.arXiv preprint arXiv:2210.03629.
Yasunaga et al., (2022)Yasunaga, M., Aghajanyan, A., Shi, W., James, R., Leskovec, J., Liang, P., Lewis, M., Zettlemoyer, L., and Yih, W.-t. (2022).Retrieval-augmented multimodal language modeling.arXiv preprint arXiv:2211.12561.
(487)Ye, J., Hu, A., Xu, H., Ye, Q., Yan, M., Dan, Y., Zhao, C., Xu, G., Li, C., Tian, J., et al. (2023a).mplug-docowl: Modularized multimodal large language model for document understanding.arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.02499.
(488)Ye, L., Rochan, M., Liu, Z., and Wang, Y. (2019a).Cross-modal self-attention network for referring image segmentation.In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pages 10502–10511.
(489)Ye, M., Zhang, X., Yuen, P. C., and Chang, S.-F. (2019b).Unsupervised embedding learning via invariant and spreading instance feature.In CVPR.
(490)Ye, Q., Xu, H., Xu, G., Ye, J., Yan, M., Zhou, Y., Wang, J., Hu, A., Shi, P., Shi, Y., et al. (2023b).mplug-owl: Modularization empowers large language models with multimodality.arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.14178.
Yi et al., (2022)Yi, K., Ge, Y., Li, X., Yang, S., Li, D., Wu, J., Shan, Y., and Qie, X. (2022).Masked image modeling with denoising contrast.arXiv preprint arXiv:2205.09616.
Yilmaz et al., (2006)Yilmaz, A., Javed, O., and Shah, M. (2006).Object tracking: A survey.Acm computing surveys (CSUR), 38(4):13–es.
Yin et al., (2022)Yin, D., Dong, L., Cheng, H., Liu, X., Chang, K.-W., Wei, F., and Gao, J. (2022).A survey of knowledge-intensive nlp with pre-trained language models.arXiv preprint arXiv:2202.08772.
Yin et al., (2023)Yin, Z., Wang, J., Cao, J., Shi, Z., Liu, D., Li, M., Sheng, L., Bai, L., Huang, X., Wang, Z., et al. (2023).Lamm: Language-assisted multi-modal instruction-tuning dataset, framework, and benchmark.arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.06687.
Yoon et al., (2021)Yoon, S., Kang, W. Y., Jeon, S., Lee, S., Han, C., Park, J., and Kim, E.-S. (2021).Image-to-image retrieval by learning similarity between scene graphs.In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, volume 35, pages 10718–10726.
Yu et al., (2021)Yu, J., Li, X., Koh, J. Y., Zhang, H., Pang, R., Qin, J., Ku, A., Xu, Y., Baldridge, J., and Wu, Y. (2021).Vector-quantized image modeling with improved vqgan.arXiv preprint arXiv:2110.04627.
(497)Yu, J., Wang, Z., Vasudevan, V., Yeung, L., Seyedhosseini, M., and Wu, Y. (2022a).Coca: Contrastive captioners are image-text foundation models.TMLR.
(498)Yu, J., Xu, Y., Koh, J. Y., Luong, T., Baid, G., Wang, Z., Vasudevan, V., Ku, A., Yang, Y., Ayan, B. K., et al. (2022b).Scaling autoregressive models for content-rich text-to-image generation.Transactions on Machine Learning Research.
Yu and et al, (2023)Yu, L. and et al (2023).Scaling autoregressive multi-modal models: Pretraining and instruction tuning.
Yu et al., (2016)Yu, L., Poirson, P., Yang, S., Berg, A. C., and Berg, T. L. (2016).Modeling context in referring expressions.In ECCV.
(501)Yu, Q., He, J., Deng, X., Shen, X., and Chen, L.-C. (2023a).Convolutions die hard: Open-vocabulary segmentation with single frozen convolutional clip.arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.02487.
(502)Yu, Q., Li, J., Ye, W., Tang, S., and Zhuang, Y. (2023b).Interactive data synthesis for systematic vision adaptation via llms-aigcs collaboration.arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.12799.
(503)Yu, T., Feng, R., Feng, R., Liu, J., Jin, X., Zeng, W., and Chen, Z. (2023c).Inpaint anything: Segment anything meets image inpainting.arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.06790.
(504)Yu, W., Yang, Z., Li, L., Wang, J., Lin, K., Liu, Z., Wang, X., and Wang, L. (2023d).Mm-vet: Evaluating large multimodal models for integrated capabilities.arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.02490.
Yu et al., (2019)Yu, Z., Yu, J., Cui, Y., Tao, D., and Tian, Q. (2019).Deep modular co-attention networks for visual question answering.In CVPR.
Yuan et al., (2021)Yuan, L., Chen, D., Chen, Y.-L., Codella, N., Dai, X., Gao, J., Hu, H., Huang, X., Li, B., Li, C., Liu, C., Liu, M., Liu, Z., Lu, Y., Shi, Y., Wang, L., Wang, J., Xiao, B., Xiao, Z., Yang, J., Zeng, M., Zhou, L., and Zhang, P. (2021).Florence: A new foundation model for computer vision.arXiv preprint arXiv:2111.11432.
Zamir et al., (2018)Zamir, A. R., Sax, A., Shen, W., Guibas, L. J., Malik, J., and Savarese, S. (2018).Taskonomy: Disentangling task transfer learning.In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pages 3712–3722.
Zang et al., (2023)Zang, Y., Li, W., Han, J., Zhou, K., and Loy, C. C. (2023).Contextual object detection with multimodal large language models.arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.18279.
Zang et al., (2022)Zang, Y., Li, W., Zhou, K., Huang, C., and Loy, C. C. (2022).Open-vocabulary detr with conditional matching.arXiv preprint arXiv:2203.11876.
Zareian et al., (2021)Zareian, A., Rosa, K. D., Hu, D. H., and Chang, S.-F. (2021).Open-vocabulary object detection using captions.In CVPR.
Zbontar et al., (2021)Zbontar, J., Jing, L., Misra, I., LeCun, Y., and Deny, S. (2021).Barlow twins: Self-supervised learning via redundancy reduction.In ICML.
Zellers et al., (2019)Zellers, R., Bisk, Y., Farhadi, A., and Choi, Y. (2019).From recognition to cognition: Visual commonsense reasoning.In CVPR.
Zeng et al., (2023)Zeng, Y., Lin, Z., Zhang, J., Liu, Q., Collomosse, J., Kuen, J., and Patel, V. M. (2023).Scenecomposer: Any-level semantic image synthesis.In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 22468–22478.
Zeng et al., (2022)Zeng, Y., Zhang, X., and Li, H. (2022).Multi-grained vision language pre-training: Aligning texts with visual concepts.In ICML.
(515)Zhai, X., Kolesnikov, A., Houlsby, N., and Beyer, L. (2022a).Scaling vision transformers.In CVPR.
Zhai et al., (2023)Zhai, X., Mustafa, B., Kolesnikov, A., and Beyer, L. (2023).Sigmoid loss for language image pre-training.arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.15343.
(517)Zhai, X., Wang, X., Mustafa, B., Steiner, A., Keysers, D., Kolesnikov, A., and Beyer, L. (2022b).Lit: Zero-shot transfer with locked-image text tuning.In CVPR.
(518)Zhang, C., Liu, L., Cui, Y., Huang, G., Lin, W., Yang, Y., and Hu, Y. (2023a).A comprehensive survey on segment anything model for vision and beyond.arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.08196.
Zhang et al., (2020)Zhang, C., Yang, Z., He, X., and Deng, L. (2020).Multimodal intelligence: Representation learning, information fusion, and applications.JSTSP.
(520)Zhang, C., Zhang, C., Zhang, M., and Kweon, I. S. (2023b).Text-to-image diffusion model in generative ai: A survey.arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.07909.
(521)Zhang, C., Zheng, S., Li, C., Qiao, Y., Kang, T., Shan, X., Zhang, C., Qin, C., Rameau, F., Bae, S.-H., et al. (2023c).A survey on segment anything model (sam): Vision foundation model meets prompt engineering.arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.06211.
(522)Zhang, D., Li, S., Zhang, X., Zhan, J., Wang, P., Zhou, Y., and Qiu, X. (2023d).Speechgpt: Empowering large language models with intrinsic cross-modal conversational abilities.arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.11000.
(523)Zhang, H., Li, F., Liu, S., Zhang, L., Su, H., Zhu, J., Ni, L. M., and Shum, H.-Y. (2022a).Dino: Detr with improved denoising anchor boxes for end-to-end object detection.arXiv preprint arXiv:2203.03605.
(524)Zhang, H., Li, F., Zou, X., Liu, S., Li, C., Gao, J., Yang, J., and Zhang, L. (2023e).A simple framework for open-vocabulary segmentation and detection.arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.08131.
(525)Zhang, H., Li, X., and Bing, L. (2023f).Video-llama: An instruction-tuned audio-visual language model for video understanding.arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.02858.
(526)Zhang, H., Zhang, P., Hu, X., Chen, Y.-C., Li, L. H., Dai, X., Wang, L., Yuan, L., Hwang, J.-N., and Gao, J. (2022b).Glipv2: Unifying localization and vision-language understanding.In ECCV.
(527)Zhang, J., Huang, J., Jin, S., and Lu, S. (2023g).Vision-language models for vision tasks: A survey.arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.00685.
Zhang et al., (2018)Zhang, J., Shen, F., Liu, L., Zhu, F., Yu, M., Shao, L., Shen, H. T., and Van Gool, L. (2018).Generative domain-migration hashing for sketch-to-image retrieval.In Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV), pages 297–314.
Zhang and Agrawala, (2023)Zhang, L. and Agrawala, M. (2023).Adding conditional control to text-to-image diffusion models.arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.05543.
Zhang et al., (2021)Zhang, P., Li, X., Hu, X., Yang, J., Zhang, L., Wang, L., Choi, Y., and Gao, J. (2021).VinVL: Revisiting visual representations in vision-language models.In CVPR.
(531)Zhang, R., Jiang, Z., Guo, Z., Yan, S., Pan, J., Dong, H., Gao, P., and Li, H. (2023h).Personalize segment anything model with one shot.arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.03048.
(532)Zhang, S., Dong, L., Li, X., Zhang, S., Sun, X., Wang, S., Li, J., Hu, R., Zhang, T., Wu, F., et al. (2023i).Instruction tuning for large language models: A survey.arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.10792.
(533)Zhang, S., Gong, C., Wu, L., Liu, X., and Zhou, M. (2023j).Automl-gpt: Automatic machine learning with gpt.arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.02499.
(534)Zhang, S., Sun, P., Chen, S., Xiao, M., Shao, W., Zhang, W., Chen, K., and Luo, P. (2023k).Gpt4roi: Instruction tuning large language model on region-of-interest.arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.03601.
Zhang et al., (2019)Zhang, T., Kishore, V., Wu, F., Weinberger, K. Q., and Artzi, Y. (2019).Bertscore: Evaluating text generation with bert.arXiv preprint arXiv:1904.09675.
(536)Zhang, W., Aljunied, S. M., Gao, C., Chia, Y. K., and Bing, L. (2023l).M3exam: A multilingual, multimodal, multilevel benchmark for examining large language models.arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.05179.
(537)Zhang, X., Chen, J., Yuan, J., Chen, Q., Wang, J., Wang, X., Han, S., Chen, X., Pi, J., Yao, K., et al. (2022c).Cae v2: Context autoencoder with clip target.arXiv preprint arXiv:2211.09799.
(538)Zhang, X., Tian, Y., Huang, W., Ye, Q., Dai, Q., Xie, L., and Tian, Q. (2022d).Hivit: Hierarchical vision transformer meets masked image modeling.arXiv preprint arXiv:2205.14949.
(539)Zhang, X., Wu, C., Zhao, Z., Lin, W., Zhang, Y., Wang, Y., and Xie, W. (2023m).Pmc-vqa: Visual instruction tuning for medical visual question answering.arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.10415.
(540)Zhang, Y., Huang, X., Ma, J., Li, Z., Luo, Z., Xie, Y., Qin, Y., Luo, T., Li, Y., Liu, S., et al. (2023n).Recognize anything: A strong image tagging model.arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.03514.
Zhang and Jiao, (2023)Zhang, Y. and Jiao, R. (2023).How segment anything model (sam) boost medical image segmentation?arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.03678.
(542)Zhang, Y., Zhang, R., Gu, J., Zhou, Y., Lipka, N., Yang, D., and Sun, T. (2023o).Llavar: Enhanced visual instruction tuning for text-rich image understanding.arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.17107.
(543)Zhao, B., Wu, B., and Huang, T. (2023a).Svit: Scaling up visual instruction tuning.arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.04087.
(544)Zhao, S., Chen, D., Chen, Y.-C., Bao, J., Hao, S., Yuan, L., and Wong, K.-Y. K. (2023b).Uni-controlnet: All-in-one control to text-to-image diffusion models.arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.16322.
(545)Zhao, Y., Lin, Z., Zhou, D., Huang, Z., Feng, J., and Kang, B. (2023c).Bubogpt: Enabling visual grounding in multi-modal llms.arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.08581.
(546)Zhao, Y., Pang, T., Du, C., Yang, X., Li, C., Cheung, N.-M., and Lin, M. (2023d).On evaluating adversarial robustness of large vision-language models.arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.16934.
(547)Zhao, Z., Guo, L., Yue, T., Chen, S., Shao, S., Zhu, X., Yuan, Z., and Liu, J. (2023e).Chatbridge: Bridging modalities with large language model as a language catalyst.arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.16103.
Zhao et al., (2021)Zhao, Z., Wallace, E., Feng, S., Klein, D., and Singh, S. (2021).Calibrate before use: Improving few-shot performance of language models.In International Conference on Machine Learning, pages 12697–12706. PMLR.
(549)Zhong, Y., Yang, J., Zhang, P., Li, C., Codella, N., Li, L. H., Zhou, L., Dai, X., Yuan, L., Li, Y., et al. (2022a).Regionclip: Region-based language-image pretraining.In CVPR.
(550)Zhong, Y., Yang, J., Zhang, P., Li, C., Codella, N., Li, L. H., Zhou, L., Dai, X., Yuan, L., Li, Y., et al. (2022b).Regionclip: Region-based language-image pretraining.In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 16793–16803.
Zhou et al., (2017)Zhou, B., Zhao, H., Puig, X., Fidler, S., Barriuso, A., and Torralba, A. (2017).Scene parsing through ade20k dataset.In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pages 633–641.
(552)Zhou, C., Liu, P., Xu, P., Iyer, S., Sun, J., Mao, Y., Ma, X., Efrat, A., Yu, P., Yu, L., et al. (2023a).Lima: Less is more for alignment.arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.11206.
(553)Zhou, C., Loy, C. C., and Dai, B. (2022a).Extract free dense labels from clip.In ECCV.
(554)Zhou, G., Hong, Y., and Wu, Q. (2023b).Navgpt: Explicit reasoning in vision-and-language navigation with large language models.arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.16986.
(555)Zhou, J., Dong, L., Gan, Z., Wang, L., and Wei, F. (2023c).Non-contrastive learning meets language-image pre-training.In CVPR.
Zhou et al., (2021)Zhou, J., Wei, C., Wang, H., Shen, W., Xie, C., Yuille, A., and Kong, T. (2021).ibot: Image bert pre-training with online tokenizer.arXiv preprint arXiv:2111.07832.
(557)Zhou, T., Zhang, Y., Zhou, Y., Wu, Y., and Gong, C. (2023d).Can sam segment polyps?arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.07583.
(558)Zhou, X., Girdhar, R., Joulin, A., Krähenbühl, P., and Misra, I. (2022b).Detecting twenty-thousand classes using image-level supervision.In European Conference on Computer Vision, pages 350–368. Springer.
(559)Zhou, Y., Li, C., Chen, C., Gao, J., and Xu, J. (2022c).Lafite2: Few-shot text-to-image generation.arXiv preprint arXiv:2210.14124.
Zhou and Shimada, (2023)Zhou, Y. and Shimada, N. (2023).Vision + language applications: A survey.In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 826–842.
(561)Zhu, D., Chen, J., Shen, X., Li, X., and Elhoseiny, M. (2023a).Minigpt-4: Enhancing vision-language understanding with advanced large language models.
Zhu et al., (2019)Zhu, P., Wang, H., and Saligrama, V. (2019).Zero shot detection.IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 30(4):998–1010.
Zhu et al., (2020)Zhu, P., Wang, H., and Saligrama, V. (2020).Don’t even look once: Synthesizing features for zero-shot detection.In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 11693–11702.
(564)Zhu, W., Hessel, J., Awadalla, A., Gadre, S. Y., Dodge, J., Fang, A., Yu, Y., Schmidt, L., Wang, W. Y., and Choi, Y. (2023b).Multimodal c4: An open, billion-scale corpus of images interleaved with text.arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.06939.
Zong et al., (2023)Zong, Z., Song, G., and Liu, Y. (2023).Detrs with collaborative hybrid assignments training.
(566)Zou, X., Dou, Z.-Y., Yang, J., Gan, Z., Li, L., Li, C., Dai, X., Behl, H., Wang, J., Yuan, L., et al. (2023a).Generalized decoding for pixel, image, and language.In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.
Zou et al., (2022)Zou, X., Liu, H., and Lee, Y. J. (2022).End-to-end instance edge detection.arXiv preprint arXiv:2204.02898.
(568)Zou, X., Yang, J., Zhang, H., Li, F., Li, L., Gao, J., and Lee, Y. J. (2023b).Segment everything everywhere all at once.arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.06718.
【全文完】
参考资料:
Chuanyuan Li, Zhe Gan, Zhengyuan Yang, et al., Multimodal Foundation Models: From Specialists to General-Purpose Assistants, Microsoft Corporation, arxiv.org/html/2309.10020 v1
版权声明:
youcans@xidian 作品,转载必须标注原文链接:
【微软报告:多模态基础模型】(1)从专家模型到通用助手 https://blog.csdn.net/youcans/category_12244543.html
Copyright 2024 youcans, XIDIAN
Crated:2024-11




























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










