一、前置
jdbc操作数据库
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
// 加载数据库驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// 通过驱动管理类获取数据库链接
connection =
DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis? characterEncoding=utf-8", "root", "root");
// 定义sql语句?表示占位符
String sql = "select * from user where username = ?";
// 获取预处理statement
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
// 设置参数,第一个参数为sql语句中参数的序号(从1开始),第二个参数为设置的参数值
preparedStatement.setString(1, "tom");
// 向数据库发出sql执行查询,查询出结果集
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
// 遍历查询结果集
while (resultSet.next()) {
int id = resultSet.getInt("id");
String username = resultSet.getString("username");
// 封装User
user.setId(id);
user.setUsername(username);
}
System.out.println(user);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 释放资源
if (resultSet != null) {
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (preparedStatement != null) {
try {
preparedStatement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (connection != null) {
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
上面这段代码是用jdbc来操作数据库,大概分为加载数据库配置(硬编码),获取连接(频繁创建连接,消耗资源),定义sql,设置参数(太硬了不灵活),执行语句,获取结果集并封装为对象(太硬了不灵活),释放资源(频繁释放,消耗资源)。
由此我们可以采取配置文件,池化,反射等方式来改善问题。持久层框架MyBatis正是解决了这些问题,MyBatis说到底就是对jdbc操作数据库的封装,由此,后面的源码剖析部分也会根据上面代码的几个步骤来学习源码。
二、MyBatis架构及组件
1、架构
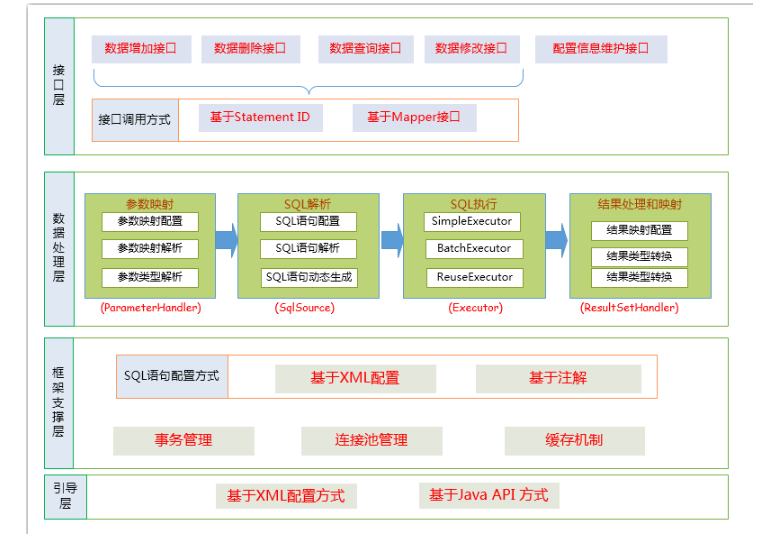
接口层:顾名思义提供API接口供用户对数据库操作,SqlSession就是主要的API接口类
数据处理层:核心的处理sql语句,执行sql语句,处理结果集的架构层
框架支撑层:也就是提供基础服务支撑的,如sql语句配置,事务,连接池等等组件的封装
引导层:配置和启动MyBatis 配置信息的方式
2、组件
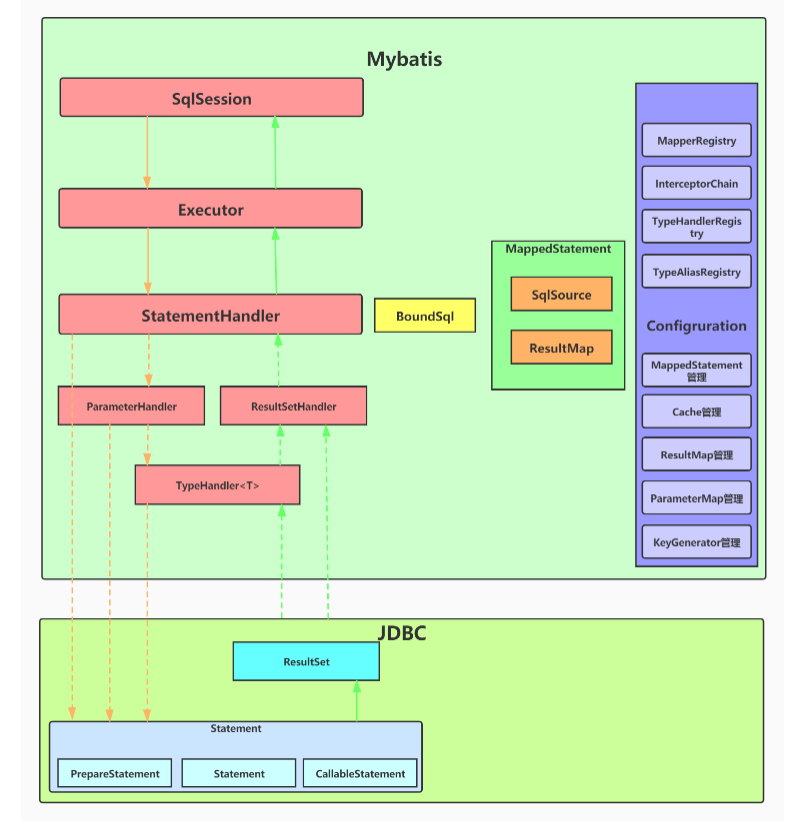
组件:
-
操作SqlSession的API执行sql查询,实际上SqlSession是委托了Executor执行真正的操作,StatementHandler负责对Statement的操作。
-
ParameterHandler是StatementHandler内部一个组件,主要负责对ParameterStatement参数的设置。
-
ResultSetHandler是StatementHandler内部一个组件,主要负责对ResultSet结果集的处理,封装成目标对象返回。
-
TypeHandler:用于Java类型与JDBC类型之间的数据转换,ParameterHandler和ResultSetHandler会分别使用到它的类型转换功能。
-
MappedStatement:是对Mapper配置文件或Mapper接口方法上通过注解申明SQL的封装
-
Configuration:Mybatis所有配置都统一由Configuration进行管理,内部由具体对象分别管理各自的小功能模块
三、源码
public void test1() throws IOException {
// 1. 通过类加载器对配置文件进行加载,加载成了字节输入流,存到内存中 注意:配置文件并没有被解析
InputStream resourceAsStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("sqlMapConfig.xml");
// 2. (1)解析了配置文件,封装configuration对象 (2)创建了DefaultSqlSessionFactory工厂对象
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(resourceAsStream);
// 3.问题:openSession()执行逻辑是什么?
// 3. (1)创建事务对象 (2)创建了执行器对象cachingExecutor (3)创建了DefaultSqlSession对象
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
// 4. 委派给Executor来执行,Executor执行时又会调用很多其他组件(参数设置、解析sql的获取,sql的执行、结果集的封装)
User user = sqlSession.selectOne("com.itheima.mapper.UserMapper.findByCondition", 1);
System.out.println(user);
System.out.println("MyBatis源码环境搭建成功....");
sqlSession.close();
}
我们将由这段测试代码(下面的测试代码均指此段代码)展开来学习源码,这段代码其实就是前面第一章前置的jdbc操作数据库的封装
1、加载配置文件
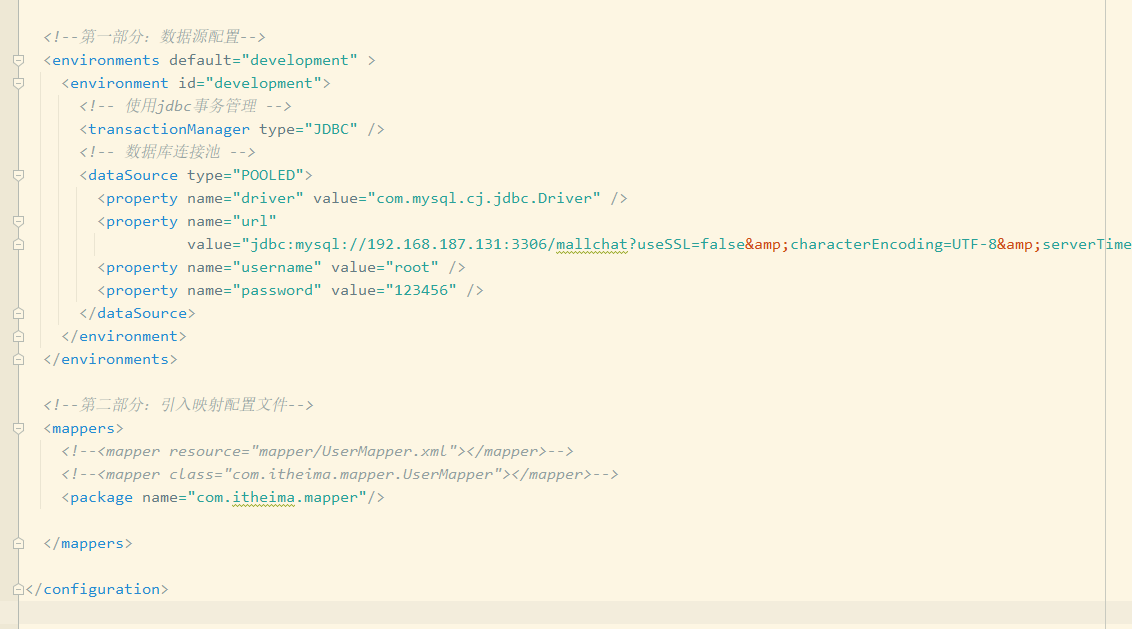
首先在测试代码中,可以看到我们的配置文件被加载进内存中,上图是我们的xml配置文件内容,可以看到里面由数据源的配置信息,mapper信息
2、构建SqlSessionFactory
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(resourceAsStream);
利用建造者模式(复杂对象的构建可以采用此模式)构建SqlSessionFactory,点击SqlSessionFactoryBuilder的build方法进入

这里面有3步:创建XMLConfigBuilder对象,调用该对象的parse()方法,调用SqlSessionFactoryBuilder类的build重载方法。我们来一步一步看。
(1)创建XMLConfigBuilder对象
无参构造,new了一个XPathParser(用于解析xml文件),并扔进重载方法
public XMLConfigBuilder(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties props) {
// XPathParser基于 Java XPath 解析器,用于解析 MyBatis中的配置文件
this(new XPathParser(inputStream, true, props, new XMLMapperEntityResolver()), environment, props);
}
//XPathParser将配置文件输入流解析成了Document对象
public XPathParser(InputStream inputStream, boolean validation, Properties variables, EntityResolver entityResolver) {
commonConstructor(validation, variables, entityResolver);
// 解析XML文档为Document对象
this.document = createDocument(new InputSource(inputStream));
}
进入重载方法
private XMLConfigBuilder(XPathParser parser, String environment, Properties props) {
// 创建Configuration对象,并通过TypeAliasRegistry注册一些Mybatis内部相关类的别名
super(new Configuration());
ErrorContext.instance().resource("SQL Mapper Configuration");
this.configuration.setVariables(props);
this.parsed = false;
this.environment = environment;
// paser就是上面无参方法扔进来的new的XPathParser
this.parser = parser;
}
//进入super方法,XMLConfigBuilder继承了BaseBuilder
public BaseBuilder(Configuration configuration) {
this.configuration = configuration;
//TypeAliasRegistry和TypeHandlerRegistry埋个坑
this.typeAliasRegistry = this.configuration.getTypeAliasRegistry();
this.typeHandlerRegistry = this.configuration.getTypeHandlerRegistry();
}
- 至此XMLConfigBuilder对象就有了一个配置文件的文档对象XPathParser(parser),便于后续解析赋值给全局配置对象Configuration,且初始化了一个空的Configuration对象
(2)重要—调用parse()方法
这是解析配置文件主入口
调用XMLConfigBuilder的parse()方法
public Configuration parse() {
// 如果该对象已经被解析过了,就抛出异常
if (parsed) {
throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once.");
}
parsed = true;
// parser.evalNode("/configuration"):通过XPATH解析器,解析configuration根节点
// 从configuration根节点开始解析,最终将解析出的内容封装到Configuration对象中
parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration"));
return configuration;
}
进入parseConfiguration方法,解析了配置文件中的各个标签属性赋值给空的Configuration对象
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) {
try {
// issue #117 read properties first
// 解析</properties>标签 赋值给Configuration的variables属性,该属性是Properties类
propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties"));
// 解析</settings>标签
Properties settings = settingsAsProperties(root.evalNode("settings"));
loadCustomVfs(settings);
loadCustomLogImpl(settings);
// 解析</typeAliases>标签
typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases"));
// 解析</plugins>标签
pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins"));
// 解析</objectFactory>标签
objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory"));
// 解析</objectWrapperFactory>标签
objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory"));
// 解析</reflectorFactory>标签
reflectorFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectorFactory"));
settingsElement(settings);
// read it after objectFactory and objectWrapperFactory issue #631
// 解析</environments>标签
environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments"));
// 解析</databaseIdProvider>标签
databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider"));
// 解析</typeHandlers>标签
typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers"));
// 解析</mappers>标签 加载映射文件流程主入口
mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
进入mapperElement()方法,这个方法就是把mapper接口以及它的代理对象存储到一个Map集合中,key为mapper接口类型,value为代理对象工厂
private void mapperElement(XNode parent) throws Exception {
if (parent != null) {
// 获取<mappers>标签的子标签
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {
// <package>子标签
if ("package".equals(child.getName())) {
// 获取mapper接口和mapper映射文件对应的package包名
String mapperPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name");
// 将包下所有的mapper接口以及它的代理工厂对象存储到一个Map集合中,key为mapper接口类型,value为代理对象工厂
configuration.addMappers(mapperPackage);
} else {// <mapper>子标签
// 获取<mapper>子标签的resource属性
String resource = child.getStringAttribute("resource");
// 获取<mapper>子标签的url属性
String url = child.getStringAttribute("url");
// 获取<mapper>子标签的class属性
String mapperClass = child.getStringAttribute("class");
// 它们是互斥的
if (resource != null && url == null && mapperClass == null) {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(resource);
try(InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource)) {
// 专门用来解析mapper映射文件
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, resource, configuration.getSqlFragments());
// 通过XMLMapperBuilder解析mapper映射文件
mapperParser.parse();
}
} else if (resource == null && url != null && mapperClass == null) {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(url);
try(InputStream inputStream = Resources.getUrlAsStream(url)){
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, url, configuration.getSqlFragments());
// 通过XMLMapperBuilder解析mapper映射文件
mapperParser.parse();
}
} else if (resource == null && url == null && mapperClass != null) {
Class<?> mapperInterface = Resources.classForName(mapperClass);
// 将指定mapper接口以及它的代理对象存储到一个Map集合中,key为mapper接口类型,value为代理对象工厂
configuration.addMapper(mapperInterface);
} else {
throw new BuilderException("A mapper element may only specify a url, resource or class, but not more than one.");
}
}
}
}
}
addMapper是上面一步方法中的核心
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {
if (type.isInterface()) {
// 如果Map集合中已经有该mapper接口的映射,就不需要再存储了
if (hasMapper(type)) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
boolean loadCompleted = false;
try {
// 将mapper接口以及它的代理对象存储到一个Map集合中,key为mapper接口类型,value为代理对象工厂
// knownMappers的类型:Map<Class<?>, MapperProxyFactory<?>> knownMappers
knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<>(type));
// It's important that the type is added before the parser is run
// otherwise the binding may automatically be attempted by the
// mapper parser. If the type is already known, it won't try.
// 用来解析注解方式的mapper接口
MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);
// 解析注解方式的mapper接口
parser.parse();
loadCompleted = true;
} finally {
if (!loadCompleted) {
knownMappers.remove(type);
}
}
}
}
MapperAnnotationBuilder#parse 解析mapper接口中方法成为MappedStatement对象
public void parse() {
// 获取mapper接口的全路径
String resource = type.toString();
// 是否解析过该mapper接口
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
// 先解析mapper映射文件
loadXmlResource();
// 设置解析标识
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
// Mapper构建者助手
assistant.setCurrentNamespace(type.getName());
// 解析CacheNamespace注解
parseCache();
// 解析CacheNamespaceRef注解
parseCacheRef();
Method[] methods = type.getMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
try {
// issue #237
if (!method.isBridge()) {
// 每个mapper接口中的方法,都解析成MappedStatement对象
parseStatement(method);
}
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
configuration.addIncompleteMethod(new MethodResolver(this, method));
}
}
}
//去检查所有的incompleteMethods,如果可以解析了.那就移除
parsePendingMethods();
}
<1> 读取mapper的xml文件中的sql为MappedStatement对象
MapperAnnotationBuilder#loadXmlResource
private void loadXmlResource() {
// Spring may not know the real resource name so we check a flag
// to prevent loading again a resource twice
// this flag is set at XMLMapperBuilder#bindMapperForNamespace
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded("namespace:" + type.getName())) {
String xmlResource = type.getName().replace('.', '/') + ".xml";
// #1347
InputStream inputStream = type.getResourceAsStream("/" + xmlResource);
if (inputStream == null) {
// Search XML mapper that is not in the module but in the classpath.
try {
inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(type.getClassLoader(), xmlResource);
} catch (IOException e2) {
// ignore, resource is not required
}
}
if (inputStream != null) {
XMLMapperBuilder xmlParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, assistant.getConfiguration(), xmlResource, configuration.getSqlFragments(), type.getName());
xmlParser.parse();
}
}
}
XMLMapperBuilder#parse
public void parse() {
// mapper映射文件是否已经加载过
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
// 从映射文件中的<mapper>根标签开始解析,直到完整的解析完毕
configurationElement(parser.evalNode("/mapper"));
// 标记已经解析
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
// 为命名空间绑定映射
bindMapperForNamespace();
}
// 解析ResultMap
parsePendingResultMaps();
// 解析缓存
parsePendingCacheRefs();
// 解析statement
parsePendingStatements();
}
XMLMapperBuilder#configurationElement,解析我们自己的Mapper.xml文件
private void configurationElement(XNode context) {
try {
// 获取<mapper>标签的namespace值,也就是命名空间
String namespace = context.getStringAttribute("namespace");
// 命名空间不能为空
if (namespace == null || namespace.isEmpty()) {
throw new BuilderException("Mapper's namespace cannot be empty");
}
// MapperBuilderAssistant:构建MappedStatement对象的构建助手,设置当前的命名空间为namespace的值
builderAssistant.setCurrentNamespace(namespace);
// 解析<cache-ref>子标签
cacheRefElement(context.evalNode("cache-ref"));
// 解析<cache>子标签
cacheElement(context.evalNode("cache"));
// 解析<parameterMap>子标签
parameterMapElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/parameterMap"));
// 解析<resultMap>子标签
resultMapElements(context.evalNodes("/mapper/resultMap"));
// 解析<sql>子标签,也就是SQL片段
sqlElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/sql"));
// 解析<select>\<insert>\<update>\<delete>子标签
buildStatementFromContext(context.evalNodes("select|insert|update|delete"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing Mapper XML. The XML location is '" + resource + "'. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
XMLMapperBuilder#buildStatementFromContext,用于解析MappedStatement
private void buildStatementFromContext(List<XNode> list, String requiredDatabaseId) {
for (XNode context : list) {
// MappedStatement解析器
final XMLStatementBuilder statementParser = new XMLStatementBuilder(configuration, builderAssistant, context, requiredDatabaseId);
try {
// // 解析select等4个标签,创建MappedStatement对象
statementParser.parseStatementNode();
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
configuration.addIncompleteStatement(statementParser);
}
}
}
XMLMapperBuilder#parseStatementNode,解析<insert><update><delete>子标签为MappedStatement对象
public void parseStatementNode() {
// 获取statement的id属性(特别关键的值)
String id = context.getStringAttribute("id");
String databaseId = context.getStringAttribute("databaseId");
if (!databaseIdMatchesCurrent(id, databaseId, this.requiredDatabaseId)) {
return;
}
String nodeName = context.getNode().getNodeName();
// 解析SQL命令类型是什么?确定操作是CRUD中的哪一种
SqlCommandType sqlCommandType = SqlCommandType.valueOf(nodeName.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH));
//是否查询语句
boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT;
boolean flushCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("flushCache", !isSelect);
boolean useCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("useCache", isSelect);
boolean resultOrdered = context.getBooleanAttribute("resultOrdered", false);
// Include Fragments before parsing
// <include>标签解析
XMLIncludeTransformer includeParser = new XMLIncludeTransformer(configuration, builderAssistant);
includeParser.applyIncludes(context.getNode());
// 获取入参类型
String parameterType = context.getStringAttribute("parameterType");
// 别名处理,获取入参对应的Java类型
Class<?> parameterTypeClass = resolveClass(parameterType);
String lang = context.getStringAttribute("lang");
LanguageDriver langDriver = getLanguageDriver(lang);
// Parse selectKey after includes and remove them.
// 解析<selectKey>标签
processSelectKeyNodes(id, parameterTypeClass, langDriver);
// Parse the SQL (pre: <selectKey> and <include> were parsed and removed)
KeyGenerator keyGenerator;
String keyStatementId = id + SelectKeyGenerator.SELECT_KEY_SUFFIX;
keyStatementId = builderAssistant.applyCurrentNamespace(keyStatementId, true);
if (configuration.hasKeyGenerator(keyStatementId)) {
keyGenerator = configuration.getKeyGenerator(keyStatementId);
} else {
keyGenerator = context.getBooleanAttribute("useGeneratedKeys",
configuration.isUseGeneratedKeys() && SqlCommandType.INSERT.equals(sqlCommandType))
? Jdbc3KeyGenerator.INSTANCE : NoKeyGenerator.INSTANCE;
}
// *******创建SqlSource,解析SQL,封装SQL语句(未参数绑定)和入参信息
// 问题:sql占位符如何进行的替换?动态sql如何进行的解析?
SqlSource sqlSource = langDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, context, parameterTypeClass);
// 设置默认StatementType为Prepared,该参数指定了后面的JDBC处理时,采用哪种Statement
StatementType statementType = StatementType.valueOf(context.getStringAttribute("statementType", StatementType.PREPARED.toString()));
Integer fetchSize = context.getIntAttribute("fetchSize");
Integer timeout = context.getIntAttribute("timeout");
String parameterMap = context.getStringAttribute("parameterMap");
// 获取结果映射类型
String resultType = context.getStringAttribute("resultType");
// 别名处理,获取返回值对应的Java类型
Class<?> resultTypeClass = resolveClass(resultType);
// 获取ResultMap
String resultMap = context.getStringAttribute("resultMap");
String resultSetType = context.getStringAttribute("resultSetType");
ResultSetType resultSetTypeEnum = resolveResultSetType(resultSetType);
if (resultSetTypeEnum == null) {
resultSetTypeEnum = configuration.getDefaultResultSetType();
}
String keyProperty = context.getStringAttribute("keyProperty");
String keyColumn = context.getStringAttribute("keyColumn");
String resultSets = context.getStringAttribute("resultSets");
// 通过构建者助手,创建MappedStatement对象
builderAssistant.addMappedStatement(id, sqlSource, statementType, sqlCommandType,
fetchSize, timeout, parameterMap, parameterTypeClass, resultMap, resultTypeClass,
resultSetTypeEnum, flushCache, useCache, resultOrdered,
keyGenerator, keyProperty, keyColumn, databaseId, langDriver, resultSets);
}
sql占位符替换和动态sql的解析流程
创建SqlSource,解析SQL,封装SQL语句(未参数绑定)和入参信息
1.XMLLanguageDriver#createSqlSource 解析SQL,封装SQL语句(未参数绑定)和入参信息进DynamicSqlSource或者StaticSqlSource(因为RawSqlSource的方法最终还是将sql信息封装到了StaticSqlSource中)
/**
* 解析select\insert\ update\delete标签中的SQL语句,最终将解析到的SqlNode封装到MixedSqlNode中的List集合中
* @return
*/
public SqlSource parseScriptNode() {
// ****将带有${}号的SQL信息封装到TextSqlNode
// ****将带有#{}号的SQL信息封装到StaticTextSqlNode
// ****将动态SQL标签中的SQL信息分别封装到不同的SqlNode中
MixedSqlNode rootSqlNode = parseDynamicTags(context);
SqlSource sqlSource;
// 如果SQL中包含${}和动态SQL语句,则将SqlNode封装到DynamicSqlSource
if (isDynamic) {
sqlSource = new DynamicSqlSource(configuration, rootSqlNode);
} else {
// 如果SQL中包含#{},则将SqlNode封装到RawSqlSource中,并指定parameterType
sqlSource = new RawSqlSource(configuration, rootSqlNode, parameterType);
}
return sqlSource;
}
2.XMLScriptBuilder#parseDynamicTags 将SQL信息分别封装到不同的SqlNode中
/**
* 解析select\insert\ update\delete标签中的SQL语句,最终将解析到的SqlNode封装到MixedSqlNode中的List集合中。
*
* - 将带有${}号的SQL信息封装到TextSqlNode;
* - 将带有#{}号的SQL信息封装到StaticTextSqlNode
* - 将动态SQL标签中的SQL信息分别封装到不同的SqlNode中
* @param node
* @return
*/
protected MixedSqlNode parseDynamicTags(XNode node) {
List<SqlNode> contents = new ArrayList<>();
//获取<select>\<insert>等4个标签的子节点,子节点包括元素节点和文本节点
NodeList children = node.getNode().getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < children.getLength(); i++) {
XNode child = node.newXNode(children.item(i));
// 处理文本节点
if (child.getNode().getNodeType() == Node.CDATA_SECTION_NODE || child.getNode().getNodeType() == Node.TEXT_NODE) {
String data = child.getStringBody("");
// 将文本内容封装到SqlNode中
TextSqlNode textSqlNode = new TextSqlNode(data);
// SQL语句中带有${}的话,就表示是dynamic的
if (textSqlNode.isDynamic()) {
contents.add(textSqlNode);
isDynamic = true;
} else {
// SQL语句中(除了${}和下面的动态SQL标签),就表示是static的
// StaticTextSqlNode的apply只是进行字符串的追加操作
contents.add(new StaticTextSqlNode(data));
}
//处理元素节点(就是sql语句中的动态标签,例如<if>,<where>,<choose>,<foreach>)
} else if (child.getNode().getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE) { // issue #628
String nodeName = child.getNode().getNodeName();
// 动态SQL标签处理器
NodeHandler handler = nodeHandlerMap.get(nodeName);
if (handler == null) {
throw new BuilderException("Unknown element <" + nodeName + "> in SQL statement.");
}
handler.handleNode(child, contents);
// 动态SQL标签是dynamic的
isDynamic = true;
}
}
return new MixedSqlNode(contents);
}
3.RawSqlSource#RawSqlSource构造方法 如果SQL中包含#{},则将SqlNode封装到StaticSqlSource中,并指定parameterType
public RawSqlSource(Configuration configuration, String sql, Class<?> parameterType) {
// 解析SQL语句
SqlSourceBuilder sqlSourceParser = new SqlSourceBuilder(configuration);
// 获取入参类型
Class<?> clazz = parameterType == null ? Object.class : parameterType;
// 开始解析
sqlSource = sqlSourceParser.parse(sql, clazz, new HashMap<>());
}
4.SqlSourceBuilder#parse 把原始sql中的#{id} 替换为 ?,也就是变成预编译语句,同时把#{}里面的内容即id信息存起来,由此StaticSqlSource存了预编译sql语句和 “?” 对应的参数内容及其类型,以及Configuration对象
public SqlSource parse(String originalSql, Class<?> parameterType, Map<String, Object> additionalParameters) {
//这个handler里面的ParameterMappings存储#{}里面的参数内容以及其参数类型
ParameterMappingTokenHandler handler = new ParameterMappingTokenHandler(configuration, parameterType, additionalParameters);
// 创建分词解析器
GenericTokenParser parser = new GenericTokenParser("#{", "}", handler);
String sql;
//ShrinkWhitespacesInSql表示是否从SQL中删除多余的空格字符。请注意,这也会影响SQL中的文字字符串。
if (configuration.isShrinkWhitespacesInSql()) {
sql = parser.parse(removeExtraWhitespaces(originalSql));
} else {
// 解析#{},并保存#{}里面的参数内容及其进handler里面的ParameterMappings
sql = parser.parse(originalSql);
}
// 将解析之后的SQL信息,封装到StaticSqlSource对象中
// SQL字符串是带有?号的字符串,?相关的参数信息,封装到ParameterMapping集合中
return new StaticSqlSource(configuration, sql, handler.getParameterMappings());
}
<2>读取mapper的接口文件中的注解式sql为MappedStatement对象
MapperAnnotationBuilder#parseStatement ,若mapper接口中的方法上有以注解方式写的sql,这个方法将会对这个注解解析成MappedStatement对象
void parseStatement(Method method) {
// 获取Mapper接口的形参类型
final Class<?> parameterTypeClass = getParameterType(method);
final LanguageDriver languageDriver = getLanguageDriver(method);
getAnnotationWrapper(method, true, statementAnnotationTypes).ifPresent(statementAnnotation -> {
final SqlSource sqlSource = buildSqlSource(statementAnnotation.getAnnotation(), parameterTypeClass, languageDriver, method);
final SqlCommandType sqlCommandType = statementAnnotation.getSqlCommandType();
final Options options = getAnnotationWrapper(method, false, Options.class).map(x -> (Options)x.getAnnotation()).orElse(null);
final String mappedStatementId = type.getName() + "." + method.getName();
final KeyGenerator keyGenerator;
String keyProperty = null;
String keyColumn = null;
if (SqlCommandType.INSERT.equals(sqlCommandType) || SqlCommandType.UPDATE.equals(sqlCommandType)) {
// first check for SelectKey annotation - that overrides everything else
SelectKey selectKey = getAnnotationWrapper(method, false, SelectKey.class).map(x -> (SelectKey)x.getAnnotation()).orElse(null);
if (selectKey != null) {
keyGenerator = handleSelectKeyAnnotation(selectKey, mappedStatementId, getParameterType(method), languageDriver);
keyProperty = selectKey.keyProperty();
} else if (options == null) {
keyGenerator = configuration.isUseGeneratedKeys() ? Jdbc3KeyGenerator.INSTANCE : NoKeyGenerator.INSTANCE;
} else {
keyGenerator = options.useGeneratedKeys() ? Jdbc3KeyGenerator.INSTANCE : NoKeyGenerator.INSTANCE;
keyProperty = options.keyProperty();
keyColumn = options.keyColumn();
}
} else {
keyGenerator = NoKeyGenerator.INSTANCE;
}
Integer fetchSize = null;
Integer timeout = null;
StatementType statementType = StatementType.PREPARED;
ResultSetType resultSetType = configuration.getDefaultResultSetType();
boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT;
boolean flushCache = !isSelect;
boolean useCache = isSelect;
if (options != null) {
if (FlushCachePolicy.TRUE.equals(options.flushCache())) {
flushCache = true;
} else if (FlushCachePolicy.FALSE.equals(options.flushCache())) {
flushCache = false;
}
useCache = options.useCache();
fetchSize = options.fetchSize() > -1 || options.fetchSize() == Integer.MIN_VALUE ? options.fetchSize() : null; //issue #348
timeout = options.timeout() > -1 ? options.timeout() : null;
statementType = options.statementType();
if (options.resultSetType() != ResultSetType.DEFAULT) {
resultSetType = options.resultSetType();
}
}
String resultMapId = null;
if (isSelect) {
ResultMap resultMapAnnotation = method.getAnnotation(ResultMap.class);
if (resultMapAnnotation != null) {
resultMapId = String.join(",", resultMapAnnotation.value());
} else {
resultMapId = generateResultMapName(method);
}
}
assistant.addMappedStatement(
mappedStatementId,
sqlSource,
statementType,
sqlCommandType,
fetchSize,
timeout,
// ParameterMapID
null,
parameterTypeClass,
resultMapId,
getReturnType(method),
resultSetType,
flushCache,
useCache,
// TODO gcode issue #577
false,
keyGenerator,
keyProperty,
keyColumn,
statementAnnotation.getDatabaseId(),
languageDriver,
// ResultSets
options != null ? nullOrEmpty(options.resultSets()) : null);
});
}
- 至此Configuration对象在xml文件中的配置信息封装完成
(3)调用build()重载方法
public SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config) {
return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config);
}
创建并返回一个默认SqlSessionFactory,且Configuration对象配置信息也被赋上去了
3、构建SqlSession,开启session
SqlSessionFactory有2个实现类DefaultSqlSessionFactory和SqlSessionManager,我们一般选DefaultSqlSessionFactory,这也是默认的
DefaultSqlSessionFactory#openSession
public SqlSession openSession() {
// 调用openSessionFromDataSource 参数1:执行器类型 参数2:事务隔离级别 参数三:指定事务是否自动提交
// 默认执行器类型是: protected ExecutorType defaultExecutorType = ExecutorType.SIMPLE;
return openSessionFromDataSource(configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(), null, false);
}
DefaultSqlSessionFactory#openSessionFromDataSource
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
// 从configuration对象中获取environment对象
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
// 获得事务工厂对象
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
// 构建事务对象
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
// 创建执行器对象
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
// 创建DefaultSqlSession对象
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close()
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
事务工厂有2个实现类JdbcTransactionFactory(其创建的事务对象JdbcTransaction有事务控制)和ManagedTransactionFactory(其创建的事务对象ManagedTransaction无事务控制),JdbcTransaction对事务的控制是对connection的提交和回滚来进行控制的
JdbcTransaction#commit&rollback
@Override
public void commit() throws SQLException {
if (connection != null && !connection.getAutoCommit()) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Committing JDBC Connection [" + connection + "]");
}
connection.commit();
}
}
@Override
public void rollback() throws SQLException {
if (connection != null && !connection.getAutoCommit()) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Rolling back JDBC Connection [" + connection + "]");
}
connection.rollback();
}
}
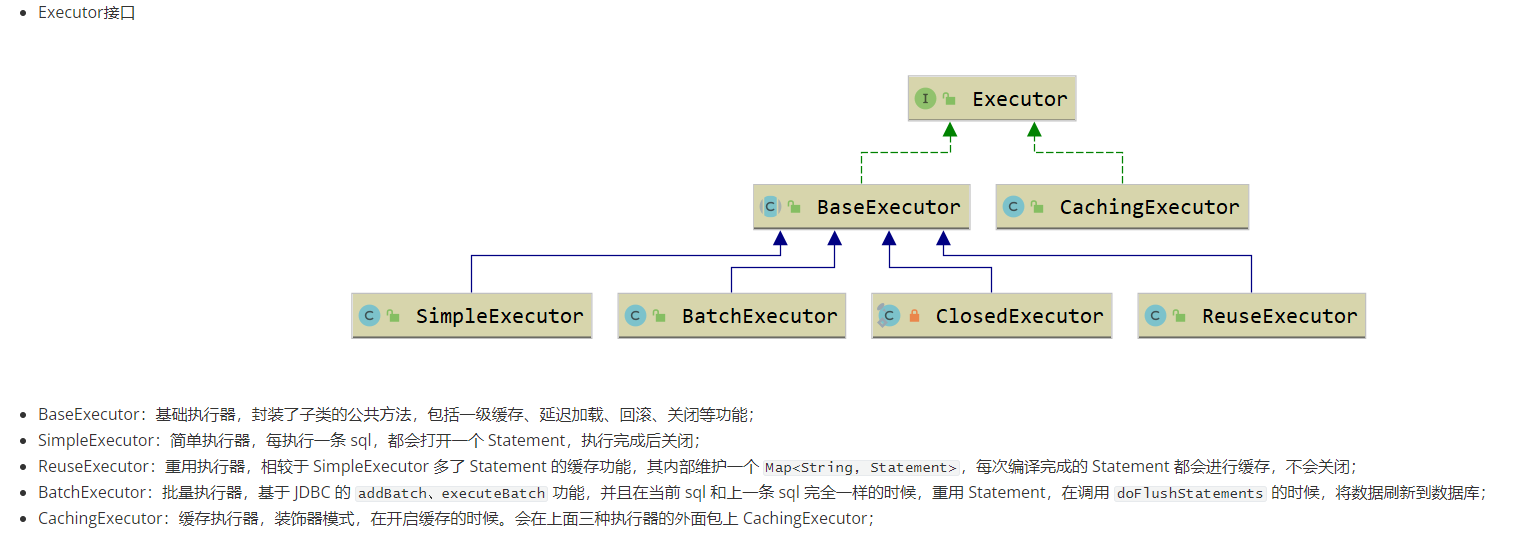
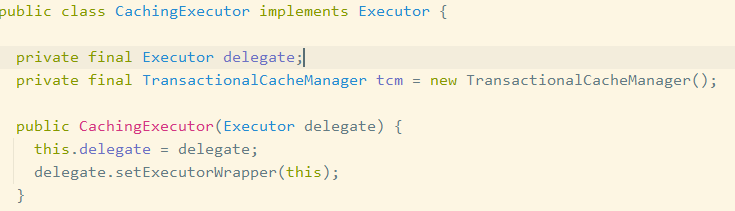
Configuration#newExecutor 创建执行器对象,CachingExecutor是的装饰类,delegate就是存放BaseExecutor三种实现类
另外注意到创建执行器对象时,还会被插件拦截处理,提供给用户的扩展点
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
// 如果允许缓存,会通过CachingExecutor 去代理一层
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
// 拦截器插件
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}
4、sqlSession执行语句流程

在测试代码中,操作SqlSession 的API 执行selectOne方法,最终委派到Executor来执行,这里是一个CachingExecutor,而CachingExecutor最终会委派到其包装的SimpleExecutor
DefaultSqlSession#selectList
private <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler handler) {
try {
// 根据传入的statementId,获取MappedStatement对象
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
// 调用执行器的查询方法
// wrapCollection(parameter)是用来装饰集合或者数组参数
return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, handler);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
CachingExecutor#query
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
// 获取绑定的SQL语句,比如 "SELECT * FROM user WHERE id = ? "
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
// 生成缓存Key
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, boundSql);
return query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
CachingExecutor#query重载方法 , 这里是先查二级缓存再查一级缓存再查数据库 。二级缓存是在MappedStatement中的,它是mapper级别(namespace界别)的,支持不同的Session共享缓存,一级缓存是在Executor中的localCache,类型是PerpetualCache,这是Session级别的,也就是一次查询中含有多个条件相同的查询;注意这里是把结果放到tcm(TransactionalCacheManager 事务缓存管理器)里面而不是真正的二级缓存,只有等事务提交后,二次缓存才真正保存进MappedStatement
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql)
throws SQLException {
// 获取二级缓存
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
if (cache != null) {
// 刷新二级缓存 (存在缓存且flushCache为true时)
/*(1)当为select语句时:
flushCache默认为false,表示任何时候语句被调用,都不会去清空本地缓存和二级缓存。
useCache默认为true,表示会将本条语句的结果进行二级缓存。
(2)当为insert、update、delete语句时:
flushCache默认为true,表示任何时候语句被调用,都会导致本地缓存和二级缓存被清空。
useCache属性在该情况下没有。
*/
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) {
// 和存储过程有关
ensureNoOutParams(ms, boundSql);
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
// 从二级缓存中查询数据
List<E> list = (List<E>) tcm.getObject(cache, key);
// 如果二级缓存中没有查询到数据,则查询一级缓存及数据库
if (list == null) {
// 委托给BaseExecutor执行
list = delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
// 将查询结果 要存到二级缓存中(注意:此处只是存到map集合中,没有真正存到二级缓存中)
tcm.putObject(cache, key, list); // issue #578 and #116
}
return list;
}
}
// 委托给BaseExecutor执行
return delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
来看看CachingExecutor中的TransactionalCacheManager所执行部分的方法
@Override
public void close(boolean forceRollback) {
try {
// issues #499, #524 and #573
if (forceRollback) {
tcm.rollback();
} else {
tcm.commit();
}
} finally {
delegate.close(forceRollback);
}
}
@Override
public void commit(boolean required) throws SQLException {
delegate.commit(required);
tcm.commit();
}
@Override
public void rollback(boolean required) throws SQLException {
try {
delegate.rollback(required);
} finally {
if (required) {
tcm.rollback();
}
}
}
BaseExecutor#query
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId());
// 如果该执行器已经关闭,则抛出异常
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
// 1. 如果配置了flushCacheRequired为true,则会在执行器执行之前就清空本地一级缓存
if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
// 1.1. 清空缓存
clearLocalCache();
}
List<E> list;
try {
// 2. 查询堆栈 + 1
queryStack++;
// 从一级缓存中获取数据
list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null;
if (list != null) {
// 3.1. 已有缓存结果,则处理本地缓存结果输出参数
handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);
} else {
// 3.2. 没有缓存结果,则从数据库查询结果
list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
} finally {
// 查询堆栈数 -1
queryStack--;
}
if (queryStack == 0) {
// 懒加载相关
for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) {
deferredLoad.load();
}
// issue #601
deferredLoads.clear();
if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) {
// issue #482
clearLocalCache();
}
}
return list;
}
BaseExecutor#queryFromDatabase
private <E> List<E> queryFromDatabase(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
List<E> list;
// 1. 首先向本地缓存中存入一个ExecutionPlaceholder的枚举类占位value
localCache.putObject(key, EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER);
try {
// 2. 执行doQuery方法
list = doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
} finally {
// 3. 执行完成移除这个key
localCache.removeObject(key);
}
// 4. 查询结果存入缓存中
localCache.putObject(key, list);
// 5. 如果MappedStatement的类型为CALLABLE,表明是存储过程,则向localOutputParameterCache缓存中存入value为parameter的缓存
if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) {
localOutputParameterCache.putObject(key, parameter);
}
return list;
}
SimpleExecutor#doQuery
public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
// 1. 获取配置实例
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
// 2. new一个StatementHandler实例
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
// 3. 准备处理器,主要包括创建statement以及动态参数的设置
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
// 4. 执行真正的数据库操作调用
return handler.query(stmt, resultHandler);
} finally {
// 5. 关闭statement
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
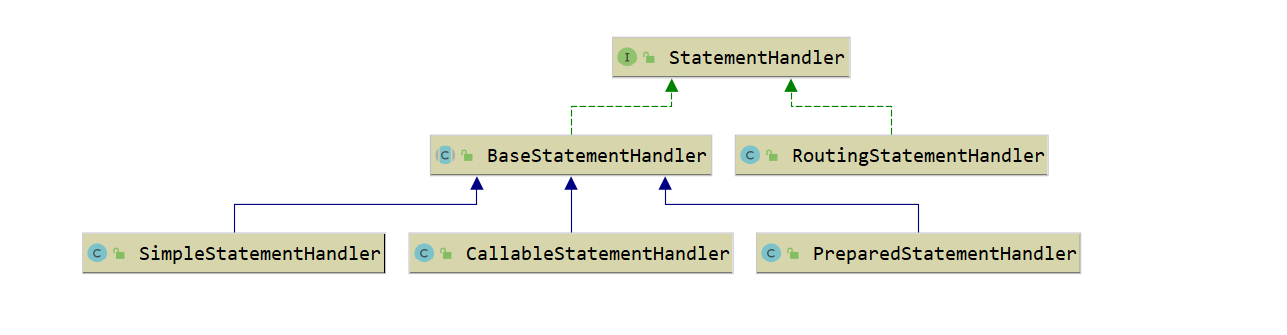
- BaseStatementHandler:基础语句处理器(抽象类),它基本把语句处理器接口的核心部分都实现了,包括配置绑定、执行器绑定、映射器绑定、参数处理器构建、结果集处理器构建、语句超时设置、语句关闭等,并另外定义了新的方法 instantiateStatement 供不同子类实现以便获取不同类型的语句连接,子类可以普通执行 SQL 语句,也可以做预编译执行,还可以执行存储过程等。
- SimpleStatementHandler:普通语句处理器,继承 BaseStatementHandler 抽象类,对应 java.sql.Statement 对象的处理,处理普通的不带动态参数运行的 SQL,即执行简单拼接的字符串语句,同时由于 Statement 的特性,SimpleStatementHandler 每次执行都需要编译 SQL (注意:我们知道 SQL 的执行是需要编译和解析的)。
- PreparedStatementHandler:预编译语句处理器,继承 BaseStatementHandler 抽象类,对应 java.sql.PrepareStatement 对象的处理,相比上面的普通语句处理器,它支持可变参数 SQL 执行,由于 PrepareStatement 的特性,它会进行预编译,在缓存中一旦发现有预编译的命令,会直接解析执行,所以减少了再次编译环节,能够有效提高系统性能,并预防 SQL 注入攻击(所以是系统默认也是我们推荐的语句处理器)。
- CallableStatementHandler:存储过程处理器,继承 BaseStatementHandler 抽象类,对应 java.sql.CallableStatement 对象的处理,很明了,它是用来调用存储过程的,增加了存储过程的函数调用以及输出/输入参数的处理支持。
- RoutingStatementHandler:路由语句处理器,直接实现了 StatementHandler 接口,作用如其名称,确确实实只是起到了路由功能,并把上面介绍到的三个语句处理器实例作为自身的委托对象而已,所以执行器在构建语句处理器时,都是直接 new 了 RoutingStatementHandler 实例。
Configuration#newStatementHandler
public StatementHandler newStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
// 创建路由功能的StatementHandler,根据MappedStatement中的StatementType
StatementHandler statementHandler = new RoutingStatementHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
// 插件机制:对核心对象进行拦截
statementHandler = (StatementHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(statementHandler);
return statementHandler;
}
SimpleExecutor#prepareStatement
private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt;
// 1. 获取连接,获取代理后(增加日志功能)的Connection对象
Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog);
// 2. 创建Statement对象(可能是一个SimpleStatement,一个PreparedStatement或CallableStatement)
stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout());
// 3. 参数化处理
handler.parameterize(stmt);
// 4. 返回执行前最后准备好的Statement对象
return stmt;
}
PreparedStatementHandler#parameterize 参数化处理
public void parameterize(Statement statement) throws SQLException {
parameterHandler.setParameters((PreparedStatement) statement);
}
DefaultParameterHandler#setParameters
public void setParameters(PreparedStatement ps) {
ErrorContext.instance().activity("setting parameters").object(mappedStatement.getParameterMap().getId());
// 1. 获取boundSql中的参数映射信息列表
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
if (parameterMappings != null) {
// 1.1. 遍历参数映射列表,这个列表信息就是我们xml文件中定义的某个查询语句的所有参数映射信息,注意这个List中的参数映射元素的顺序是和真实xml中sql的参数顺序对应的
for (int i = 0; i < parameterMappings.size(); i++) {
ParameterMapping parameterMapping = parameterMappings.get(i);
// 1.2. 只有入参类型才会设置PreparedStatement
if (parameterMapping.getMode() != ParameterMode.OUT) {
Object value;
// 取出参数名,这里比如说是'id'
String propertyName = parameterMapping.getProperty();
if (boundSql.hasAdditionalParameter(propertyName)) { // issue #448 ask first for additional params
value = boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(propertyName);
} else if (parameterObject == null) {
value = null;
} else if (typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(parameterObject.getClass())) {
value = parameterObject;
} else {
// 1.3. 这一步的工作就是从当前实际传入的参数中获取到指定key('id')的value值,比如是'15800000000'
MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(parameterObject);
value = metaObject.getValue(propertyName);
}
// 2. 获取该参数对应的typeHandler
TypeHandler typeHandler = parameterMapping.getTypeHandler();
// 2.1. 获取该参数对应的jdbcType
JdbcType jdbcType = parameterMapping.getJdbcType();
if (value == null && jdbcType == null) {
jdbcType = configuration.getJdbcTypeForNull();
}
try {
// 3. 重点是调用每个参数对应的typeHandler的setParameter方法为该ps设置正确的参数值
typeHandler.setParameter(ps, i + 1, value, jdbcType);
} catch (TypeException | SQLException e) {
throw new TypeException("Could not set parameters for mapping: " + parameterMapping + ". Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
}
}
}
执行真正query
RoutingStatementHandler#query
public <E> List<E> query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
return delegate.query(statement, resultHandler);
}
PreparedStatementHandler#query
public <E> List<E> query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
PreparedStatement ps = (PreparedStatement) statement;
ps.execute();
// 结果集处理
return resultSetHandler.handleResultSets(ps);
}
结果集处理流程
DefaultResultSetHandler#handleResultSets
public List<Object> handleResultSets(Statement stmt) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().activity("handling results").object(mappedStatement.getId());
//创建结果容器
final List<Object> multipleResults = new ArrayList<>();
int resultSetCount = 0;
// 这里是获取第一个结果集,将传统JDBC的ResultSet包装成一个包含结果列元信息的ResultSetWrapper对象
ResultSetWrapper rsw = getFirstResultSet(stmt);
// 这里是获取所有要映射的ResultMap(按照逗号分割出来的)
List<ResultMap> resultMaps = mappedStatement.getResultMaps();
// 要映射的ResultMap的数量
int resultMapCount = resultMaps.size();
validateResultMapsCount(rsw, resultMapCount);
// 循环处理每个ResultMap,从第一个开始处理
while (rsw != null && resultMapCount > resultSetCount) {
// 得到结果映射信息(取出第一个结果集)
ResultMap resultMap = resultMaps.get(resultSetCount);
/*
* 根据映射规则对结果集进行pojo转化(最后放入multipleResults结果集中)
*/
handleResultSet(rsw, resultMap, multipleResults, null);
// 处理下个结果集
rsw = getNextResultSet(stmt);
cleanUpAfterHandlingResultSet();
resultSetCount++;
}
// 对应<select>标签的resultSets属性,一般不使用该属性,忽略
String[] resultSets = mappedStatement.getResultSets();
if (resultSets != null) {
while (rsw != null && resultSetCount < resultSets.length) {
ResultMapping parentMapping = nextResultMaps.get(resultSets[resultSetCount]);
if (parentMapping != null) {
String nestedResultMapId = parentMapping.getNestedResultMapId();
ResultMap resultMap = configuration.getResultMap(nestedResultMapId);
handleResultSet(rsw, resultMap, null, parentMapping);
}
rsw = getNextResultSet(stmt);
cleanUpAfterHandlingResultSet();
resultSetCount++;
}
}
// 如果只有一个结果集合,则直接从多结果集中取出第一个
return collapseSingleResultList(multipleResults);
}
DefaultResultSetHandler#handleRowValues 处理行数据,其实就是完成结果映射
public void handleRowValues(ResultSetWrapper rsw, ResultMap resultMap, ResultHandler<?> resultHandler,
RowBounds rowBounds, ResultMapping parentMapping) throws SQLException {
// 是否有内置嵌套的结果映射
if (resultMap.hasNestedResultMaps()) {
ensureNoRowBounds();
checkResultHandler();
// 嵌套结果映射
handleRowValuesForNestedResultMap(rsw, resultMap, resultHandler, rowBounds, parentMapping);
} else {
// 简单结果映射
handleRowValuesForSimpleResultMap(rsw, resultMap, resultHandler, rowBounds, parentMapping);
}
}
DefaultResultSetHandler#handleRowValuesForSimpleResultMap 简单结果映射
private void handleRowValuesForSimpleResultMap(ResultSetWrapper rsw, ResultMap resultMap,
ResultHandler<?> resultHandler, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultMapping parentMapping) throws SQLException {
DefaultResultContext<Object> resultContext = new DefaultResultContext<>();
// 获取结果集信息
ResultSet resultSet = rsw.getResultSet();
// 使用rowBounds的分页信息,进行逻辑分页(也就是在内存中分页)
skipRows(resultSet, rowBounds);
while (shouldProcessMoreRows(resultContext, rowBounds) && !resultSet.isClosed() && resultSet.next()) {
// 通过<resultMap>标签的子标签<discriminator>对结果映射进行鉴别
ResultMap discriminatedResultMap = resolveDiscriminatedResultMap(resultSet, resultMap, null);
// 将查询结果封装到POJO中
Object rowValue = getRowValue(rsw, discriminatedResultMap, null);
// 处理对象嵌套的映射关系
storeObject(resultHandler, resultContext, rowValue, parentMapping, resultSet);
}
}
-
DefaultResultSetHandler#getRowValue 将查询结果封装到POJO中
private Object getRowValue(ResultSetWrapper rsw, ResultMap resultMap, String columnPrefix) throws SQLException { // 延迟加载的映射信息 final ResultLoaderMap lazyLoader = new ResultLoaderMap(); // 创建要映射的PO类对象 Object rowValue = createResultObject(rsw, resultMap, lazyLoader, columnPrefix); if (rowValue != null && !hasTypeHandlerForResultObject(rsw, resultMap.getType())) { final MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(rowValue); boolean foundValues = this.useConstructorMappings; // 是否应用自动映射,也就是通过resultType进行映射 if (shouldApplyAutomaticMappings(resultMap, false)) { // 根据columnName和type属性名映射赋值 foundValues = applyAutomaticMappings(rsw, resultMap, metaObject, columnPrefix) || foundValues; } // 根据我们配置ResultMap的column和property映射赋值 // 如果映射存在nestedQueryId,会调用getNestedQueryMappingValue方法获取返回值 foundValues = applyPropertyMappings(rsw, resultMap, metaObject, lazyLoader, columnPrefix) || foundValues; foundValues = lazyLoader.size() > 0 || foundValues; rowValue = foundValues || configuration.isReturnInstanceForEmptyRow() ? rowValue : null; } return rowValue; }
1.1 DefaultResultSetHandler#createResultObject 创建映射结果对象
private Object createResultObject(ResultSetWrapper rsw, ResultMap resultMap, ResultLoaderMap lazyLoader,
String columnPrefix) throws SQLException {
this.useConstructorMappings = false; // reset previous mapping result
final List<Class<?>> constructorArgTypes = new ArrayList<>();
final List<Object> constructorArgs = new ArrayList<>();
// 创建结果映射的PO类对象
Object resultObject = createResultObject(rsw, resultMap, constructorArgTypes, constructorArgs, columnPrefix);
if (resultObject != null && !hasTypeHandlerForResultObject(rsw, resultMap.getType())) {
// 获取要映射的PO类的属性信息
final List<ResultMapping> propertyMappings = resultMap.getPropertyResultMappings();
for (ResultMapping propertyMapping : propertyMappings) {
// issue gcode #109 && issue #149
// 延迟加载处理
if (propertyMapping.getNestedQueryId() != null && propertyMapping.isLazy()) {
// 通过动态代理工厂,创建延迟加载的代理对象
resultObject = configuration.getProxyFactory().createProxy(resultObject, lazyLoader, configuration,
objectFactory, constructorArgTypes, constructorArgs);
break;
}
}
}
this.useConstructorMappings = resultObject != null && !constructorArgTypes.isEmpty(); // set current mapping
// result
return resultObject;
}
private Object createResultObject(ResultSetWrapper rsw, ResultMap resultMap, List<Class<?>> constructorArgTypes,
List<Object> constructorArgs, String columnPrefix) throws SQLException {
final Class<?> resultType = resultMap.getType();
final MetaClass metaType = MetaClass.forClass(resultType, reflectorFactory);
final List<ResultMapping> constructorMappings = resultMap.getConstructorResultMappings();
if (hasTypeHandlerForResultObject(rsw, resultType)) {
return createPrimitiveResultObject(rsw, resultMap, columnPrefix);
} else if (!constructorMappings.isEmpty()) {
return createParameterizedResultObject(rsw, resultType, constructorMappings, constructorArgTypes,
constructorArgs, columnPrefix);
} else if (resultType.isInterface() || metaType.hasDefaultConstructor()) {
// 对象工厂创建对象
return objectFactory.create(resultType);
} else if (shouldApplyAutomaticMappings(resultMap, false)) {
return createByConstructorSignature(rsw, resultType, constructorArgTypes, constructorArgs, columnPrefix);
}
throw new ExecutorException("Do not know how to create an instance of " + resultType);
}
1.2 DefaultResultSetHandler#applyAutomaticMappings 根据columnName和type属性名映射赋值
private boolean applyAutomaticMappings(ResultSetWrapper rsw, ResultMap resultMap, MetaObject metaObject,
String columnPrefix) throws SQLException {
List<UnMappedColumnAutoMapping> autoMapping = createAutomaticMappings(rsw, resultMap, metaObject, columnPrefix);
boolean foundValues = false;
if (!autoMapping.isEmpty()) {
for (UnMappedColumnAutoMapping mapping : autoMapping) {
final Object value = mapping.typeHandler.getResult(rsw.getResultSet(), mapping.column);
if (value != null) {
foundValues = true;
}
if (value != null || (configuration.isCallSettersOnNulls() && !mapping.primitive)) {
// gcode issue #377, call setter on nulls (value is not 'found')
metaObject.setValue(mapping.property, value);
}
}
}
return foundValues;
}
1.3 DefaultResultSetHandler#applyPropertyMappings 根据我们配置ResultMap的column和property映射赋值,如果映射存在nestedQueryId,会调用getNestedQueryMappingValue方法获取返回值
private boolean applyPropertyMappings(ResultSetWrapper rsw, ResultMap resultMap, MetaObject metaObject,
ResultLoaderMap lazyLoader, String columnPrefix) throws SQLException {
final List<String> mappedColumnNames = rsw.getMappedColumnNames(resultMap, columnPrefix);
boolean foundValues = false;
final List<ResultMapping> propertyMappings = resultMap.getPropertyResultMappings();
for (ResultMapping propertyMapping : propertyMappings) {
String column = prependPrefix(propertyMapping.getColumn(), columnPrefix);
if (propertyMapping.getNestedResultMapId() != null) {
// the user added a column attribute to a nested result map, ignore it
column = null;
}
if (propertyMapping.isCompositeResult()
|| (column != null && mappedColumnNames.contains(column.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH)))
|| propertyMapping.getResultSet() != null) {
Object value = getPropertyMappingValue(rsw.getResultSet(), metaObject, propertyMapping, lazyLoader,
columnPrefix);
// issue #541 make property optional
final String property = propertyMapping.getProperty();
if (property == null) {
continue;
} else if (value == DEFERRED) {
foundValues = true;
continue;
}
if (value != null) {
foundValues = true;
}
if (value != null || (configuration.isCallSettersOnNulls()
&& !metaObject.getSetterType(property).isPrimitive())) {
// gcode issue #377, call setter on nulls (value is not 'found')
metaObject.setValue(property, value);
}
}
}
return foundValues;
}
总结:
执行sqlsession:参数有两个(statementId和参数对象)
- 根据statementId,去Configuration中的MappedStatement集合中查找 对应的MappedStatement对象;
- 取出MappedStatement中的SQL信息;
- 取出MappedStatement中的statementType,用来创建Statement对象;
- 取出MappedStatement中的Configuration对象,通过Configuration对象,获取DataSource对象,通过DataSource对象,创建Connection,通过Connection创建Statement对象。
- 设置参数
- 执行Statement
- 处理结果集
5、获取Mapper代理对象流程(其他)
入口:DefaultSqlSession#getMapper
从Configuration对象中,根据Mapper接口,获取Mapper代理对象
@Override
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type) {
// 从Configuration对象中,根据Mapper接口,获取Mapper代理对象
return configuration.<T>getMapper(type, this);
}
Configuration#getMapper
获取Mapper代理对象
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
return mapperRegistry.getMapper(type, sqlSession);
}
1. MapperRegistry#getMapper
通过代理对象工厂,获取代理对象:
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
// 根据Mapper接口的类型,从Map集合中获取Mapper代理对象工厂
final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
try {
// 通过MapperProxyFactory生产MapperProxy,通过MapperProxy产生Mapper代理对象
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
1.1 MapperProxyFactory#newInstance
调用JDK的动态代理方式,创建Mapper代理
//1
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
// 使用JDK动态代理方式,生成代理对象
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}
//2
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
// 根据Mapper接口的类型,从Map集合中获取Mapper代理对象工厂
final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
try {
// 通过MapperProxyFactory生产MapperProxy,通过MapperProxy产生Mapper代理对象
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
2.invoke方法
// 通过JDK动态代理生成并获取代理对象
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
// 代理对象对象调用方法,底层执行invoke方法
List<User> allUser = userMapper.findAllUser();
在动态代理返回了示例后,我们就可以直接调用mapper类中的方法了,但代理对象调用方法,执行是在MapperProxy中的invoke方法,该类实现InvocationHandler接口,并重写invoke()方法。
问题:invoke方法执行逻辑是什么?
入口:MapperProxy#invoke
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
// 如果是 Object 定义的方法,直接调用
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} else if (isDefaultMethod(method)) {
return invokeDefaultMethod(proxy, method, args);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
// 获得 MapperMethod 对象
final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
// 重点在这:MapperMethod最终调用了执行的方法
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
MapperMethod
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
//判断mapper中的方法类型,最终调用的还是SqlSession中的方法
switch (command.getType()) {
case INSERT: {
// 转换参数
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
// 执行 INSERT 操作
// 转换 rowCount
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case UPDATE: {
// 转换参数
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
// 转换 rowCount
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case DELETE: {
// 转换参数
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
// 转换 rowCount
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case SELECT:
// 无返回,并且有 ResultHandler 方法参数,则将查询的结果,提交给 ResultHandler 进行处理
if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {
executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
// 执行查询,返回列表
} else if (method.returnsMany()) {
result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
// 执行查询,返回 Map
} else if (method.returnsMap()) {
result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
// 执行查询,返回 Cursor
} else if (method.returnsCursor()) {
result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);
// 执行查询,返回单个对象
} else {
// 转换参数
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
// 查询单条
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
if (method.returnsOptional() &&
(result == null || !method.getReturnType().equals(result.getClass()))) {
result = Optional.ofNullable(result);
}
}
break;
case FLUSH:
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
break;
default:
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
// 返回结果为 null ,并且返回类型为基本类型,则抛出 BindingException 异常
if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()
+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");
}
// 返回结果
return result;
}
四、插件机制
- 问题:什么是Mybatis插件?有什么作用?
一般开源框架都会提供扩展点,让开发者自行扩展,从而完成逻辑的增强。
基于插件机制可以实现了很多有用的功能,比如说分页,字段加密,监控等功能,这种通用的功能,就如同AOP一样,横切在数据操作上
而通过Mybatis插件可以实现对框架的扩展,来实现自定义功能,并且对于用户是无感知的。
4.2 Mybatis插件介绍
Mybatis插件本质上来说就是一个拦截器,它体现了JDK动态代理和责任链设计模式的综合运用
Mybatis中针对四大组件提供了扩展机制,这四个组件分别是:
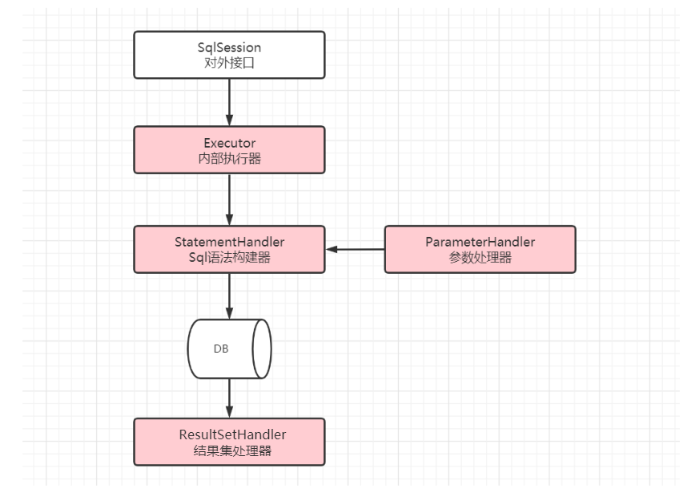
Mybatis中所允许拦截的方法如下:
- Executor 【SQL执行器】【update,query,commit,rollback】
- StatementHandler 【Sql语法构建器对象】【prepare,parameterize,batch,update,query等】
- ParameterHandler 【参数处理器】【getParameterObject,setParameters等】
- ResultSetHandler 【结果集处理器】【handleResultSets,handleOuputParameters等】
能干什么?
- 分页功能:mybatis的分页默认是基于内存分页的(查出所有,再截取),数据量大的情况下效率较低,不过使用mybatis插件可以改变该行为,只需要拦截StatementHandler类的prepare方法,改变要执行的SQL语句为分页语句即可
- 性能监控:对于SQL语句执行的性能监控,可以通过拦截Executor类的update, query等方法,用日志记录每个方法执行的时间
如何自定义插件?
在使用之前,我们先来看看Mybatis提供的插件相关的类,过一遍它们分别提供了哪些功能,最后我们自己定义一个插件
用于定义插件的类
前面已经知道Mybatis插件是可以对Mybatis中四大组件对象的方法进行拦截,那拦截器拦截哪个类的哪个方法如何知道,就由下面这个注解提供拦截信息
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
public @interface Intercepts {
Signature[] value();
}
由于一个拦截器可以同时拦截多个对象的多个方法,所以就使用了Signture数组,该注解定义了拦截的完整信息
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({})
public @interface Signature {
// 拦截的类
Class<?> type();
// 拦截的方法
String method();
// 拦截方法的参数
Class<?>[] args();
}
已经知道了该拦截哪些对象的哪些方法,拦截后要干什么就需要实现Intercetor#intercept方法,在这个方法里面实现拦截后的处理逻辑
public interface Interceptor {
/**
* 真正方法被拦截执行的逻辑
*
* @param invocation 主要目的是将多个参数进行封装
*/
Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable;
// 生成目标对象的代理对象
default Object plugin(Object target) {
return Plugin.wrap(target, this);
}
// 可以拦截器设置一些属性
default void setProperties(Properties properties) {
// NOP
}
}
4.3 自定义插件
需求:把Mybatis所有执行的sql都记录下来
步骤:① 创建Interceptor的实现类,重写方法
② 使用@Intercepts注解完成插件签名 说明插件的拦截四大对象之一的哪一个对象的哪一个方法
③ 将写好的插件注册到全局配置文件中
①.创建Interceptor的实现类
public class MyPlugin implements Interceptor {
private final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
// //这里是每次执行操作的时候,都会进行这个拦截器的方法内
Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
//增强逻辑
StatementHandler statementHandler = (StatementHandler) invocation.getTarget();
BoundSql boundSql = statementHandler.getBoundSql();
String sql = boundSql.getSql();
logger.info("mybatis intercept sql:{}", sql);
return invocation.proceed(); //执行原方法
}
/**
*
* ^Description包装目标对象 为目标对象创建代理对象
* @Param target为要拦截的对象
* @Return代理对象
*/
Override
public Object plugin(Object target) {
System.out.println("将要包装的目标对象:"+target);
return Plugin.wrap(target,this);
}
/**获取配置文件的属性**/
//插件初始化的时候调用,也只调用一次,插件配置的属性从这里设置进来
Override
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
System.out.println("插件配置的初始化参数:"+properties );
}
}
② 使用@Intercepts注解完成插件签名 说明插件的拦截四大对象之一的哪一个对象的哪一个方法
@Intercepts({ @Signature(type = StatementHandler.class,
method = "prepare",
args = { Connection.class, Integer.class}) })
public class SQLStatsInterceptor implements Interceptor {
③ 将写好的插件注册到全局配置文件中
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<plugins>
<plugin interceptor="com.itheima.interceptor.MyPlugin">
<property name="dialect" value="mysql" />
</plugin>
</plugins>
</configuration>
核心思想:
就是使用JDK动态代理的方式,对这四个对象进行包装增强。具体的做法是,创建一个类实现Mybatis的拦截器接口,并且加入到拦截器链中,在创建核心对象的时候,不直接返回,而是遍历拦截器链,把每一个拦截器都作用于核心对象中。这么一来,Mybatis创建的核心对象其实都是代理对象,都是被包装过的。
4.4 源码分析-插件
- 插件的初始化:插件对象是如何实例化的? 插件的实例对象如何添加到拦截器链中的? 组件对象的代理对象是如何产生的?
- 拦截逻辑的执行
插件配置信息的加载
我们定义好了一个拦截器,那我们怎么告诉Mybatis呢?Mybatis所有的配置都定义在XXx.xml配置文件中
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<plugins>
<plugin interceptor="com.itheima.interceptor.MyPlugin">
<property name="dialect" value="mysql" />
</plugin>
</plugins>
</configuration>
对应的解析代码如下(XMLConfigBuilder#pluginElement):
private void pluginElement(XNode parent) throws Exception {
if (parent != null) {
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {
// 获取拦截器
String interceptor = child.getStringAttribute("interceptor");
// 获取配置的Properties属性
Properties properties = child.getChildrenAsProperties();
// 根据配置文件中配置的插件类的全限定名 进行反射初始化
Interceptor interceptorInstance = (Interceptor) resolveClass(interceptor).getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();
// 将属性添加到Intercepetor对象
interceptorInstance.setProperties(properties);
// 添加到配置类的InterceptorChain属性,InterceptorChain类维护了一个List<Interceptor>
configuration.addInterceptor(interceptorInstance);
}
}
}
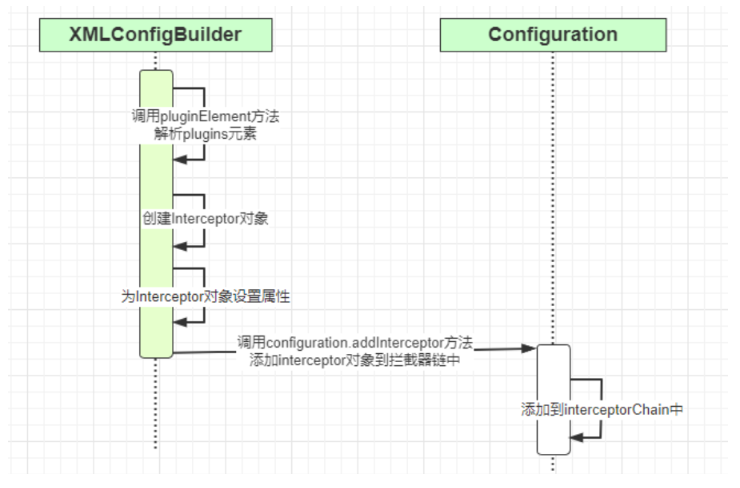
主要做了以下工作:
- 遍历解析plugins标签下每个plugin标签
- 根据解析的类信息创建Interceptor对象
- 调用setProperties方法设置属性
- 将拦截器添加到Configuration类的IntercrptorChain拦截器链中
对应时序图如下:
代理对象的生成
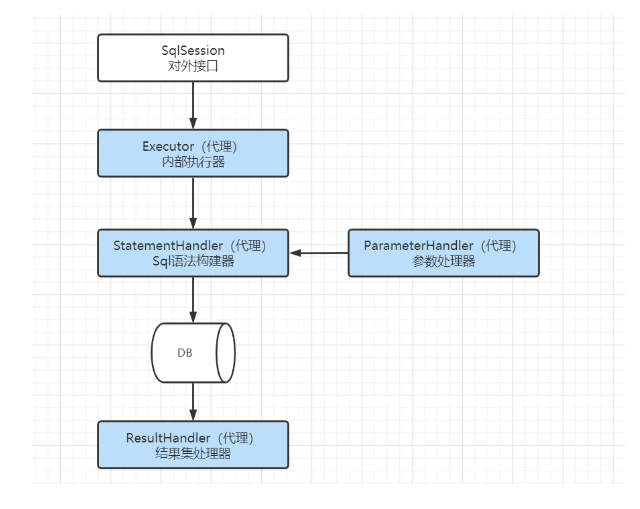
Executor代理对象(Configuration#newExecutor)
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
// 生成Executor代理对象逻辑
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}
ParameterHandler代理对象(Configuration#newParameterHandler)
public ParameterHandler newParameterHandler(MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, BoundSql boundSql) {
ParameterHandler parameterHandler = mappedStatement.getLang().createParameterHandler(mappedStatement, parameterObject, boundSql);
// 生成ParameterHandler代理对象逻辑
parameterHandler = (ParameterHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(parameterHandler);
return parameterHandler;
}
ResultSetHandler代理对象(Configuration#newResultSetHandler)
public ResultSetHandler newResultSetHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, RowBounds rowBounds, ParameterHandler parameterHandler,
ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
ResultSetHandler resultSetHandler = new DefaultResultSetHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterHandler, resultHandler, boundSql, rowBounds);
// 生成ResultSetHandler代理对象逻辑
resultSetHandler = (ResultSetHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(resultSetHandler);
return resultSetHandler;
}
StatementHandler代理对象(Configuration#newStatementHandler)
public StatementHandler newStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
StatementHandler statementHandler = new RoutingStatementHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
// 生成StatementHandler代理对象逻辑
statementHandler = (StatementHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(statementHandler);
return statementHandler;
}
通过查看源码会发现,所有代理对象的生成都是通过InterceptorChain#pluginAll方法来创建的,进一步查看pluginAll方法
public Object pluginAll(Object target) {
for (Interceptor interceptor : interceptors) {
target = interceptor.plugin(target);
}
return target;
}
InterceptorChain#pluginAll内部通过遍历Interceptor#plugin方法来创建代理对象,并将生成的代理对象又赋值给target,如果存在多个拦截器的话,生成的代理对象会被另一个代理对象所代理,从而形成一个代理链,执行的时候,依次执行所有拦截器的拦截逻辑代码,我们再跟进去
default Object plugin(Object target) {
return Plugin.wrap(target, this);
}
Interceptor#plugin方法最终将目标对象和当前的拦截器交给Plugin.wrap方法来创建代理对象。该方法是默认方法,是Mybatis框架提供的一个典型plugin方法的实现。让我们看看在Plugin#wrap方法中是如何实现代理对象的
public static Object wrap(Object target, Interceptor interceptor) {
// 1.解析该拦截器所拦截的所有接口及对应拦截接口的方法
Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap = getSignatureMap(interceptor);
Class<?> type = target.getClass();
// 2.获取目标对象实现的所有被拦截的接口
Class<?>[] interfaces = getAllInterfaces(type, signatureMap);
// 3.目标对象有实现被拦截的接口,生成代理对象并返回
if (interfaces.length > 0) {
// 通过JDK动态代理的方式实现
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(
type.getClassLoader(),
interfaces,
new Plugin(target, interceptor, signatureMap));
}
// 目标对象没有实现被拦截的接口,直接返回原对象
return target;
}
最终我们看到其实是通过JDK提供的Proxy.newProxyInstance方法来生成代理对象
以上代理对象生成过程的时序图如下:

拦截逻辑的执行
通过上面的分析,我们知道Mybatis框架中执行Executor、ParameterHandler、ResultSetHandler和StatementHandler中的方法时真正执行的是代理对象对应的方法。而且该代理对象是通过JDK动态代理生成的,所以执行方法时实际上是调用InvocationHandler#invoke方法(Plugin类实现InvocationHandler接口),下面是Plugin#invoke方法
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
Set<Method> methods = signatureMap.get(method.getDeclaringClass());
if (methods != null && methods.contains(method)) {
return interceptor.intercept(new Invocation(target, method, args));
}
return method.invoke(target, args);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(e);
}
}
注:一个对象被代理很多次
问题:同一个组件对象的同一个方法是否可以被多个拦截器进行拦截?
答案是肯定的,所以我们配置在最前面的拦截器最先被代理,但是执行的时候却是最外层的先执行。
具体点:
假如依次定义了三个插件:插件1,插件2 和 插件3。
那么List中就会按顺序存储:插件1,插件2 和 插件3。
而解析的时候是遍历list,所以解析的时候也是按照:插件1,插件2,插件3的顺序。
但是执行的时候就要反过来了,执行的时候是按照:插件3,插件2和插件1的顺序进行执行。
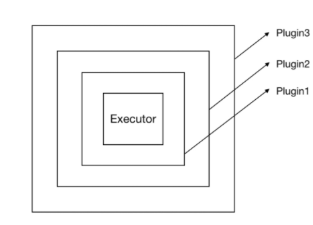
当 Executor 的某个方法被调用的时候,插件逻辑会先行执行。执行顺序由外而内,比如上图的执行顺序为 plugin3 → plugin2 → Plugin1 → Executor。
方法是默认方法,是Mybatis框架提供的一个典型plugin方法的实现。让我们看看在Plugin#wrap方法中是如何实现代理对象的
public static Object wrap(Object target, Interceptor interceptor) {
// 1.解析该拦截器所拦截的所有接口及对应拦截接口的方法
Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap = getSignatureMap(interceptor);
Class<?> type = target.getClass();
// 2.获取目标对象实现的所有被拦截的接口
Class<?>[] interfaces = getAllInterfaces(type, signatureMap);
// 3.目标对象有实现被拦截的接口,生成代理对象并返回
if (interfaces.length > 0) {
// 通过JDK动态代理的方式实现
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(
type.getClassLoader(),
interfaces,
new Plugin(target, interceptor, signatureMap));
}
// 目标对象没有实现被拦截的接口,直接返回原对象
return target;
}
最终我们看到其实是通过JDK提供的Proxy.newProxyInstance方法来生成代理对象
以上代理对象生成过程的时序图如下:

拦截逻辑的执行
通过上面的分析,我们知道Mybatis框架中执行Executor、ParameterHandler、ResultSetHandler和StatementHandler中的方法时真正执行的是代理对象对应的方法。而且该代理对象是通过JDK动态代理生成的,所以执行方法时实际上是调用InvocationHandler#invoke方法(Plugin类实现InvocationHandler接口),下面是Plugin#invoke方法
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
Set<Method> methods = signatureMap.get(method.getDeclaringClass());
if (methods != null && methods.contains(method)) {
return interceptor.intercept(new Invocation(target, method, args));
}
return method.invoke(target, args);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(e);
}
}
注:一个对象被代理很多次
问题:同一个组件对象的同一个方法是否可以被多个拦截器进行拦截?
答案是肯定的,所以我们配置在最前面的拦截器最先被代理,但是执行的时候却是最外层的先执行。
具体点:
假如依次定义了三个插件:插件1,插件2 和 插件3。
那么List中就会按顺序存储:插件1,插件2 和 插件3。
而解析的时候是遍历list,所以解析的时候也是按照:插件1,插件2,插件3的顺序。
但是执行的时候就要反过来了,执行的时候是按照:插件3,插件2和插件1的顺序进行执行。
[外链图片转存中…(img-zi97hQXZ-1704892805635)]
当 Executor 的某个方法被调用的时候,插件逻辑会先行执行。执行顺序由外而内,比如上图的执行顺序为 plugin3 → plugin2 → Plugin1 → Executor。





















 599
599











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








