
“侧影”就是从左侧或者右侧去观察物体所看到的内容。例如上图中男生的侧影是从他右侧看过去的样子,叫“右视图”;女生的侧影是从她左侧看过去的样子,叫“左视图”。
520 这个日子还在打比赛的你,也就抱着一棵二叉树左看看右看看了……
我们将二叉树的“侧影”定义为从一侧能看到的所有结点从上到下形成的序列。例如下图这棵二叉树,其右视图就是 { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 },左视图就是 { 1, 6, 7, 8, 5 }。
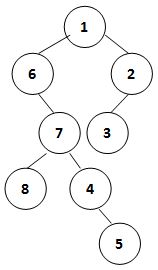
于是让我们首先通过一棵二叉树的中序遍历序列和后序遍历序列构建出一棵树,然后你要输出这棵树的左视图和右视图。
输入格式:
输入第一行给出一个正整数 N (≤20),为树中的结点个数。随后在两行中先后给出树的中序遍历和后序遍历序列。树中所有键值都不相同,其数值大小无关紧要,都不超过 int 的范围。
输出格式:
第一行输出右视图,第二行输出左视图,格式如样例所示。
输入样例:
8
6 8 7 4 5 1 3 2
8 5 4 7 6 3 2 1
输出样例:
R: 1 2 3 4 5
L: 1 6 7 8 5
分析:
后序遍历:左→右→中 中序遍历:左→中→右
先建树:根据后续遍历的结果可以判断每棵树的根结点,再去中序遍历中找到根结点的位置,在这个位置左边的就是它的左子树的结点,右边的就是它的右子树的结点
再输出:用队列来进行层序遍历
c++:
#include"iostream"
#include"queue"
#include"vector"
using namespace std;
typedef struct node* tree;
struct node {
int data;
tree l;
tree r;
};
tree build(int a1[], int a2[], int n) {
if (!n)return NULL;
tree t = (tree)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
t->data = a1[n - 1];
t->l = t->r = NULL;
int i = 0;
for (;i < n;i++) {
if (a2[i] == a1[n - 1])break;
}
// a[0]到a[i-1]为左子树的结点,a[i]到a[len-2]为右子树的结点
// b[0]到b[i-1]为左子树的结点,b[i+1]到b[len-1]为右子树的结点
t->l = build(a1, a2, i);
t->r = build(a1 + i, a2 + i + 1, n - i - 1);
return t;
}
vector<int> vl, vr;
queue<tree> q;
void print(tree t) {
if (t) {
q.push(t);
while (!q.empty()) {
int len = q.size(); // 先记录这一层结点的个数
for (int i = 0;i < len;i++) { // 遍历一层结点
tree tt = q.front();
q.pop();
if (!i)vl.push_back(tt->data); // 左侧能看到每层最左边的结点
if (i == len - 1)vr.push_back(tt->data); // 右侧能看到每层最右边的结点
if (tt->l)q.push(tt->l);
if (tt->r)q.push(tt->r);
}
}
}
cout << "R:";
for (auto a : vr)cout << " " << a;
cout << endl << "L:";
for (auto a : vl)cout << " " << a;
}
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
int hx[25], zx[25];
for (int i = 0;i < n;i++)cin >> zx[i];
for (int i = 0;i < n;i++)cin >> hx[i];
tree t = build(hx, zx, n);
print(t);
}python(因为数据量比较小,用列表玩也可以过):
n = int(input())
zx = list(map(int, input().split())) # 中序遍历序列
hx = list(map(int, input().split())) # 后序遍历序列
def build(a_start, a_end, b_start, b_end):
if a_start > a_end:
return None
newtree = [hx[a_end], -1, -1]
# 在中序遍历序列中查找根节点的位置
root_index = b_start
while zx[root_index] != newtree[0]:
root_index += 1
left_length = root_index - b_start
newtree[1] = build(a_start, a_start + left_length - 1, b_start, root_index - 1)
newtree[2] = build(a_start + left_length, a_end - 1, root_index + 1, b_end)
return newtree
tree = build(0, n - 1, 0, n - 1)
if tree:
res1 = []
res2 = []
queue = [tree]
while queue:
now_nodes = [] # 这层的结点的键值
next_level = [] # 下一层的结点
for x in queue:
now_nodes.append(x[0])
if x[1]:
next_level.append(x[1])
if x[2]:
next_level.append(x[2])
res1.append(now_nodes[0])
res2.append(now_nodes[-1])
queue = next_level
print("R:", *res2)
print("L:", *res1)





















 3244
3244

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








