原文地址:SectionIndexer中的getSectionForPosition()与getPositionForSection()解惑
原文地址:Android学习系列(15)--App列表之游标ListView(索引ListView)
原文地址:Android系统联系人全特效实现(上),分组导航和挤压动画
原文地址:Android系统联系人全特效实现(下),字母表快速滚动
第一部分:
大家在做字母索引的时候常常会用到SectionIndexer这个类,里面有2个重要的方法
1. getSectionForPosition() 通过该项的位置,获得所在分类组的索引号
2. getPositionForSection() 根据分类列的索引号获得该序列的首个位置
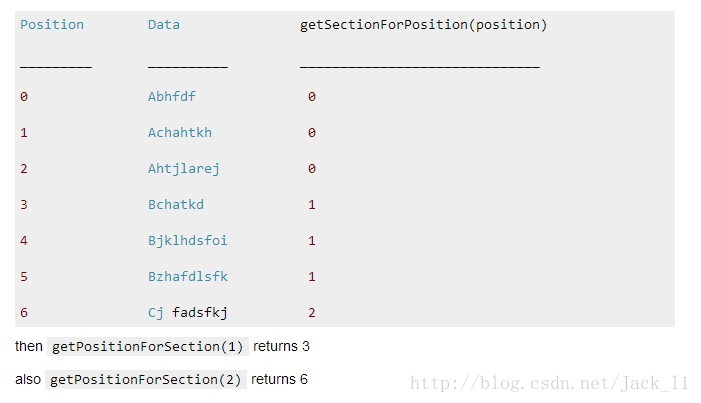
举个例子吧:
getSectionForPosition(0) 返回 0
getSectionForPosition(1) 返回 0
getSectionForPosition(2) 返回 0
getSectionForPosition(3) 返回 1
懂了吧? 是不是很简单?
所以一般有如下代码,来确定是否滑动到了分类的首字母位置:
/*
* 这是在ListView控件中滑动时触发的事件onScroll
* */
public void onScroll(AbsListView view, int firstVisibleItem, int visibleItemCount,
int totalItemCount) {
// 获得索引号,也就是分组号。
int section = indexer.getSectionForPosition(firstVisibleItem);
// 根据索引号获得下一个索引的初始位置,因为我们要实现的就是这个分组和下个分组的头部的关系。
int nextSecPosition = indexer.getPositionForSection(section + 1);
// 设置最上面的标题栏,设置它的参数,设置它该显示的字母。
if (firstVisibleItem != lastFirstVisibleItem) {
MarginLayoutParams params = (MarginLayoutParams) titleLayout.getLayoutParams();
params.topMargin = 0;
titleLayout.setLayoutParams(params);
title.setText(String.valueOf(alphabet.charAt(section)));
}
// 若是下一个索引号的位置与当前所见的项+1,则进行位移
if (nextSecPosition == firstVisibleItem + 1) {
View childView = view.getChildAt(0);
if (childView != null) {
int titleHeight = titleLayout.getHeight();
int bottom = childView.getBottom();
MarginLayoutParams params = (MarginLayoutParams) titleLayout
.getLayoutParams();
// 判断有没有变更。
if (bottom < titleHeight) {
float pushedDistance = bottom - titleHeight;
params.topMargin = (int) pushedDistance;
titleLayout.setLayoutParams(params);
} else {
if (params.topMargin != 0) {
params.topMargin = 0;
titleLayout.setLayoutParams(params);
}
}
}
}
lastFirstVisibleItem = firstVisibleItem;
}
}); 第二部分:
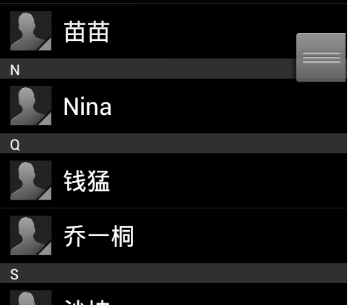
游标ListView,提供索引标签,使用户能够快速定位列表项。也可以叫索引ListView,有的人称也为Tweaked ListView,可能更形象些吧。
一看图啥都懂了:

1.游标(Fast scroll thumb)
就是右边的那个拖动的方块,这个非常的简单:设置 android:fastScrollEnabled="true"。
<ListView
android:id="@+id/tweaked_list"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:fastScrollEnabled="true"/>tweakedListView.setFastScrollEnabled(true);简单,这也是我为什么私下里喜欢自己写控件,但是工作中却喜欢用通用控件。
我们看下源代码,其实就是启用FastScroller对象:
//启用FastScroller对象
public void setFastScrollEnabled(boolean enabled) {
mFastScrollEnabled = enabled;
if (enabled) {
if (mFastScroller == null) {
mFastScroller = new FastScroller(getContext(), this);
}
} else {
if (mFastScroller != null) {
mFastScroller.stop();
mFastScroller = null;
}
}
}在 Android学习系列(10)--App列表之拖拽ListView(上)中我们使用了一种 WindowManager在ListView中添加一些自定义影像,这种方法我觉得一定是可行的。
但是,android系统给我们提供了一个更简单的方法:使用AlphabetIndexer。
AlphabetIndexer,实现了SectionIndexer接口, 是adapter的一个辅助类,辅助实现在快滑时,显示索引字母。
使用字母索引的话,必须保证数据列表是按字母顺序排序,以便AlphabetIndexerh采用二分查找法快速定位。
/**
* Cursor表示数据游标
* sortedColumnIndex数据集合中的第几列
* alphabet字母列表,用的最多的是"ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ"
**/
public AlphabetIndexer(Cursor cursor, int sortedColumnIndex, CharSequence alphabet) {}//这三个方法,实现了索引数据和列表数据的对应和定位
public int getPositionForSection(int section) {}
public int getSectionForPosition(int position) {}
public Object[] getSections() {}Cursor接口的实现,有两种选择:
(1).直接使用数据库查询返回的cursor
(2).自定义实现Cursor接口的新类
第一种方式很简单,查询一下数据库返回Cursor即可。
这里我们以第二种方式实践,伪装一个Cursor,主要是实现3个方法:
(1).getCount()
(2). moveToPosition()
(3). getString()
/**
* 伪装一个Cursor供AlphabetIndexer作数据索引源
*/
private class IndexCursor implements Cursor{
private ListAdapter adapter;
private int position;
private Map<String, String> map;
public IndexCursor(ListAdapter adapter){
this.adapter = adapter;
}
@Override
public int getCount() {return this.adapter.getCount();}
/**
* 取得索引字母,这个方法非常重要,根据实际情况具体处理
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@Override
public String getString(int columnIndex) {
map = (HashMap<String, String>)adapter.getItem(position);
return map.get(key).substring(0,1);
}
@Override
public boolean moveToPosition(int position) {
if(position<-1||position>getCount()){
return false;
}
this.position = position;
//如果不满意位置有点向上偏的话,下面这几行代码是修复定位索引值为顶部项值的问题
//if(position+2>getCount()){
// this.position = position;
//}else{
// this.position = position + 2;
//}
return true;
}
@Override
public void close() {}
@Override
public void copyStringToBuffer(int arg0, CharArrayBuffer arg1) {}
@Override
public void deactivate() {}
@Override
public byte[] getBlob(int arg0) {return null;}
@Override
public int getColumnCount() {return 0;}
@Override
public int getColumnIndex(String columnName) {return 0;}
@Override
public int getColumnIndexOrThrow(String columnName) throws IllegalArgumentException {return 0;}
@Override
public String getColumnName(int columnIndex) {return null;}
@Override
public String[] getColumnNames() {return null;}
@Override
public double getDouble(int columnIndex) {return 0;}
@Override
public Bundle getExtras() {return null;}
@Override
public float getFloat(int columnIndex) {return 0;}
@Override
public int getInt(int columnIndex) {return 0;}
@Override
public long getLong(int columnIndex) {return 0;}
@Override
public int getPosition() {return position;}
@Override
public short getShort(int columnIndex) {return 0;}
@Override
public boolean getWantsAllOnMoveCalls() {return false;}
@Override
public boolean isAfterLast() {return false;}
@Override
public boolean isBeforeFirst() {return false;}
@Override
public boolean isClosed() {return false;}
@Override
public boolean isFirst() {return false;}
@Override
public boolean isLast() {return false;}
@Override
public boolean isNull(int columnIndex) {return false;}
@Override
public boolean move(int offset) {return false;}
@Override
public boolean moveToFirst() {return false;}
@Override
public boolean moveToLast() {return false;}
@Override
public boolean moveToNext() {return false;}
@Override
public boolean moveToPrevious() {return false;}
@Override
public void registerContentObserver(ContentObserver observer) {}
@Override
public void registerDataSetObserver(DataSetObserver observer) {}
@Override
public boolean requery() {return false;}
@Override
public Bundle respond(Bundle extras) {return null;}
@Override
public void setNotificationUri(ContentResolver cr, Uri uri) {}
@Override
public void unregisterContentObserver(ContentObserver observer) {}
@Override
public void unregisterDataSetObserver(DataSetObserver observer) {}
}4.自定义Adapter的实现
使用前面介绍的东西,我们来实现最终的IndexAdapter:
class IndexAdapter extends SimpleAdapter implements SectionIndexer{
private AlphabetIndexer alphabetIndexer;
public IndexAdapter(Context context,List<? extends Map<String, ?>> data, int resource,String[] from, int[] to) {
super(context, data, resource, from, to);
//设置数据游标
//设置索引字母列表
alphabetIndexer = new AlphabetIndexer(new IndexCursor(this), 0, "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ");
}
@Override
public Object[] getSections() {
return alphabetIndexer.getSections();
}
@Override
public int getPositionForSection(int section) {
return alphabetIndexer.getPositionForSection(section);
}
@Override
public int getSectionForPosition(int position) {
return alphabetIndexer.getSectionForPosition(position);
}
}提供样本数据如下:
public List<Map<String, String>> getData(){
List<Map<String, String>> itemList = new ArrayList<Map<String, String>>();
String alphas = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ";
Map<String, String> map = null;
for(char c:alphas.toCharArray()){
for(int i=0; i<10; i++){
map = new HashMap<String, String>();
map.put("itemText", ""+c+i);
itemList.add(map);
}
}
return itemList;
}<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="50dip"
android:gravity="center_vertical"
>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tweaked_item_text"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
</LinearLayout>protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.tweake_list);
tweakedListView = (ListView)findViewById(R.id.tweaked_list);
//获取数据
List<Map<String, String>> itemList = getData();
ListAdapter adapter = new IndexAdapter(this, itemList, R.layout.tweake_list_item, new String[]{"itemText"}, new int[]{R.id.tweaked_item_text});
tweakedListView.setAdapter(adapter);
}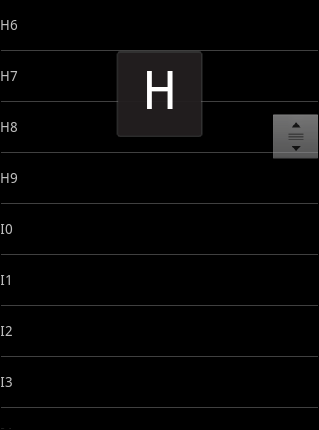 6.小结
6.小结
这种索引效果,在大数据量列表显示中非常的实用,是android开发必备常识。
本文只是一个简单的sample,实际工作中肯定会需要进一步扩展定义:
(1).对于复杂类型的处理,可根据Map<String,?>扩展自定义实体类,再通过adapter转换使用即可。
(2).对于索引字母列表,可动态设置,举个例子,你的列表只有ABCD四个字母,如果索引字母列表还是设置“ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ”就不合适了,会有个索引偏位的问题。
(3).对于复杂界面的显示,可重写adapter的getView方法自定义视图。
第三部分:
首先讲一下需要提前了解的知识点,这里我们最需要用到的就是SectionIndexer,它能够有效地帮助我们对分组进行控制。由于SectionIndexer是一个接口,你可以自定义一个子类来实现SectionIndexer,不过自己再写一个SectionIndexer的实现太麻烦了,这里我们直接使用Android提供好的实现AlphabetIndexer,用它来实现联系人分组功能已经足够了。
AlphabetIndexer的构造函数需要传入三个参数,第一个参数是cursor,第二个参数是sortedColumnIndex整型,第三个参数是alphabet字符串。
其中:
cursor就是把我们从数据库中查出的游标传进去,
sortedColumnIndex就是指明我们是使用哪一列进行排序的,
alphabet则是指定字母表排序规则。比如:"ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ"。
有了AlphabetIndexer,我们就可以通过它的getPositionForSection和getSectionForPosition方法,找出当前位置所在的分组,和当前分组所在的位置,从而实现类似于系统联系人的分组导航和挤压动画效果,关于AlphabetIndexer更详细的详解,请参考官方文档。
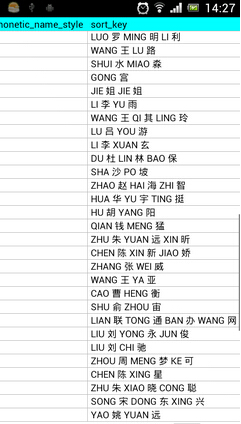
那么我们应该怎样对联系人进行排序呢?前面也提到过,有一个sortedColumnIndex参数,这个sortedColumn到底在哪里呢?我们来看一下系统联系人的raw_contacts这张表(/data/data/com.android.providers.contacts/databases/contacts2.db),这个表结构比较复杂,里面有二十多个列,其中有一列名叫sort_key,这就是我们要找的了!如下图所示:
可以看到,这一列非常人性化地帮我们记录了汉字所对应的拼音,这样我们就可以通过这一列的值轻松为联系人进行排序了。
下面我们就来开始实现,新建一个Android项目,命名为ContactsDemo。首先我们还是先来完成布局文件,打开或新建activity_main.xml作为程序的主布局文件,在里面加入如下代码:
布局文件很简单,里面放入了一个ListView,用于展示联系人信息。另外还在头部放了一个LinearLayout,里面包含了一个TextView,它的作用是在界面头部始终显示一个当前分组。
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<ListView
android:id="@+id/contacts_list_view"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:fadingEdge="none" >
</ListView>
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/title_layout"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="18dip"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:background="#303030" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/title"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dip"
android:textColor="#ffffff"
android:textSize="13sp" />
</LinearLayout>
</RelativeLayout> 在这个布局文件中,首先是放入了一个和前面完成一样的分组布局,因为不仅界面头部需要展示分组,在每个分组内的第一个无素之前都需要展示分组布局。然后是加入一个简单的LinearLayout,里面包含了一个ImageView用于显示联系人头像,还包含一个TextView用于显示联系人姓名。
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/sort_key_layout"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="18dip"
android:background="#303030" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/sort_key"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dip"
android:textColor="#ffffff"
android:textSize="13sp" />
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/name_layout"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="50dip" >
<ImageView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_vertical"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dip"
android:layout_marginRight="10dip"
android:src="@drawable/icon" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/name"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_vertical"
android:textColor="#ffffff"
android:textSize="22sp" />
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout> 这样我们的布局文件就全部写完了,下面开始来真正地实现功能。
先从简单的开始,新建一个Contact实体类:
public class Contact {
/**
* 联系人姓名
*/
private String name;
/**
* 排序字母
*/
private String sortKey;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getSortKey() {
return sortKey;
}
public void setSortKey(String sortKey) {
this.sortKey = sortKey;
}
}
接下来完成联系人列表适配器的编写,新建一个ContactAdapter类继承自ArrayAdapter,加入如下代码:
public class ContactAdapter extends ArrayAdapter<Contact> {
/**
* 需要渲染的item布局文件
*/
private int resource;
/**
* 字母表分组工具
*/
private SectionIndexer mIndexer;
public ContactAdapter(Context context, int textViewResourceId, List<Contact> objects) {
super(context, textViewResourceId, objects);
resource = textViewResourceId;
}
/*
* 这个方法是最重要的
* */
@Override
public View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
Contact contact = getItem(position);
LinearLayout layout = null;
if (convertView == null) {
layout = (LinearLayout) LayoutInflater.from(getContext()).inflate(resource, null);
} else {
layout = (LinearLayout) convertView;
}
TextView name = (TextView) layout.findViewById(R.id.name);
LinearLayout sortKeyLayout = (LinearLayout) layout.findViewById(R.id.sort_key_layout);
TextView sortKey = (TextView) layout.findViewById(R.id.sort_key);
name.setText(contact.getName());
/*
* 我们使用SectionIndexer的getSectionForPosition方法,
* 通过当前的position值拿到了对应的section值,
* 然后再反向通过刚刚拿到的section值,
* 调用getPositionForSection方法,取回新的position值。
* */
int section = mIndexer.getSectionForPosition(position);
if (position == mIndexer.getPositionForSection(section)) {
/*
* 如果当前的position值和新的position值是相等的,
* 那么我们就可以认为当前position的项是某个分组下的第一个元素,我们应该将分组布局显示出来,
* 而其它的情况就应该将分组布局隐藏。
* */
sortKey.setText(contact.getSortKey());
sortKeyLayout.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
} else {
sortKeyLayout.setVisibility(View.GONE);
}
return layout;
}
/**
* 给当前适配器传入一个分组工具。
*
* @param indexer
*/
public void setIndexer(SectionIndexer indexer) {
mIndexer = indexer;
}
}
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
/**
* 分组的布局
*/
private LinearLayout titleLayout;
/**
* 分组上显示的字母
*/
private TextView title;
/**
* 联系人ListView
*/
private ListView contactsListView;
/**
* 联系人列表适配器
*/
private ContactAdapter adapter;
/**
* 用于进行字母表分组
*/
private AlphabetIndexer indexer;
/**
* 存储所有手机中的联系人
*/
private List<Contact> contacts = new ArrayList<Contact>();
/**
* 定义字母表的排序规则
*/
private String alphabet = "#ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ";
/**
* 上次第一个可见元素,用于滚动时记录标识。
*/
private int lastFirstVisibleItem = -1;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
adapter = new ContactAdapter(this, R.layout.contact_item, contacts);
titleLayout = (LinearLayout) findViewById(R.id.title_layout);
title = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.title);
contactsListView = (ListView) findViewById(R.id.contacts_list_view);
/*
* 在onCreate方法中,
* 我们从系统联系人数据库中去查询联系人的姓名和排序键,
* 之后将查询返回的cursor直接传入AlphabetIndexer作为第一个参数。
* */
Uri uri = ContactsContract.CommonDataKinds.Phone.CONTENT_URI;
Cursor cursor = getContentResolver().query(uri,
new String[] { "display_name", "sort_key" }, null, null, "sort_key");//服务器返回的cursor
if (cursor.moveToFirst()) {//读取联系人信息
do {
String name = cursor.getString(0);
String sortKey = getSortKey(cursor.getString(1));
Contact contact = new Contact();
contact.setName(name);
contact.setSortKey(sortKey);
contacts.add(contact);
} while (cursor.moveToNext());
}
startManagingCursor(cursor);
/*
* 由于我们一共就查了两列,排序键在第二列,所以我们第二个sortedColumnIndex参数传入1。
* 第三个alphabet参数这里传入了"#ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ"字符串,
* 因为可能有些联系人的姓名不在字母表范围内,我们统一用#来表示这部分联系人。
* */
indexer = new AlphabetIndexer(cursor, 1, alphabet);
adapter.setIndexer(indexer);
if (contacts.size() > 0) {
setupContactsListView();
}
}
/**
* 然后我们在setupContactsListView方法中监听了ListView的滚动,
* 为联系人ListView设置监听事件,根据当前的滑动状态来改变分组的显示位置,从而实现挤压动画的效果。
*/
private void setupContactsListView() {
contactsListView.setAdapter(adapter);
contactsListView.setOnScrollListener(new OnScrollListener() {
@Override
public void onScrollStateChanged(AbsListView view, int scrollState) {
}
@Override
public void onScroll(AbsListView view, int firstVisibleItem, int visibleItemCount,
int totalItemCount) {
/*
* 在onScroll方法中通过getSectionForPosition方法获取第一个可见元素的分组值,
* */
int section = indexer.getSectionForPosition(firstVisibleItem);
/*
* 再通过getPositionForSection方法获得到下一个分组中的第一个元素,
* */
int nextSecPosition = indexer.getPositionForSection(section + 1);
if (firstVisibleItem != lastFirstVisibleItem) {
MarginLayoutParams params = (MarginLayoutParams) titleLayout.getLayoutParams();
params.topMargin = 0;
titleLayout.setLayoutParams(params);
title.setText(String.valueOf(alphabet.charAt(section)));
}
/**
* 如果下个分组的第一个元素值等于第一个可见元素的值加1,
* 那就说明下个分组的布局要和界面顶部分组布局相碰了。
* */
if (nextSecPosition == firstVisibleItem + 1) {
/**
* 之后再通过ListView的getChildAt(0)方法,获取到界面上显示的第一个子View,
* */
View childView = view.getChildAt(0);
if (childView != null) {
int titleHeight = titleLayout.getHeight();
/*
* 再用view.getBottom获取底部距离父窗口的位置,
* */
int bottom = childView.getBottom();
MarginLayoutParams params = (MarginLayoutParams) titleLayout
.getLayoutParams();
/*
* 对比分组布局的高度来对顶部分组布局进行纵向偏移,就可以实现挤压动画的效果了。这段有点不太懂逻辑
* */
if (bottom < titleHeight) {
float pushedDistance = bottom - titleHeight;
params.topMargin = (int) pushedDistance;
titleLayout.setLayoutParams(params);
} else {
if (params.topMargin != 0) {
params.topMargin = 0;
titleLayout.setLayoutParams(params);
}
}
}
}
lastFirstVisibleItem = firstVisibleItem;
}
});
}
/**
* 获取sort key的首个字符,如果是英文字母就直接返回,否则返回#。
*
* @param sortKeyString
* 数据库中读取出的sort key
* @return 英文字母或者#
*/
private String getSortKey(String sortKeyString) {
String key = sortKeyString.substring(0, 1).toUpperCase();
if (key.matches("[A-Z]")) {
return key;
}
return "#";
}
}
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.example.contactsdemo"
android:versionCode="1"
android:versionName="1.0" >
<uses-sdk
android:minSdkVersion="8"
android:targetSdkVersion="8" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.READ_CONTACTS"></uses-permission>
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:theme="@android:style/Theme.NoTitleBar"
>
<activity
android:name="com.example.contactsdemo.MainActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name" >
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
</application>
</manifest>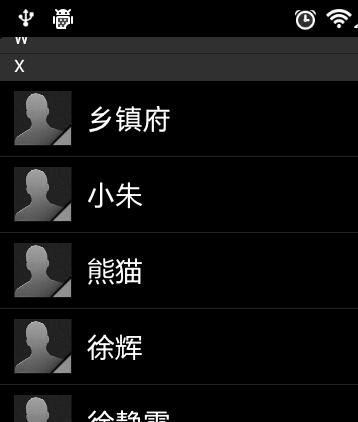
第四部分:
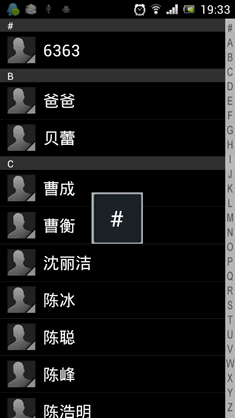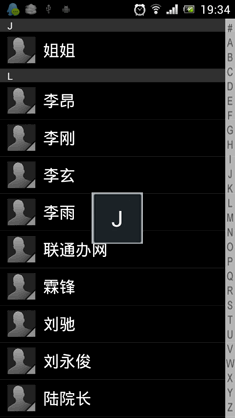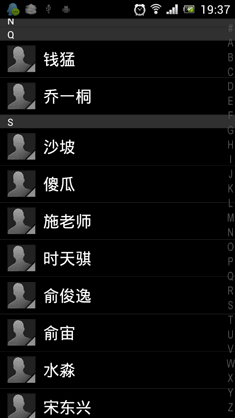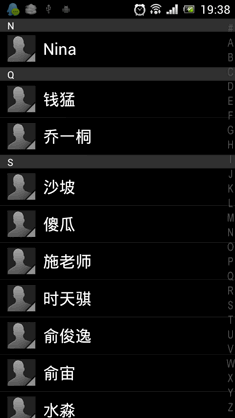
其实ListView本身是有一个快速滚动属性的,可以通过在XML中设置android:fastScrollEnabled="true"来启用。包括以前老版本的Android联系人中都是使用这种方式来进行快速滚动的。效果如下图所示:
不过这种快速滚动方式比较丑陋,到后来很多手机厂商在定制自己ROM的时候都将默认快速滚动改成了类似iPhone上A-Z字母表快速滚动的方式。这里我们怎么能落后于时代的潮流呢!我们的快速滚动也要使用A-Z字母表的方式!
下面就来开始实现,首先打开上次的ContactsDemo工程,修改activity_main.xml布局文件。由于我们要在界面上加入字母表,因此我们需要一个Button,将这个Button的背景设为一张A-Z排序的图片,然后居右对齐。另外还需要一个TextView,用于在弹出式分组布局上显示当前的分组,默认是gone掉的,只有手指在字母表上滑动时才让它显示出来。修改后的布局文件代码如下:
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<ListView
android:id="@+id/contacts_list_view"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:scrollbars="none"
android:fadingEdge="none" >
</ListView>
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/title_layout"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="18dip"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:background="#303030" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/title"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dip"
android:textColor="#ffffff"
android:textSize="13sp" />
</LinearLayout>
<Button
android:id="@+id/alphabetButton"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
android:background="@drawable/a_z"
/>
<RelativeLayout
android:id="@+id/section_toast_layout"
android:layout_width="70dip"
android:layout_height="70dip"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:background="@drawable/section_toast"
android:visibility="gone"
>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/section_toast_text"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:textColor="#fff"
android:textSize="30sp"
/>
</RelativeLayout>
</RelativeLayout>
/*
* 在这个方法中我们注册了字母表按钮的onTouch事件,然后在onTouch方法里做了一些逻辑判断和处理
* */
private void setAlpabetListener() {
alphabetButton.setOnTouchListener(new OnTouchListener() {
@Override
public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) {
// 首先通过字母表按钮的getHeight方法获取到字母表的总高度,
float alphabetHeight = alphabetButton.getHeight();
// 然后用event.getY方法获取到目前手指在字母表上的纵坐标,
float y = event.getY();
// 用纵坐标除以总高度就可以得到一个用小数表示的当前手指所在位置(0表在#端,1表示在Z端)。
// 由于我们的字母表中一共有27个字符,再用刚刚算出的小数再除以1/27就可以得到一个0到27范围内的浮点数,
// 之后再把这个浮点数向下取整,就可以算出我们当前按在哪个字母上了
int sectionPosition = (int) ((y / alphabetHeight) / (1f / 27f));
if (sectionPosition < 0) {
sectionPosition = 0;
} else if (sectionPosition > 26) {
sectionPosition = 26;
}
String sectionLetter = String.valueOf(alphabet.charAt(sectionPosition));
int position = indexer.getPositionForSection(sectionPosition);
/*
* 然后再对event的action进行判断,
* 如果是ACTION_DOWN或ACTION_MOVE,就在弹出式分组上显示当前手指所按的字母,
* 并调用ListView的setSelection方法把列表滚动到相应的分组。
* */
switch (event.getAction()) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
alphabetButton.setBackgroundResource(R.drawable.a_z_click);
sectionToastLayout.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
sectionToastText.setText(sectionLetter);
contactsListView.setSelection(position);
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
sectionToastText.setText(sectionLetter);
contactsListView.setSelection(position);
break;
// 如果是其它的action,就将弹出式分组布局隐藏。
default:
alphabetButton.setBackgroundResource(R.drawable.a_z);
sectionToastLayout.setVisibility(View.GONE);
}
return true;
}
});
}
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
/**
* 分组的布局
*/
private LinearLayout titleLayout;
/**
* 弹出式分组的布局
*/
private RelativeLayout sectionToastLayout;
/**
* 右侧可滑动字母表
*/
private Button alphabetButton;
/**
* 分组上显示的字母
*/
private TextView title;
/**
* 弹出式分组上的文字
*/
private TextView sectionToastText;
/**
* 联系人ListView
*/
private ListView contactsListView;
/**
* 联系人列表适配器
*/
private ContactAdapter adapter;
/**
* 用于进行字母表分组
*/
private AlphabetIndexer indexer;
/**
* 存储所有手机中的联系人
*/
private List<Contact> contacts = new ArrayList<Contact>();
/**
* 定义字母表的排序规则
*/
private String alphabet = "#ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ";
/**
* 上次第一个可见元素,用于滚动时记录标识。
*/
private int lastFirstVisibleItem = -1;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
adapter = new ContactAdapter(this, R.layout.contact_item, contacts);
titleLayout = (LinearLayout) findViewById(R.id.title_layout);
sectionToastLayout = (RelativeLayout) findViewById(R.id.section_toast_layout);
title = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.title);
sectionToastText = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.section_toast_text);
alphabetButton = (Button) findViewById(R.id.alphabetButton);
contactsListView = (ListView) findViewById(R.id.contacts_list_view);
Uri uri = ContactsContract.CommonDataKinds.Phone.CONTENT_URI;
Cursor cursor = getContentResolver().query(uri,
new String[] { "display_name", "sort_key" }, null, null, "sort_key");
if (cursor.moveToFirst()) {
do {
String name = cursor.getString(0);
String sortKey = getSortKey(cursor.getString(1));
Contact contact = new Contact();
contact.setName(name);
contact.setSortKey(sortKey);
contacts.add(contact);
} while (cursor.moveToNext());
}
startManagingCursor(cursor);
indexer = new AlphabetIndexer(cursor, 1, alphabet);
adapter.setIndexer(indexer);
if (contacts.size() > 0) {
setupContactsListView();
setAlpabetListener();
}
}
/**
* 为联系人ListView设置监听事件,根据当前的滑动状态来改变分组的显示位置,从而实现挤压动画的效果。
*/
private void setupContactsListView() {
contactsListView.setAdapter(adapter);
contactsListView.setOnScrollListener(new OnScrollListener() {
@Override
public void onScrollStateChanged(AbsListView view, int scrollState) {
}
@Override
public void onScroll(AbsListView view, int firstVisibleItem, int visibleItemCount,
int totalItemCount) {
int section = indexer.getSectionForPosition(firstVisibleItem);
int nextSecPosition = indexer.getPositionForSection(section + 1);
if (firstVisibleItem != lastFirstVisibleItem) {
MarginLayoutParams params = (MarginLayoutParams) titleLayout.getLayoutParams();
params.topMargin = 0;
titleLayout.setLayoutParams(params);
title.setText(String.valueOf(alphabet.charAt(section)));
}
if (nextSecPosition == firstVisibleItem + 1) {
View childView = view.getChildAt(0);
if (childView != null) {
int titleHeight = titleLayout.getHeight();
int bottom = childView.getBottom();
MarginLayoutParams params = (MarginLayoutParams) titleLayout
.getLayoutParams();
if (bottom < titleHeight) {
float pushedDistance = bottom - titleHeight;
params.topMargin = (int) pushedDistance;
titleLayout.setLayoutParams(params);
} else {
if (params.topMargin != 0) {
params.topMargin = 0;
titleLayout.setLayoutParams(params);
}
}
}
}
lastFirstVisibleItem = firstVisibleItem;
}
});
}
/**
* 设置字母表上的触摸事件,根据当前触摸的位置结合字母表的高度,计算出当前触摸在哪个字母上。
* 当手指按在字母表上时,展示弹出式分组。手指离开字母表时,将弹出式分组隐藏。
*/
private void setAlpabetListener() {
alphabetButton.setOnTouchListener(new OnTouchListener() {
@Override
public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) {
float alphabetHeight = alphabetButton.getHeight();
float y = event.getY();
int sectionPosition = (int) ((y / alphabetHeight) / (1f / 27f));
if (sectionPosition < 0) {
sectionPosition = 0;
} else if (sectionPosition > 26) {
sectionPosition = 26;
}
String sectionLetter = String.valueOf(alphabet.charAt(sectionPosition));
int position = indexer.getPositionForSection(sectionPosition);
switch (event.getAction()) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
alphabetButton.setBackgroundResource(R.drawable.a_z_click);
sectionToastLayout.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
sectionToastText.setText(sectionLetter);
contactsListView.setSelection(position);
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
sectionToastText.setText(sectionLetter);
contactsListView.setSelection(position);
break;
default:
alphabetButton.setBackgroundResource(R.drawable.a_z);
sectionToastLayout.setVisibility(View.GONE);
}
return true;
}
});
}
/**
* 获取sort key的首个字符,如果是英文字母就直接返回,否则返回#。
*
* @param sortKeyString
* 数据库中读取出的sort key
* @return 英文字母或者#
*/
private String getSortKey(String sortKeyString) {
alphabetButton.getHeight();
String key = sortKeyString.substring(0, 1).toUpperCase();
if (key.matches("[A-Z]")) {
return key;
}
return "#";
}
}






















 103
103

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








