前言
有段时间没有更新博文了,一直在忙工作很少有时间静下心来继续研究点东西,说来也惭愧,归咎原因最主要的还是因为懒惰。空想也是不管用的,有时候很多想法被扼杀到了摇篮里,还没开始做就放弃了,这是多数人会有的恶习,世界上最不缺少的就是空想家,而是实践者,有句俗话说的好不怕千招会,只怕一招绝,能踏踏实实做好一件事的人才是人生的赢家。另外在平时也有研究过很多有趣的技术,但往往是没有研究到最后,只是研究了如何使用它,然后想要写成文章就是很危险的事情,如果对某项技术研究的并不通透,这时候发表见解的话这样只会害人,不会帮助人,要知道一知半解最后害的会是自己。
一、架构浅析
该篇文章将会使用前几篇文章讨论到的技术来搭一套小的框架,主要是实现Application(电脑或者移动端)和Web Service之间互相的通信,中间的消息中介服务使用上文讨论到的MQ来实现,具体的架构如下图所示:
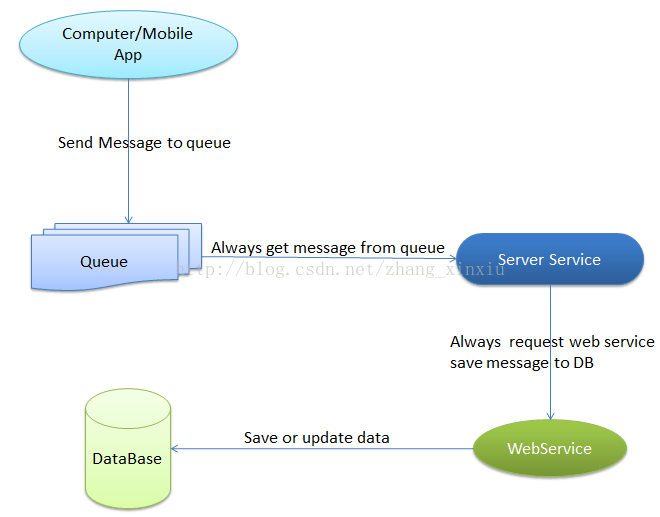
关于上图的实现,本例中的Application只是使用了Computer端的WPF来做的一个小的应用,消息队列方是使用微软的Message Queue来开发,Server Service开发的是Windows Service,远程端的Web Service使用WCF来做的开发。具体开发的代码将会在下文中详细讨论。
Note:这种架构下近端的实体、远程端的实体、WebService的实体以及数据契约的结构必须保持一致,这样在开发时可以避免写很多转换的中间代码。
二、架构代码
2.1 近端App
应用程序端做的是简单的WPF应用程序,模拟了近端应用程序在执行完成后发送的消息信息到消息队列中,本例中的消息队列存储的是xml格式的对象信息,所以在发送消息对象时需要首先指定消息队列中信息的存储方式,具体的模拟代码如下:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Net.Security;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Messaging;
using System.Xml.Serialization;
namespace MQSend
{
public class SendMQ
{
public void Send()
{
MessageQueue mq = null;
if (!MessageQueue.Exists(".\\private$\\MSMQ"))
{
mq = MessageQueue.Create(".\\private$\\MSMQ");
}
else
{
mq = new MessageQueue(".\\private$\\MSMQ");
}
mq.Formatter = new XmlMessageFormatter(new Type[] { typeof(Student),typeof(Teacher) });
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++)
{
mq.Send(new Student(){Id =i,Age = "13",Name = "张三"+i.ToString(),
Teachers = new List<Teacher>()
{
new Teacher() { Id = 2,
Name = "李老师"+i.ToString() }
}
});
}
mq.Close();
}
}
[Serializable]
public class Student
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Age { get; set; }
public List<Teacher> Teachers { get; set; }
}
[Serializable]
public class Teacher
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public List<Student> Students { get; set; }
}
}
Note:上面的代码实体对象Student和Teacher存在多对多的关系,这种关系在序列化时往往会出现循环引用的问题,因为序列化实际上是一种属性的遍历,会沿着对象一直向下循环序列化,所以在编程的时候一定要注意循环应用的
问题。
Note:另外在引用属性集合时不要声明接口类型的集合,因为在发送消息队列进行序列化时不允许声明接口类型的集合,否则会发生类似于“XX是接口,因此无法将其序列化。”的问题。
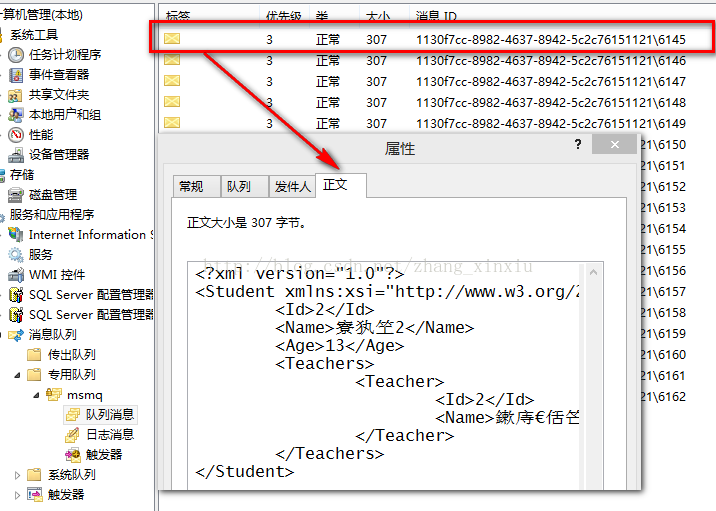
运行该应用程序后,消息会被发送到本机的消息队列中,具体的消息示意图如下:
2.2 远程端Server Service
远程端的Service本例开发的是Windows的服务,因为服务自开机之后可以时刻的在运行,也就是说可以时刻的获取消息队列中的消息,然后调用远程端的Web Service对消息进行处理。由于近端的消息发送的内容是xml序列化后的对象,所以在远程端server在操作消息对象时需要将对象首先反序列化为Service的实体对象(这里的实体对象是指Web Service的实体对象),然后对实体对象做所有的操作。
另外在开发Service的时候最好中间可以记录Service的运行过程,也就是将Service的运行过程记录到日志文件中,因为Service在运行过程中很容易出现问题,在出现问题时将问题的内容记录到日志文件中,这样能够较快的找到并修复问题。
每个Service都会有很多事件,其中使用最多的就是Service的开启事件OnStart和结束事件OnStop,该例中在这两个事件中分别添加了日志记录的功能,也就是在服务开启和关闭时都会将服务的运行状况写入日志。另外在该服务中添加了一个Timer控件,该控件的Interval时间设置为1000ms,这样可以实时的请求消息,然后对消息做操作,并保存日志信息。
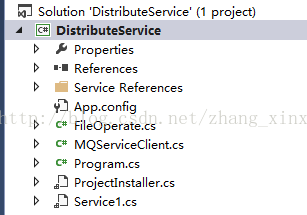
项目结构如下图所示,项目中添加了系统的WebService,并为该WebService添加了具体的代理类MQServiceClient以及工具类FileOperate。
Service的具体代码如下所示:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
using System.Messaging;
using System.ServiceModel;
using System.ServiceProcess;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using DistributeService.MQService;
namespace DistributeService
{
public partial class Service1 : ServiceBase
{
public Service1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private ServiceHost host;
private FileOperate fileOperate
{
get
{
return FileOperate.GetFileOperate();
}
}
protected override void OnStart(string[] args)
{
try
{
var str = "▌▌▌▌▌▌▌MQService start at " + DateTime.Now.ToString() + "▌▌▌▌▌▌▌\r\n";
fileOperate.WriteText(str, fileOperate.FileS);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
fileOperate.WriteText(ex.Message, fileOperate.FileS);
throw;
}
}
protected override void OnStop()
{
Thread.Sleep(30000);
var str = "▌▌▌▌▌▌▌MQService stop at " + DateTime.Now.ToString() + "▌▌▌▌▌▌▌\r\n"; ;
fileOperate.WriteText(str,fileOperate.FileS);
if (this.host!=null)
{
this.host.Close();
}
}
private void timer1_Elapsed(object sender, System.Timers.ElapsedEventArgs e)
{
MessageQueue mq = null;
if (MessageQueue.Exists(".\\private$\\MSMQ"))
{
mq = new MessageQueue(".\\private$\\MSMQ");
try
{
mq.Formatter = new XmlMessageFormatter(new Type[] {typeof (Student)});
var me = mq.Receive();
var stu = me.Body;
fileOperate.WriteText(stu.ToString() + "\r\n", fileOperate.FileM);
var client = new MQHandlerClient();//.GetMqHandlerService();
client.Add((Student) stu);
client.Close();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
fileOperate.WriteText(ex.ToString() + "\r\n", fileOperate.FileM);
throw;
}
finally
{
mq.Close();
}
}
}
}
}
其中的 WebSerivceClient 的代码如下所示:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Management.Instrumentation;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using DistributeService.MQService;
namespace DistributeService
{
public class MQServiceClient
{
private static MQHandlerClient instance;
private static object _object = new object();
private MQServiceClient()
{
}
public static MQHandlerClient GetMqHandlerService()
{
if (instance == null)
{
lock (_object)
{
if (instance==null)
{
instance=new MQHandlerClient();
}
}
}
return instance;
}
~MQServiceClient()
{
if (instance!=null)
{
instance.Close();
instance.Abort();
}
}
}
}
Note:这里的代码主要是做的消息处理,但是往往会出现错误,所以要记录运行日志,推荐使用开源的log4net或者Nlog,但是本例中是自己将堆栈信息写入到文本文件当中,可以方便查看。
2.3 远程端Web Service
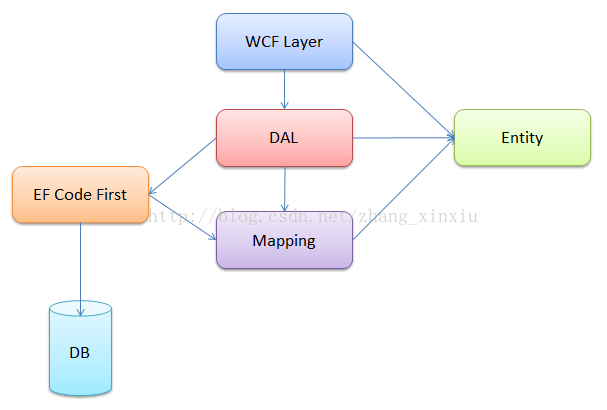
远程端Web Service公开了对消息的处理接口,主要是做的DB的增删改查的操作。该例的Web Service使用的是WCF来开发的,后台使用了EF 的Code First作为系统的ORM框架,并使用FluentAPI来搭建了系统的映射部分,系统对外公布了数据库的增删改查接口,具体的结构图如下所示:
2.3.1 WCF层增删改查
下面的代码是使用WCF来开发的Service,该Service在创建客户端对象时会同时创建数据库的一个上下文对象,最后将数据同步到Context中,由EF管理并同步到DB中。using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using DAL;
using Entitys;
namespace DistributeWCF
{
// NOTE: You can use the "Rename" command on the "Refactor" menu to change the class name "MQHandler" in code, svc and config file together.
// NOTE: In order to launch WCF Test Client for testing this service, please select MQHandler.svc or MQHandler.svc.cs at the Solution Explorer and start debugging.
public class MQHandler: IMQHandler
{
private TestContext context;
public MQHandler()
{
this.context=new TestContext();
}
public bool Add(Student stu)
{
this.context.Students.Add(new Entitys.Student(){Name = stu.Name,Teachers = new List<Entitys.Teacher>()});
this.context.SaveChanges();
return true;
}
public bool Delete(int stuId)
{
var stu = this.context.Students.Find(new {stuId});
this.context.Students.Remove(stu);
this.context.SaveChanges();
return true;
}
public bool Update(Student stu) { return true; }
public List<Student> FindAll()
{
var lists = this.context.Students.SqlQuery("select * from student");
var liststu = new List<Student>();
foreach (var student in lists)
{
var stu = new Student();
stu.StudentId = student.Id;
stu.Name = student.Name;
stu.Sex = student.Age;
stu.Teachers = new List<Teacher>();
foreach (var teacher in student.Teachers)
{
stu.Teachers.Add(new Teacher()
{
Id = teacher.Id,
Name = teacher.Name,
});
}
}
return liststu;
}
}
}
2.3.2 Fluent API的Mapping映射代码
该例使用的是Fluent API来做的映射,因为这种映射在修改时会非常的方便,并且在开发时控制对象关系编译的过程,所以使用此种方法映射功能,该种映射非常的简单,只要熟悉映射的规则就可以很容易操作。如下代码演示了该例中学生和老师的多对多关系之间的映射。对应的Teacher的Entity以及Mapping代码如下:
using System.Data.Entity.ModelConfiguration;
using Entitys;
namespace Mapping
{
public class TeacherMapping:EntityTypeConfiguration<Teacher>
{
public TeacherMapping()
{
this.ToTable("Teacher");
this.HasKey(x => x.Id);
this.Property(x => x.Id).HasColumnName("Id");
this.Property(x => x.Name);
this.HasMany(x=>x.Students)
.WithMany(x=>x.Teachers)
.Map(x => x.ToTable("StuTeahcer").MapLeftKey("TeacherId")
.MapRightKey("StudentId")
);
}
}
public class Teacher
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public IList<Student> Students { get; set; }
}
}
对应的Student的Entity以及Mapping代码如下:
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema;
using System.Data.Entity.ModelConfiguration;
using Entitys;
namespace Mapping
{
public class StudentMapping:EntityTypeConfiguration<Student>
{
public StudentMapping()
{
this.ToTable("Student");
this.HasKey(x => x.Id);
this.Property(x => x.Id)
.HasColumnName("Id")
.HasDatabaseGeneratedOption(DatabaseGeneratedOption.Identity)
.HasColumnType("int");
this.Property(x => x.Name);
this.Property(x => x.Age);
}
}
public class Student
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Age { get; set; }
public IList<Teacher> Teachers { get; set; }
}
}
Note:EF的实体到对象的映射有多种方式,最常用的是DataAnnotations数据注解以及Fluent API两种方式来编写映射。该例中的学生和老师属于多对多的关系,在使用Fluent API添加映射的时候只需要在对象的一端添加相互之间的多对多关系,因为此种关系要生成中间表所以要使用ToTable来指定中间表的表明,以及使用MapLeftKey和MapRightKey指定表的主键。
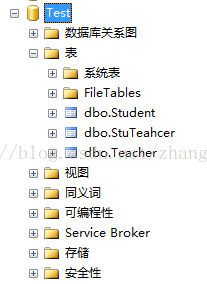
上面的代码就是远程端的主要代码,在运行代码后会在数据库中添加对应的表结构,开发时很简单,生成的数据库的表结构如下图所示:






















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








