一、前言
曾提到过 dma_buf_fd() 这个函数,该函数用于创建一个新的 fd,并与dma_buf 的文件关联起来。本篇我们一起来重点学习 dma-buf 与 file 相关的操作接口,以及它们的注意事项。
二、 file
dma-buf 本质上是 buffer 与 file 的结合,不仅如此,该 file 还是个被 open 过的 file。从我们调用 dma_buf_export() 开始,这个 file 就已经被 open 了。而且该 file 还是个匿名文件,因此应用程序无法通过 fd = open(“name”) 的方式来获取它所对应的 fd,只能依托于 exporter 驱动的 ioctl 接口,通过 dma_buf_fd() 来获取。
三、fd
如下内核 API 实现了 dma-buf 与 fd 之间的相互转换:
dma_buf_fd():dma-buf --> new fd
dma_buf_get():fd --> dma-buf
通常使用方法如下:
fd = dma_buf_fd(dmabuf);
dmabuf = dma_buf_get(fd);
四、get / put
只要是文件,内部都会有一个引用计数(f_count)。当使用 dma_buf_export() 函数创建 dma-buf 时,该引用计数被初始化为1;当这个引用计数为0时,则会自动触发 dma_buf_ops 的 release 回调接口,并释放 dma-buf 对象。
在 linux 内核中操作 file 引用计数的常用函数为 fget() 和 fput(),而 dma-buf 又在此基础上进行了封装,如下:
get_dma_buf()dma_buf_get()dma_buf_put()
为了不让大家混淆,我做了如下表格区分:
| 函数 | 区别 |
|---|---|
| get_dma_buf() | 仅引用计数加1 |
| dma_buf_get() | 引用计数加1,并将 fd 转换成 dma_buf 指针 |
| dma_buf_put() | 引用计数减1 |
| dma_buf_fd() | 引用计数不变,仅创建 fd |
五、release
通常 release 回调接口用来释放 dma-buf 所对应的物理 buffer。当然,凡是所有和该 dma-buf 相关的私有数据也都应该在这里被 free 掉。
前面说过,只有当 dma-buf 的引用计数递减到0时,才会触发 release 回调接口。因此
如果不想让你正在使用的 buffer 被突然释放,请提前 get;
如果想在 kernel space 释放 buffer,请使劲 put;
如果想从 user space 释放 buffer,请尝试 close;
这就是为什么在内核设备驱动中,我们会看到那么多 dma-buf get 和 put 的身影。
一旦 export_test.ko 被成功加载了,就无法被 rmmod 的原因。因为没有任何程序来修改该 dma-buf 的引用计数,自始自终都保持为1,所以也就无法执行 release 接口,更不会执行 module put。
六、示例
在前面所有的 exporter 驱动中,都定义了一个 dmabuf_export全局变量,方便 importer 驱动通过 extern 关键字来引用。这就造成了 exporter 驱动与 importer 驱动之间的强耦合,不仅编译时 importer 需要依赖 exporter 的文件,就连运行时也要依赖 exporter 模块先加载。
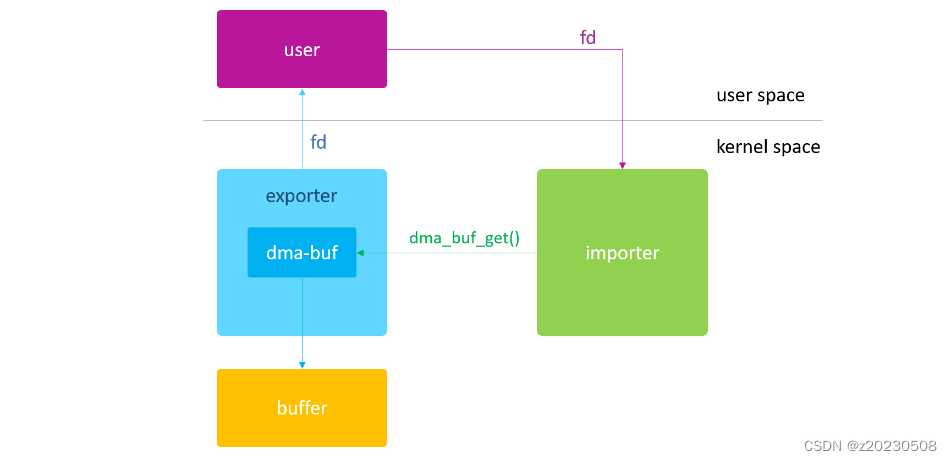
这次,我们将 dmabuf_exported 全局变量改为 static 静态变量,并借助于
dma_buf_fd()与dma_buf_get()来彻底解除 importer 与 exporter 驱动之间的耦合。
export_test.c
将 dmabuf_exported 全局变量修改为 static 静态变量,其它代码不做修改。
#include <linux/dma-buf.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <linux/mm.h>
#include <linux/miscdevice.h>
static struct dma_buf *dmabuf_export;
//EXPORT_SYMBOL(dmabuf_export);
static int exporter_attach(struct dma_buf* dmabuf, struct dma_buf_attachment *attachment)
{
pr_info("dmanbuf attach device :%s \n",dev_name(attachment->dev));
return 0;
}
static void exporter_detach(struct dma_buf *dmabuf, struct dma_buf_attachment *attachment)
{
pr_info("dmabuf detach device :%s \n",dev_name(attachment->dev));
}
static struct sg_table *exporter_map_dma_buf(struct dma_buf_attachment *attachment,
enum dma_data_direction dir)
{
// void *vaddr = attachment->dmabuf->priv;
struct sg_table *table;
int ret;
table = kmalloc(sizeof(struct sg_table),GFP_KERNEL);
ret = sg_alloc_table(table, 1, GFP_KERNEL);
if(ret)
pr_info("sg_alloc_table err\n");
sg_dma_len(table->sgl) = PAGE_SIZE;
pr_info("sg_dma_len: %d\n ", sg_dma_len(table->sgl));
// sg_dma_address(table->sgl) = dma_map_single(NULL, vaddr, PAGE_SIZE,dir);
// pr_info("sg_dma_address: 0x%llx\n",(unsigned long long)sg_dma_address(table->sgl));
return table;
}
static void exporter_unmap_dma_buf(struct dma_buf_attachment *attachment,
struct sg_table *table,
enum dma_data_direction dir)
{
dma_unmap_single(NULL, sg_dma_address(table->sgl), PAGE_SIZE, dir);
sg_free_table(table);
kfree(table);
}
static void exporter_release(struct dma_buf *dmabuf)
{
return kfree(dmabuf->priv);
}
/*static void *exporter_kmap_atomic(struct dma_buf *dmabuf, unsigned long page_num)
{
return NULL;
}
static void *exporter_kmap(struct dma_buf *dmabuf, unsigned long page_num)
{
return NULL;
}*/
static void* exporter_vmap(struct dma_buf *dmabuf)
{
return dmabuf->priv;
}
static int exporter_mmap(struct dma_buf *dmabuf, struct vm_area_struct *vma)
{
void *vaddr = dmabuf->priv;
struct page * page_ptr = virt_to_page(vaddr);
return remap_pfn_range(vma,vma->vm_start, page_to_pfn(page_ptr),
PAGE_SIZE, vma->vm_page_prot);
}
static const struct dma_buf_ops exp_dmabuf_ops = {
.attach = exporter_attach,
.detach = exporter_detach,
.map_dma_buf = exporter_map_dma_buf,
.unmap_dma_buf = exporter_unmap_dma_buf,
.release = exporter_release,
// .map_atomic = exporter_kmap_atomic,
// .map = exporter_kmap,
.vmap = exporter_vmap,
.mmap = exporter_mmap,
};
static struct dma_buf *exporter_alloc_page(void)
{
DEFINE_DMA_BUF_EXPORT_INFO(exp_info);
struct dma_buf *dmabuf;
void *vaddr;
vaddr = kzalloc(PAGE_SIZE,GFP_KERNEL);
exp_info.ops = &exp_dmabuf_ops;
exp_info.size = PAGE_SIZE;
exp_info.flags = O_CLOEXEC;
exp_info.priv = vaddr;
dmabuf= dma_buf_export(&exp_info);
if(dmabuf == NULL)
printk(KERN_INFO"DMA buf export error\n");
sprintf(vaddr, "hello world");
return dmabuf;
}
static long exporter_ioctl(struct file *filp, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg)
{
int fd = dma_buf_fd(dmabuf_export, O_CLOEXEC);
if(unlikely(copy_to_user((void __user*)arg, &fd,sizeof(fd)))){
return -EFAULT;
}
return 0;
}
static int exporter_misc_mmap(struct file *file, struct vm_area_struct *vma)
{
return dma_buf_mmap(dmabuf_export, vma, 0);
}
static struct file_operations exporter_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.unlocked_ioctl = exporter_ioctl,
.mmap = exporter_misc_mmap,
};
static struct miscdevice mdev ={
.minor = MISC_DYNAMIC_MINOR,
.name = "exporter",
.fops = &exporter_fops,
};
static int __init exporter_init(void)
{
dmabuf_export = exporter_alloc_page();
return misc_register(&mdev);
}
static void __exit exporter_exit(void)
{
misc_deregister(&mdev);
}
module_init(exporter_init);
module_exit(exporter_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
MODULE_AUTHOR("ZWQ");
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("zwq dma used buffer");
在 ioctl 中,通过 dma_buf_fd() 创建一个新的 fd,并通过 copy_to_user() 将该 fd 的值传给上层应用程序。
import_test.c 驱动
#include <linux/dma-buf.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
//#include <linux/dma-buf-map.h>
#include <linux/miscdevice.h>
//extern struct dma_buf *dmabuf_export;
static int importer_read(struct dma_buf *dmabuf)
{
#if 1
void * addr;
// struct dma_buf_map map;
// int ret =0;
addr = dma_buf_vmap(dmabuf);
// printk(KERN_INFO "read from dma_buf :%s \n",(char *)addr);
pr_info("read from dma_buf:%s \n",(char*)addr);
dma_buf_vunmap(dmabuf,addr);
#endif
#if 0
struct dma_buf_attachment *attachment;
struct sg_table *table;
struct device *dev;
dma_addr_t reg_addr;
unsigned int reg_size;
int err;
dev = kzalloc(sizeof(*dev), GFP_KERNEL);
dev_set_name(dev,"importer");
attachment = dma_buf_attach(dmabuf, dev);
if(IS_ERR(attachment)){
err = PTR_ERR(attachment);
pr_info("dma_buf_attach err\n");
return err;
}
table = dma_buf_map_attachment(attachment, DMA_BIDIRECTIONAL);
if(IS_ERR(table)){
err = PTR_ERR(table);
pr_info("dma_buf_map_attachment err\n");
return err;
}
reg_addr = sg_dma_address(table->sgl);
reg_size = sg_dma_len(table->sgl);
pr_info("reg_addr = 0x%08x, reg_size = 0x%08x\n" , reg_addr, reg_size);
dma_buf_unmap_attachment(attachment, table, DMA_BIDIRECTIONAL);
dma_buf_detach(dmabuf, attachment);
return 0;
#endif
return 0;
}
static long importer_ioctl(struct file *filp, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg)
{
int fd;
struct dma_buf *dmabuf;
if(unlikely(copy_from_user(&fd,(void __user *)arg, sizeof(int)))){
return -EFAULT;
}
dmabuf = dma_buf_get(fd);
importer_read(dmabuf);
dma_buf_put(dmabuf);
return 0;
}
static struct file_operations importer_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.unlocked_ioctl = importer_ioctl,
};
static struct miscdevice mdev ={
.minor = MISC_DYNAMIC_MINOR,
.name = "importer",
.fops = &importer_fops,
};
static int __init import_init(void)
{
// importer_read(dmabuf_export);
return misc_register(&mdev);
}
static void __exit import_exit(void)
{
misc_deregister(&mdev);
}
module_init(import_init);
module_exit(import_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
MODULE_AUTHOR("zwq");
与 importer-kmap 驱动相比,上面的驱动新增了 misc driver 部分,通过 ioctl 接口来接收上层传下来的 fd,并通过 dma_buf_get() 将 fd 转换成 dma-buf 指针。随后便在 kernel 空间通过 kmap/vmap 来访问该 dma-buf 的物理内存。
需要注意的是,dma_buf_get() 会增加 dma-buf 的引用计数,所以在使用完 dma-buf 后,要记得用 dma_buf_put() 将引用计数再减回来,否则引用计数不匹配,将导致 dma-buf 的 release 接口无法被回调,从而导致 buffer 无法被释放,造成内存泄漏。
userspace 程序
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stddef.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int fd;
int dmabuf_fd = 0;
fd = open("/dev/exporter", O_RDONLY);
ioctl(fd, 0, &dmabuf_fd);
close(fd);
fd = open("/dev/importer", O_RDONLY);
ioctl(fd, 0, &dmabuf_fd);
close(fd);
return 0;
}
加载驱动,然后运行结果:

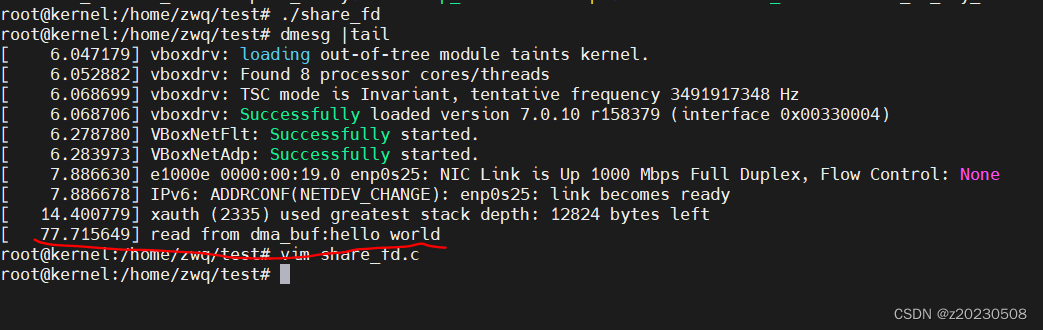
通过上面的运行结果我们看到,即使 importer 驱动先加载,也不会影响应用程序的输出结果,真正实现了 importer 驱动与 exporter 驱动之间的解耦合。
上面的实现解耦的方法,值得学习
七、跨进程 fd
做 Linux 应用开发的同事都知道,fd 属于进程资源,它的作用域只在单个进程空间范围内有效,即同样的 fd 值,在进程 A 和 进程 B 中所指向的文件是不同的。因此 fd 是不能在多个进程之间共享的,也就是说 dma_buf_fd() 与 dma_buf_get() 只能是在同一进程中调用。
但是有的小伙伴就会问了:在 Android 系统中,dma-buf 几乎都是由 ION 来统一分配的,ION 所在进程(Allocator)在分配好 buffer 以后,会将该 buffer 所对应的 fd 传给其它进程,如 SurfaceFlinger 或 CameraService,而这些进程在收到 fd 后在各自的底层驱动中都能正确的转换成相应的 dma-buf,那这又是如何做到的呢?
fd 并不是完全不能在多进程中共享,而是需要采用特殊的方式进行传递。在 linux 系统中,最常用的做法就是通过 socket 来实现 fd 的传递。而在 Android 系统中,则是通过 Binder 来实现的。需要注意的是,传递后 fd 的值可能会发生变化,但是它们所指向的文件都是同一文件。关于 Binder 如何实现 fd 跨进程共享,请见参考资料中的第一篇文章,这里不做赘述。总之,有了 Binder,dma_buf_fd() 和 dma_buf_get() 就可以不用严格限制在同一进程中使用了。
八、总结
- 为什么需要 fd ?
- 方便应用程序直接在 user space 访问该 buffer(通过 mmap);
- 方便该 buffer 在各个驱动模块之间流转,而无需拷贝;
- 降低了各驱动之间的耦合度;
- 如何实现 fd 跨进程共享? Binder!
- get / put 将影响 dma-buf 的内存释放
参考资料





















 2万+
2万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








