问题及代码:
例一:
/*
*Copyright (c) 2015,烟台大学计算机学院
*All rights reserved.
*文件名称:test.cpp
*作者:吴胜男
*完成日期:2015年06月05日
*版本号:v1.0
*
*问题描述:1、阅读并运行下面的示例程序,掌握标准输入输出流的控制
*输入描述:略
*程序输出:略
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <math.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
float a,b,c,disc;
cout<<"please input a,b,c:";
cin>>a>>b>>c;
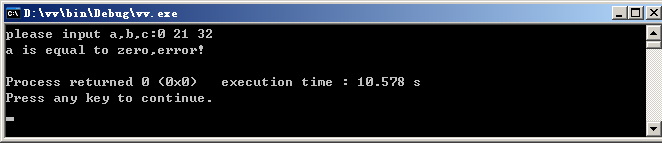
if (a==0)
cerr<<"a is equal to zero,error!"<<endl;
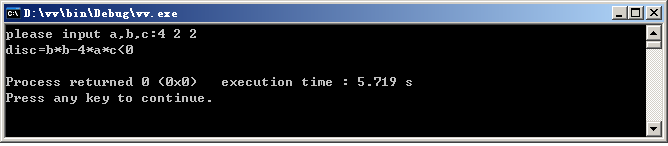
else if ((disc=b*b-4*a*c)<0)
cerr<<"disc=b*b-4*a*c<0"<<endl;
else
{
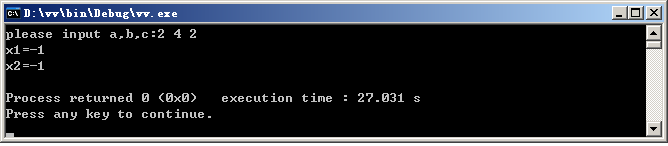
cout<<"x1="<<(-b+sqrt(disc))/(2*a)<<endl;
cout<<"x2="<<(-b-sqrt(disc))/(2*a)<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
运行结果:
例二:
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a;
cout<<"input a:";
cin>>a;
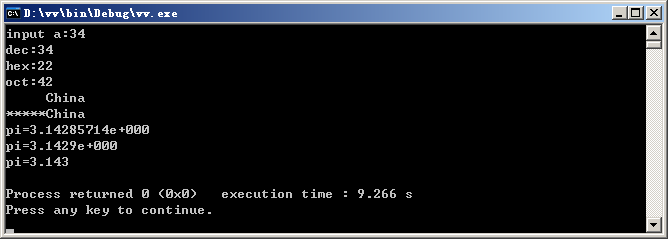
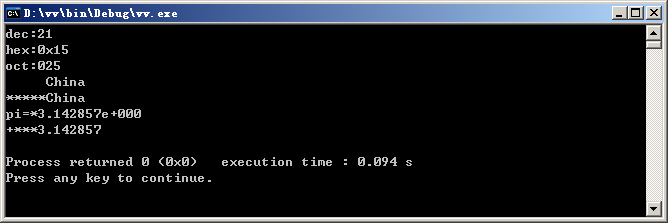
cout<<"dec:"<<dec<<a<<endl;
cout<<"hex:"<<hex<<a<<endl;
cout<<"oct:"<<setbase(8)<<a<<endl;
char *pt="China";
cout<<setw(10)<<pt<<endl;
cout<<setfill('*')<<setw(10)<<pt<<endl;
double pi=22.0/7.0;
cout<<setiosflags(ios::scientific)<<setprecision(8);
cout<<"pi="<<pi<<endl;
cout<<"pi="<<setprecision(4)<<pi<<endl;
cout<<"pi="<<setiosflags(ios::fixed)<<pi<<endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:
例三:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a=21;
cout.setf(ios::showbase);
cout<<"dec:"<<a<<endl;
cout.unsetf(ios::dec);
cout.setf(ios::hex);
cout<<"hex:"<<a<<endl;
cout.unsetf(ios::hex);
cout.setf(ios::oct);
cout<<"oct:"<<a<<endl;
char *pt="China";
cout.width(10);
cout<<pt<<endl;
cout.width(10);
cout.fill('*');
cout<<pt<<endl;
double pi=22.0/7.0;
cout.setf(ios::scientific);
cout<<"pi=";
cout.width(14);
cout<<pi<<endl;
cout.unsetf(ios::scientific);
cout.setf(ios::fixed);
cout.width(12);
cout.setf(ios::showpos);
cout.setf(ios::internal);
cout.precision(6);
cout<<pi<<endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:
例4-1:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main( )
{
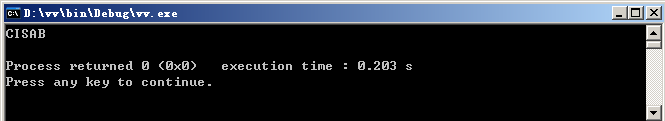
char *a="BASIC"; //字符指针指向'B'
for(int i=4; i>=0; i--)
cout.put(*(a+i)); //从最后一个字符开始输出
cout.put('\n');
return 0;
}
运行结果:
例4-2:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
int main()
{
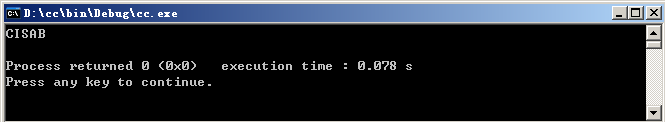
char *a="BASIC";
for(int i=4; i>=0; i--)
putchar(*(a+i));
putchar('\n');
return 0;
}
运行结果:
例五:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main( )
{
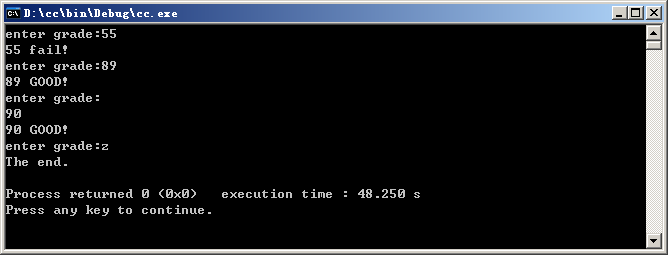
float grade;
cout<<"enter grade:";
while(cin>>grade) //能从cin流读取数据
{
if(grade>=85)
cout<<grade<<" GOOD!"<<endl;
if(grade<60)
cout<<grade<<" fail!"<<endl;
cout<<"enter grade:";
}
cout<<"The end."<<endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:
例六:(1)不带参数的get函数
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
int main( )
{
int c;
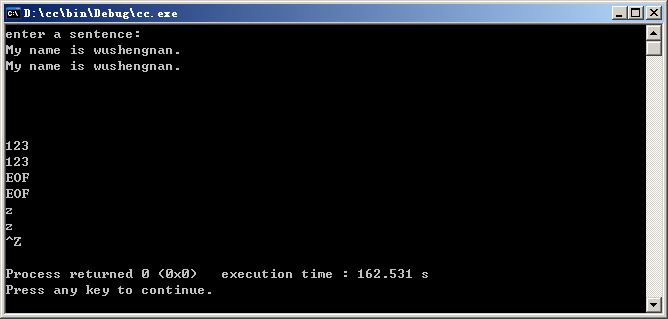
cout<<"enter a sentence:"<<endl;
while((c=cin.get())!=EOF)
cout.put(c);
return 0;
}
运行结果:
总结:EOF是指的文件结束,可以是ctrl +z。
例六:(2) 有一个参数的get函数#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
int main( )
{
char c;
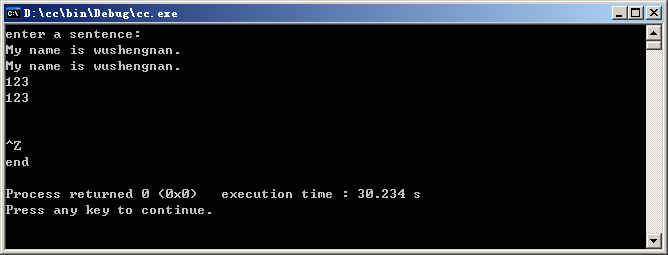
cout<<"enter a sentence:"<<endl;
while(cin.get(c)) //读取一个字符赋给字符变量c,如果读取成功,cin.get(c)为真
cout.put(c);
cout<<"end"<<endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:
例六:(3)有3个参数的get函数
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main( )
{
char ch[20];
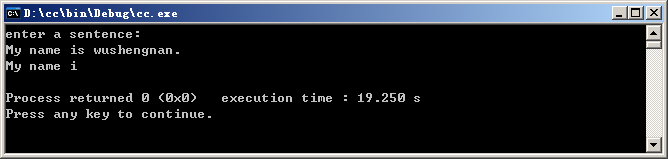
cout<<"enter a sentence:"<<endl;
cin.get(ch,10,'\n');//指定换行符为终止字符
cout<<ch<<endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:
总结:读取九个字符。
例七:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main( )
{
char ch[20];
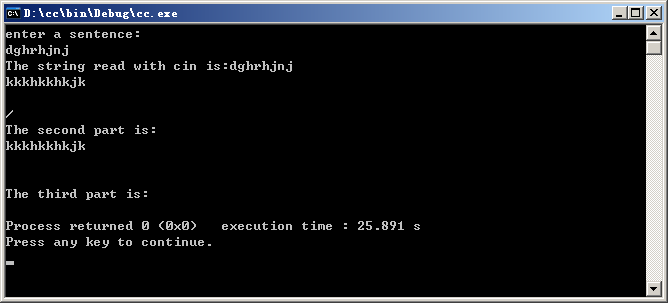
cout<<"enter a sentence:"<<endl;
cin>>ch;
cout<<"The string read with cin is:"<<ch<<endl;
cin.getline(ch,20,'/');//读19个字符或遇'/'结束
cout<<"The second part is:"<<ch<<endl;
cin.getline(ch,20); //读19个字符或遇'/n'结束
cout<<"The third part is:"<<ch<<endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:






















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








