MybatisPlus
MyBatisPlus在mapper层可以完成所有CRUD代码,不在需要手写mapper.xml文件,节省大量时间
MyBatisPlus、JPA、tk-mapper
简介
是什么?
MyBatis-Plus (opens new window)(简称 MP)是一个 MyBatis (opens new window)的增强工具,在 MyBatis 的基础上只做增强不做改变,为简化开发、提高效率而生。
官网:MyBatis-Plus (baomidou.com)


特性
- 无侵入:只做增强不做改变,引入它不会对现有工程产生影响,如丝般顺滑
- 损耗小:启动即会自动注入基本 CURD,性能基本无损耗,直接面向对象操作
- 强大的 CRUD 操作:内置通用 Mapper、通用 Service,仅仅通过少量配置即可实现单表大部分 CRUD 操作,更有强大的条件构造器,满足各类使用需求
- 支持 Lambda 形式调用:通过 Lambda 表达式,方便的编写各类查询条件,无需再担心字段写错
- 支持主键自动生成:支持多达 4 种主键策略(内含分布式唯一 ID 生成器 - Sequence),可自由配置,完美解决主键问题
- 支持 ActiveRecord 模式:支持 ActiveRecord 形式调用,实体类只需继承 Model 类即可进行强大的 CRUD 操作
- 支持自定义全局通用操作:支持全局通用方法注入( Write once, use anywhere )
- 内置代码生成器:采用代码或者 Maven 插件可快速生成 Mapper 、 Model 、 Service 、 Controller 层代码,支持模板引擎,更有超多自定义配置等您来使用(自动生成代码)
- 内置分页插件:基于 MyBatis 物理分页,开发者无需关心具体操作,配置好插件之后,写分页等同于普通 List 查询
- 分页插件支持多种数据库:支持 MySQL、MariaDB、Oracle、DB2、H2、HSQL、SQLite、Postgre、SQLServer 等多种数据库
- 内置性能分析插件:可输出 SQL 语句以及其执行时间,建议开发测试时启用该功能,能快速揪出慢查询
- 内置全局拦截插件:提供全表 delete 、 update 操作智能分析阻断,也可自定义拦截规则,预防误操作
快速上手mybatisplus
官方文档:简介 | MyBatis-Plus (baomidou.com)
使用第三方组件通用步骤:
1、导入对应的依赖
2、研究依赖如何编写
3、代码如何编写
4、提升扩展(依据官网文档)
步骤
1 创建mybatis_plus数据库
2 创建user表
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS user;
CREATE TABLE user
(
id BIGINT(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '主键ID',
name VARCHAR(30) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '姓名',
age INT(11) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '年龄',
email VARCHAR(50) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '邮箱',
PRIMARY KEY (id)
);
-- 真实开发中,version(乐观锁)、deleted(逻辑删除,不是真正删除)、gmt_create(创建时间)、gmt_modified
-- 数据
INSERT INTO user (id, name, age, email) VALUES
(1, 'Jone', 18, 'test1@baomidou.com'),
(2, 'Jack', 20, 'test2@baomidou.com'),
(3, 'Tom', 28, 'test3@baomidou.com'),
(4, 'Sandy', 21, 'test4@baomidou.com'),
(5, 'Billie', 24, 'test5@baomidou.com');
3 编写项目
导入依赖
<!--mybatisplus 是自己开发的,并非官方的-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.0.5</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2database</groupId>
<artifactId>h2</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
注意:尽量不要同时导入mybatis和mybatis-plus。只需导入mybatis-plus即可
4 连接数据库!这一步和mybatis相同,都是在application配置文件中写
#配置MySQL
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=123456
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?serverTimezone=UTC&useSSL=false&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
5
传统方式:model-mapper接口(连接mybats,配置mapper.xml文件)-service-ctrl
使用mybatis-plus:model-mapper接口(不用写mapper.xml文件)-service-ctrl
mapper接口只需继承BaseMapper接口
// mapper继承mybatisplus的BaseMapper就行,BaseMapper中写好了CRUD,mapper继承后只需拿过来用就行了
//但我们也同样可以编写我们自己的扩展方法
@Mapper
public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper<User> {
//所有的CRUD操作已编写完成
}
注意点:需要在主启动类上扫描我们mapper(如下代码所示)@MapperScan("com.zhou.mapper")
@MapperScan("com.zhou.mapper")//扫描mapper包
@SpringBootApplication
public class Demo1Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Demo1Application.class, args);
}
}
测试类中测试
@SpringBootTest
class Demo1ApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Test
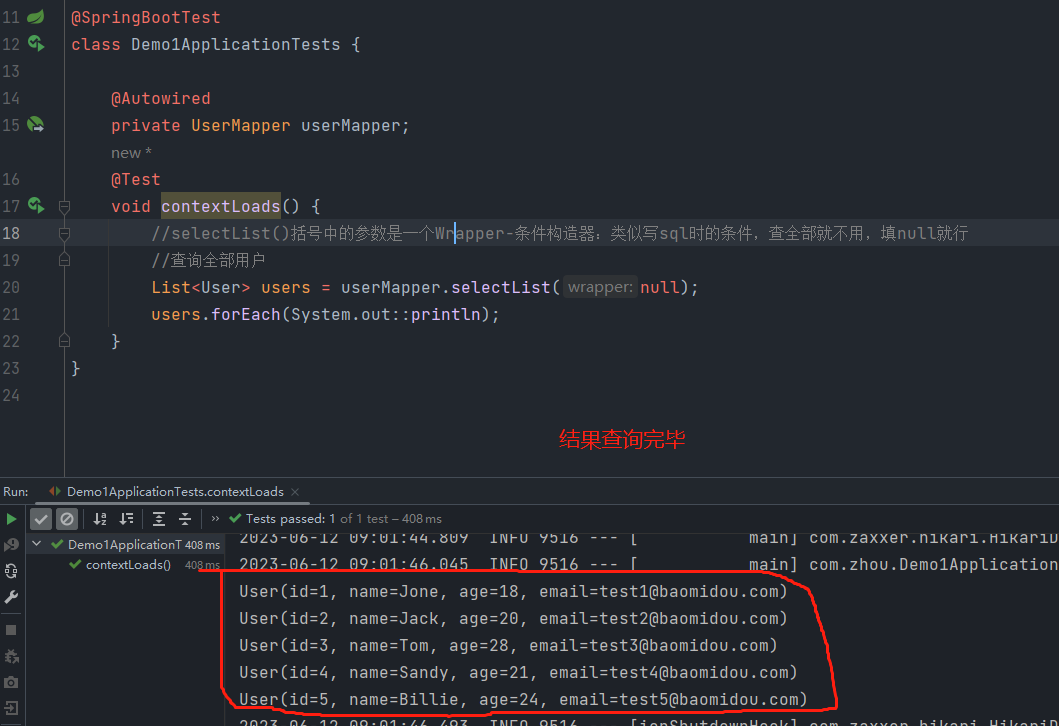
void contextLoads() {
//selectList()括号中的参数是一个Wrapper-条件构造器:类似写sql时的条件,查全部就不用,填null就行
//查询全部用户
List<User> users = userMapper.selectList(null);
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
思考问题?
1 SQL语句谁帮我们写的? 答:Mybatis-plus
2 方法哪里来的?答:Mybatis-plus
配置日志
所有的sql现在是不可见的,但我们希望知道它是怎么执行的,所有我们必须要看日志!
mybatis-plus.configuration.log-impl=org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl

后面的学习就需要注意在日志中自动生成的SQL
主键生成策略 @TableId()
学习要求:精通
分布式系统唯一id生成:https://www.cnblogs.com/haoxinyue/p/5208136.html
雪花算法:snowflake是Twitter开源的分布式ID生成算法,结果是一个long型的ID。其核心思想是:使用41bit作为毫秒数,10bit作为机器的ID(5个bit是数据中心——北京,上海,5个bit的机器ID),12bit作为毫秒内的流水号(意味着每个节点在每毫秒可以产生 4096 个 ID),最后还有一个符号位,永远是0。可以保证几乎全球唯一!
默认 ID_WORKER ,全局唯一id
@TableId(type = IdType.ID_WORKER )//ID_WORKER 表示全局唯一id,该注解放在实体类主键的上一行
@TableId注解中IdType的六个参数各自含义:
public enum IdType {
AUTO(0),//自增
NONE(1),//不使用主键生成策略,需要手动设置主键值。
INPUT(2),// 手动输入主键值
ID_WORKER(3),//使用雪花算法生成 64 位的唯一 ID,适用于分布式系统中的主键生成。
UUID(4),//使用 JDK 自带的 UUID 生成 32 位的唯一 ID,不依赖数据库。
ID_WORKER_STR(5);//和 ID_WORKER 类似,但主键值为字符串类型。
}
AUTO(0): 自动选择主键生成策略,根据数据库自动选择使用 ID_WORKER 或 UUID 策略。
NONE(1): 不使用主键生成策略,需要手动设置主键值。
INPUT(2): 手动输入主键值,需要在插入数据时手动设置主键值。
ID_WORKER(3): 使用雪花算法生成 64 位的唯一 ID,适用于分布式系统中的主键生成。
UUID(4): 使用 JDK 自带的 UUID 生成 32 位的唯一 ID,不依赖数据库。
ID_WORKER_STR(5): 和 ID_WORKER 类似,但主键值为字符串类型。
实现主键自增步骤
1、在实体类主键上@TableId(type = IdType.AUTO )
2、数据库主键字段一定要自增类型

CRUD扩展
学习要求:精通
增 insert插入
//插入测试
@Test
public void testInsert(){
User user = new User();
user.setName("zwx");
user.setAge(25);
user.setEmail("1804808430@qq.com");
int result = userMapper.insert(user);//帮我们自动生成id,在实体类主键上@TableId(type = IdType.AUTO )
System.out.println(result); //受影响的行数
System.out.println(user); //发现id会自动回填
}

数据库插入的id默认值为:全局唯一id
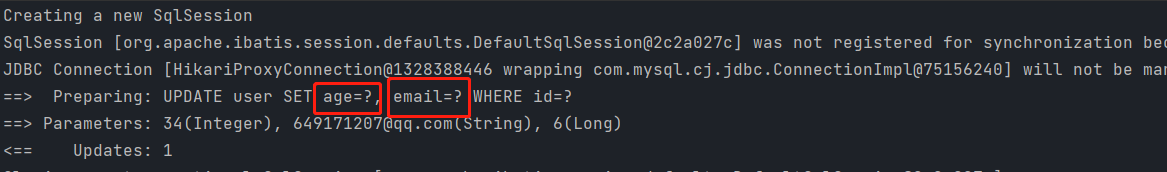
改 update更新
updateById()
注意:updateById()的参数是一个对象
//测试更新
@Test
public void testUpdate(){
User user = new User();
//通过条件自动拼接动态sql
user.setId(6l);
//user.setName("wahaha");
//user.setAge(34);
user.setEmail("649171207@qq.com");
//注意:updateById()的参数是一个对象
int i = userMapper.updateById(user);
System.out.println(i);//i表示受影响的行数
}

自动填充 @TableField
创建时间,修改时间!这些操作都是自动完成的,我们不希望手动更新!
1 删除数据库的默认值,更新

改成下图
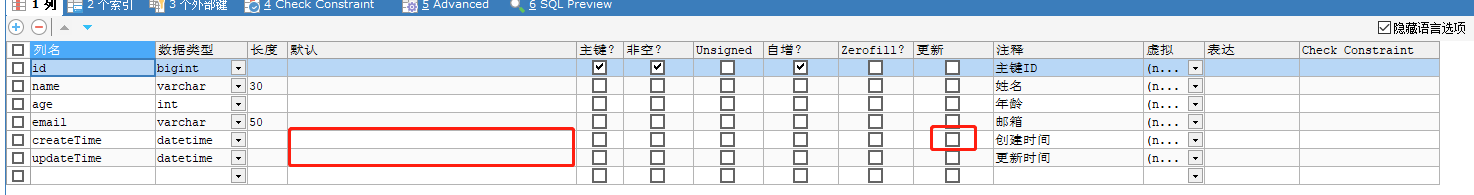
2 实体类属性上需要增加注解
//字段添加填充内容
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT) //新增 Field-字段的意思
private Date createTime;
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT_UPDATE)
private Date updateTime;
3 编写处理器来处理这个注解
@Slf4j
@Component //一定不要忘记把处理器加到IOC容器中---就是说一定别把Component丢了
public class MyMetaObjectHandler implements MetaObjectHandler {
//插入时的填充策略
@Override
public void insertFill(MetaObject metaObject) {
log.info("start insert fill....."); //打印日志
//setFieldValByName(String fieldName, Object fieldVal, MetaObject metaObject)
this.setFieldValByName("createTime", new Date(),metaObject) ;
this.setFieldValByName("updateTime", new Date(),metaObject) ;
}
//更新时的填充策略
@Override
public void updateFill(MetaObject metaObject) {
log.info("start insert fill.....");
this.setFieldValByName("updateTime",new Date(),metaObject);
}
}
4 测试 执行插入,更新方法
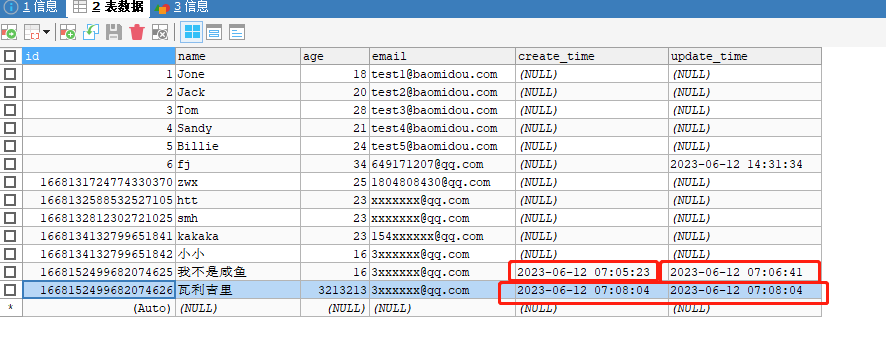
乐观锁 @version
一、乐观锁应用场景:当要更新一条记录的时候,希望这条记录没有被别人更新
乐观锁:十分乐观,总是认为不会出现问题,无论干什么都不上锁!如果出现问题,就再次更新值来测试
悲观锁: 十分悲观,总认为总是会出现问题,无论干什么都上锁!再去操作
二、乐观锁实现方式:
1 取出记录时,获取当前 version
2 更新时,带上这个 version
3 执行更新时, set version = newVersion where version = oldVersion
4 如果 version 不对,就更新失败
乐观锁:先查询,获得版本号 version = 1
--A
update user set name = "zwx", version = version + 1
where id = 2 and version = 1
--B 线程抢先完成,这个时候version = 2,导致A线程修改失败
update user set name = "haha", version = version + 1
where id = 2 and version = 1
三、使用mybatisplus乐观锁插件
step1 给数据库中增加version字段

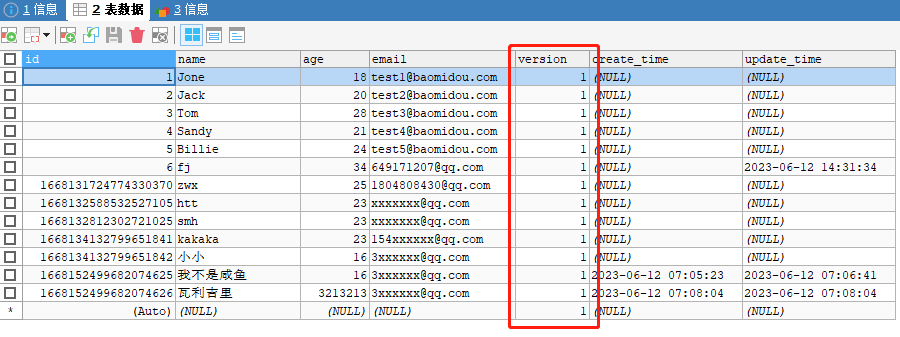
step2 对应实体类加上version属性,并在改属性上加@Version
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class User {
@TableId(type = IdType.AUTO)//默认使用ID_WORKER 表示全局唯一id
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String email;
@Version //乐观锁注解
private Integer version;//step2 对应实体类加上version属性,并在改属性上加@Version
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT) //新增 Field-字段的意思
private Date createTime;
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT_UPDATE)
private Date updateTime;
}
step3 注册组件
@MapperScan("com.zhou.mapper")
@Configuration
public class MyBatisPlusConfig {
//注册乐观锁插件,官方文档有代码
@Bean
public OptimisticLockerInterceptor optimisticLockerInterceptor() {
return new OptimisticLockerInterceptor();
}
}
step4 测试 看能否使用乐观锁
//测试乐观锁成功!
@Test
public void testOpLocker(){
//1 查询用户信息
User user = userMapper.selectById(1l);
//2 修改用户信息
user.setName("zhouwenxing");
user.setEmail("1804808430@qq.com");
//3 执行更新操作
userMapper.updateById(user);
}
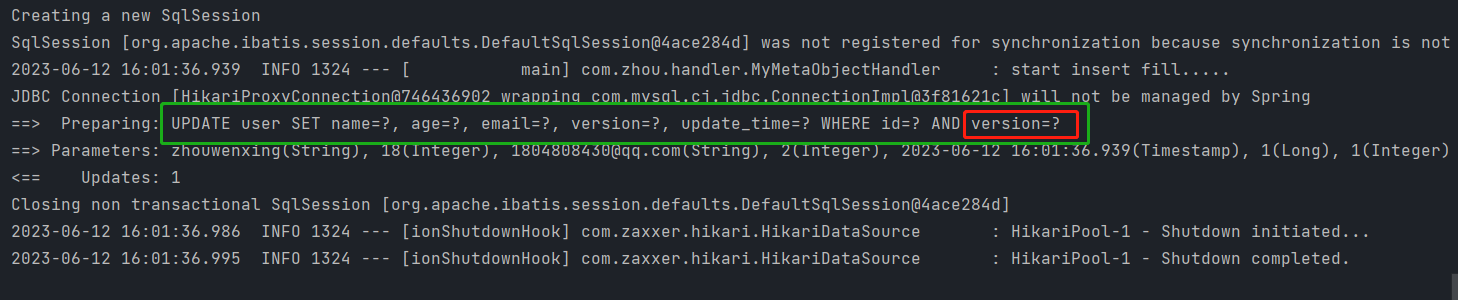
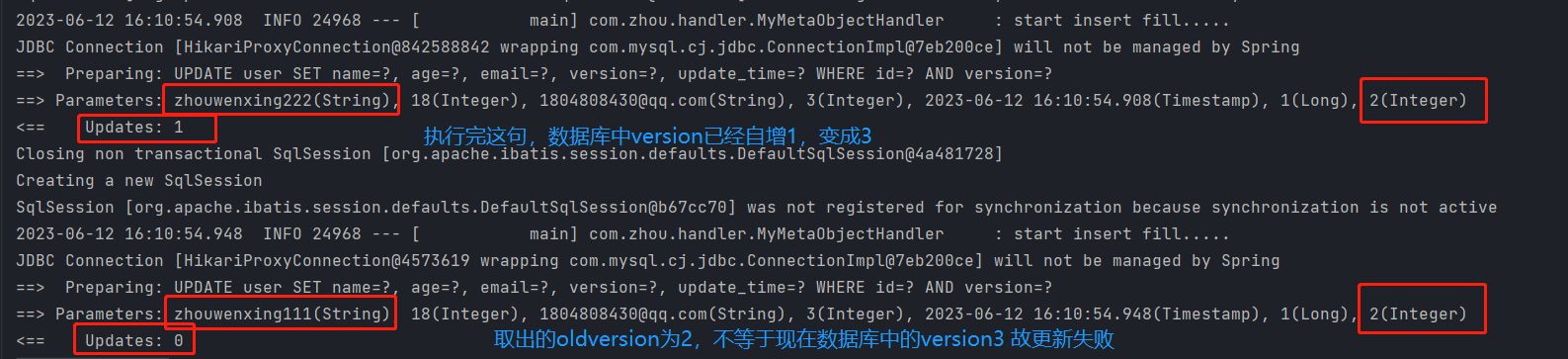
//测试乐观锁失败!多线程下
@Test
public void testOpLocker2(){
//线程1
User user1 = userMapper.selectById(1l);
user1.setName("zhouwenxing111");
user1.setEmail("1804808430@qq.com");
//线程2 模拟插队操作
User user2 = userMapper.selectById(1l);
user2.setName("zhouwenxing222");
user2.setEmail("1804808430@qq.com");
userMapper.updateById(user2);
userMapper.updateById(user1); //如果没有乐观锁 就会覆盖插队线程的值,最终name还是改成zhouwenixng111
}
查 select查找
1根据id单一查询—selectById(id)
@Test
public void testSelectById(){
User user = userMapper.selectById(1l);
System.out.println(user);
}

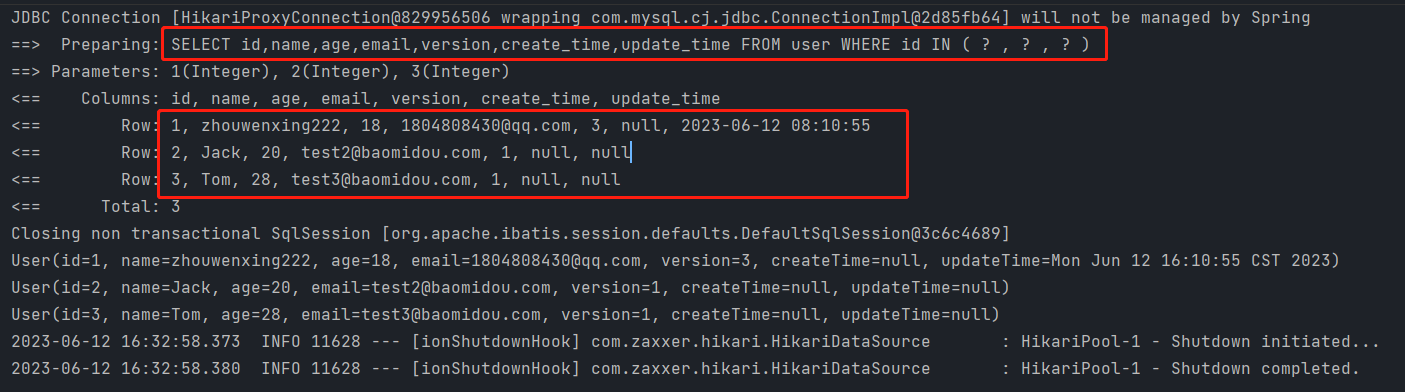
2 根据id批量查询—selectBatchIds(array)
//根据id查多个用户
@Test
public void testSelectByBatchId(){
List<User> users = userMapper.selectBatchIds(Arrays.asList(1,2,3));
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}
3 根据map条件查询—selectByMap(map)
// 条件查询 使用map封装
@Test
public void testSelectByBatchIds(){
HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
//自定义要查询的记录
map.put("name","zwx");
List<User> users = userMapper.selectByMap(map);
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}

@Test
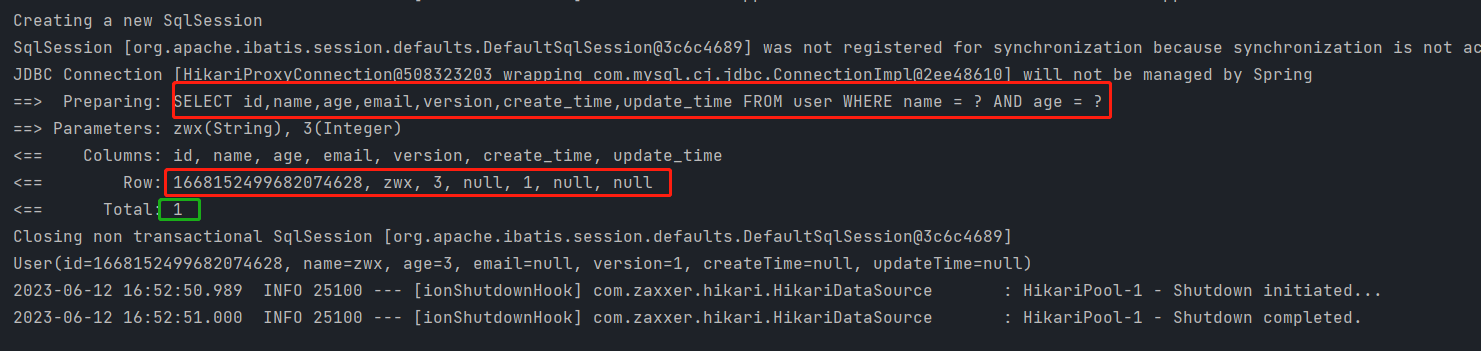
public void testSelectByBatchIds(){
HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
//查询name=”zwx“,且age=3的记录
map.put("name","zwx");
map.put("age",3);
List<User> users = userMapper.selectByMap(map);
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}
总结查代码
查测试
//根据id查单个用户
@Test
public void testSelectById(){
User user = userMapper.selectById(1l);
System.out.println(user);
}
//根据id查多个用户
@Test
public void testSelectByBatchId(){
List<User> users = userMapper.selectBatchIds(Arrays.asList(1,2,3));
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}
// 条件查询 使用map封装
@Test
public void testSelectByBatchIds(){
HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
//查询name=”zwx“,且age=3的记录
map.put("name","zwx");
map.put("age",3);
List<User> users = userMapper.selectByMap(map);
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}
分页查询
分页在项目中使用的很多,以下是可以实现分页的一些方法
1 原始limit进行分页
2 pageHelper第三方插件
3 mybatisplus内置分页插件(底层也是通过limit来实现的)
mybatisplus内置分页插件使用步骤
step1 配置分页插件
@Configuration
public class MyBatisPlusConfig {
//分页插件
@Bean
public PaginationInterceptor paginationInterceptor(){
return new PaginationInterceptor();
}
}
step2 直接使用Page对象即可
//分页查询 测试
@Test
public void testPage(){
//new Page<>(参数1,参数2);参数1:要查询的页 参数2:页面大小(每页显示的记录数)
Page<User> page = new Page<>(2,5); //查询第二页,每页只有五条记录
userMapper.selectPage(page,null);//这里把wrapper条件设置为null
//打印
page.getRecords().forEach(System.out::println);
//page.getTotal() 获得总记录数
System.out.println(page.getTotal());
}

底层也是通过limit来实现的
正好对应数据库中第6-第10条记录(从第1开始)

MybatisPlus中的Page类提供了以下18个方法:
hasPrevious():判断是否有上一页。返回类型boolean
hasNext():判断是否有下一页。返回类型boolean
getRecords():获取当前页的记录列表。返回类型List
setRecords(List records):设置当前页的记录列表。返回类型Page
getTotal():获取总记录数。返回类型long。返回类型long
setTotal(long total):设置总记录数。返回类型Page
getSize():获取每页显示的记录数(==获取分页大小)。返回类型long
setSize(long size):设置每页显示的记录数(设置分页大小)。无返回值
getCurrent():获取当前页码。返回类型long
setCurrent(long current):设置当前页码。返回类型Page
ascs():获取排序的升序字段列表。返回类型String[]
setAscs(List ascs):设置排序的升序字段列表。返回类型Page
setAsc(String… ascs):设置排序的升序字段数组。返回类型Page
descs():获取排序的降序字段列表。返回类型String[]
setDescs(List descs):设置排序的降序字段列表。返回类型Page
setDesc(String… descs):设置排序的降序字段数组。返回类型Page
optimizeCountSql():获取是否进行 count 查询的优化。返回类型boolean
setOptimizeCountSql(boolean optimizeCountSql):设置是否进行 count 查询的优化,并返回当前 Page 对象。如果设置为 true,则在进行分页查询时,不会再执行一次 count 查询来获取总记录数。返回类型Page
删 delete
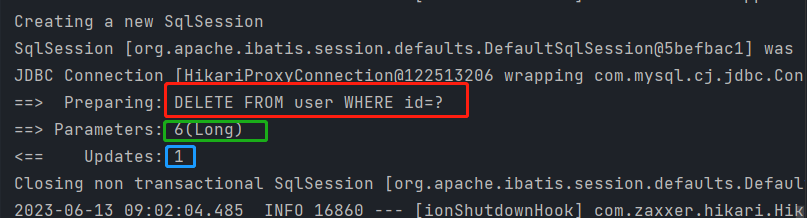
1 根据id单一删除—deleteById()
@Test
public void testDelete(){
userMapper.deleteById(6l);
}
2 根据id批量删除—deleteBatchIds()
//根据id批量删除
@Test
public void testDelete1(){
userMapper.deleteBatchIds(Arrays.asList(1668131724774330370l,1668132588532527105l,1668132812302721025l,1668134132799651841l,1668134132799651842l));
}

3 根据map条件删除—deleteByMap() (可删除多个也可只删除一个,根据条件来判定)
@Test
public void testDelete2(){
HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("name","zwx");
map.put("age",3);
userMapper.deleteByMap(map);
}
逻辑删除
工作中非常重要
物理删除:直接从数据库移除
逻辑删除:没有从数据库移除,而是通过一个变量让其失效! 如 delete=0 执行删除后 ==> delete=1
管理员可以查看被删除的记录!防止数据的丢失,类似于回收站!
逻辑删除只需要配置,不需要额外写代码,仍然用usermapper的deleteById(),deleteBatchIds(),deleteByMap() 方法操作即可,只不过底层删除操作实质变成更新操作,删除等于更新deleted值为1。
实现逻辑删除后,查询操作会自动过滤掉已被逻辑删除的记录(deleted=1的记录),底层是查询的时候多加了一个where deleted=0的条件。
实现逻辑删除后,进行的CRUD操作仍然是使用usermapper自带的方法即可。
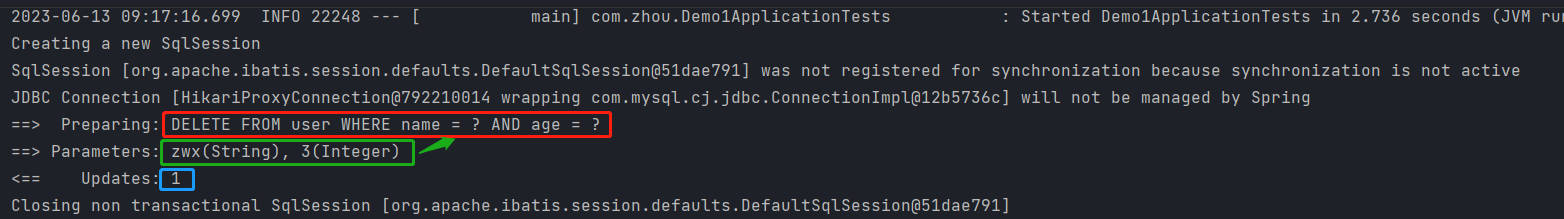
实现逻辑删除:
step1 在数据表中增加一个deleted字段,设置默认值为0

step2 在实体类中增加deleted属性,并增加注解@TableLogic
@TableLogic
private Integer deleted;
step3 配置逻辑删除组件
在mybatisplush的配置类MyBatisPlusConfig中加入逻辑删除组件
@Bean
public ISqlInjector sqlInjector(){
return new LogicSqlInjector();
}
在application.properties中 配置逻辑删除
# 配置逻辑删除
mybatis-plus.global-config.db-config.logic-delete-value=1 #1表示已删除
mybatis-plus.global-config.db-config.logic-not-delete-value=0 #0表示未删除
step4 测试逻辑删除
逻辑删除底层是update,把deleted值更新为1,表示已删除。并不是用delete操作
实现逻辑删除后,使得每次删除只把deleted更新为1,而不真正删除数据库中记录
//逻辑删除id为1的用户
@Test
public void testDelete(){
userMapper.deleteById(1l);
}
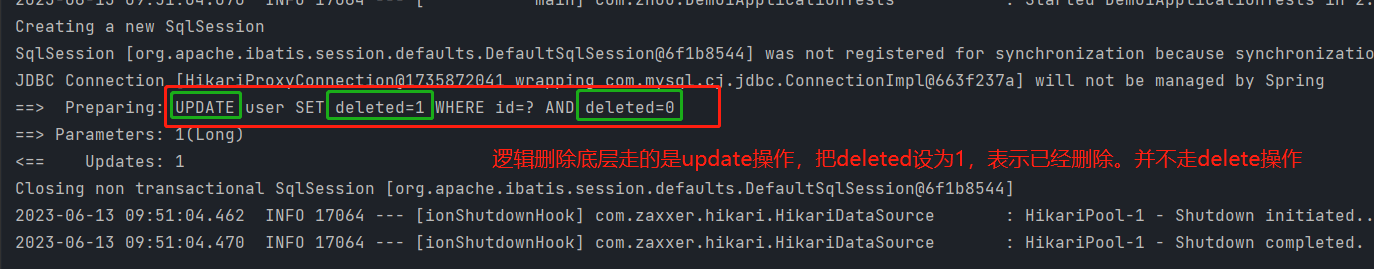
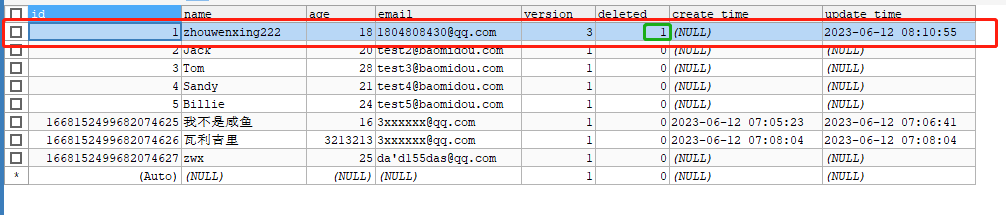
逻辑删除id为1的用户之后,再查询1号用户,查询不出来
因为逻辑删除id=1后deleted被改为1;查询id=1要求deleted=0,故查询失败。但id=1的记录仍在数据库中
实现逻辑删除后,使得每次查找会自动过滤已逻辑删除的记录(deleted=1的记录)
//逻辑删除后,查id为1的用户
@Test
public void testSelectById(){
User user = userMapper.selectById(1l);
System.out.println(user);
}
真正删除(自定义方法)
另外关于mybatis-plus写自定义方法参照:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_51447496/article/details/131093751
Mapper类
@Mapper
public interface TaskMapper extends BaseMapper<Task> {
@Delete("delete from task where id = #{id} and deleted = 1")
Integer deleteTrue(@Param("id") Integer id);
}
Service接口
Integer deleteTrue(Integer id);
ServiceImpl类
@Override
public Integer deleteTrue(Integer id) {
return taskMapper.deleteTrue(id);
}
Controller类 加入以下方法
@ApiOperation("根据id删除,删除数据库中该id对应记录")
@DeleteMapping("/idTrue/{id}")
public Boolean deleteTrue(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) {
if (taskService.deleteTrue(id) > 0){
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
性能分析插件
用户等待不能等太久,所以需要通过sql性能分析插件来找出慢sql进行优化(也可以用druid找出)
性能分析插件作用:输出每条SQL及其执行时间
实现性能分析插件:
step1 导入插件
@MapperScan("com.zhou.mapper")
@Configuration
public class MyBatisPlusConfig {
/**
* SQL执行效率插件
*/
@Bean
@Profile({"dev","test"})//设置 dev test 环境开启,保证我们的效率
public PerformanceInterceptor performanceInterceptor(){
PerformanceInterceptor performanceInterceptor = new PerformanceInterceptor();
performanceInterceptor.setMaxTime(1);//设置sql执行的最大时间为1毫秒,如果超过这个时间则会抛出异常
performanceInterceptor.setFormat(true);//开启sql格式化
return performanceInterceptor;
}
}
#设置开发环境
spring.profiles.active=dev
step2 测试使用
@Test
void contextLoads() {
//查询全部用户
List<User> users = userMapper.selectList(null);
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}
查询全部用户对应的sql语句执行了40ms(蓝框左上角),超过了我们设置的sql最大执行时间1ms,故报错!
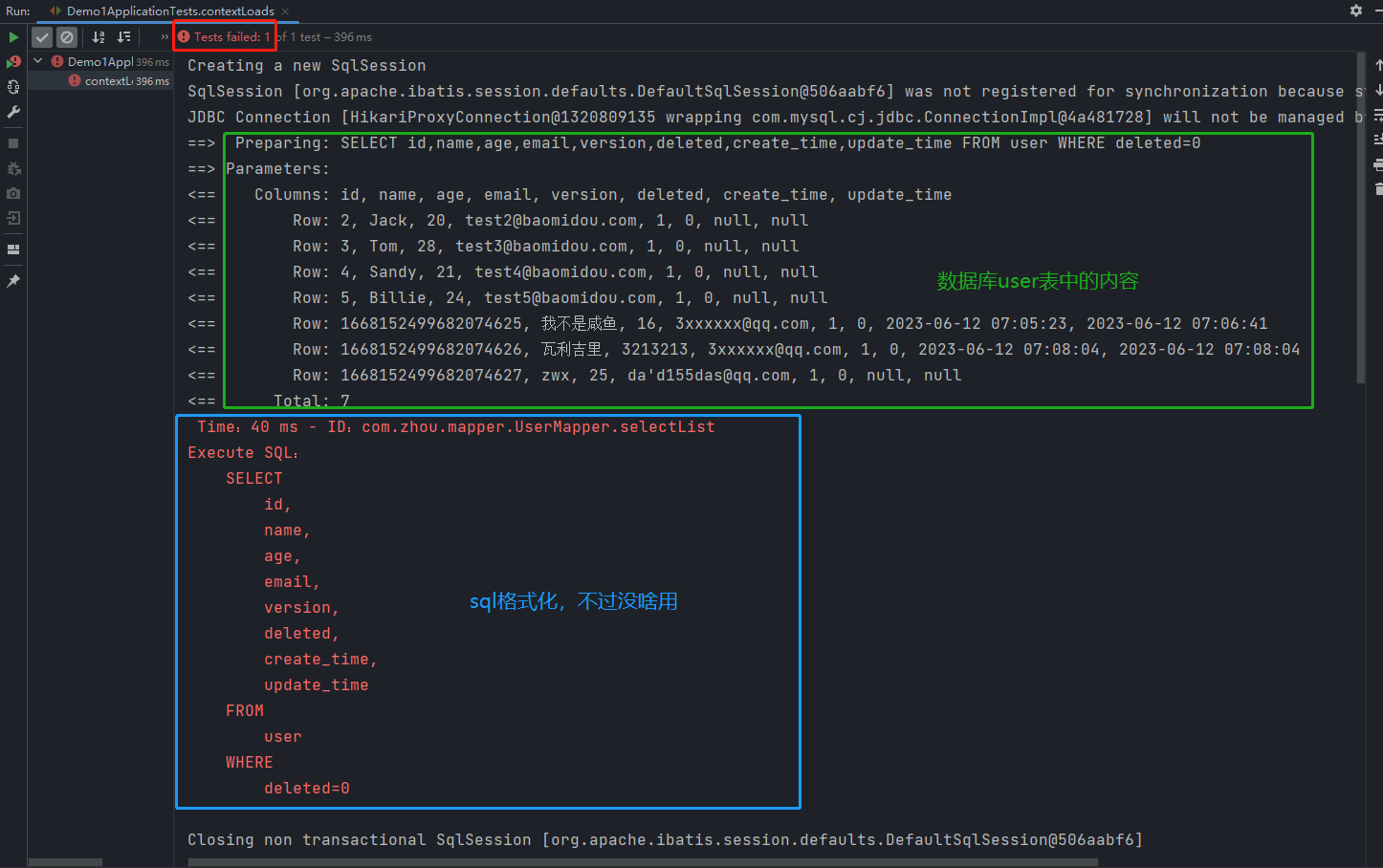

performanceInterceptor.setMaxTime(1)—>performanceInterceptor.setMaxTime(100)之后,运行不报错!sql执行最大时间一般设为100ms
条件构造器 Wrapper
非常重要
要写复杂的sql就可以使用Wrapper来替代
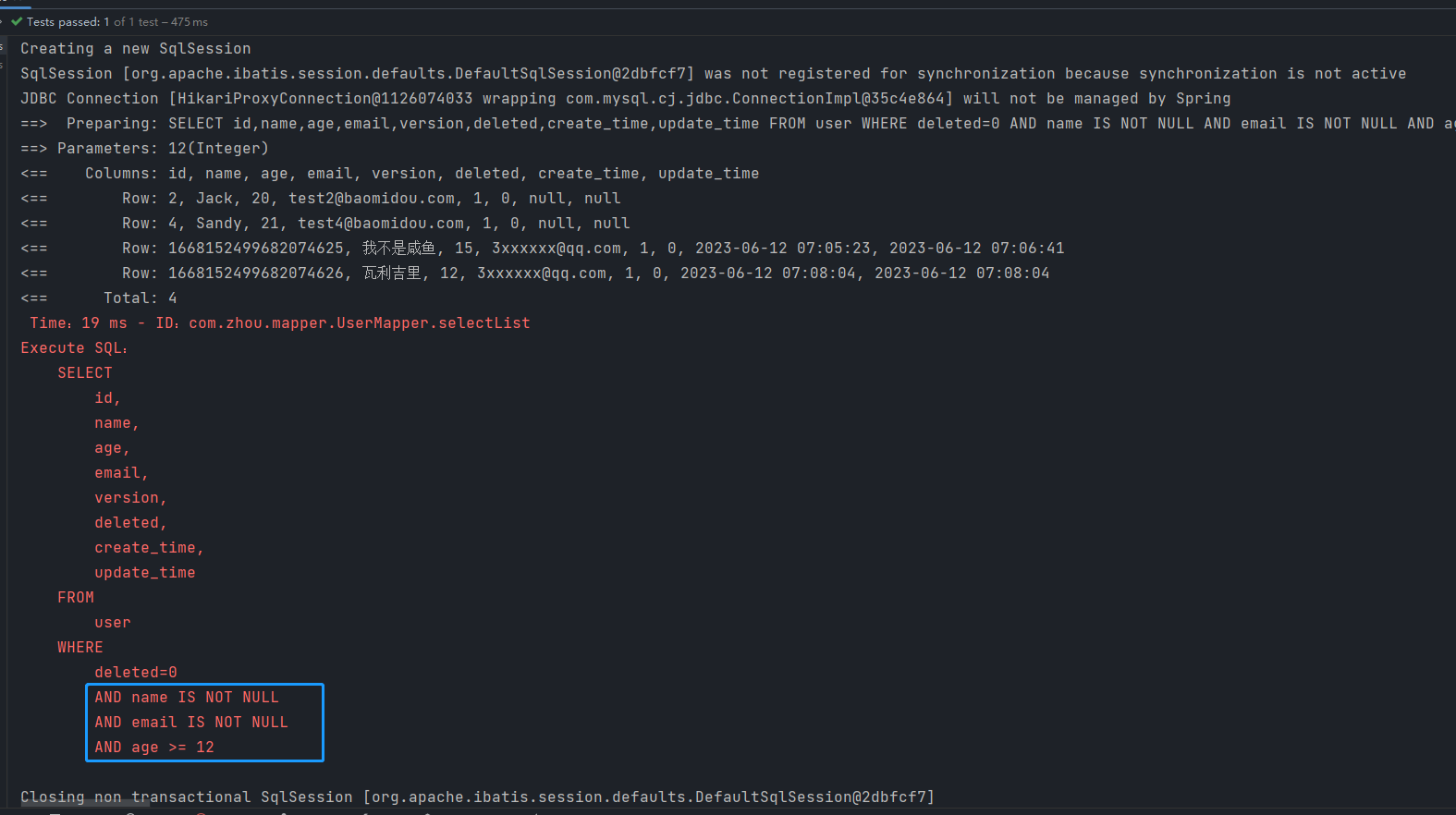
测试1 查询名字不为空,邮箱也不为空,且年龄>=12岁的用户
@SpringBootTest
public class WrapperTest {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
//查询测试
@Test
void contextLoads() {
QueryWrapper<User> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
//查询 name不为空, 邮箱也不为空, 且年龄>=12岁的用户
wrapper
.isNotNull("name")
.isNotNull("email")
.ge("age",12);
//打印输出
userMapper.selectList(wrapper).forEach(System.out::println);//和map对比学习
}
}
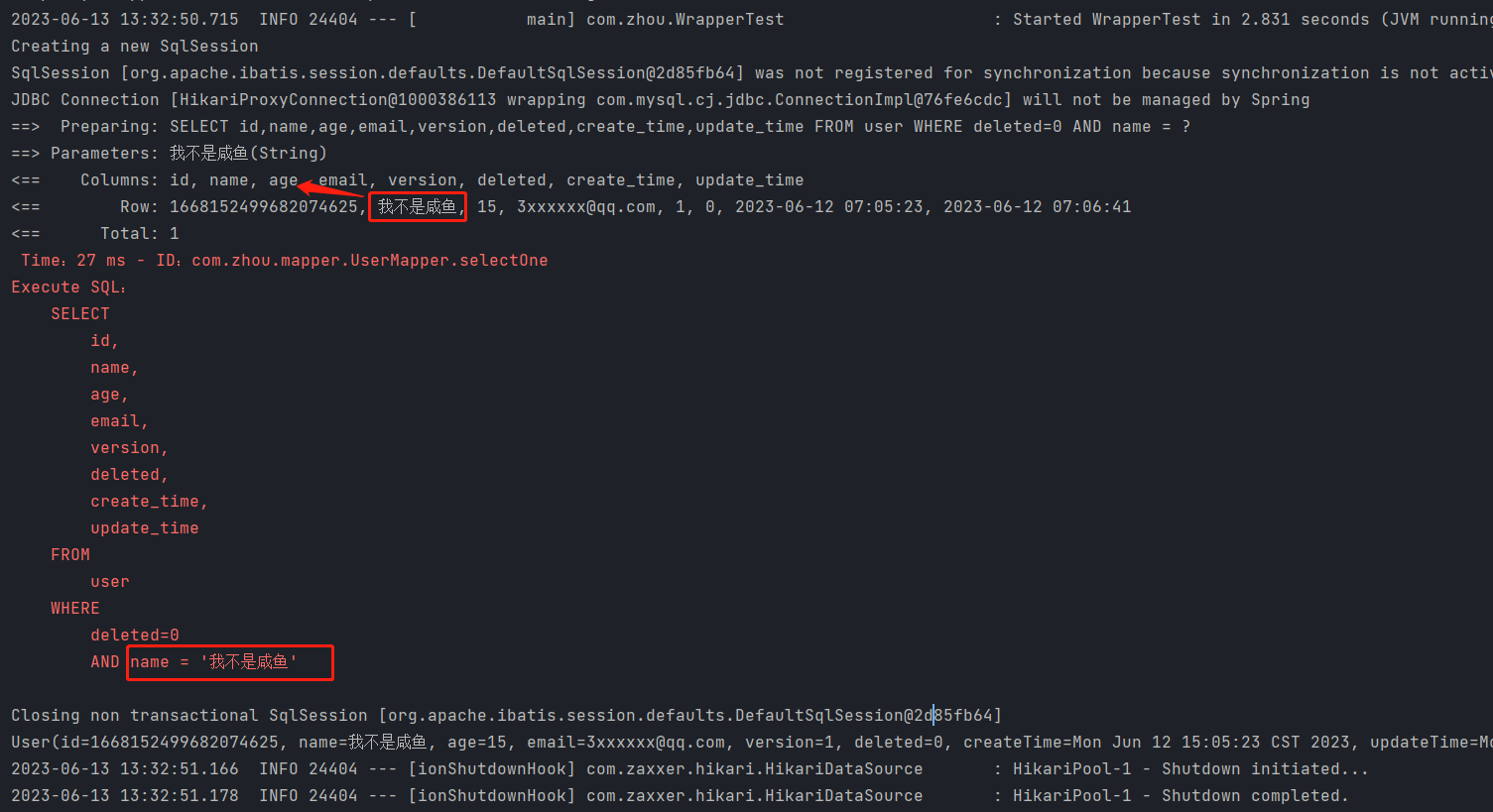
测试2 查询名字叫"我不是咸鱼"的记录
@Test
void test2() {
QueryWrapper<User> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
//查询名字叫"我不是咸鱼"的记录
wrapper.eq("name","我不是咸鱼");//错误写法:wrapper.equals("name","我不是咸鱼");
//打印输出
System.out.println(userMapper.selectOne(wrapper)); //一个就.sout输出
}
测试3 查询年龄在[20,30]区间的记录
@Test
void test3(){
QueryWrapper<User> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
wrapper.between("age",20,30);//查询age在[20,30]区间的记录
userMapper.selectCount(wrapper);//得到age在[20,30]区间的记录个数
userMapper.selectList(wrapper);//得到age在[20,30]区间的记录
}

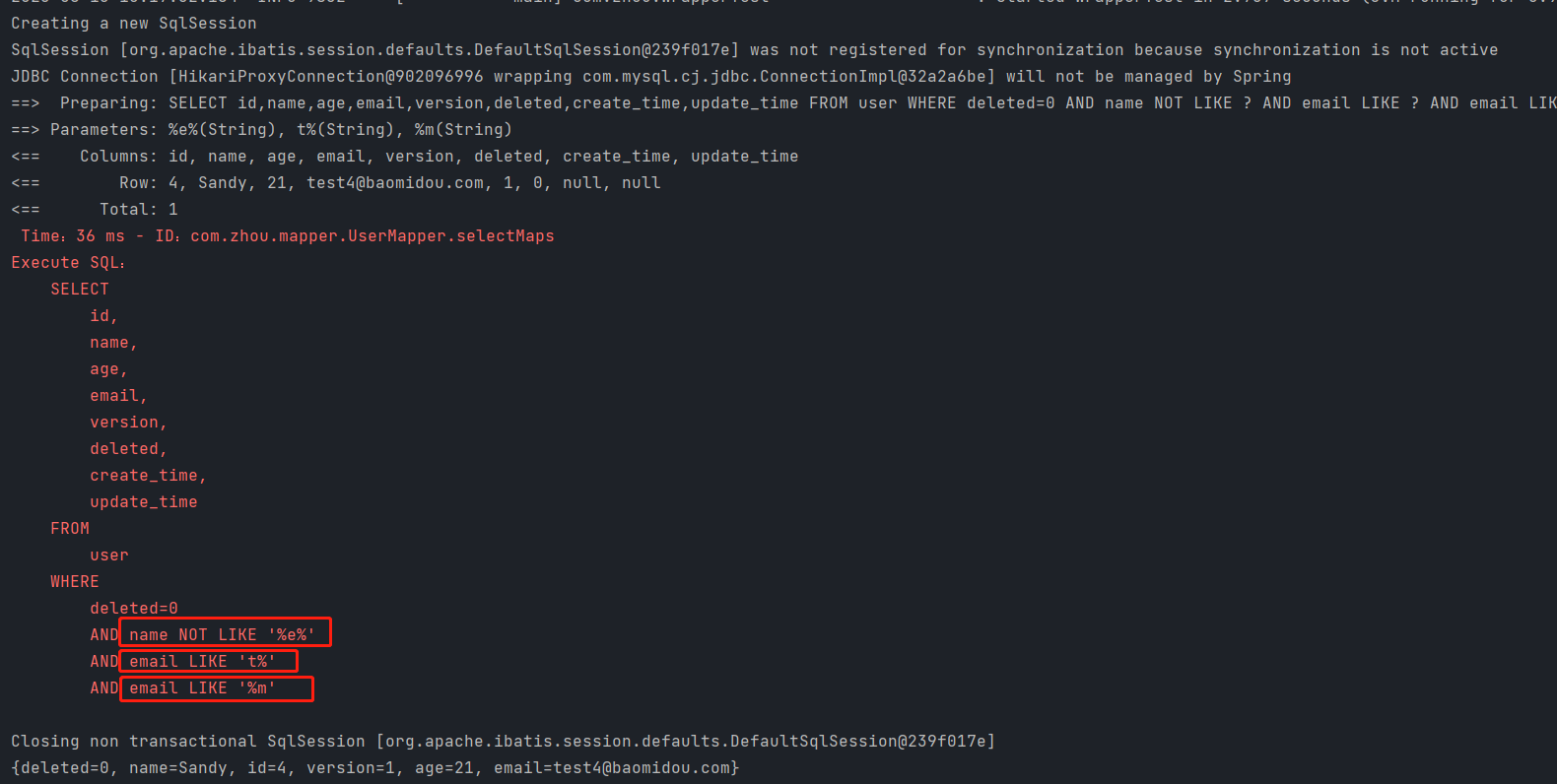
测试4 模糊查询——查询名字里面不包含’e’字母,且邮箱以’t’开头以’m’结尾的记录
//模糊查询 查询名字里面不包含'e'字母,且邮箱以't'开头以'm'结尾的记录
@Test
void test4(){
QueryWrapper<User> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
//条件:名字里面不包含'e'字母,且邮箱以't'开头以'm'结尾的记录
wrapper
.notLike("name","e")//notLike,Like 都代表 %e%,百分号左右都有! notLike:不包含, Like:包含。
.likeRight("email","t")//代表 t% ,百分号在右边,邮箱以t开头
.likeLeft("email","m");//代表 %m,百分号在左边,邮箱以m结尾
userMapper.selectMaps(wrapper).forEach(System.out::println);
}
测试五 联表IN子查询
@Test
void test5(){
QueryWrapper<User> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
//id在子查询中查出来
/**
* SELECT * FROM user
* WHERE
* deleted=0
* AND id IN (
* select id from user
* where id<3 )
*/
wrapper.inSql("id","select id from user where id<3");
userMapper.selectObjs(wrapper).forEach(System.out::println);
}
测试6 按名字升序排序,按年龄降序排序
//根据列属性1升序排序,列属性2降序排序
@Test
void test6(){
QueryWrapper<User> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
wrapper.orderByAsc("name");//根据name升序排列
wrapper.orderByDesc("age");//根据age降序排列
userMapper.selectObjs(wrapper).forEach(System.out::println);
}
测试7 分组查询 , 按性别分组查询,查出男,女各有多少人
//分组查询 查出表中男性成员
@Test
void test7(){
QueryWrapper<User> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
wrapper.select("gender, count(*) as count").groupBy("gender");
userMapper.selectObjs(wrapper).forEach(System.out::println);
}

注意:
selctList() 方法用于查询多条记录,返回一个 List 集合。可以传入一个Wrapper对象作为查询条件。
优点:方便快捷,返回结果为 List 集合,适用于查询多条记录的场景。
selectMap() 方法用于查询多条记录,返回一个 Map 集合,其中键为指定的列名,值为该列的值(value为对应的实体对象)。可以传入一个Wrapper对象作为查询条件。
优点:返回结果为 Map 集合,方便使用,适用于查询多条记录,并需要按照某个列名进行分组的场景。
selectObjs() 方法用于查询单个值,返回一个 Object 对象。可以传入一个Wrapper对象作为查询条件。
优点:返回结果为 Object 对象,适用于查询单个值的场景,如分组查询、统计查询等。
区别:
- selectList() 返回的是实体对象的List集合,selectMap() 返回的是Map集合,selectObjs() 返回的是指定字段的List集合。
- selectList() 和 selectMap() 返回的数据可以直接用于业务处理,而 selectObjs() 返回的数据通常用于统计或者分组查询。
优点:
- selectList() 和 selectMap() 可以返回实体对象或者Map对象,便于业务处理。
- selectObjs() 返回的数据较为轻量,适合用于数据统计或者分组查询。
适用场景:
- selectList() 适用于需要返回多条实体对象的查询场景。
- selectMap() 适用于需要返回多条数据,并且需要按照指定字段进行分组的场景。
- selectObjs() 适用于需要统计某个字段的总数、平均值等数据的场景。
代码自动生成器
controller,service,dao(mapper),model(pojo)自动生成
AutoGenerator 是 MyBatis-Plus 的代码生成器,通过 AutoGenerator 可以快速生成 Entity、Mapper、Mapper XML、Service、Controller 等各个模块的代码,极大的提升了开发效率。
自己写 运行报错,原因没加入以下配置,
第一个是mybatisplus的正常配置一般不会漏,但要加最后两个配置到pom.xml,否则运行报错!
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.0.5</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.velocity</groupId>
<artifactId>velocity-engine-core</artifactId>
<version>2.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.freemarker</groupId>
<artifactId>freemarker</artifactId>
<version>2.3.28</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
生成器代码如下! 以后拿来就可以用了。
只需要在 2.数据源dsc.setUrl()中更换数据库名,在4.策略配置 strategy.setInclude()更换表名即可。其他都不用更换
package com.zhou;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.DbType;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.FieldFill;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.IdType;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.generator.AutoGenerator;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.generator.config.DataSourceConfig;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.generator.config.GlobalConfig;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.generator.config.PackageConfig;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.generator.config.StrategyConfig;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.generator.config.po.TableField;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.generator.config.po.TableFill;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.generator.config.rules.DateType;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.generator.config.rules.NamingStrategy;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
//代码自动生成器
public class ZhouAutoCode {
public static void main(String[] args) {
需要构建一个 代码生成器对象(万物皆对象)
AutoGenerator mpg = new AutoGenerator();
配置策略(怎样去执行)
//1 全局配置
GlobalConfig gc = new GlobalConfig();
String projectPath = System.getProperty("user.dir");//System.getProperty("user.dir")表示获取user的目录
gc.setOutputDir(projectPath + "/src/main/java"); //代码输出目录
gc.setAuthor("周文星"); //设置作者名
gc.setOpen(false); //是否打开资源管理器
gc.setFileOverride(false); //是否覆盖原来生成的
gc.setServiceName("%sService"); //去Servive的I前缀
gc.setIdType(IdType.ID_WORKER); //设置主键id自动生成
gc.setDateType(DateType.ONLY_DATE); //设置日期类型
gc.setSwagger2(true); //是否生成Swagger文档
mpg.setGlobalConfig(gc);
//2 设置数据源 数据源就是配置用户名 连接密码这些
/**
* spring.datasource.username=root
* spring.datasource.password=123456
* spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis_plus?serverTimezone=UTC&useSSL=false&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8
* spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
*/
DataSourceConfig dsc = new DataSourceConfig();
dsc.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis_plus?serverTimezone=UTC&useSSL=false&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8");
dsc.setDriverName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); //设置数据库连接驱动的名字
dsc.setUsername("root");
dsc.setPassword("123456");
dsc.setDbType(DbType.MYSQL); //设置数据库类型
mpg.setDataSource(dsc); //放入自动生成器
//3 包配置
PackageConfig pc = new PackageConfig();
pc.setModuleName("blog"); //设置模块名为blog,下面生成的包都在blog模块中
pc.setParent("com.zhou"); //blog生成在com.zhou下
pc.setEntity("model"); //生成model包
pc.setMapper("mapper"); //生成mapper包
pc.setService("service"); //生成service包
pc.setController("controller"); //生成controller包
mpg.setPackageInfo(pc); //放入自动生成器
//4 策略配置 如自动配置时间,乐观锁
StrategyConfig strategy = new StrategyConfig();
strategy.setInclude("user"); //设置要映射到表名
strategy.setNaming(NamingStrategy.underline_to_camel); //支持下划线转驼峰命名
strategy.setColumnNaming(NamingStrategy.underline_to_camel);
//strategy.setSuperEntityClass("你自己的父类实体,没有就不用设置!");
strategy.setEntityLombokModel(true); //自动生成lombok,自动加上对应注解
//strategy.setRestControllerStyle(true);
strategy.setLogicDeleteFieldName("deleted"); //设置逻辑删除配置
//自动填充配置 有逻辑删除,那就要有自动填充啊。得给逻辑删除自动填充初值!
TableFill createTime = new TableFill("create_time", FieldFill.INSERT);
TableFill updateTime = new TableFill("update_time", FieldFill.INSERT_UPDATE);
ArrayList<TableFill> tableFills = new ArrayList<>();
tableFills.add(createTime);
tableFills.add(updateTime);
strategy.setTableFillList(tableFills);
//乐观锁
strategy.setVersionFieldName("version");
//设置驼峰命名
strategy.setRestControllerStyle(true); //开启restful的驼峰命名格式
//设置url用下划线
strategy.setControllerMappingHyphenStyle(true); //localhost:8080/hello_id_2
mpg.setStrategy(strategy);
执行
mpg.execute();
}
}
























 987
987











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








