Future是啥我懒得解释,想知道可以自己去vertx官网翻译,但是怎么用可以通过下面的例子去体会。这就好比锤子是怎么定义的我不知道,但是你给我个锤子,我知道怎么去用它就可以了,至于用得对不对,还看悟性了... ...
Future给我的感觉就是协调异步操作结果的,可以让异步操作,多个并行操作,也可以让其按照顺序串行操作,先来个例子展示一下这个按照顺序的串行操作,其实上一节的Promise中回调地狱的解决例子就可以,但是为了和并行的例子一起做完,就换个更简单的例子来展示一下吧:
package cn.zcrazy.giveupvertx.future;
import io.vertx.core.*;
public class FutureExample extends AbstractVerticle {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Vertx.vertx().deployVerticle("cn.zcrazy.giveupvertx.future.FutureExample");
}
@Override
public void start() throws Exception {
Future<String> future = world("");
future.compose(this::your)
.compose(this::hello)
.onComplete(ar -> {
if (ar.failed()) {
System.out.println("Something bad happened");
ar.cause().printStackTrace();
} else {
System.out.println("Result: " + ar.result());
}
});
}
private Future<String> hello(String str){
Promise<String> promise = Promise.promise();
vertx.setTimer(100, l -> promise.complete(" hello"+str));
return promise.future();
}
private Future<String> your(String str){
Promise<String> promise = Promise.promise();
vertx.setTimer(100, l -> promise.complete(" your"+str));
return promise.future();
}
private Future<String> world(String str){
Promise<String> promise = Promise.promise();
vertx.setTimer(100, l -> promise.complete(" world"+str));
return promise.future();
}
}上述代码输出如下:

上面的三个操作都是按照顺序执行,下面再来一个例子,是三个操作同时进行,必须全部成功,最终才算成功的的例子:
package cn.zcrazy.giveupvertx.future;
import io.vertx.core.*;
public class FutureExample extends AbstractVerticle {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Vertx.vertx().deployVerticle("cn.zcrazy.giveupvertx.future.FutureExample");
}
@Override
public void start() {
Future<String> future1 = world("");
Future<String> future2 = your("");
Future<String> future3 = hello("");
CompositeFuture.all(future3, future2, future1).onComplete(ar -> {
if (ar.failed()) {
System.out.println("Something bad happened");
ar.cause().printStackTrace();
} else {
System.out.println(ar.result().list());
}
});
}
private Future<String> hello(String str) {
Promise<String> promise = Promise.promise();
vertx.setTimer(100, l -> promise.complete(" hello" + str));
return promise.future();
}
private Future<String> your(String str) {
Promise<String> promise = Promise.promise();
vertx.setTimer(100, l -> promise.complete(" your" + str));
return promise.future();
}
private Future<String> world(String str) {
Promise<String> promise = Promise.promise();
vertx.setTimer(100, l -> promise.complete(" world" + str));
return promise.future();
}
}最终输出的结果为:

如果我在下面任意一个方法中故意添加一个错误,则会有如下输出:
首先我将hello方法修改如下:
private Future<String> hello(String str) {
Promise<String> promise = Promise.promise();
try {
String result = " hello" + str + (10 / 0);
vertx.setTimer(100, l -> promise.complete(result));
} catch(Exception e){
promise.fail(e.getCause());
}
return promise.future();
}输出:

从上面的例子来看,只要有一个方法执行失败,最终就算是失败,future还提供了any,只要有一个方法成功,就算成功,我们将上面的例子中的all改为any,再运行一遍这个报错的例子:
CompositeFuture.all(future3, future2, future1).onComplete(ar -> {
if (ar.failed()) {
System.out.println("Something bad happened");
ar.cause().printStackTrace();
} else {
System.out.println(ar.result().list());
}
});
||
||
||
CompositeFuture.any(future3, future2, future1).onComplete(ar -> {
if (ar.failed()) {
System.out.println("Something bad happened");
ar.cause().printStackTrace();
} else {
System.out.println(ar.result().list());
}
});这次程序的输出如下:
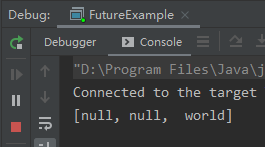 或者
或者 
只要有一个成功就立马返回,也不管其余两个是否成功,只有当所有都返回失败的时候才会显示失败。
当然CompositeFuture还有一个join方法,和all方法类似,都是要全部成功才会成功,但是all是执行到错误直接就结束了,join是等到所有Future执行结束之后,再进行判断。
以上就是今天的全部内容,有不懂的下方留言讨论~








 本文主要介绍了Vert.x中Future的使用。Future可协调异步操作结果,能让异步操作并行或串行执行。文中通过多个例子展示了串行操作、并行操作中全部成功才算成功、任意一个成功就算成功等情况,还提到了CompositeFuture的join方法与all方法的区别。
本文主要介绍了Vert.x中Future的使用。Future可协调异步操作结果,能让异步操作并行或串行执行。文中通过多个例子展示了串行操作、并行操作中全部成功才算成功、任意一个成功就算成功等情况,还提到了CompositeFuture的join方法与all方法的区别。


















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










