首发于微信公众号 公众号链接,欢迎关注

太复杂说明的题,面试不考;太easy,太tricky的题也不收录。
11. Container With Most Water
33. Search in Rotated Sorted Array
55. Jump Game
94. Binary Tree Inorder Traversal
109. Convert Sorted List to Binary Search Tree
137. Single Number II
11. Container With Most Water
Given n non-negative integers a1, a2, ..., an , where each represents a point at coordinate (i, ai). n vertical lines are drawn such that the two endpoints of the line i is at (i, ai) and (i, 0). Find two lines, which, together with the x-axis forms a container, such that the container contains the most water.
Notice that you may not slant the container.
Example 1:

Input: height = [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]
Output: 49
Explanation: The above vertical lines are represented by array [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]. In this case, the max area of water (blue section) the container can contain is 49.
Example 2:
Input: height = [1,1]
Output: 1
Example 3:
Input: height = [4,3,2,1,4]
Output: 16
Example 4:
Input: height = [1,2,1]
Output: 2
Constraints:
-
n = height.length -
2 <= n <= 3 * 104 -
0 <= height[i] <= 3 * 104
思路:two pointer,而非stack
class Solution:def maxArea(self, h):""":type height: List[int]:rtype: int"""i,j=0,len(h)-1res=0while i<j:res=max(res, (j-i)*min(h[i],h[j]))if h[i]<h[j]: i+=1else: j-=1return ress=Solution()print(s.maxArea([1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]))
33. Search in Rotated Sorted Array
You are given an integer array nums sorted in ascending order, and an integer target.
Suppose that nums is rotated at some pivot unknown to you beforehand (i.e., [0,1,2,4,5,6,7] might become [4,5,6,7,0,1,2]).
If target is found in the array return its index, otherwise, return -1.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [4,5,6,7,0,1,2], target = 0
Output: 4
Example 2:
Input: nums = [4,5,6,7,0,1,2], target = 3
Output: -1
Example 3:
Input: nums = [1], target = 0
Output: -1
Constraints:
-
1 <= nums.length <= 5000 -
-10^4 <= nums[i] <= 10^4 -
All values of
numsare unique. -
numsis guranteed to be rotated at some pivot. -
-10^4 <= target <= 10^4
思路:总有一半的array是排好序的
class Solution:def search(self, a, target):""":type nums: List[int]:type target: int:rtype: int"""if not a: return -1lo,hi=0,len(a)-1while lo<hi:mid=(lo+hi)//2if a[mid]==target: return midelif a[mid]<a[hi]:if a[mid]<target<=a[hi]:lo=mid+1else:hi=mid-1else:if a[lo]<=target<a[mid]:hi=mid-1else:lo=mid+1return lo if a[lo]==target else -1s=Solution()print(s.search(a = [4,5,6,7,0,1,2], target = 0))print(s.search(a = [4,5,6,7,0,1,2], target = 3))
55. Jump Game
Given an array of non-negative integers, you are initially positioned at the first index of the array.
Each element in the array represents your maximum jump length at that position.
Determine if you are able to reach the last index.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [2,3,1,1,4]
Output: true
Explanation: Jump 1 step from index 0 to 1, then 3 steps to the last index.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [3,2,1,0,4]
Output: false
Explanation: You will always arrive at index 3 no matter what. Its maximum jump length is 0, which makes it impossible to reach the last index.
Constraints:
-
1 <= nums.length <= 3 * 10^4 -
0 <= nums[i][j] <= 10^5
思路:维护最远能到的位置
class Solution {public boolean canJump(int[] a) {int max=0;for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++) {if(max<i) return false;max=Math.max(max, i+a[i]);}return true;}}
94. Binary Tree Inorder Traversal
Given the root of a binary tree, return the inorder traversal of its nodes' values.
思路:牢记非递归版本的写法
# Definition for a binary tree node.# class TreeNode(object):# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):# self.val = val# self.left = left# self.right = rightclass Solution(object):def inorderTraversal(self, root):""":type root: TreeNode:rtype: List[int]"""st,res = [],[]p = rootwhile p or st:while p:st.append(p)p = p.lefts = st.pop()res.append(s.val)p = s.rightreturn res
109. Convert Sorted List to Binary Search Tree
Given the head of a singly linked list where elements are sorted in ascending order, convert it to a height balanced BST.
For this problem, a height-balanced binary tree is defined as a binary tree in which the depth of the two subtrees of every node never differ by more than 1.
Example 1:
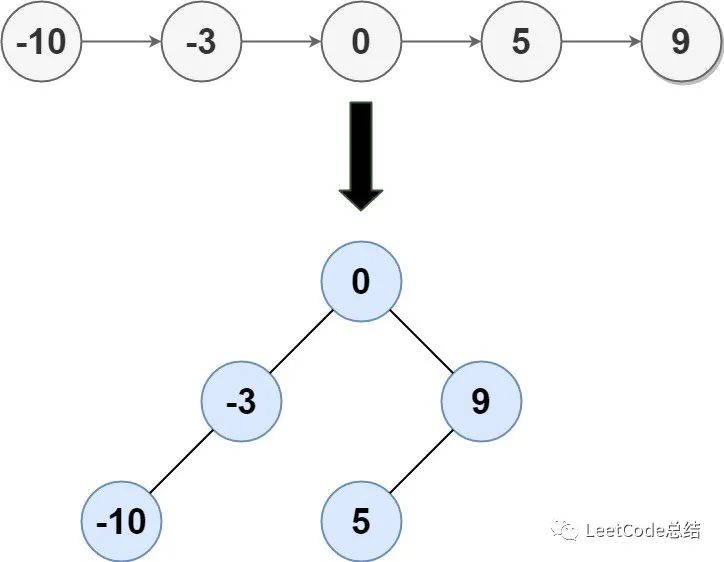
Input: head = [-10,-3,0,5,9]
Output: [0,-3,9,-10,null,5]
Explanation: One possible answer is [0,-3,9,-10,null,5], which represents the shown height balanced BST.
Example 2:
Input: head = []
Output: []
Example 3:
Input: head = [0]
Output: [0]
Example 4:
Input: head = [1,3]
Output: [3,1]
Constraints:
-
The number of nodes in
headis in the range[0, 2 * 104]. -
-10^5 <= Node.val <= 10^5
思路:核心在于slow、fast指针找到中间节点
public class Solution {public TreeNode sortedListToBST(ListNode head) {if(head == null) return null;if(head.next == null) return new TreeNode(head.val);ListNode mid = getMid(head);TreeNode rst = new TreeNode(mid.val);rst.left = sortedListToBST(head);rst.right = sortedListToBST(mid.next);return rst;}private ListNode getMid(ListNode head) {ListNode slow = head, fast = head, preSlow = null;while(fast != null) {fast = fast.next;if(fast != null) {fast = fast.next;preSlow = slow;slow = slow.next;}}preSlow.next = null;return slow;}}
137. Single Number II
Given an integer array nums where every element appears three times except for one, which appears exactly once. Find the single element and return it.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [2,2,3,2]
Output: 3
Example 2:
Input: nums = [0,1,0,1,0,1,99]
Output: 99
Constraints:
-
1 <= nums.length <= 3 * 104 -
-231 <= nums[i] <= 231 - 1 -
Each element in
numsappears exactly three times except for one element which appears once.
Follow up: Your algorithm should have a linear runtime complexity. Could you implement it without using extra memory?
思路:开一个大小为32的数组,维护每个bit位置的信息
class Solution:def singleNumber(self, a):""":type nums: List[int]:rtype: int"""count=[0]*32for i in a:for j in range(32):count[j] += (i>>j) & 1res=0for i,v in enumerate(count):if v%3==1:res+=(1<<i)return res if res<=2**31-1 else res-2**32print(Solution().singleNumber([2,2,3,2]))print(Solution().singleNumber([-2,-2,1,1,-3,1,-3,-3,-4,-2]))






















 1112
1112











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








