1. HBase 环境搭建(略).
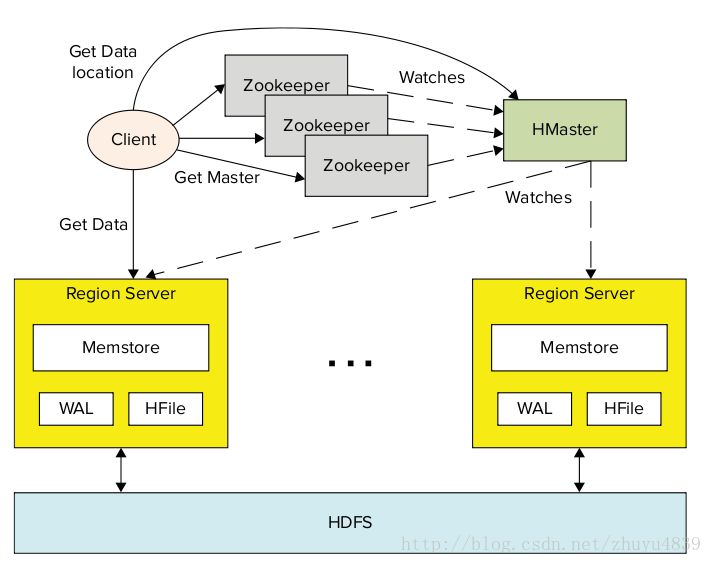
2. 高效的Hbase架构:
其中:menstore 是HBase的内存数据缓存,WAL(Write-Ahead-Log)记录HBase所有数据的修改操作,,HFile是HDFS的一个特例,用于HBase的文件系统,region server负责读写HFile和HDFS文件系统.
4. zookeeper 与HBase: zookeeper是一个同步服务, 因为数据分布在多个节点上(节点集叫ensemble-组),只要有一个主节点在运行,zookeeper的节点组就必须运行.
一个分布式的HBase实例要依靠运行的zookeeper集群,HBase所有的分散节点和client端必须通过访问zookeeper实例才能访问HBase,同时HBase也默认管理着一个Zookeeper的集群(虚拟的),这个Zookeeper的启动停止是HBase进程启动和停止的一部分.因为HBase的主机可能会重新部署,所以客户端的引导程序只寻找为当前HBase主机服务的Zookeeper和-Root-表. HBase底层支撑着一个.META表(由-Root-表指向),它包含HBase可用的region server的列表和用户表的列表.这样Zookeeper持有了-ROOT-表后,就能获取region server和Users的信息.
HBase表是一个分布式的,可靠的多维的有序map.支持get,put,scan,delete操作,get和scan操作支持在region server上实现的filter.
5. java api访问HBase:
a) 创建HTable实例:
// 获取Configuration对象
Configuration config = new Configuration();
// 创建表
HTable table = new HTable(config, "tableName");
通过这种方式访问HBase时HTable始终是单线程访问的, 如果需要支持多线程访问,则需要使用HTablePool
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
HTablePool pool = new HTablePool(config, mSize);
HTableInterface table = pool.getTable("Table");
b) HTable的get操作:
HTable table = new HTable(configuration, "table");
Get get = new Get(Bytes.toBytes("key"));
Result result = table.get(get);
NavigableMap<byte[], byte[]> familyValues = result.getFamilyMap(Bytes.toBytes
"columnFamily"));
for(Map.Entry<byte[], byte[]> entry : familyValues.entrySet()){
String column = Bytes.toString(entry.getKey);
Byte[] value = entry.getValue();
...................................................................................................
}
c) HTable 的put操作(多put):
Map<String, byte[]> rows = ...................;
HTable table = new HTable(configuration, "table");
List<Put> puts = new ArrayList<Put>();
for(Map.Entry<String, byte[]> row : rows.entrySet()){
byte[] bkey = Bytes.toBytes(row.getKey());
Put put = new Put(bkey);
put.add(Bytes.toBytes("family"), Bytes.toBytes("column"),row.getValue());
puts.add(put);
}
table.put(puts);
d) HTable的scan操作:
Put put = new Put(Bytes.toBytes("b"));
put.add(famA, coll1, Bytes.toBytes("0.,0."));
put.add(famA, coll2, Bytes.toBytes("hello world!"));
hTable.put(put);
put = new Put(Bytes.toBytes("d"));
put.add(famA, coll1, Bytes.toBytes("0.,1."));
put.add(famA, coll2, Bytes.toBytes("hello HBase!"));
hTable.put(put);
put = new Put(Bytes.toBytes("f"));
put.add(famA, coll1, Bytes.toBytes("0.,2."));
put.add(famA, coll2, Bytes.toBytes("blahblah"));
hTable.put(put);
// Scan data
Scan scan = new Scan(Bytes.toBytes("a"), Bytes.toBytes("z"));
scan.addColumn(famA, coll1);
scan.addColumn(famA, coll2);
WritableByteArrayComparable customFilter = new BoundingBoxFilter("-1.,-1., 1.5,
1.5");
SingleColumnValueFilter singleColumnValueFilterA = new SingleColumnValueFilter(
famA, coll1, CompareOp.EQUAL, customFilter);
singleColumnValueFilterA.setFilterIfMissing(true);
SingleColumnValueFilter singleColumnValueFilterB = new SingleColumnValueFilter(
famA, coll2, CompareOp.EQUAL, Bytes.toBytes("hello HBase!"));
singleColumnValueFilterB.setFilterIfMissing(true);
FilterList filter = new FilterList(Operator.MUST_PASS_ALL, Arrays
.asList((Filter) singleColumnValueFilterA,
singleColumnValueFilterB));
scan.setFilter(filter);
ResultScanner scanner = hTable.getScanner(scan);
for (Result result : scanner) {
System.out.println(Bytes.toString(result.getValue(famA, coll1)) + " , "
+ Bytes.toString(result.getValue(famA, coll2)));
}
HBase get多行:
使用scan.setCaching(int row); 设置缓存行数,这样处理效率更高,但是当处理大数据时,region server可能访问到了下一个数据集会造成超时,并抛出异常.
e) filter操作:
(待后续整理....)
























 423
423

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








