一、文件操作概述.
1.文件内容操作:
创建文件 打开文件 关闭保存 读 写 调整文件内容指针
2.操作方法:
用现成的软件 、操作系统的命令、自己写的软件
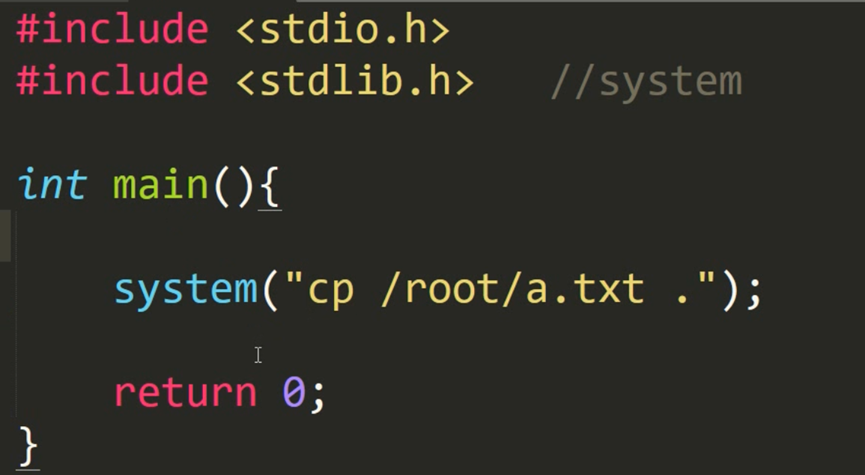
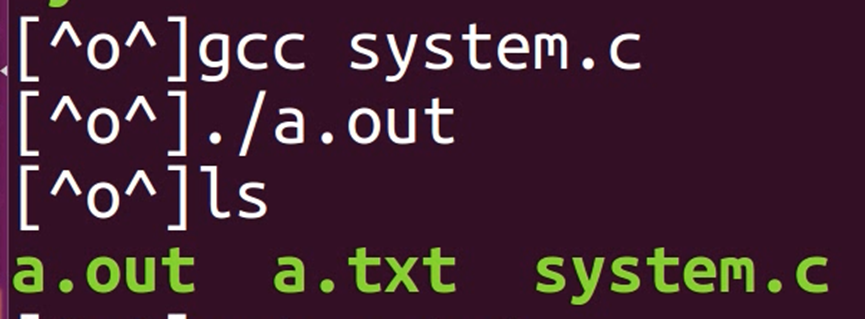
示例:system函数启动脚本程序 脚本程序中执行命令
(本质还是在调用命令(将/root/a.txt文件复制到当前目录下(.))
注:Linux系统中,system函数接口在stdlib的头文件中,放到windows中就是windows.h)
二、 Linux上操作文件常用命令or函数
1.常用的命令和函数
命令 : read write open 操作系统提前安装好的 应用程序
函数 : read write open
2.linux用文件描述符号来对应文件 文件描述符号是个整数
int fd; //file description
fd 指向一块内存, 这块内存中可以存储硬盘里 一个文件的 信息
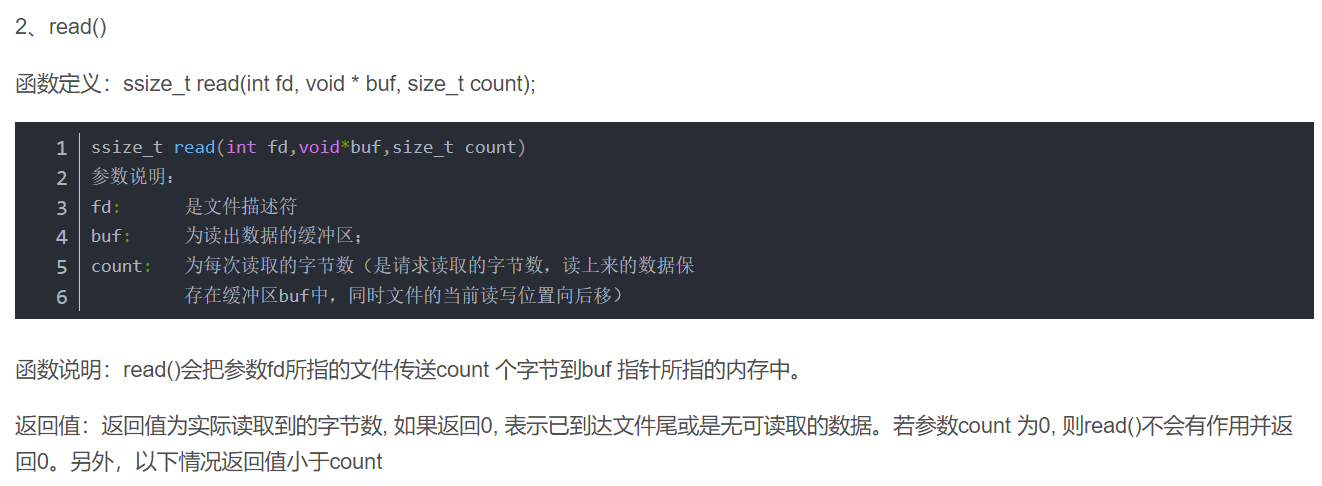
3.open(底层和ioct有关)
int open(
const char *pathname, //带路径的文件名
int flags, //方式
O_RDONLY O_WRONLY O_RDWR
mode_t mode); //权限(创建的方式open的时候才需要带上权限) 4.标准io :
0 stdin 1 stdout 2 stderror
0 : 标准输入设备
1 : 标准输出设备
2 : 标注错误输出描述符号
万物皆文件:linux系统之上 任何东西都是以文件的形式存在
看上述例子:
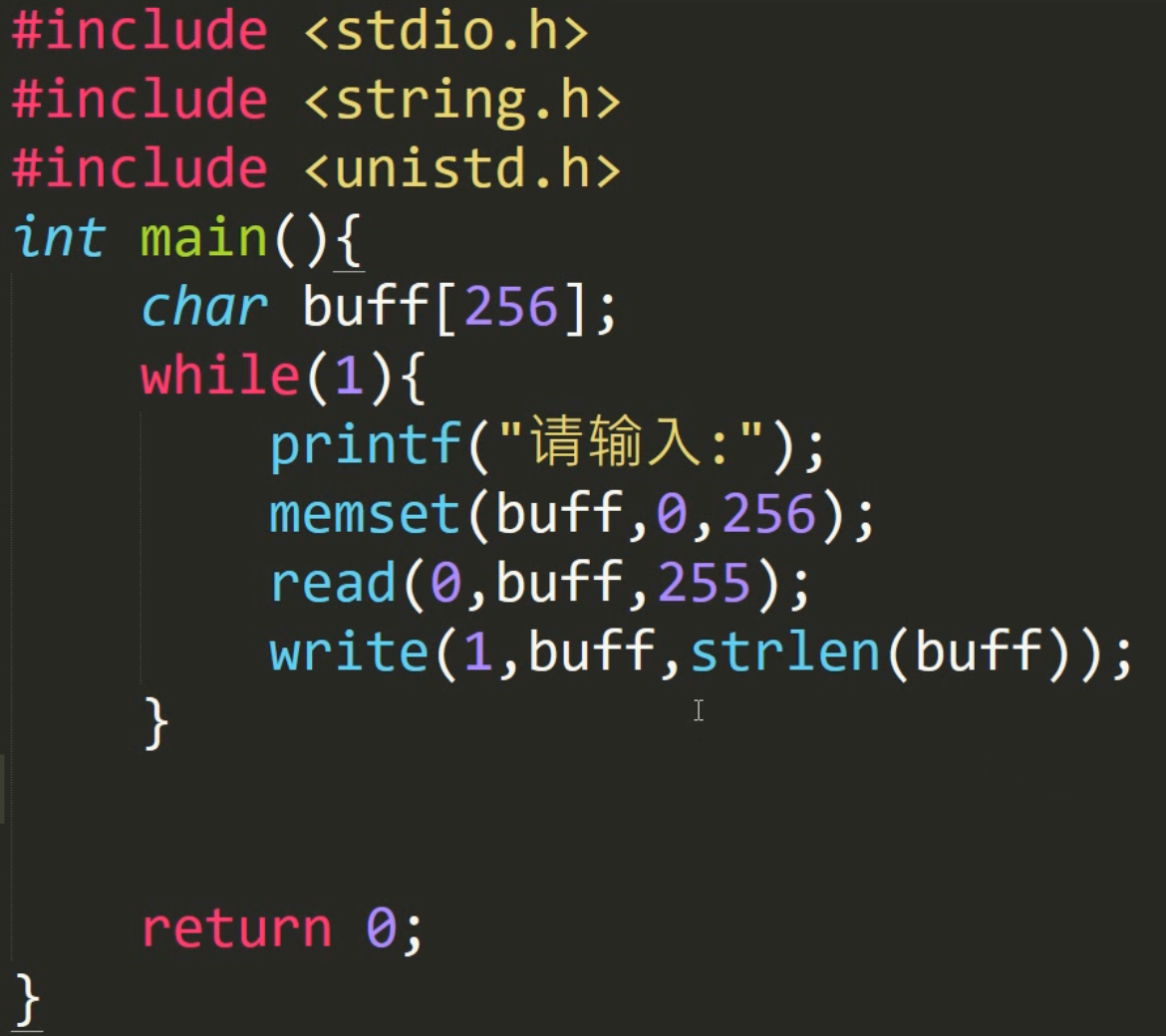
①主程序中的read和write函数都是<unistd.h>中的函数,(即linux中的函数
②第一个参数在此处传入的是标准io,
read第一个传入0,表示从输入设备读取内容
write第一个传入1,表示将内存中的内容输出到输出设备上。
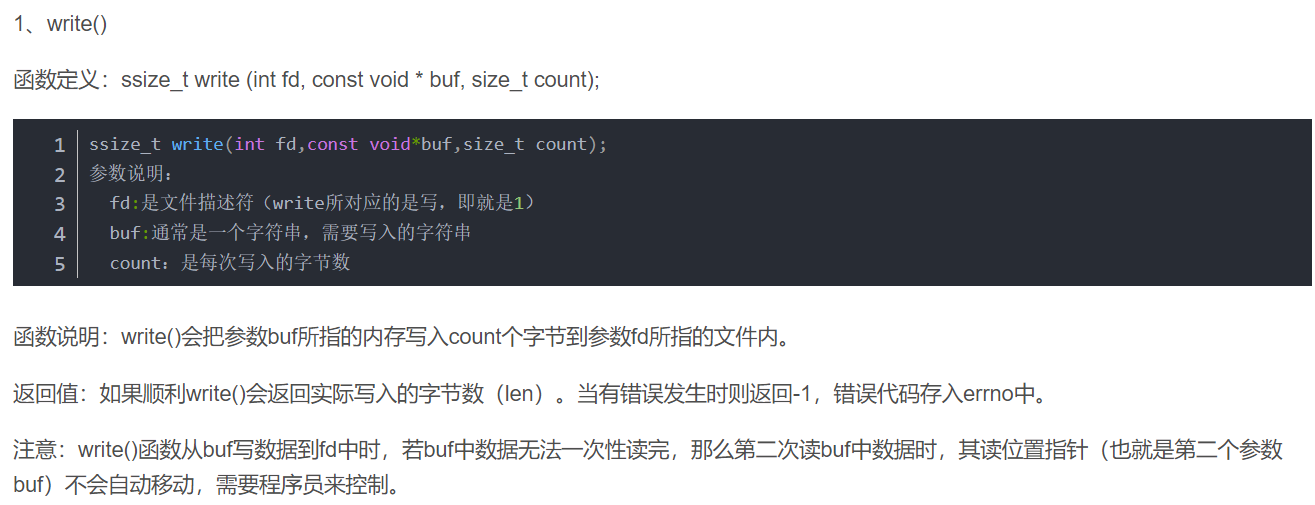
5.write和read函数
注:
进行的是二进制操作!而非字符文件操作。
C语言里打开文件的时候:
b : 字节文件 不会进行字节到字符之间的转化
不带b:字符文件 自动进行字节到字符之间的转化类似---->fwrite fprintf的区别 fread和fscanf的区别
①write函数:(注意一定要close,否则大概率不会保存文件信息)
#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <stdlib.h> struct Student{ char name[20]; int age; double score; }; int main(){ struct Student s[3] = { {"李世莒",20,10000}, {"余香" , 17 , 100}, {"钟帅",22,100} }; int fd = open("zhangsan.txt",O_CREAT|O_WRONLY,0333); if(-1 == fd){ printf("创建文件失败:%m\n"); exit(-1); } printf("创建文件成功!\n"); #if 0 write(fd,s,3*sizeof(struct Student)); #else for(int i=0;i<3;i++) write(fd,&s[i],sizeof(struct Student)); #endif close(fd);//关闭才会保存 return 0; }②read函数:
#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <stdlib.h> struct Student{ char name[20]; int age; double score; }; int main(){ struct Student s[3] = {0}; int fd = open("zhangsan.txt",O_RDONLY); if(-1 == fd){ printf("打开文件失败:%m\n"); exit(-1); } printf("打开文件成功!\n"); read(fd,s,3*sizeof(struct Student)); for(int i=0;i<3;i++) printf("%d:%s,%d,%g\n", i,s[i].name,s[i].age,s[i].score); close(fd);//关闭才会保存 return 0; }
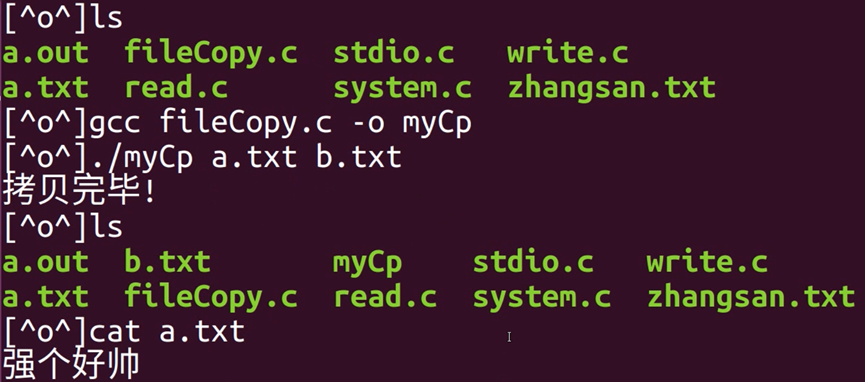
6.文件拷贝操作(自己实现)
//实现cp命令
步骤:
1. 打开待拷贝文件 argv[1] 待拷贝文件名称
2. 创建拷贝后文件 argv[2] 拷贝后的文件名称
3. 循环一个个字符读取,一个个字符写入
4. 关闭保存
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
//实现cp命令
int main(int argc,char* argv[])
{
if(argc != 3)
{
write(2,"请输入正确的命令行参数!",
strlen("请输入正确的命令行参数!"));
exit(-1);
}
//1. 打开待拷贝文件 argv[1]
int fdSrc = open(argv[1],O_RDONLY);
if(-1 == fdSrc)
{
printf("打开 %s 失败:%m\n",argv[1]);
exit(-1);
}
//2. 创建拷贝后文件 argv[2]
int fdDst = open(argv[2],O_CREAT|O_WRONLY,0666);
if(-1 == fdDst)
{
printf("创建 %s 失败:%m\n",argv[2]);
exit(-1);
}
//3. 循环一个个字符读取,一个个字符写入
char c;//保存读到的
char temp[44];
int r;//接受read的返回值
while(1){
r = read(fdSrc,&c,1);//r = read(fdSrc,temp,44);
if(1 != r)
{//if(r<=0)
printf("拷贝完毕!\n");
break;
}
//加密
write(fdDst,&c,1);//write(fdDst,temp,r);
}
//4. 关闭保存
close(fdSrc);close(fdDst);
return 0;
}使用:
补充:read也可以先获取到文件的总的字节数再去操作
lseek:
和fseek一样
SEEK_SET : 文件头
SEEK_CUR : 当前位置
SEEK_END : 文件末尾
7.简单实现mv命令
如果是在当前目录下 是重命名
如果是在其他目录下 是剪切
三 、其他常识
1.帮助命令
man open 弹出来的是 open 命令的 帮助
man 1 open 命令
man 2 open 标准函数
man 3 open 第三方库函数2.
将write.c文件拷贝到主目录下将write.c文件拷贝到主目录下
3.打开失败的时候,%m会自动抛出失败的相关信息

























 8612
8612











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










