ServiceManager管理着系统中的所有服务,服务在启动的时候会注册到ServiceManager,其他进程要使用相应服务时需要先去ServiceManager中寻找,然后使用。
ServiceManager本身运行在一个单独的进程service_manager
api 23版本的源码分析:
bindService(intent, connection, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
ContextWrapper#bindService()
ContextImpl#bindService()
ContextImpl#bindServiceCommon()
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().bindService
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault() 返回的是一个Proxy对象,因此就相当于 Proxy.bindService
IActivityManager(继承IInterface接口), IActivityManager就相当于我们自定义的 IMyAidl 接口
ActivityManagerNative 就是 Stub类,只是命名为具体的名字ActivityManagerNative
ActivityManagerProxy 就是 Proxy类,是 ActivityManagerNative 的内部类
ActivityManagerNative#ActivityManagerProxy#bindService:
public int bindService(IApplicationThread caller, IBinder token,
Intent service, String resolvedType, IServiceConnection connection,
int flags, String callingPackage, int userId) throws RemoteException {
Parcel data = Parcel.obtain();
Parcel reply = Parcel.obtain();
data.writeInterfaceToken(IActivityManager.descriptor);
data.writeStrongBinder(caller != null ? caller.asBinder() : null);
data.writeStrongBinder(token);
service.writeToParcel(data, 0);
data.writeString(resolvedType);
data.writeStrongBinder(connection.asBinder());
data.writeInt(flags);
data.writeString(callingPackage);
data.writeInt(userId);
mRemote.transact(BIND_SERVICE_TRANSACTION, data, reply, 0);
reply.readException();
int res = reply.readInt();
data.recycle();
reply.recycle();
return res;
}
里面会调用mRemote.transact方法,然后经过Binder驱动后到达服务端的ActivityManagerNative对象的onTransact方法:
//ActivityManagerNative.java
@Override
public boolean onTransact(int code, Parcel data, Parcel reply, int flags)
throws RemoteException {
switch (code) {
...
case BIND_SERVICE_TRANSACTION: {
data.enforceInterface(IActivityManager.descriptor);
IBinder b = data.readStrongBinder();
IApplicationThread app = ApplicationThreadNative.asInterface(b);
IBinder token = data.readStrongBinder();
Intent service = Intent.CREATOR.createFromParcel(data);
String resolvedType = data.readString();
b = data.readStrongBinder();
int fl = data.readInt();
String callingPackage = data.readString();
int userId = data.readInt();
IServiceConnection conn = IServiceConnection.Stub.asInterface(b);
int res = bindService(app, token, service, resolvedType, conn, fl,
callingPackage, userId);
reply.writeNoException();
reply.writeInt(res);
return true;
}
...
}
会调用bindService(app, token, service, resolvedType, conn, fl, callingPackage, userId);
这个bindService方法就是ActivityManagerService中的bindService方法,因为ActivityManagerService是继承ActivityManagerNative的:
public final class ActivityManagerService extends ActivityManagerNative
implements Watchdog.Monitor, BatteryStatsImpl.BatteryCallback {
}
ActivityManagerService#bindService:
//ActivityManagerService.java
public int bindService(IApplicationThread caller, IBinder token, Intent service,
String resolvedType, IServiceConnection connection, int flags, String callingPackage,
int userId) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
enforceNotIsolatedCaller("bindService");
// Refuse possible leaked file descriptors
if (service != null && service.hasFileDescriptors() == true) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("File descriptors passed in Intent");
}
if (callingPackage == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("callingPackage cannot be null");
}
synchronized(this) {
return mServices.bindServiceLocked(caller, token, service,
resolvedType, connection, flags, callingPackage, userId);
}
}
会调用ActiveServices的bindServiceLocked()方法,
ActiveServices#bindServiceLocked()这个方法分两种情况:
情况1. ActiveServices#bringUpServiceLocked()
情况2. ActiveServices#requestServiceBindingLocked(s, b.intent, callerFg, true);
为什么分为两种情况,涉及到 A进程访问B进程时的几种状态:
-
进程B没有启动,即整个B进程都没有启动
-
进程B启动了,但是里面的Service没创建出来
-
进程B启动了,里面的Service也创建了,但是Service没有被绑定过,回调onBind()
-
进程B启动了,里面的Service也创建了,但是Service已经被绑定过,回调onRebind()
1,2对应代码中的情况1;
3,4对应代码中的情况2。
ActiveServices#bindServiceLocked()的两种情况:
情况1,ActiveServices#bringUpServiceLocked()
1.1 APP已经创建
// APP 已经创建了,即进程已经启动了
if (app != null && app.thread != null) {
//则启动服务
realStartServiceLocked(r, app, execInFg);
private final void realStartServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r,
ProcessRecord app, boolean execInFg) throws RemoteException {
...
app.thread.scheduleCreateService(r,
r.serviceInfo,
mAm.compatibilityInfoForPackageLocked(r.serviceInfo.applicationInfo),
app.repProcState);
...
}
参数app是一个 ProcessRecord 对象,每启动一个app就创建了一个进程,进程信息就保存在ProcessRecord里面。
app.thread就是ApplicationThread对象,ApplicationThread类定义在ActivityThread.java中,ApplicationThread对象保存在ActivityThread.java中。
/**
* This manages the execution of the main thread in an
* application process, scheduling and executing activities,
* broadcasts, and other operations on it as the activity
* manager requests.
*
* {@hide}
*/
public final class ActivityThread {
...
final ApplicationThread mAppThread = new ApplicationThread();
...
public static void main(String[] args) {
...
//创建ActivityThread对象
ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread();
thread.attach(false);
...
}
}
ActivityThread对象在ActivityThread的main方法里创建,也就是只要App启动了,必定会创建ActivityThread对象,也就必定会创建其成员属性ApplicationThread对象。
app.thread.scheduleCreateService(),会调用Handler发送一个CREATE_SERVICE消息,然后执行handleCreateService()方法:
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
...
case CREATE_SERVICE:
handleCreateService((CreateServiceData)msg.obj);
...
}
//ActivityThread.java
//创建服务的方法
private void handleCreateService(CreateServiceData data) {
...
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = packageInfo.getClassLoader();
service = (Service) cl.loadClass(data.info.name).newInstance();//这里通过类加载器和反射加载的类在上述例子中就是Myservice
...
Application app = packageInfo.makeApplication(false, mInstrumentation);
service.attach(context, this, data.info.name, data.token, app,
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault());
service.onCreate();
mServices.put(data.token, service);//mServices是一个ArrayMap,final ArrayMap<IBinder, Service> mServices = new ArrayMap<>();
...
}
为什么要将service put到mServices中,因为service只能创建一次,只能bind一次,下次再调用bindService进行绑定服务时,先从mServices中寻找,如果找到了则判断service是否绑定了,如果还没有绑定,则调onBind进行绑定,如果已经绑定了,则调用onRebind。这个过程zhandleBindService()中:
private void handleBindService(BindServiceData data) {
...
if (!data.rebind) {
IBinder binder = s.onBind(data.intent);
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().publishService(
data.token, data.intent, binder);
} else {
s.onRebind(data.intent);
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().serviceDoneExecuting(
data.token, SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_ANON, 0, 0);
}
...
}
1.2 APP没有创建
回到ActiveServices#bringUpServiceLocked()方法中看第2种情况:
private final String bringUpServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r, int intentFlags, boolean execInFg,
boolean whileRestarting) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
...
//APP没有创建,即B进程还没有启动,则启动B进程
// Not running -- get it started, and enqueue this service record
// to be executed when the app comes up.
if (app == null) {
if ((app=mAm.startProcessLocked(procName, r.appInfo, true, intentFlags,
"service", r.name, false, isolated, false)) == null) {
String msg = "Unable to launch app "
+ r.appInfo.packageName + "/"
+ r.appInfo.uid + " for service "
+ r.intent.getIntent() + ": process is bad";
Slog.w(TAG, msg);
bringDownServiceLocked(r);
return msg;
}
...
}
mAm是一个ActivityManagerService对象 final ActivityManagerService mAm;
ActivityManagerService#startProcessLocked:
private final void startProcessLocked(ProcessRecord app, String hostingType,
String hostingNameStr, String abiOverride, String entryPoint, String[] entryPointArgs) {
...
Process.ProcessStartResult startResult = Process.start(entryPoint,
app.processName, uid, uid, gids, debugFlags, mountExternal,
app.info.targetSdkVersion, app.info.seinfo, requiredAbi, instructionSet,
app.info.dataDir, entryPointArgs);
...
}
最终会调用Process.start启动B进程,B进程启动后会启动Service。
情况2,ActiveServices#requestServiceBindingLocked(s, b.intent, callerFg, true)
private final boolean requestServiceBindingLocked(ServiceRecord r, IntentBindRecord i,
boolean execInFg, boolean rebind) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
...
r.app.thread.scheduleBindService(r, i.intent.getIntent(), rebind,
r.app.repProcState);
...
}
如果还没有绑定过(即Service的onBind方法还没有调用过),那么参数rebind为false;
如果已经绑定过(即Service的onBind方法已经调用过),那么参数rebind为true;
scheduleBindService方法会调用Handler发送一个BIND_SERVICE消息,然后调用handleBindService方法:
//ActivityThread.java
//处理服务的绑定过程,根据Service是否已经绑定调用Service#onBind还是Service#onRebind
private void handleBindService(BindServiceData data) {
...
if (!data.rebind) {//不是rebind,即Service还没有绑定过,则调用onBind
IBinder binder = s.onBind(data.intent);//获得了iBinder对象
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().publishService(
data.token, data.intent, binder);
} else {//是rebind,即Service已经绑定过,则调用onRebind
s.onRebind(data.intent);
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().serviceDoneExecuting(
data.token, SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_ANON, 0, 0);
}
...
}
2.1 rebind为false,则调用onBind
private void handleBindService(BindServiceData data) {
...
if (!data.rebind) {//不是rebind,即Service还没有绑定过,则调用onBind
IBinder binder = s.onBind(data.intent);//获得了iBinder对象
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().publishService(
data.token, data.intent, binder);
}
...
}
先调用了onBind获得了iBinder对象,这个iBinder对象在上述例子中就是MyService中创建的Stub对象。
然后调用 ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().publishService()
即调用ActivityManagerProxy.publishService(),通过Binder驱动最终调用ActivityManagerService.publishService()方法(这个过程和bindService过程一模一样,参看上面的bindService分析过程,这里就不分析了)。
ActivityManagerService.publishService():
public void publishService(IBinder token, Intent intent, IBinder service) {
// Refuse possible leaked file descriptors
if (intent != null && intent.hasFileDescriptors() == true) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("File descriptors passed in Intent");
}
synchronized(this) {
if (!(token instanceof ServiceRecord)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid service token");
}
mServices.publishServiceLocked((ServiceRecord)token, intent, service);
}
}
ActiveServices#publishServiceLocked:
//ActiveServices.java
void publishServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r, Intent intent, IBinder service) {
...
//最终会调用客户端进程绑定服务时传入的ServiceConnection的onServiceConnected()回调方法
c.conn.connected(r.name, service);
...
}
ConnectionRecord c
IServiceConnection conn;
final class ConnectionRecord {
final AppBindRecord binding; // The application/service binding.
final ActivityRecord activity; // If non-null, the owning activity.
//conn是客户端进程的IServiceConnection对象在AMS进程的代理对象
final IServiceConnection conn; // The client connection.
...
}
即conn是一个IServiceConnection对象,IServiceConnection是一个aidl接口,也就是说conn.connected方法调用过程也是一个Binder机制跨进程调用的过程。
AMS进程的 conn.connected 是如何调用到app进程的connection.onServiceConnected()方法的?
先看下app进程的ServiceConnection对象是如何转为IServiceConnection对象的,app调用bindService方法进行绑定服务时会在ContextImpl的bindServiceCommon()方法中对参数conn对象进行封装,转换为IServiceConnection对象sd,
private boolean bindServiceCommon(Intent service, ServiceConnection conn, int flags,
UserHandle user) {
IServiceConnection sd;
if (conn == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("connection is null");
}
if (mPackageInfo != null) {
sd = mPackageInfo.getServiceDispatcher(conn, getOuterContext(),
mMainThread.getHandler(), flags);
...
}
mPackageInfo时是LoadedApk对象,
LoadedApk#getServiceDispatcher方法:
//LoadedApk.java
public final IServiceConnection getServiceDispatcher(ServiceConnection c,
Context context, Handler handler, int flags) {
synchronized (mServices) {
LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd = null;
ArrayMap<ServiceConnection, LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher> map = mServices.get(context);
if (map != null) {
sd = map.get(c);
}
if (sd == null) {
sd = new ServiceDispatcher(c, context, handler, flags);
if (map == null) {
map = new ArrayMap<ServiceConnection, LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher>();
mServices.put(context, map);
}
map.put(c, sd);
} else {
sd.validate(context, handler);
}
return sd.getIServiceConnection();
}
}
static final class ServiceDispatcher {
private final ServiceDispatcher.InnerConnection mIServiceConnection;
...
private static class InnerConnection extends IServiceConnection.Stub {
final WeakReference<LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher> mDispatcher;
InnerConnection(LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd) {
mDispatcher = new WeakReference<LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher>(sd);
}
public void connected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) throws RemoteException {
LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd = mDispatcher.get();
if (sd != null) {
sd.connected(name, service);
}
}
}
...
IServiceConnection getIServiceConnection() {
return mIServiceConnection;
}
...
}
也就是说客户端进程的bindService方法会把传递进去的ServiceConnection conn参数转为InnerConnection对象sd,InnerConnection实现了IServiceConnection接口,并且是Stub类,而AMS进程的conn对象也实现了IServiceConnection接口,是个Proxy类。
也就是AMS进程调用 conn.connected 方法最终调用到app进程的connection.onServiceConnected()方法的过程是一个Binder机制跨进程调用的过程,这个过程中AMS进程是客户端(IServiceConnection.Stub.Proxy),app进程是服务端(IServiceConnection.Stub)。
2.2 rebind为true,则调用onRebind
回到handleBindService()方法看onRebind过程:
private void handleBindService(BindServiceData data) {
...
else {//是rebind,即Service已经绑定过,则调用onRebind
s.onRebind(data.intent);
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().serviceDoneExecuting(
data.token, SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_ANON, 0, 0);
}
...
}
总结
调用bindService()执行的流程:
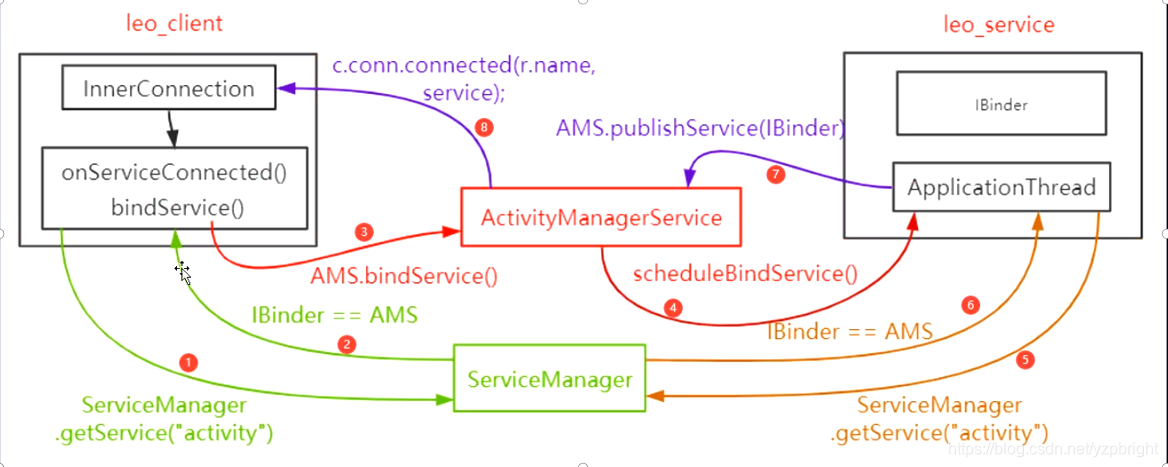
ServiceManager是系统服务,运行在系统进程(service_manager进程)
ActivityManagerService是系统服务,运行在系统进程(system_server进程)
api 28版本的上述源码分析:
ContextWrapper#bindService():
@Override
public boolean bindService(Intent service, int flags, Executor executor,
ServiceConnection conn) {
return mBase.bindService(service, flags, executor, conn);
}
mBase是一个ContextImpl对象,
ContextImpl#bindService():
@Override
public boolean bindService(
Intent service, int flags, Executor executor, ServiceConnection conn) {
warnIfCallingFromSystemProcess();
return bindServiceCommon(service, conn, flags, null, null, executor, getUser());
}
ContextImpl#bindServiceCommon
private boolean bindServiceCommon(Intent service, ServiceConnection conn, int flags,
String instanceName, Handler handler, Executor executor, UserHandle user) {
...
int res = ActivityManager.getService().bindService(
mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), getActivityToken(), service,
service.resolveTypeIfNeeded(getContentResolver()),
sd, flags, getOpPackageName(), user.getIdentifier());
...
}
分析下ActivityManager.getService().bindService:
//android/app/ActivityManager.java
private static final Singleton<IActivityManager> IActivityManagerSingleton =
new Singleton<IActivityManager>() {
@Override
protected IActivityManager create() {
final IBinder b = ServiceManager.getService(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE);
final IActivityManager am = IActivityManager.Stub.asInterface(b);
return am;
}
};
/**
* @hide
*/
public static IActivityManager getService() {
return IActivityManagerSingleton.get();
}
是不是看到了熟悉的IActivityManager.Stub.asInterface(b);也就是getService()返回的是IActivityManager.Stub.Proxy对象,即ActivityManager.getService().bindService最终调用的是IActivityManager.Stub.Proxy.bindService






















 241
241











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








