1.CountDownLatch
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
/**
* @author zj
* 用给定的计数 初始化 CountDownLatch。由于调用了 countDown() 方法,所以在当前计数到达零之前,await 方法会一直受阻塞。
*
* CountDownLatch犹如倒计时计数器,调用CountDownLatch对象的countDown方法就将计数器减1,当计数器到达0时,
* 则所有等待者开始执行。
*
* 下面的示例:
* 裁判员一声口令,运动员同时开始奔跑;所有运动员跑到终点,裁判才可以公布结果
*/
public class CountDownLatchDemo {
public static void main(String[] args){
ExecutorService threadPool=Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
final CountDownLatch cdOrder=new CountDownLatch(1);
final CountDownLatch cdAnswer=new CountDownLatch(3);
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
Runnable r=new Runnable(){
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("线程"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"正准备接受命令");
try {
cdOrder.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("线程"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"已接受命令");
//处理命名
try {
Thread.sleep((long) (Math.random()*10000));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("线程"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"回应命令处理结果");
cdAnswer.countDown();
}
};
threadPool.execute(r);
}
try {
Thread.sleep((long) (Math.random()*10000));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("线程"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"即将发布命令");
cdOrder.countDown();
System.out.println("线程"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"已经发送命令,正在等待结果.....");
try {
cdAnswer.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("线程"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"收到处理结果,程序结束......");
threadPool.shutdown();
}
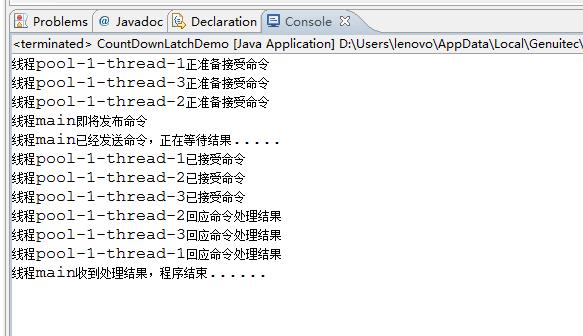
}运行结果如下:
2. CyclicBarrier
import java.util.concurrent.BrokenBarrierException;
import java.util.concurrent.CyclicBarrier;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
/**
* @author zj
* 一个同步辅助类,它允许一组线程互相等待,直到到达某个公共屏障点 (common barrier point)。
* 在涉及一组固定大小的线程的程序中,这些线程必须不时地互相等待,此时 CyclicBarrier 很有用。
* 因为该 barrier 在释放等待线程后可以重用,所以称它为循环 的 barrier。
*
*/
public class CyclicBarrierDemo {
public static void main(String[] args){
ExecutorService threadPool=Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
final CyclicBarrier cb=new CyclicBarrier(3);
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
Runnable r=new Runnable(){
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep((long) (Math.random()*10000));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("线程"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"即将到达集合地点1,当前已有"+(cb.getNumberWaiting()+1)+"个到达,"+(cb.getNumberWaiting()==2?"都到齐了,继续走啊":"正在等候"));
try {
cb.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (BrokenBarrierException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
Thread.sleep((long) (Math.random()*10000));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("线程"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"即将到达集合地点2,当前已有"+(cb.getNumberWaiting()+1)+"个到达,"+(cb.getNumberWaiting()==2?"都到齐了,到达目的地,结束.....":"正在等候"));
try {
cb.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (BrokenBarrierException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
threadPool.execute(r);
}
threadPool.shutdown();
}
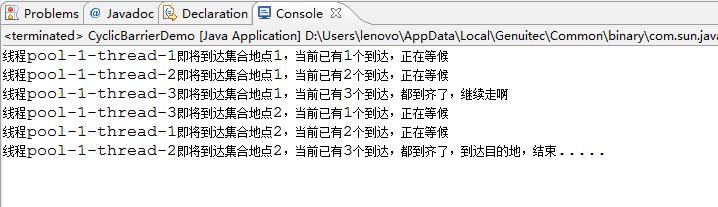
}运行结果如下:
3. Exchanger
import java.util.concurrent.Exchanger;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
/**
* @author zj
*
* Exchanger用于实现两个人之间的数据交换,每个人在完成一定的事物后想与对方交换数据,第一个先拿出数据的人将
* 一直等待第二个人拿着数据来到时,才能彼此交换数据。
*
*/
public class ExchangerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService threadPool=Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
final Exchanger exchanger=new Exchanger();
Runnable r1=new Runnable(){
@Override
public void run() {
String data1="Elana";
try {
Thread.sleep((long) (Math.random()*10000));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("线程"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"正准备把数据"+data1+"换出去");
try {
String data2=(String) exchanger.exchange(data1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("线程"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"换回的数据为"+data1);
}
};
Runnable r2=new Runnable(){
@Override
public void run() {
String data2="Damon";
try {
Thread.sleep((long) (Math.random()*10000));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("线程"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"正准备把数据"+data2+"换出去");
try {
String data1=(String) exchanger.exchange(data2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("线程"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"换回的数据为"+data2);
}
};
threadPool.execute(r1);
threadPool.execute(r2);
threadPool.shutdown();
}
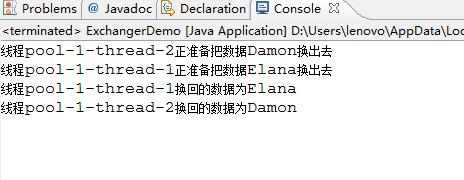
}运行结果如下:





















 468
468











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








