目录
1 基本查询
1.1 查询相关列 (select * / 列名)
1.2 别名 (as)
1.3 去重 (distinct)
1.4 对列中的数据进行运算 (+、-、*、/)
2 条件查询 (where)
2.1 等值查询 (=)
2.2 非等值查询 (>、<、>=、<=、!=、><)
2.3 逻辑判断 (and、or、not)
2.4 区间判断 (between and)
2.5 NULL 值判断 (is null、is not null)
2.6 in 运算符
2.7 模糊查询 (like)
3 分支查询
4 排序 (order by)
5 日期和时间函数
1 基本查询
goods 表
drop table if exists goods;
create table goods (
id int(10) primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(14),
netprice float(7,2),
saleprice float(7,2),
weight float(7,2),
stockdate date
)charset=utf8;
#单条插入
insert into goods(name,netprice, saleprice, weight, stockdate) values('香蕉', 2.5, 3.8, 24, '2024-02-13');
#多条插入
insert into goods(name,netprice, saleprice, weight, stockdate) values
('苹果', 4.5, 7.2, 15, '2024-02-12'),
('苹果', 4.5, 7.5, 65, '2024-02-14'),
('橘子', 3.2, 4.5, 52, str_to_date('02-12-2024', '%m-%d-%Y')),
('橘子', 2.8, 4.5, 76, '2024-02-13'),
('橘子', 3.1, 5.2, 63, '2024-02-14'),
('葡萄', 2.1, 4.7, 26, str_to_date('2024/02/14', '%Y/%m/%d'));
1.1 查询相关列 (select * / 列名)
生产环境下,优先使用列名查询。* 的方式虽然看起来便捷,但实际上需要转换成全列名,效率低,可读性差
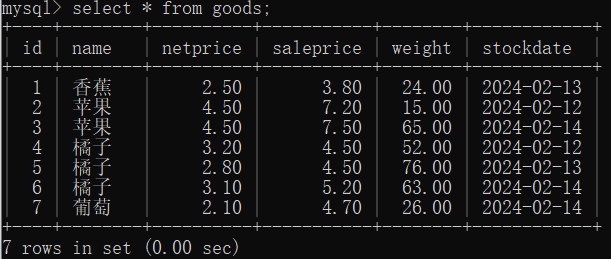
select * from goods;
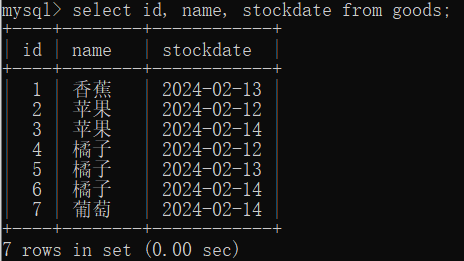
select id, name, stockdate from goods;
关键字顺序
select
...
from
...
以上语句执行顺序:
- from
- select
|
1.2 别名 (as)
通过 as 可以对列名取别名,as 可以省略(列名和别名之间用空格隔开)
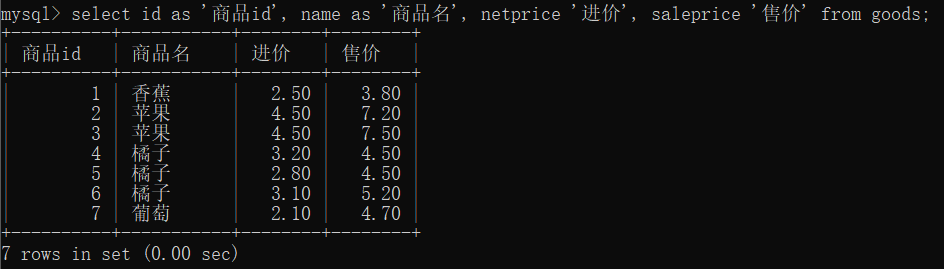
select id as '商品id', name as '商品名', netprice '进价', saleprice '售价' from goods;
|
1.3 去重 (distinct)
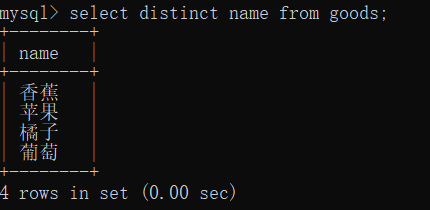
通过 distinct 将查询结果中的重复行去除
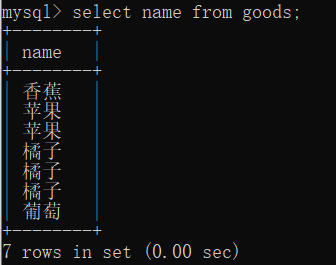
select name from goods;
select distinct name from goods;
|
1.4 对列中的数据进行运算 (+、-、*、/)
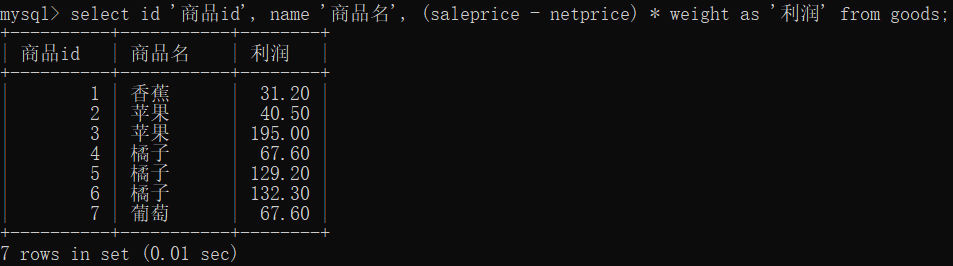
可以对列中的数据进行加 +、减 -、乘 *、除 /
select id '商品id', name '商品名', (saleprice - netprice) * weight as '利润' from goods;
|
2 条件查询 (where)
通过 where 进行条件查询
关键字顺序
select
...
from
...
where
...
以上语句执行顺序:
- from
- where
- select
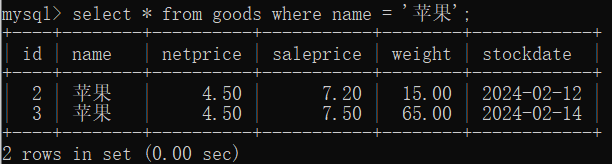
2.1 等值查询 (=)
select * from goods where name = '苹果';
|
2.2 非等值查询 (>、<、>=、<=、!=、><)
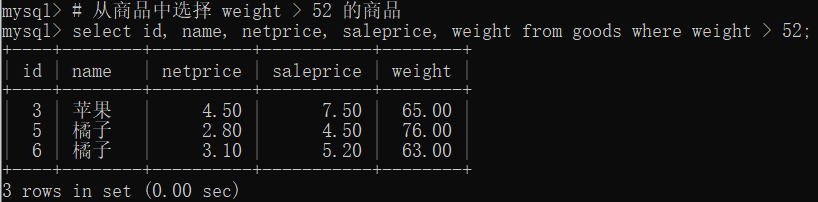
# 从商品中选择 weight > 52 的商品
select id, name, netprice, saleprice, weight from goods where weight > 52;
# 从商品中选择 weight < 52 的商品
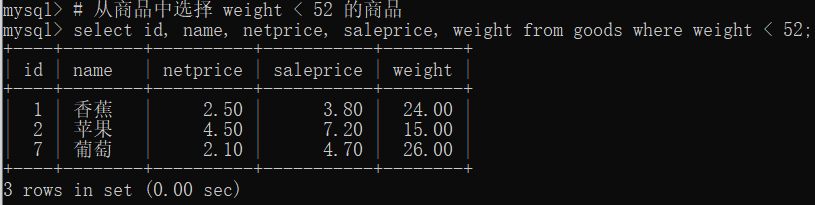
select id, name, netprice, saleprice, weight from goods where weight < 52;
# 从商品中选择 weight >= 52 的商品
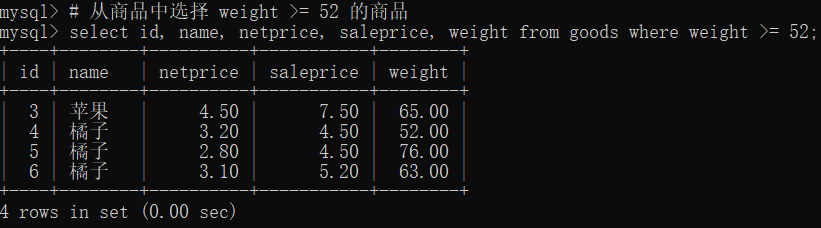
select id, name, netprice, saleprice, weight from goods where weight >= 52;
# 从商品中选择 weight <= 52 的商品
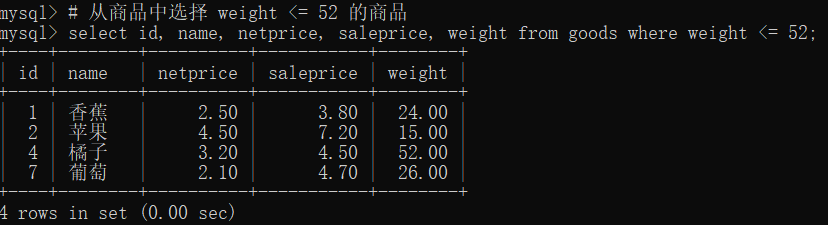
select id, name, netprice, saleprice, weight from goods where weight <= 52;
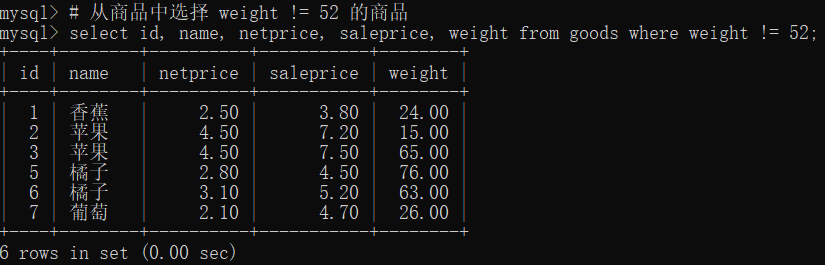
# 从商品中选择 weight != 52 的商品,此外 != 还可以这样用,如 name != '苹果'
select id, name, netprice, saleprice, weight from goods where weight != 52;
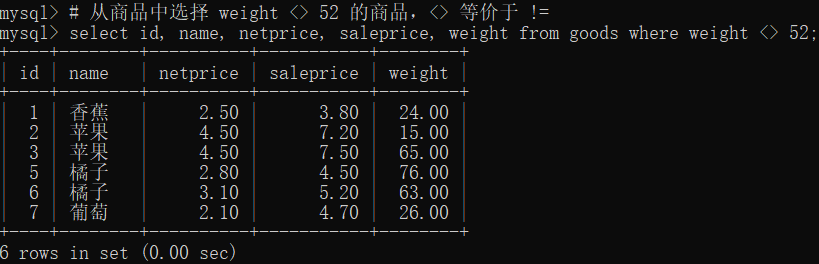
# 从商品中选择 weight <> 52 的商品,<> 等价于 !=
select id, name, netprice, saleprice, weight from goods where weight <> 52;
|
2.3 逻辑判断 (and、or、not)
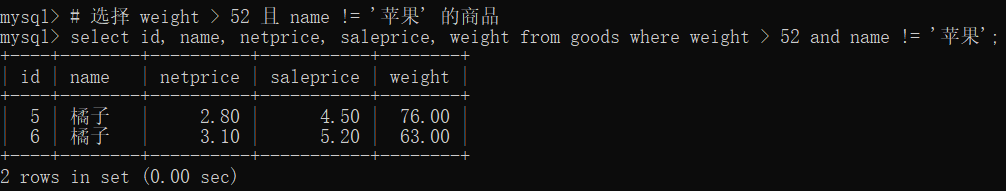
# 选择 weight > 52 且 name != '苹果' 的商品
select id, name, netprice, saleprice, weight from goods where weight > 52 and name != '苹果';
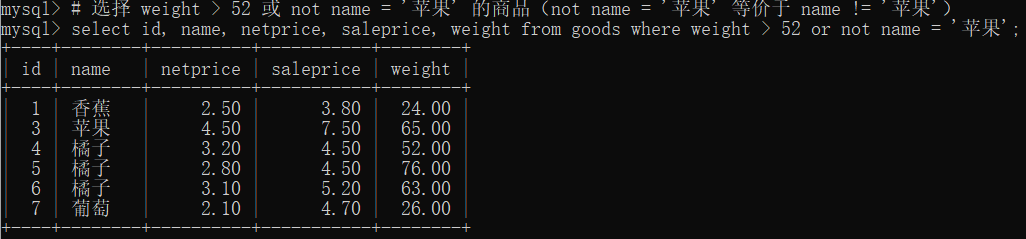
# 选择 weight > 52 或 not name = '苹果' 的商品(not name = '苹果' 等价于 name != '苹果')
select id, name, netprice, saleprice, weight from goods where weight > 52 or not name = '苹果';
|
2.4 区间判断 (between and)
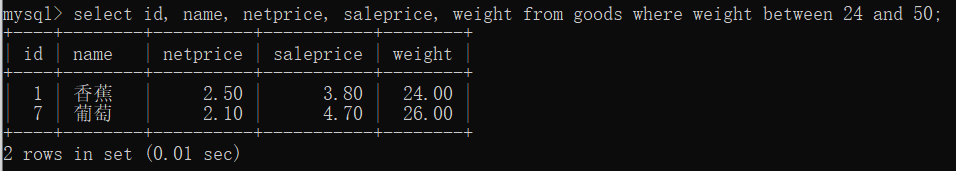
# 选择 24 <= weight <= 50 的商品
select id, name, netprice, saleprice, weight from goods where weight between 24 and 50;
|
2.5 NULL 值判断 (is null、is not null)
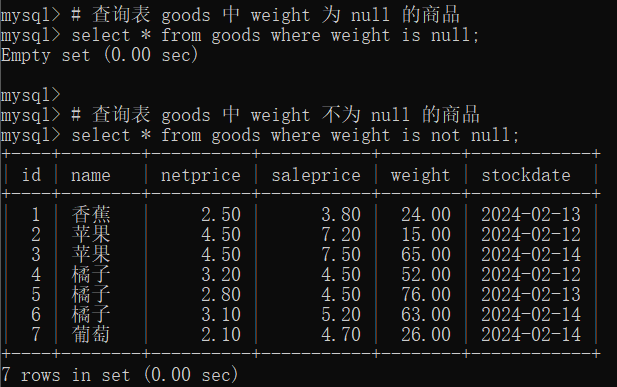
# 查询表 goods 中 weight 为 null 的商品
select * from goods where weight is null;
# 查询表 goods 中 weight 不为 null 的商品
select * from goods where weight is not null;
|
2.6 in 运算符
- in 运算符语法:
- where 列名 in (value1, value2, ...)
- where 列名 not in (value1, value2, ...)
- 只要列值在列表项 (value1, value2, ...) 中,则该行符合条件
- in 列表项不仅支持数字,也支持字符甚至时间日期类型等,并且可以将这些不同类型的数据项混合排列而无须跟 column(列) 的类型保持一致,如 in (1, 2,'str')
- in 可以和 and、or、>、<= 等运算符结合使用
- in 列表项可以是子查询
- 如果 in 的列表项是确定的,那么可以用多个 or 来代替。一般认为,如果是对索引字段进行操作,使用 or 效率高于 in,但对于列表项不确定的时候(如需要子查询得到结果),就必须使用 in 运算符。另外,对于子查询表数据小于主查询的时候,也是适用 in 运算符的
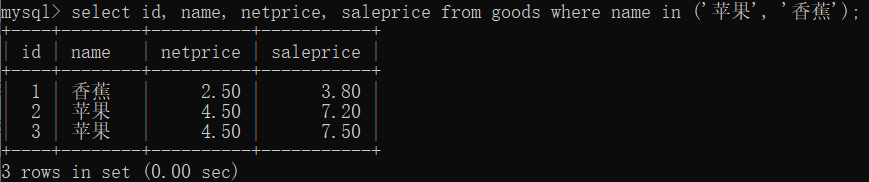
select id, name, netprice, saleprice from goods where name in ('苹果', '香蕉');
|
2.7 模糊查询 (like)
- “_” 表示单个任意字符
- “%” 表示任意个任意字符( 0 ~ n 个任意字符)
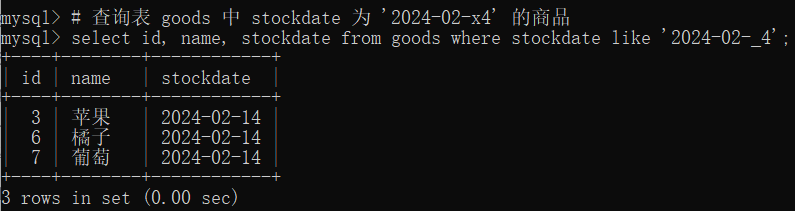
# 查询表 goods 中 stockdate 为 '2024-02-x4' 的商品
select id, name, stockdate from goods where stockdate like '2024-02-_4';
# 查询表 goods 中 saleprice 为 7.xx 的商品
select id, name, saleprice from goods where saleprice like '7.%';
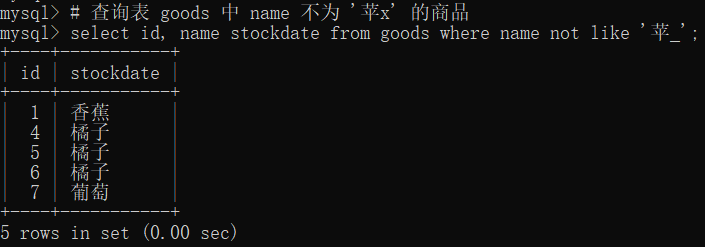
# 查询表 goods 中 name 不为 '苹x' 的商品
select id, name stockdate from goods where name not like '苹_';

|
3 分支查询
分支查询语法:
case
when 条件1 then 结果1
when 条件2 then 结果2
...
else 结果n
end
|
代码放在表格中,居然不能缩进。。。
select id, name, stockdate,
case
when stockdate = '2024-02-12' then '前天'
when stockdate = '2024-02-13' then '昨天'
when stockdate = '2024-02-14' then '今天'
else '不知道'
end as time
from goods;

4 排序 (order by)
order by 列名 asc / desc;
asc 表示升序,desc 表示降序,默认是升序
关键字顺序
select
...
from
...
where
...
order by
...
以上语句执行顺序:
- from
- where
- select
- order by
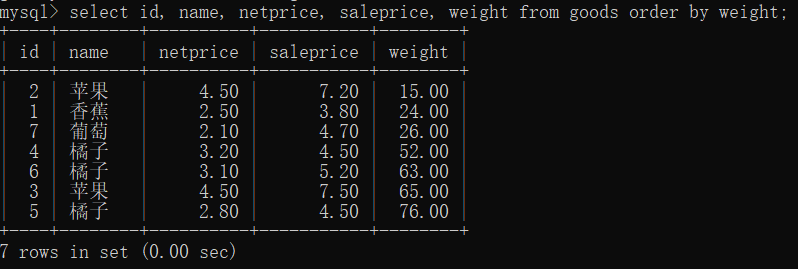
# 按照 weight 重量升序
select id, name, netprice, saleprice, weight from goods order by weight;
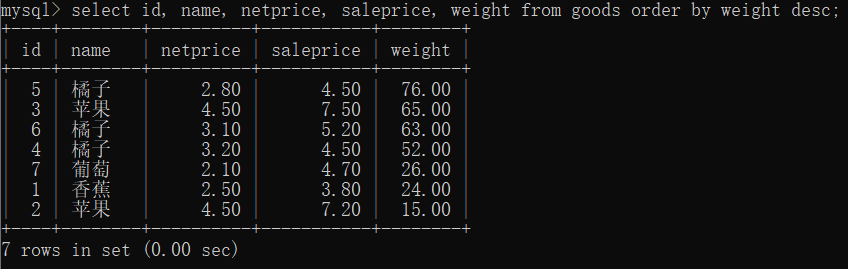
# 按照 weight 重量降序
select id, name, netprice, saleprice, weight from goods order by weight desc;
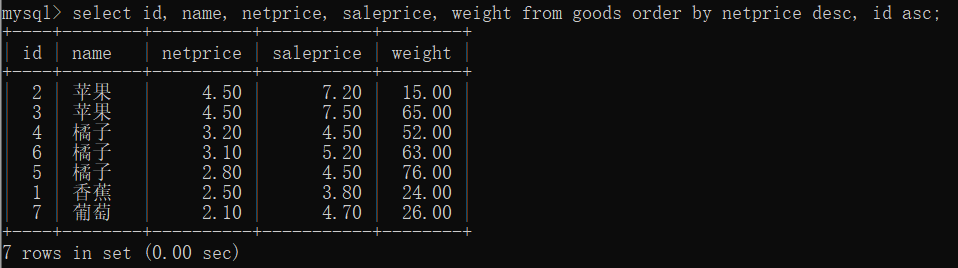
先按照 netprice 进价降序,如果 netprice 相等,则按照 id 降序
select id, name, netprice, saleprice, weight from goods order by netprice desc, id asc;
5 日期和时间函数
| 时间函数 | 描述 |
|---|
| sysdate() | 获得当前系统时间(年、月、日、时、分、秒) | | curdate() | 获得当前日期 | | curtime() | 获得当前时间 | | week(date) | 获得指定日期是一年中的第几周 | | year(date) | 获得指定日期的年份 | | month(date) | 获得指定日期的月份 | | day(date) | 获得指定日期是月份的第几天 | | hour(date) | 获得指定时间的小时值 | | minute(date) | 获得指定时间的分钟值 | | second(date) | 获得指定时间的秒值 | | datediff(enddate,startdate) | 获得两个时间相隔的天数 enddate - startdate 注意和 SQL Server 中的 datediff(datepart,startdate,enddate) 不同 | | adddate(date,n) | 在指定日期后面加 n 天 | | str_to_date(str,fmt) | 将不同时间格式的字符串转为的特定格式的日期 ('%Y-%m-%d') | | date_format(date,fmt) | 将时间转为不同时间格式的字符串 |
| 时间格式 | 描述 |
|---|
| %Y | 年,4 位 | | %y | 年,2 位 | | %X | 年,其中的星期日是周的第一天,4 位,与 %V 使用 | | %x | 年,其中的星期一是周的第一天,4 位,与 %v 使用 | | %b | 缩写月名 | | %c | 月,数值 | | %M | 月名 | | %m | 月,数值(00-12) | | %j | 年的天 (001-366) | | %D | 带有英文前缀的月中的天 | | %d | 月的天,数值(00-31) | | %e | 月的天,数值(0-31) | | %U | 周 (00-53) ,星期日是一周的第一天 | | %u | 周 (00-53) ,星期一是一周的第一天 | | %V | 周 (01-53) ,星期日是一周的第一天,与 %X 使用 | | %v | 周 (01-53) ,星期一是一周的第一天,与 %x 使用 | | %w | 周的天 (0=星期日, 6=星期六) | | %a | 缩写星期名 | | %W | 星期名 | | %T | 时间,24-小时 (hh:mm:ss) | | %r | 时间,12-小时(hh:mm:ss AM 或 PM) | | %p | AM 或 PM | | %H | 小时 (00-23) | | %h | 小时 (01-12) | | %I | 小时 (01-12) | | %k | 小时 (0-23) | | %l | 小时 (1-12) | | %i | 分钟,数值(00-59) | | %S | 秒(00-59) | | %s | 秒(00-59) | | %f | 微秒 |
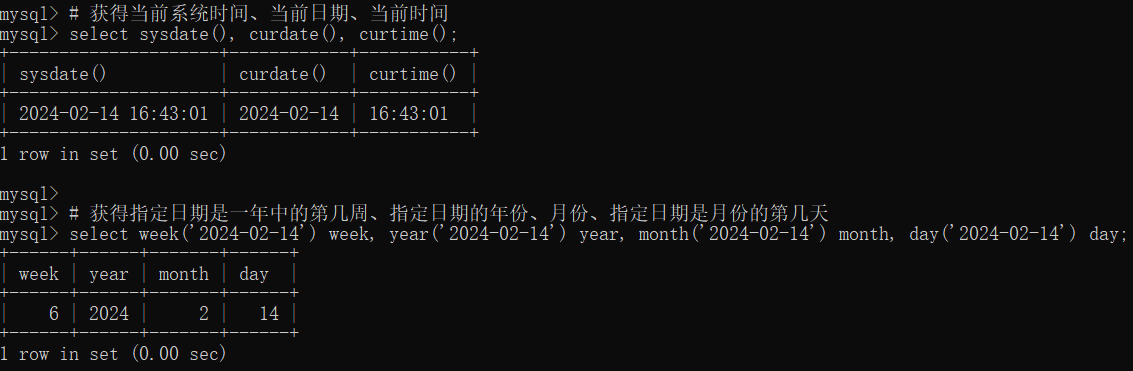
# 获得当前系统时间、当前日期、当前时间
select sysdate(), curdate(), curtime();
# 获得指定日期是一年中的第几周、指定日期的年份、月份、指定日期是月份的第几天
select week('2024-02-14') week, year('2024-02-14') year, month('2024-02-14') month, day('2024-02-14') day;
# 获得指定时间的小时值、分钟值、秒值
select hour('16:33:24'),minute('16:33:24'), second('16:33:24');
# 获得两个时间之间相隔的天数,只计算日期,这里是2024-03-02 减去 2024-02-29 得到两天
select datediff('2024-03-02 08:00:00','2024-02-29 10:00:00') day;
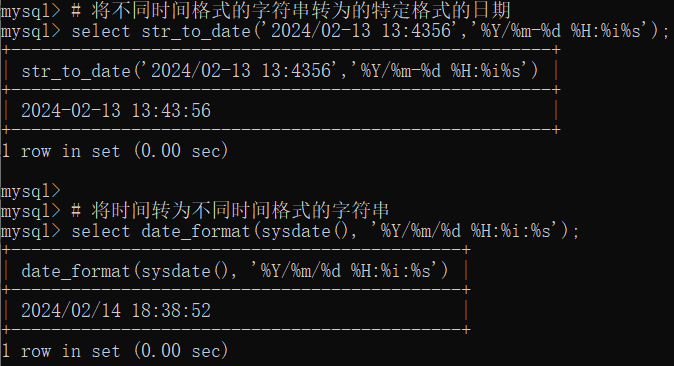
# 将不同时间格式的字符串转为的特定格式的日期
select str_to_date('2024/02-13 13:4356','%Y/%m-%d %H:%i%s');
# 将时间转为不同时间格式的字符串
select date_format(sysdate(), '%Y/%m/%d %H:%i:%s');
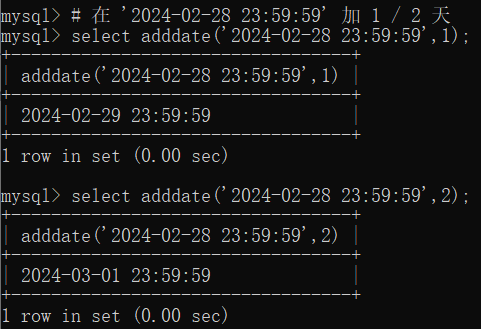
# 在 '2024-02-28 23:59:59' 加 1 / 2 天
select adddate('2024-02-28 23:59:59',1);
select adddate('2024-02-28 23:59:59',2);

|



















































 736
736











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








