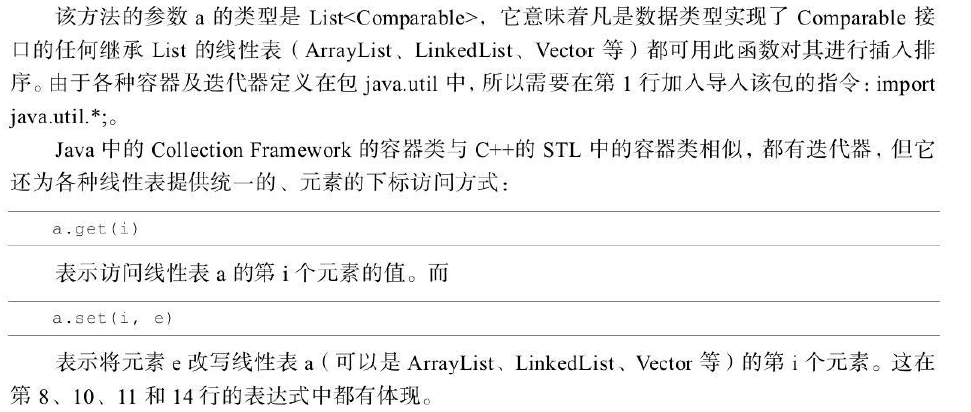
(1)算法描述与分析
(2)算法具体实现
import java.util.*;
public class Sort {
public static void insertionSort(int[] a) {
int i, j, key, n = a.length;
for (j = 1; j < n; j++) {
key = a[j];// key←a[j]
i = j - 1;
while (i >= 0 && a[i] > key) {
a[i + 1] = a[i];// a[i+1]←a[i]
i--;// i←i-1
}
a[i + 1] = key;// a[i+1]←key
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int A[] = { 5, 1, 9, 4, 6, 2, 0, 3, 8, 7 };
int i;
Sort.insertionSort(A);
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
System.out.print(A[i] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
import java.util.*;
public class Sort {
public static void insertionSort(Comparable[] a) {
int i, j, n = a.length;
Comparable key;
for (j = 1; j < n; j++) {
key = a[j];
i = j - 1;
while (i >= 0 && (a[i].compareTo(key) > 0)) {// a[i]>key
a[i + 1] = a[i];
i--;
}
a[i + 1] = key;
}
}
}
public static void main(final String args[]) {
final Integer[] a = { 5, 1, 9, 4, 6, 2, 0, 3, 8, 7 };
final String[] b = { "ChongQing", "ShangHai", "AoMen", "TianJin",
"BeiJing", "XiangGang" };
final Double[] c = { 8.5, 6.3, 1.7, 9.2, 0.5, 2.3, 4.1, 7.4, 5.9, 3.7 };
int i;
Sort.insertionSort(a);
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
System.out.print(a[i] + " ");
System.out.println();
Sort.insertionSort(b);
for (i = 0; i < 6; i++)
System.out.print(b[i] + " ");
System.out.println();
Sort.insertionSort(c);
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
System.out.print(c[i] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
public static void insertionSort(List<Comparable> a) {
int i, j, n = a.size();
Comparable key;
for (j = 1; j < n; j++) {
key = a.get(j);// key鈫恆[j]
i = j - 1;
while (i >= 0 && (a.get(i).compareTo(key) > 0))
// i>=且a[i]>key
i--;
Collections.rotate(a.subList(i + 1, j + 1), 1);
}
}测试类:
public static void main(final String args[]) {
final Integer[] a = { 5, 1, 9, 4, 6, 2, 0, 3, 8, 7 };
final String[] b = { "ChongQing", "ShangHai", "AoMen", "TianJin",
"BeiJing", "XiangGang" };
final Double[] c = { 8.5, 6.3, 1.7, 9.2, 0.5, 2.3, 4.1, 7.4, 5.9, 3.7 };
int i;
final ArrayList A = new ArrayList();
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
A.add(a[i]);
final Vector B = new Vector();
for (i = 0; i < 6; i++)
B.add(new String(b[i]));
final LinkedList C = new LinkedList();
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
C.add(c[i]);
Sort.insertionSort((List) A);
System.out.println(A);
Sort.insertionSort((List) B);
System.out.println(B);
Sort.insertionSort((List) C);
System.out.println(C);
}测试结果:
import java.util.*;
public class Sort {
public static void insertionSort(List<Comparable> a) {
int i, j, n = a.size();
Comparable key;
for (j = 1; j < n; j++) {
key = a.get(j);// key鈫恆[j]
i = j - 1;
while (i >= 0 && (a.get(i).compareTo(key) > 0))
// i>=0且a[i]>key
i--;
Collections.rotate(a.subList(i + 1, j + 1), 1);
}
}
}import java.util.*;
public class Sort {
public static void insertionSort(List<Comparable> a, Comparator comp) {
int i, j, n = a.size();
Comparable key;
for (j = 1; j < n; j++) {
key = a.get(j);// key←[j]
i = j - 1;
while (i >= 0 && comp.compare(a.get(i), key) > 0)
// i�?且a[i]>key
i--;
Collections.rotate(a.subList(i + 1, j + 1), 1);
}
}
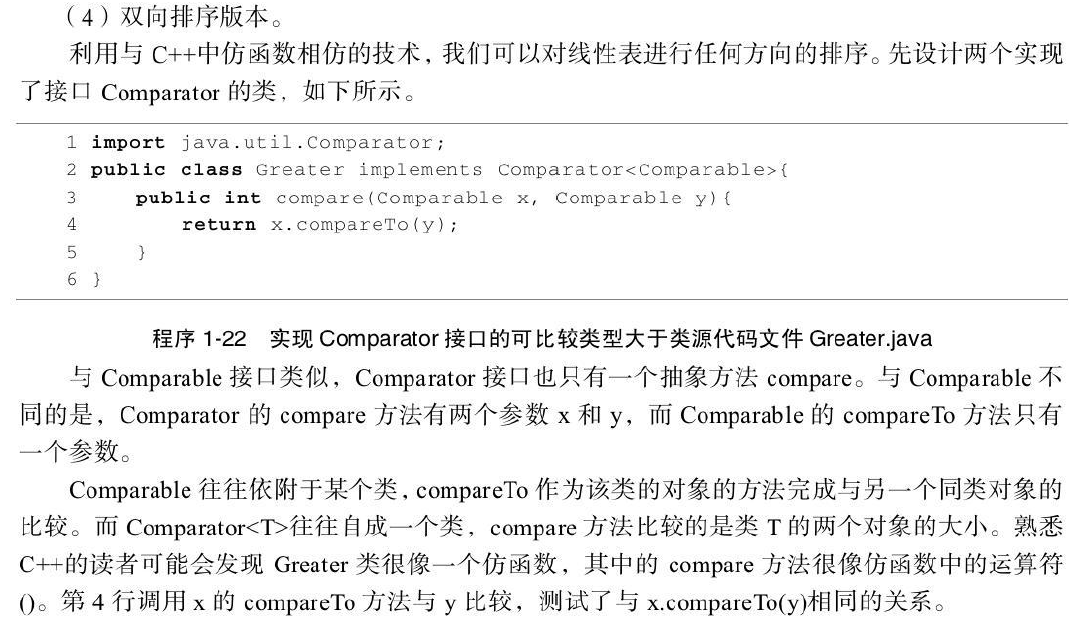
}Greater和Less程序
import java.util.Comparator;
public class Greater implements Comparator<Comparable> {
public int compare(Comparable x, Comparable y) {
return x.compareTo(y);
}
}
import java.util.Comparator;
public class Less implements Comparator<Comparable> {
public int compare(Comparable x, Comparable y) {
return y.compareTo(x);
}
}测试类:
public static void main(final String args[]) {
Integer[] a = { 5, 1, 9, 4, 6, 2, 0, 3, 8, 7 };
String[] b = { "ChongQing", "ShangHai", "AoMen", "TianJin", "BeiJing",
"XiangGang" };
Double[] c = { 8.5, 6.3, 1.7, 9.2, 0.5, 2.3, 4.1, 7.4, 5.9, 3.7 };
int i;
ArrayList<Integer> A = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
A.add(a[i]);
Vector<String> B = new Vector<String>();
for (i = 0; i < 6; i++)
B.add(new String(b[i]));
LinkedList<Double> C = new LinkedList<Double>();
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
C.add(c[i]);
Sort.insertionSort((List) A, new Greater());
System.out.println(A);
Sort.insertionSort((List) B, new Less());
System.out.println(B);
Sort.insertionSort((List) C, new Less());
System.out.println(C);
}测试结果:


































 88
88











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








