iOS页面间传值的方式(NSUserDefault/Delegate/NSNotification/Block)
实现了以下iOS页面间传值:1.委托delegate方式;2.通知notification方式;3.block方式;4.UserDefault或者文件方式;5.单例模式方式;6.通过设置属性,实现页面间传值
在iOS开发中,我们经常会遇到页面间跳转传值的问题,现归纳总结一下:
情况1:A页面跳转到B页面
方法:
在B页面的控制器中,编写对应的属性,在A页面跳转到B页面的地方,给B的属性赋值即可
在A页面的试图控制器中
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
- (IBAction)showSecondView:(id)sender {
SecondViewController *second = [[SecondViewController alloc] initWithNibName:@
"SecondViewController"
bundle:nil];
second.delegate = self;
second.flag = 0;
[self presentViewController:second animated:YES completion:nil];
}
|
情况2:A页面跳转到B页面,B页面再跳转回A页面
主流方案:
(1)通过委托delegate的方式实现
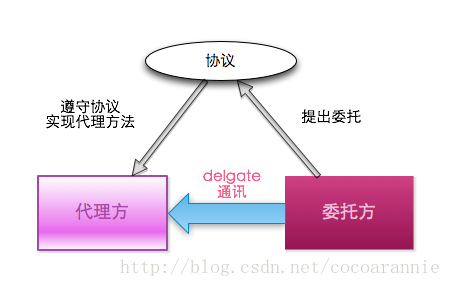
|
1
|
|
|
1
|
//SecondViewController.h
|
|
1
2
3
|
@protocol secondViewDelegate
-(
void
)showName:(NSString *)nameString;
@end
|
设置代理(为防止循环引用,此次采用了weak)
|
1
|
|
|
1
|
//SecondViewController.h
|
|
1
2
3
4
|
@interface SecondViewController : UIViewController
@property (nonatomic, weak)id<secondViewDelegate> delegate;
@property (nonatomic, copy) a<span id=
"0_nwp"
style=
"width: auto; height: auto; float: none;"
><a id=
"0_nwl"
href=
"http://cpro.baidu.com/cpro/ui/uijs.php?rs=1&u=http%3A%2F%2Fwww%2Edaxueit%2Ecom%2Farticle%2F4452%2Ehtml&p=baidu&c=news&n=10&t=tpclicked3_hc&q=00007110_cpr&k=block&k0=block&k1=%C8%ED%BC%FE&k2=%C8%ED%BC%FE%BF%AA%B7%A2&k3=%C6%BB%B9%FB&k4=%CF%B5%CD%B3&k5=ios&sid=61490806c97ccfdf&ch=0&tu=u1704338&jk=1edcfcd1d0eed3ba&cf=29&fv=16&stid=9&urlid=0&luki=3&seller_id=1&di=128"
target=
"_blank"
mpid=
"0"
style=
"text-decoration: none;"
><span style=
"color:#0000ff;font-size:14px;width:auto;height:auto;float:none;"
>block</span></a></span> block;
@end
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
//SecondViewController.m
- (IBAction)delegateMethod:(id)sender {
if
([self notEmpty]) {
[self.delegate showName:self.nameTextField.text];
[self dismissViewControllerAnimated:YES completion:nil];
}
else
{
[self showAlert];
}
}
|
调用,显示
|
1
2
3
4
|
//RootViewController.m
-(
void
)showName:(NSString *)nameString{
self.nameLabel.text = nameString;
}
|
(2)通过通知notification的方式实现
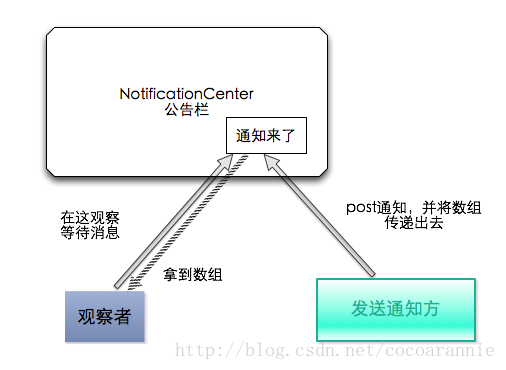
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
//SecondViewController.m
- (IBAction)notificationMethod:(id)sender {
if
([self notEmpty]) {
[[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter] postNotificationName:@
"ChangeNameNotification"
object:self userInfo:@{@
"name"
:self.nameTextField.text}];
[self dismissViewControllerAnimated:YES completion:nil];
}
else
{
[self showAlert];
}
}
|
在A页面的控制器中,注册通知:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
//RootViewController.m
- (
void
)viewDidLoad
{
[super viewDidLoad];
// Do any additional setup after loading the view from its nib.
[[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter] addObserver:self selector:@selector(ChangeNameNotification:) name:@
"ChangeNameNotification"
object:nil];
}
|
当我们不使用时,要记得删掉通知:
|
1
2
3
4
|
//RootViewController.m
-(
void
)dealloc{
[[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter] removeObserver:self];
}
|
调用,显示
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
//RootViewController.m
-(
void
)ChangeNameNotification:(NSNotification*)notification{
NSDictionary *nameDictionary = [notification userInfo];
self.nameLabel.text = [nameDictionary objectForKey:@
"name"
];
}
|
(3)block方式实现
分析:
在B试图控制器中,定义一个block,参数为字符串
|
1
2
|
//SecondViewController.h
typedef
void
(^ablock)(NSString *str);
|
|
1
2
3
|
//SecondViewController.h
@property (nonatomic, copy) ablock block;
|
在B试图控制器中,
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
- (IBAction)blockMethod:(id)sender {
if
([self notEmpty]) {
if
(self.block) {
self.block(self.nameTextField.text);
[self dismissViewControllerAnimated:YES completion:nil];
}
}
else
{
[self showAlert];
}
}
|
在A试图显示,回调block
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
- (IBAction)showSecondWithBlock:(id)sender {
SecondViewController *second = [[SecondViewController alloc] initWithNibName:@
"SecondViewController"
bundle:nil];
[self presentViewController:second animated:YES completion:nil];
second.block = ^(NSString *str){
self.nameLabel.text = str;
};
}
|
链接一篇描述block回调挺有意思的文章:http://blog.csdn.net/mobanchengshuang/article/details/11751671
在查阅资料的过程中,我还看到了以下几种方案:
(1)使用SharedApplication,定义一个变量来传递(感觉和单例的方式一样)
(2)使用文件,或者NSUserdefault来传递
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
//通过文件或者UserDefault方式存值(感觉不太适合此类传值,如果要用文件或者UserDefault方式存值的话,可以考虑此方式)
- (IBAction)userDefaultMethod:(id)sender {
if
([self notEmpty]) {
[[NSUserDefaults standardUserDefaults] setObject:self.nameTextField.text forKey:@
"myNameText"
];
[self dismissViewControllerAnimated:YES completion:nil];
}
else
{
[self showAlert];
}
}
|
在A试图控制器显示
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
-(
void
)viewDidAppear:(
BOOL
)animated{
[super viewDidAppear:animated];
//如果想测试通过UserDefault方式传值或者通过单例方式传值,取消以下注释即可
/*
if ([[[NSUserDefaults standardUserDefaults] objectForKey:@"myNameText"] length] != 0) {
self.nameLabel.text = [[NSUserDefaults standardUserDefaults] objectForKey:@"myNameText"];
[[NSUserDefaults standardUserDefaults] setObject:@"" forKey:@"myNameText"];
}
DataSource *dataSource = [DataSource sharedDataSource];
if ([dataSource.myName length] != 0) {
self.nameLabel.text = dataSource.myName;
dataSource.myName = @"";
}
*/
}
|
(3)通过一个单例的class来传递
B试图控制器
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
//通过单例方式传值(感觉不太适合此类传值,如果要用单例方式传值的话,可以考虑此方式)
- (IBAction)singletonMethod:(id)sender {
if
([self notEmpty]) {
DataSource *dataSource = [DataSource sharedDataSource];
dataSource.myName = self.nameTextField.text;
[self dismissViewControllerAnimated:YES completion:nil];
}
else
{
[self showAlert];
}
}
|
A试图控制器显示
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
-(
void
)viewDidAppear:(
BOOL
)animated{
[super viewDidAppear:animated];
//如果想测试通过UserDefault方式传值或者通过单例方式传值,取消以下注释即可
/*
if ([[[NSUserDefaults standardUserDefaults] objectForKey:@"myNameText"] length] != 0) {
self.nameLabel.text = [[NSUserDefaults standardUserDefaults] objectForKey:@"myNameText"];
[[NSUserDefaults standardUserDefaults] setObject:@"" forKey:@"myNameText"];
}
DataSource *dataSource = [DataSource sharedDataSource];
if ([dataSource.myName length] != 0) {
self.nameLabel.text = dataSource.myName;
dataSource.myName = @"";
}
*/
}
@end
|
这里面用到了单例模式,编写了DataSource这个类,存放数据
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
//
// DataSource.h
// TestCallBack
//
// Created by csdc-iMac on 14-12-24.
// Copyright (c) 2014年 赵黛阳. All rights reserved.
//
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
@interface DataSource : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSString *myName;
+(DataSource*)sharedDataSource;
@end
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
//
// DataSource.m
// TestCallBack
//
// Created by csdc-iMac on 14-12-24.
// Copyright (c) 2014年 赵黛阳. All rights reserved.
//
#import "DataSource.h"
@implementation DataSource
+(DataSource *)sharedDataSource{
static
DataSource *dataSource = nil;
static
dispatch_once_t once;
dispatch_once(&once, ^{
dataSource = [DataSource
new
];
});
return
dataSource;
}
@end
|
























 4万+
4万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








