出自——火哥
目录
1. 为什么要分词
1.1 中文分词的目的
让机器更好的“理解”文章。
1.2 英文天然分词,比中文更适合做相似度比对?
No,英文中每个单词包含很多不同的意思。
1.3 分词是越细越好吗?
视情况而定
搜索——>越细越好——>因为其比较注重召回
推荐——>粗一点好——>因为其更注重精准度(精准推荐),粒度粗有利于“保留语义”
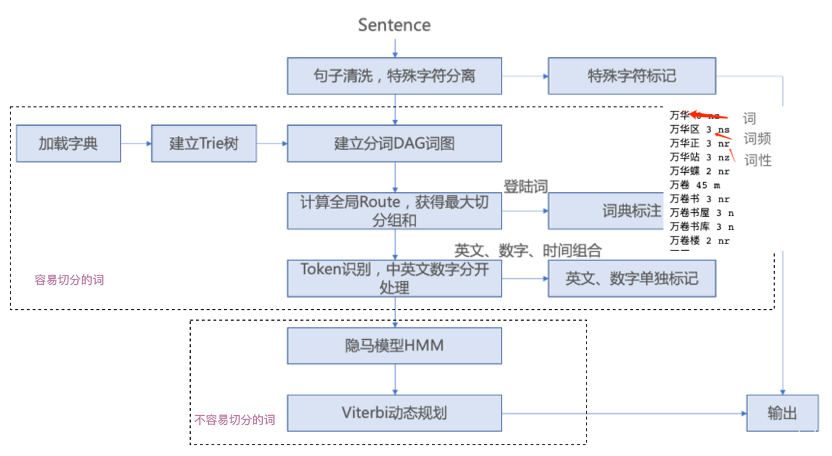
2. 怎么分词

里面涉及的一些算法:
容易切分的:用字典匹配,动态规划,vterbi算法
不容易切分的:隐马尔可夫模型
2.1 字典匹配
2.1.1前缀树
如下图所示,一共包含了8个键的trie结构:"A", "to", "tea", "ted", "ten", "i", "in", "inn".

详情见:https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trie
2.1.2字典匹配案例
词库为:北京,北京大学,大学生,生活,学生,中心,活动
需要切分的句子:北京大学生活动中心
(1) 将词库存到前缀树中:

(2) 正向匹配
计算词库中单词的最大长度maxLen。

“北京大学生活动中心”正向匹配的分词结果为:[北京大学,生活,动,中心]
(3) 反向匹配
正向匹配和反向匹配的原理相同,唯一不同的是,正向匹配是从左到右依次滑窗,反向匹配是从右向左依次滑窗。
“北京大学生活动中心”反向匹配的分词结果为:[北京,大学生,活动,中心]
2.1.3 字典匹配实现
下面是一个反向最大匹配的例子
import sys
WordDic = {}
MaxWordLen = 1
def LoadLexicon(lexiconFile):
global MaxWordLen
infile = open(lexiconFile, 'r', encoding='gb2312')
s = infile.readline().strip()
while len(s) > 0:
#s = s.decode("gb2312")
WordDic[s] = 1
if len(s) > MaxWordLen:
MaxWordLen = len(s)
s = infile.readline().strip()
infile.close()
def BMM(s):
global MaxWordLen
wordlist = []
i = len(s)
while i > 0:
start = i - MaxWordLen
if start < 0:
start = 0
while start < i:
tmpWord = s[start:i]
if tmpWord in WordDic:
wordlist.insert(0, tmpWord)
break
else:
start += 1
if start >= i:
wordlist.insert(0, s[i-1:i])
start = i - 1
i = start
return wordlist
def PrintSegResult(wordlist):
print("After word-seg:")
for i in range(len(wordlist)-1):
print(wordlist[i])
print(wordlist[len(wordlist)-1])
LoadLexicon("./lexicon.txt")
# inputStr = u"南京市长江大桥"
inputStr = u"北京大学生活动中心"
wordlist = BMM(inputStr)
PrintSegResult(wordlist)
其中BMM为Back Max Match,./lexicon.txt 为词库,比如:

正向匹配代码实现,待续:
Q:正向/反向匹配效果不好?
———主要是因为词库(lexicon)不好,词库准全的问题;
———用规则的方式永远也解决不了所有的问题。(那用什么来解决呢?)
Q:有两种切分方法,正向匹配:[北京大学,生活,动,中心],反向匹配:[北京,大学生,活动,中心], 到底用哪一个呢?机器怎么判断哪一个更好呢?
——使用概率语言模型
2.2概率语言模型
顾名思义:找概率最大方案。
2.2.1 概率语言模型的理论知识

其中C表示句子,S表示句子的切分方案。
P(C): 句子出现的概率,往往是常数。
P(C|S):在切分方案S的条件下,得到句子C的概率。为1,把切分方案S中的词拼到一起就是句子C了。
故:
![]()
其中假设: 句子中,每个词的出现独立同分布,所以:

Q:每个词出现的概率一般要怎么算呢?从哪里来呢?

Q:如果一个句子很长,切分出来了很多个词,且每个词的概率又不高,P(S)很小,向下溢出或是很难比较出两个方案的优劣(因为两个方案的P(S)很小,差0.00000000001,如果精度不够,可能就会认为两个方案是一样的?)
——万能的log登场

——使用log,一举两得
a. 防止最终结果向下溢出
b. 乘法变加法,计算速度更快
Q:句子中的词真的是独立同分布的吗?
No,实际中,独立性假设并不成立。
一元概率语言模型:我们上述的认为一个词的出现不依赖与它前面出现的词(即句子中的词是独立同分布的),叫做一元概率模型(Unigram),该模型只考虑了切分出的词数和词频。
二元概率语言模型:假设当前单词只与前一个单词有关

三元概率语言模型:假设当前单词只与前两个单词有关

……
N元概率语言模型:假设当前单词与前N个单词有关
2.2.2 概率语言模型的案例
接着2.1.2 的案例来说
词库为:北京,北京大学,大学生,生活,学生,中心,活动
需要切分的句子:北京大学生活动中心
现在有两种切分方案:
第一种正向匹配:[北京大学,生活,动,中心]
第二种反向匹配:[北京,大学生,活动,中心]
下面就可以用概率语言模型,来看一下,哪种方案更好:
P(S1) = P([北京大学,生活,动,中心]) = P(北京大学) * P(生活) * P(动)* P(中心)
P(S2) = P([北京,大学生,活动,中心]) = P(北京) * P(大学生) * P(活动)* P(中心)
2.3 viterbi算法
Viterbi算法是一种动态规划的算法。
想象一个乡村诊所。村民有着非常理想化的特性,要么健康要么发烧。他们只有问诊所的医生的才能知道是否发烧。 聪明的医生通过询问病人的感觉诊断他们是否发烧。村民只回答他们感觉正常、头晕或冷。
假设一个病人每天来到诊所并告诉医生他的感觉。医生相信病人的健康状况如同一个离散马尔可夫链。病人的状态有两种“健康”和“发烧”,但医生不能直接观察到,这意味着状态对他是“隐含”的。每天病人会告诉医生自己有以下几种由他的健康状态决定的感觉的一种:正常、冷或头晕。这些是观察结果。 整个系统为一个隐马尔可夫模型(HMM)。
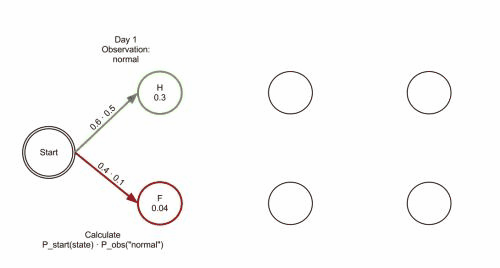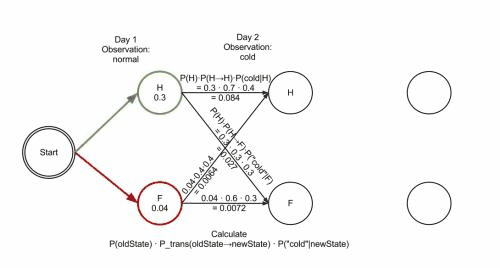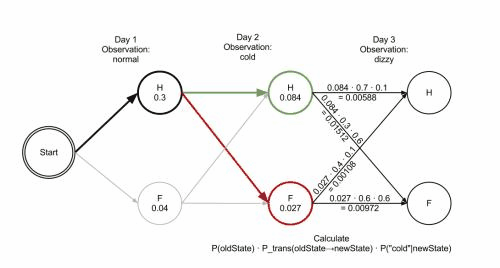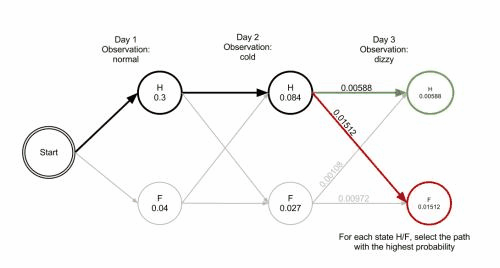
病人连续三天看医生,医生发现第一天他感觉正常,第二天感觉冷,第三天感觉头晕。 于是医生产生了一个问题:怎样的健康状态序列最能够解释这些观察结果。
维特比算法揭示了观察结果 ['normal', 'cold', 'dizzy'] 最有可能由状态序列 ['Healthy', 'Healthy', 'Fever']产生。 换句话说,对于观察到的活动, 病人第一天感到正常,第二天感到冷时都是健康的,而第三天发烧了。
维特比算法的计算过程可以直观地由格图表示。 维特比路径本质上是穿过格式结构的最长路径。 诊所例子的格式结构如下, 黑色加粗的是维特比路径:
2.3.1 viterbi算法解决什么问题
寻找最有可能产生观测时间序列的viterbi路径——隐含状态序列,特别是在马尔可夫信息源上下文和隐马尔可夫模型中。
用直白的话来说,就是寻找最优或概率最大的路径。

Q:遍历和 viterbi算法寻求最优路径的时间复杂度,why?viterbi算法的优点是什么?
2.3.2 viterbi算法在分词中的应用
给定一个句子的wordGraph,寻找最优路径

(1)通过遍历寻找最优路径。
(2)通过viterbi算法寻找最优路径,在level t+1重用t的结果。

一起用代码来用代码切分一下“容易切分”的词吧。(即句子wordGraph中的每个词都在词表中)
整体的代码逻辑如下所示:

createLexicon.py
import sys
rawDataFile = "./RenMinData.txt"
idDataFile = "./RenMinData.id.txt"
wordDicFile = "./WordDic.rm.txt"
WordIDTable = {}
id = 1
infile = open(rawDataFile, 'r', encoding='gb2312')
s = infile.readline().strip()
while len(s) > 0:
#s = s.decode("gb2312")
for word in s.split(' '):
if word not in WordIDTable:
WordIDTable[word] = id
id += 1
s = infile.readline().strip()
infile.close()
print("Reading raw data file finished!")
print("Total number of words:", len(WordIDTable))
infile = open(rawDataFile, 'r', encoding='gb2312')
outfile = open(idDataFile, 'w')
s = infile.readline().strip()
while len(s) > 0:
#s = s.decode("gb2312")
words = s.split(' ')
for i in range(len(words)-1):
word = words[i]
if word not in WordIDTable:
print("OOV word found!")
else:
outfile.write(str(WordIDTable[word]))
outfile.write(' ')
word = words[len(words)-1]
if word not in WordIDTable: # 未登录词
print("OOV word found!")
else:
outfile.write(str(WordIDTable[word]))
outfile.write("\r\n")
s = infile.readline().strip()
infile.close()
outfile.close()
print("Writing id data file finished!")
outfile = open(wordDicFile, 'w', encoding='gb2312')
for word in WordIDTable.keys():
# outfile.write(word.encode("gb2312"))
outfile.write(word)
outfile.write(' ')
outfile.write(str(WordIDTable[word]))
outfile.write("\r\n")
outfile.close()
print("Writing word id table file finished!")
BiLMTrain.py
import sys
idDataFile = "./RenMinData.id.txt"
wordDicFile = "./WordDic.rm.txt"
biModelFile = "./BiModel.rm.txt"
WordIDTable = {}
BigramTableList = [] # 一元概率模型
UnigramCountList = [] # 二元概率模型
SmoothedProbList = []
TotalNum = 0
# load wordDicFile to WordIDTable
infile = open(wordDicFile, 'r', encoding='gb2312')
s = infile.readline().strip()
while len(s) > 0:
#s = s.decode("gb2312")
words = s.split(' ')
if words[0] not in WordIDTable:
WordIDTable[words[0]] = int(words[1])
s = infile.readline().strip()
infile.close()
print("Reading word dic file finished!")
print("Total number of words:",len(WordIDTable))
# 初始化 BigramTableList UnigramCountList SmoothedProbList
lenWordIDTable = len(WordIDTable)
BigramTableList = [{} for _ in range(lenWordIDTable + 1)]
UnigramCountList = [0 for _ in range(lenWordIDTable + 1)]
SmoothedProbList = [0 for _ in range(lenWordIDTable + 1)]
infile = open(idDataFile, 'r')
s = infile.readline().strip()
while len(s) > 0:
words = s.split(' ')
widlist = []
TotalNum += len(words)
for word in words:
widlist.append(int(word))
for wordid in widlist:
UnigramCountList[wordid] += 1
for i in range(len(widlist)-1):
tmpHT = BigramTableList[widlist[i]]
if widlist[i+1] not in tmpHT:
tmpHT[widlist[i+1]] = 1
else:
tmpHT[widlist[i+1]] += 1
s = infile.readline().strip()
infile.close()
print("Reading id data file finished!")
#compute probabilities
for wid1 in range(1,len(WordIDTable)+1):
SmoothedProbList[wid1] = 1/(float)(UnigramCountList[wid1] + len(WordIDTable))
ht = BigramTableList[wid1]
for wid2 in ht.keys():
ht[wid2] = (float)(ht[wid2]+1) /(float)(UnigramCountList[wid1] + len(WordIDTable))
UnigramCountList[wid1] = (float)(UnigramCountList[wid1])/(float)(TotalNum)
#save to file
outfile = open(biModelFile, 'w')
outfile.write(str(len(WordIDTable))+" "+str(TotalNum)+"\r\n")
for wid1 in range(1,len(WordIDTable)+1):
outfile.write(str(UnigramCountList[wid1])+" ")
outfile.write(str(SmoothedProbList[wid1]))
ht = BigramTableList[wid1]
for wid2 in ht.keys():
outfile.write(" "+str(wid2)+" "+str(ht[wid2]))
outfile.write("\r\n")
outfile.close()
print("Writing model file finished!")
ViterbiCWS.py
viterbi算法的基本逻辑
BiModel.rm.txt(只择出来和“南京市长江大桥”有关的概率)

s1:createGraph
s2:利用viterbi算法搜索得到最优路径

# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import sys
import math
class Node:
def __init__(self, word):
self.bestScore = 0.0
self.bestPreNode = None
self.len = len(word)
self.word = word
class BiLM:
def __init__(self, WordDicFile, biLMFile):
self.wordNum = 0
self.wordIDTable = {}
self.unigramProb = []
self.bigramProb = []
self.unknownWordProb = 1.0
# load WordIDTable
infile = open(WordDicFile, 'r', encoding='gb2312')
sline = infile.readline().strip()
self.maxWordLen = 1
while len(sline) > 0:
# sline = sline.decode("gb2312")
items = sline.split(' ')
if len(items) != 2:
print("Lexicon format error!")
sline = infile.readline().strip()
continue
self.wordIDTable[items[0]] = int(items[1])
if len(items[0]) > self.maxWordLen:
self.maxWordLen = len(items[0])
sline = infile.readline().strip()
infile.close()
infile = open(biLMFile, 'r')
sline = infile.readline().strip()
items = sline.split(' ')
if len(items) == 2: # the first line
self.wordNum = int(items[0])
else:
print("Bad format found in LM file!")
sys.exit()
sline = infile.readline().strip()
# initialization unigramProb bigramProb
# load unigramProb bigramProb
lenWordIDTable = len(self.wordIDTable)
self.unigramProb = [0.0 for _ in range(lenWordIDTable + 1)]
self.bigramProb = [{} for _ in range(lenWordIDTable + 1)]
wid = 1
while len(sline) > 0:
items = sline.split(' ')
# self.unigramProb[wid] = float(items[1])
self.unigramProb[wid] = float(items[0])
i = 2
while i < len(items):
self.bigramProb[wid][int(items[i])] = float(items[i + 1])
i += 2
sline = infile.readline().strip()
wid += 1
infile.close()
print(len(self.wordIDTable), "words loaded")
def GetScoreBack(self, word1, word2):
wid1 = -1
wid2 = -1
if (word1 is not '' and word1 not in self.wordIDTable.keys())\
or word2 not in self.wordIDTable.keys():
print("word1 or word2 should be in wordIDTable. word1: %s, word2: %s" % (word1, word2))
sys.exit()
wid2 = self.wordIDTable[word2]
if wid2 not in self.bigramProb[wid1]:
return self.unigramProb[wid1]
return self.bigramProb[wid1][wid2]
def GetScore(self, word1, word2):
wid1 = -1
wid2 = -1
if word1 not in self.wordIDTable:
return self.unknownWordProb
wid1 = self.wordIDTable[word1]
if word2 not in self.wordIDTable:
return self.unigramProb[wid1]
wid2 = self.wordIDTable[word2]
if wid2 not in self.bigramProb[wid1]:
return self.unigramProb[wid1]
return self.bigramProb[wid1][wid2]
def CreateGraph(s):
# initializatioon WordGraph
WordGraph = [[] for _ in range(len(s) + 2)] # +2 is start and end Node
WordGraph[0] = [Node("")] # start Node
WordGraph[-1] = [Node("")] # end Node
# Other nodes
for i in range(len(s)):
j = myBiLM.maxWordLen
if i + j > len(s):
j = len(s) - i
while j > 0:
if s[i:i + j] in myBiLM.wordIDTable:
newNode = Node(s[i:i + j])
WordGraph[i + j].append(newNode)
j -= 1
if len(WordGraph[i + 1]) < 1: # why?
print("Unknown character found!", i, s[i])
sys.exit()
return WordGraph
def ViterbiSearch(WordGraph):
for i in range(len(WordGraph) - 1):
for curNode in WordGraph[i + 1]:
if curNode.len == 0:
preLevel = i
else:
preLevel = i + 1 - curNode.len # the level of the previous word. eg"南","南京市"的前一个leval为0,"市长"的前一个level为2
if preLevel < 0:
print("running error!")
sys.exit()
preNode = WordGraph[preLevel][0]
score = myBiLM.GetScore(preNode.word, curNode.word)
score = preNode.bestScore + math.log(score)
maxScore = score
curNode.bestScore = score
curNode.bestPreNode = preNode
for j in range(1, len(WordGraph[preLevel])):
preNode = WordGraph[preLevel][j]
score = myBiLM.GetScore(preNode.word, curNode.word)
score = preNode.bestScore + math.log(score)
if score > maxScore:
curNode.bestScore = score
curNode.bestPreNode = preNode
def BackSearch(WordGraph):
resultList = []
curNode = WordGraph[len(WordGraph) - 1][0].bestPreNode
while curNode.bestPreNode != None:
resultList.insert(0, curNode.word)
curNode = curNode.bestPreNode
return resultList
WordDicFile = "./WordDic.rm.txt"
BiLMFile = "./BiModel.rm.txt"
myBiLM = BiLM(WordDicFile, BiLMFile)
inputStr = u"南京市长江大桥"
WordGraph = CreateGraph(inputStr)
for NodeList in WordGraph:
for Node in NodeList:
print("CurNode Word: ", Node.word)
ViterbiSearch(WordGraph)
resultList = BackSearch(WordGraph)
for word in resultList:
print(word, '')
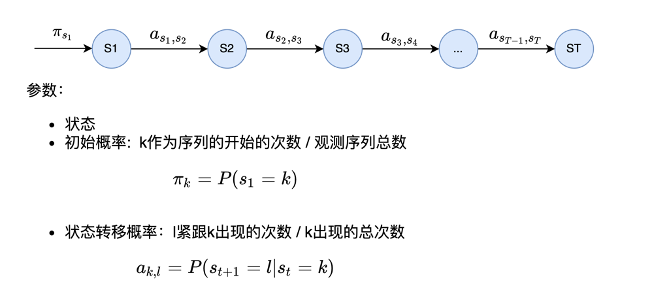
2.4 马尔可夫模型
每个状态只依赖之前有限个状态
- N阶马尔可夫:依赖之前n个状态 <——> N元概率模型
- 1阶马尔可夫:仅仅依赖前一个状态<——>1元概率模型
如下为1阶马尔可夫:
2.4.1 马尔科夫模型能解决什么问题
可以解决句子生成,文章生成
比如要生成句子——今天我写了一个程序
w1=今天,w2=我,w3=写,w4=了,w5=一个,w6=程序
p(w1=今天,w2=我,w3=写,w4=了,w5=一个,w6=程序)
=p(w1=今天)p(w2=我|w1=今天)p(w3=我|w2=今天)……p(w6=程序|w5=一个)
2.4.2 马尔科夫的局限性——不能解决什么问题
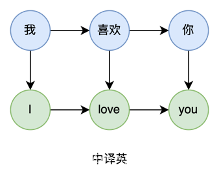
马尔可夫模型不能解决双序列问题
(1)机器翻译:源语言序列 <--> 目标语言序列
比如,中文译为英文
(2)语音识别:语音信号序列 <--> 文字序列
(3)词性标注:文字序列 <--> 词性序列
写 / 一个 / 程序
Verb / Num / Noun
(4)拼音纠错:原始文字序列 <--> 纠正过的文字序列
自己的事情自己坐
自己的事情自己做
Q:那怎么解决这些双序列问题?
隐马尔科夫模型。
2.5隐马尔可夫模型
Q:怎样判断我这词该分不该分呢?就是启动用HMM切分“未登录词”的条件是什么?
容易切分的词已经用字典匹配,匹配上了,剩下的就是不容易切分的词(即未登录词),把剩下的这部分词再放HMM里面看其是否需要被切分。
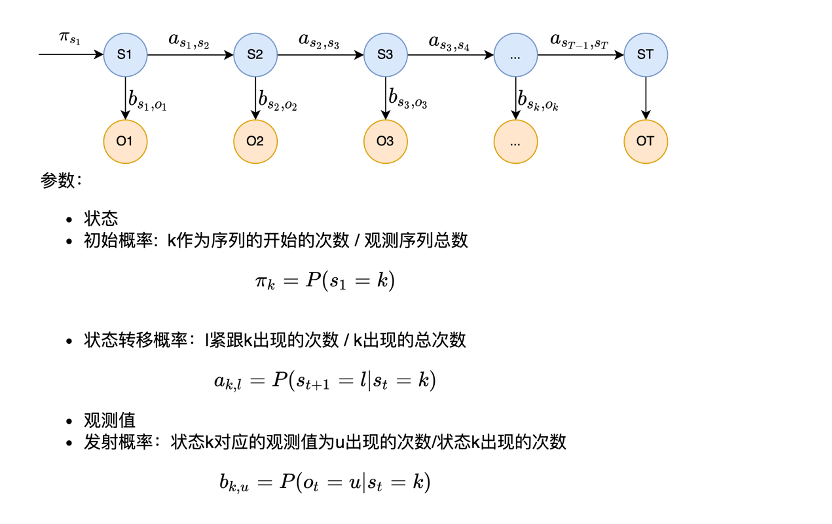
用一句话来描述HMM:
先完成第一状态,然后依次由当前状态生成下一状态,最后每个状态发射出一个观测值
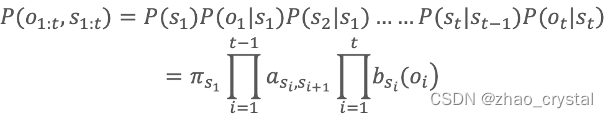
2.5.1 HMM参数的计算
HMM的参数,初始概率,状态转移概率,发射概率需要计算,观测值直接观测得到。
假设中译英的场景。
Q:在中译英的场景中,谁是观测序列,谁是状态序列?
中文是观测序列,英文是状态序列。
首先找语料库(一堆中英文对照的文章)
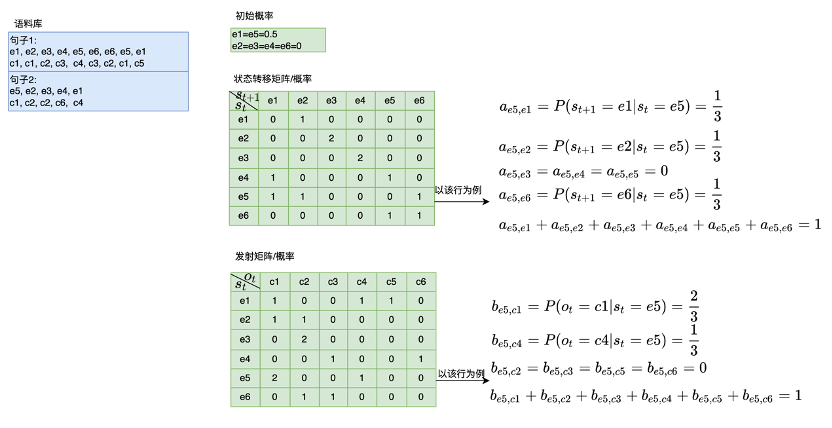
2.5.2 HMM解决不容易切分的词
HMM就是“胶水”,看哪些字可以“粘”在一起,变成词。
假设“广州塔”词表中没有,那他到底是一个词还是可以再切分出多个词呢?
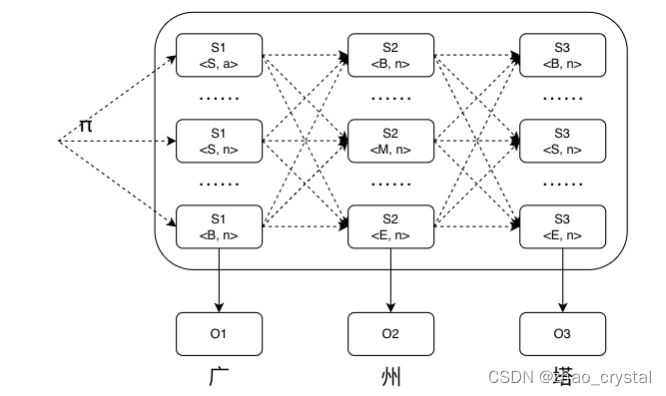
其中,每个字均用<位置,词性>来表示
- BEMS表示位置信息:B(开头)、M(中间)、E(结尾)、S(独立成词)
- 词性:n(名词)、nr(人名)、ns(地名)、v(动词)
中文分词词性对照表
中文分词词性对照表_kevin_darkelf的博客-CSDN博客_词性对照表
最终得到的状态序列为<B,n><M,n><E,n>,即表示“广州塔”是一个词。
最终得到的状态序列为<B,n><E,n><S,n>,即表示“广州塔”分为“广州/塔”。
对于HMM的应用,最典型的就属给定O,找到最优的S
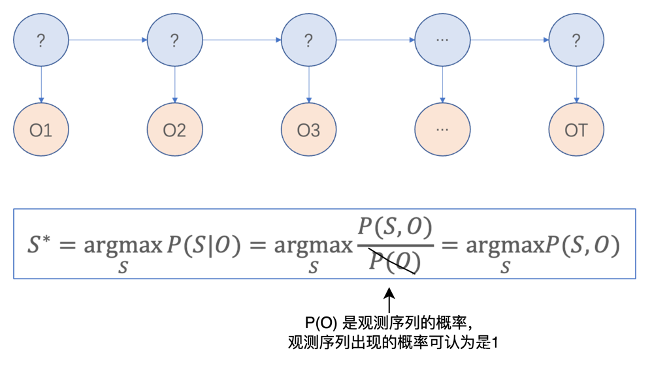
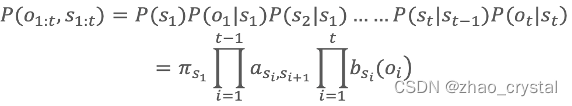
即S,O联合概率最大的状态(S序列),即我们想要的状态(S序列)。
Q:怎样找出来最优的S呢?
S1: 首先需要得到HMM模型中的初始概率,状态转移概率,发射概率。
S2:用voterbi算法得到最优的路径S
3. jieba分词——常用的中文分词工具
jieba分词GitHub - fxsjy/jieba: 结巴中文分词
和我们上面章节讲的分词思路是一致的























 1589
1589











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








