我们知道Sentinel可以用来进行流量控制、线程隔离、降级等,那么一个请求进来,它是怎么做到的?
整体执行流程
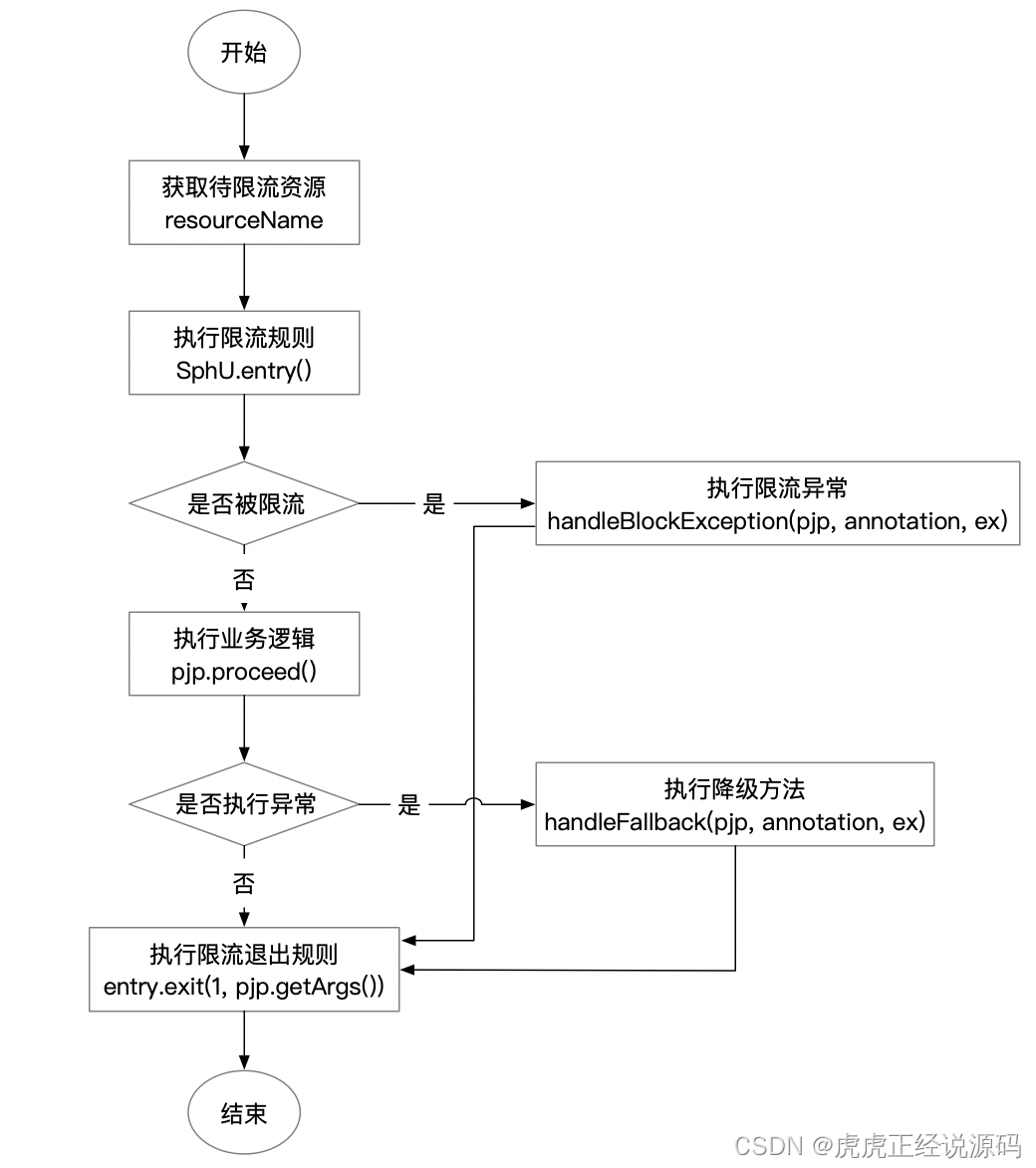
不管是通过注解方式给指定的方法进行代理,还是通过拦截的方式,Sentinel底层核心执行代码都是类似这样的。本次分享我们来关注下代理的方式,SentinelResourceAspect类的实现。
SentinelResourceAspect代码:
@Aspect
public class SentinelResourceAspect extends AbstractSentinelAspectSupport {
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.annotation.SentinelResource)")
public void sentinelResourceAnnotationPointcut() {
}
@Around("sentinelResourceAnnotationPointcut()")
public Object invokeResourceWithSentinel(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
Method originMethod = resolveMethod(pjp);
SentinelResource annotation = originMethod.getAnnotation(SentinelResource.class);
if (annotation == null) {
// Should not go through here.
throw new IllegalStateException("Wrong state for SentinelResource annotation");
}
// 获取需处理的资源,比如请求的url,方法名
String resourceName = getResourceName(annotation.value(), originMethod);
EntryType entryType = annotation.entryType();
int resourceType = annotation.resourceType();
Entry entry = null;
try {
// 核心处理逻辑在这里,流量控制、线程隔离、降级都在这里处理
entry = SphU.entry(resourceName, resourceType, entryType, pjp.getArgs());
// 处理业务逻辑
return pjp.proceed();
} catch (BlockException ex) {
// 处理被限流后的异常
return handleBlockException(pjp, annotation, ex);
} catch (Throwable ex) {
Class<? extends Throwable>[] exceptionsToIgnore = annotation.exceptionsToIgnore();
// The ignore list will be checked first.
if (exceptionsToIgnore.length > 0 && exceptionBelongsTo(ex, exceptionsToIgnore)) {
throw ex;
}
if (exceptionBelongsTo(ex, annotation.exceptionsToTrace())) {
traceException(ex);
// 降级后逻辑
return handleFallback(pjp, annotation, ex);
}
// No fallback function can handle the exception, so throw it out.
throw ex;
} finally {
if (entry != null) {
// 执行完毕,退出,将请求数、线程数等减一,如果是业务异常情况,会记录一次报错统计
entry.exit(1, pjp.getArgs());
}
}
}
}
执行流程图:
ProcessorSlot链
核心逻辑:
SphU.entry(resourceName, resourceType, entryType, pjp.getArgs());
这行代码底层会调用:
chain = SlotChainProvider.newSlotChain();
接着会调:
List<ProcessorSlot> sortedSlotList = SpiLoader.of(ProcessorSlot.class).loadInstanceListSorted();
该方法会以SPI的方式,把META-INF/services/目录下,以com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slotchain.ProcessorSlot命名的文件,把里面的类都加载出来。
默认有8个ProcessorSlot子类:
# Sentinel default ProcessorSlots
com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.nodeselector.NodeSelectorSlot
com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.clusterbuilder.ClusterBuilderSlot
com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.logger.LogSlot
com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.statistic.StatisticSlot
com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.authority.AuthoritySlot
com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.system.SystemSlot
com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.FlowSlot
com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.degrade.DegradeSlot
加载后会以注解@SPI的order大小进行排序,越小排在前面,顺序如图:
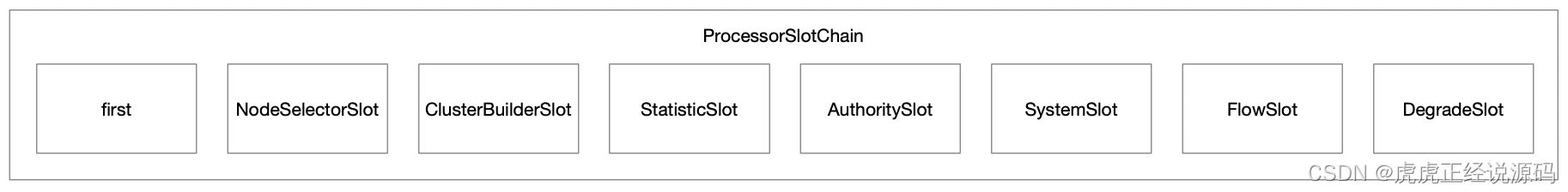
初始化slot链之后,会调用chain的entry方法,该方法会从first开始,一直调到链的end端,DegradeSlot。
chain.entry(context, resourceWrapper, null, count, prioritized, args);
一旦发生限流,会抛出异常BlockException。
执行结束并执行完业务逻辑,则会执行:
entry.exit(1, pjp.getArgs());
该方法同样也会以责任链的方式,从first开始一直到DegradeSlot,分别调用exit方法。






















 784
784











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








