Android studio提供了简单的测试,你可以测试JUnit(在jvm测试)或者进行仪器测试(真机或者虚拟器),你也可以扩展你的测试能力,比如使用Mockito来测试Android的api在unit tests,或者使用Espresso 或者UI Automator模拟用户操作在仪器测试中。
本文章主要来说JUnit测试。
测试类型
Local unit tests
位于 src/test/java
运行在JVM中,测试没有依赖于Android framework
Instrumentd tests
位于 src/androidTest/java
创建一个测试
local unit test
第一步:创建
java 类
public class User {
private String userName;
private int userAge;
private User() {
}
public User(String userName, int userAge) {
this.userAge = userAge;
this.userName = userName;
}
public void setUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
}
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
public void setUseAge(int userAge) {
this.userAge = userAge;
}
public int getUserAge() {
return userAge;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"userName='" + userName + '\'' +
", userAge=" + userAge +
'}';
}
}第二步,选择User ctrl+shift+t 创建test,生成目录src/test/java
public class UserTest {
private User user;
@Before
public void setUp() throws Exception {
user = new User("Rrtoyewx", 21);
}
@After
public void tearDown() throws Exception {
System.out.println(user.toString());
}
@Test
public void testSetUserName() throws Exception {
user.setUserName("xu");
assertTrue(user.getUserName().equals("xu"));
}
@Test
public void testSetUseAge() throws Exception {
user.setUseAge(17);
assertEquals(17, user.getUserAge(), 0);
}
}
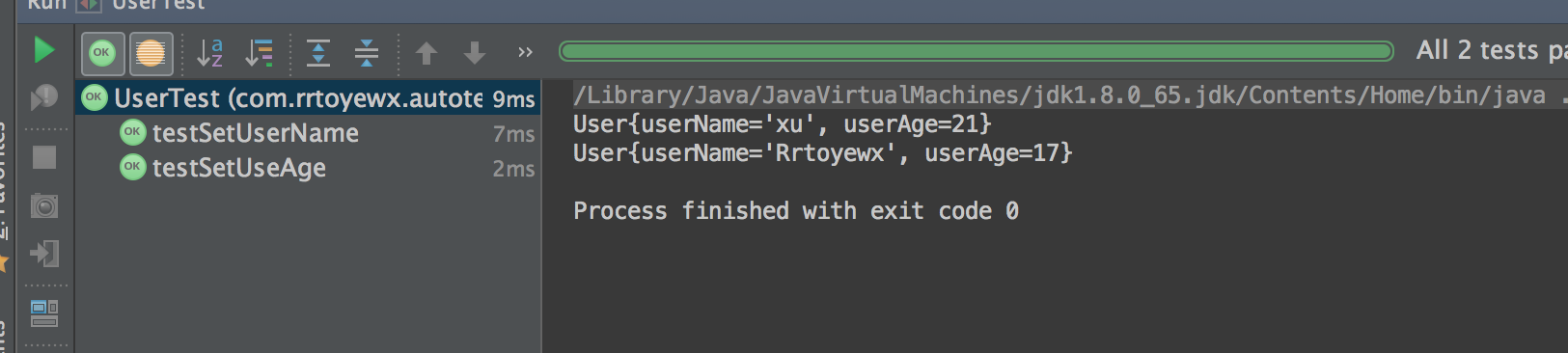
第三步:运行
- @Before test之前会调用
- @After test之后会调用
- @Test 每个test互不干扰,即test完之后执行下一个test,执行顺序依此为before test1 after before test2 after
- @BeforeClass:只加载一次
- @AfterClass:只加载一次
- Assert类提供较多验证操作,可以使用hamcrest 增加更多的验证运算符
比如下面的三个操作是一样的
assertTrue(user.getUserName().equals("xu"));
assertThat(user.getUserName(),is("xu"));
assertThat(user.getUserName(),equalTo("xu"));
顺便粘一张hamcrest的操作符
Mockito
@RunWith(MockitoJUnitRunner.class)学习网站
opearator
verify :Once created, a mock will remember all interactions. Then you can selectively verify whatever interactions you are interested in.
stubbing:
when(mock.someMethod).thenReturn()
By default, for all methods that return a value
数据类型 返回值 collection null int/integer 0 boolean/Boolean false Stubbing can be overridde
- Once stubbed, the method will always return a stubbed value, regardless of how many times it is called.
- Last stubbing is more important
Argument matchers
//any
anyInt();
anyBoolean();
anyXxx();
//custome mathcher
argThat(customeMathcher);
//eq
eq()- if you are using argument matchers, all arguments have to be provided by matchers.
Verifying exact number of invocations
vertify(mock,invocations)
//never
never()
//atLeast
atLeast()
//atMost
atMost()
//times
times();-times(1) is the default;
Stubbing void methods with exceptions
doThrow(Exception e).when(mock).someMethod();
when(mock).someMethod().thenThrow(Exception e);
Verification in order
//single
mock.doFirstSomeMethod();
InOrder order = inOrder(mock);
order.veritfy(mock).doFirstSomeMethod();
//multiple
mock1.doFirstSomeMethod();
mock2.doSecondSomeMethod();
InOrder order = inOrder(mock1,mock2);
order.veritfy(mock1).doFirstSomeMethod();
order.veritfy(mock2).doSecondSomeMethod();Making sure interaction(s) never happened on mock
//times/invocations
verify(mock,never()).someMethod
//never interactions
verifyZeroInteractions(mock...);
Finding redundant invocations
mock.someMethod("1");
//mock.someMethod("1")
mock.someMethod("2")
verify(mock).someMethod("1")
vertify(mock).someMethod("2")
verifyNoMoreInteractions(mock);
@mock
Stubbing consecutive calls
when(mock.someMethod()).thenReturn(1,2,3,4);
mock.someMethod(); // 1
mock.someMethod(); // 2
mock.someMethod(); // 3
mock.someMethod(); // 4
mock.someMethod(); // 4
mock.someMethod(); // 4 Stubbing with callbacks
public interface Answer<T> {
T answer(InvocationOnMock invocation) throws Throwable;
}
when(mock.someMethod()).thenAnswer(new Answner())
when do void method(),doReturn|doThrow()|doAnswer()|doNothing()|doCallRealMethod
doXxx().when(mock).someMethod();
doReturn() //return value;
doThrow() //throw exception;
doAnswer() //callBack
doNothing() //doNothing
doCallRealMethod() // mock 对应的队形mockObject.someMethod()
doXxx().doXxx().doXxx().when(mock).someMethod();Spying on real objects
Object object = new Object();
Spy spy = spy(object);
spy.add()
vertity(spy).add()
- spy named “partial mocking”;
- spy :can throw Exception when studding, Therefore when using spies please consider doReturn|Answer|Throw() family of methods for stubbing
Changing default return values of unstubbed invocations (1.7)
mock = mock(Object.class,Mockito.RETURNS_SMART_NULLS);
mock = mock(Object.class ,new CustomerAnsewer());
// Mockito.RETURNS_SMART_NULLS :If your code uses the object returned by an unstubbed call you get a NullPointerException. This implementation of Answer returns SmartNull instead of null. SmartNull gives nicer exception message than NPE because it points out the line where unstubbed method was called.
// CustomerAnsewerCapturing arguments for further assertions(1.8)
mock.someMethod(argument);
vertify(mock).someMethod(argument);
ArgumentCaptor<Argument> argumentCapture = ArgumentCaptor.forClass(Argument.class);
vertify(mock).someMethod(argumentCapture.capture());
assert();timeout/reset
总结
一般使用JUnit来测试一些功能性的代码,比如验证等操作,它不能使用Android Api,除非使用Mockito 来mock一些非必要在仪器上才能进行的测试。比如说sharePerference,Sqlite等一些操作。
另外功能测试尽量小,测试的功能越小,越容易定为哪儿出了问题。






















 1552
1552

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








