两个链表的第一个公共结点
描述
输入两个链表,找出它们的第一个公共结点。
分析
没有更好的思路,笨办法遍历完一个数组,把他的值存储到Map里面,利用Map的特性遍历另一个链表的时候查看是否包含这个节点
代码
public ListNode FindFirstCommonNode(ListNode pHead1, ListNode pHead2) {
Map<ListNode, Integer> map = new HashMap<ListNode, Integer>();
while (pHead1 != null) {
map.put(pHead1, null);
pHead1 = pHead1.next;
}
while (pHead2 != null) {
if (map.containsKey(pHead2)) {
return pHead2;
}
pHead2 = pHead2.next;
}
return null;
}
反转链表
题目描述
输入一个链表,反转链表后,输出链表的所有元素。
分析
代码
public class ListNode {
public int val;
public ListNode next = null;
public ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
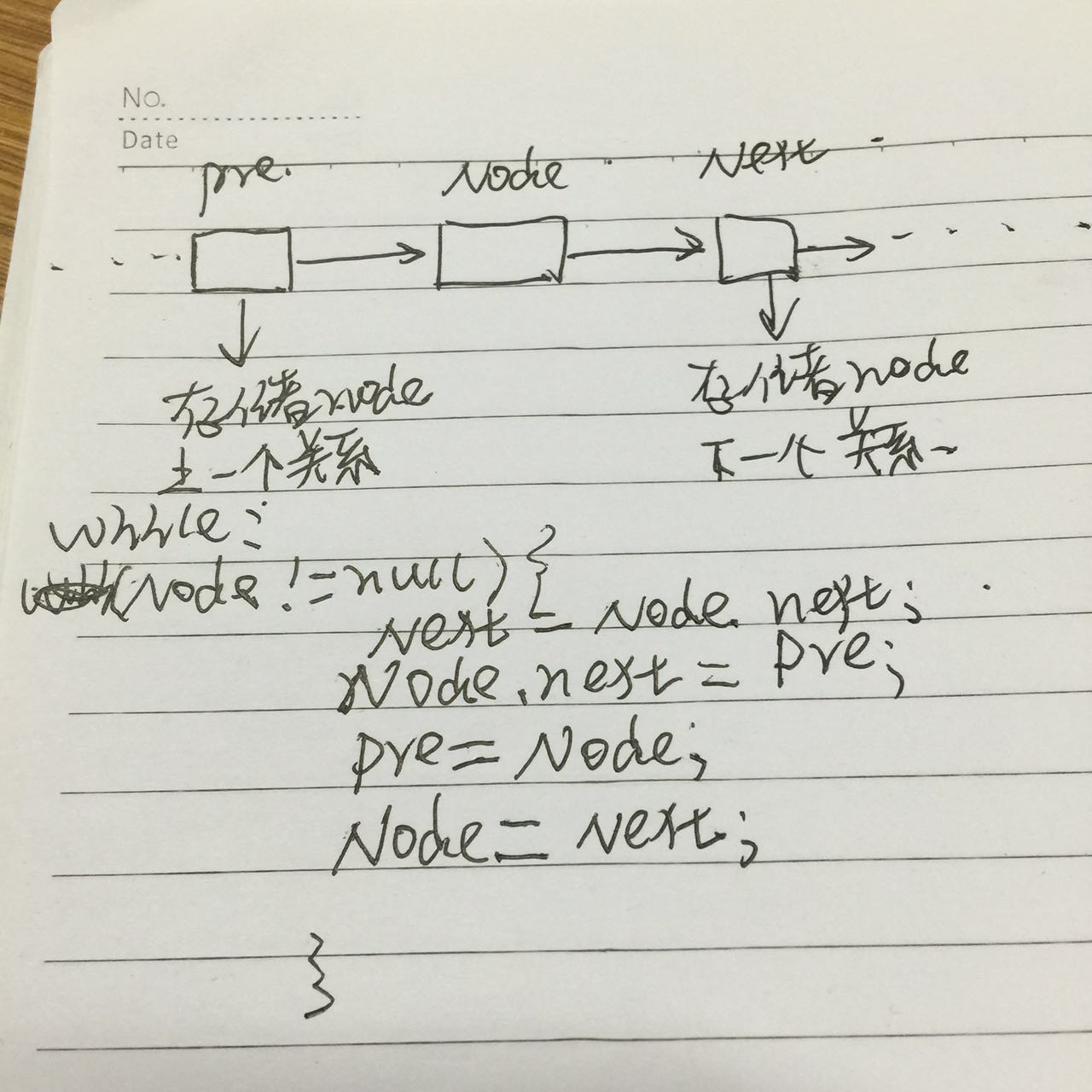
public static ListNode ReverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode next = null;
while (head != null) {
next = head.next;
head.next = pre;
pre = head;
head = next;
}
return pre;
}测试
public void testReverseList() {
ListNode l1 = new ListNode(1);
ListNode l2 = new ListNode(2);
ListNode l3 = new ListNode(3);
l1.next = l2;
l2.next = l3;
ListNode node = ListSolution.ReverseList(l1);
assertEquals(node.val, 3);
assertEquals(node.next.val, 2);
assertEquals(node.next.next.val, 1);
assertEquals(node.next.next.next, null);
}合并两个排序的链表
题目描述
输入两个单调递增的链表,输出两个链表合成后的链表,当然我们需要合成后的链表满足单调不减规则。
分析
- 比较两个长度为N和M的有序链表问题,可以分解为比较两个长度为N-1和M 或者N和M-1有序链表的问题,那么就可以通过递归来实现
- 还可以仿照,归并排序中 合并两个有序数组的方式
代码
public static ListNode Merge(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
// 新建一个头节点,用来存合并的链表。
ListNode root = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode head = root;
while (list1 != null && list2 != null) {
if (list1.val < list2.val) {
head.next = list1;
head = list1;
list1 = list1.next;
} else {
head.next = list2;
head = list2;
list2 = list2.next;
}
}
// 把未结束的链表连接到合并后的链表尾部
if (list1 == null && list2 != null) {
head.next = list2;
}
if (list1 != null && list2 == null) {
head.next = list1;
}
return root.next;
}递归版本
public ListNode MergeRes(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
if (list1 == null)
return list2;
else if (list2 == null)
return list1;
ListNode mergeHead = null;
if (list1.val < list2.val) {
mergeHead = list1;
mergeHead.next = Merge(list1.next, list2);
} else {
mergeHead = list2;
mergeHead.next = Merge(list1, list2.next);
}
return mergeHead;
}测试
private ListNode l1;
private ListNode l0;
@Override
protected void setUp() throws Exception {
l1 = new ListNode(1);
ListNode l2 = new ListNode(2);
ListNode l3 = new ListNode(3);
l1.next = l2;
l2.next = l3;
l0 = new ListNode(0);
ListNode l4 = new ListNode(4);
l0.next = l4;
super.setUp();
}
public void testMerge() {
ListNode node = ListSolution.Merge(l1, l0);
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
if (i != 5) {
assertEquals(node.val, i);
node = node.next;
} else {
assertEquals(node, null);
}
}
}





















 1455
1455

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








