Elastic Resource Capacity (Erl, Naserpour)
How can the processing capacity of virtual servers be dynamically scaled in response to fluctuating IT resource usage requirements?

Problem
When IT resources hosted by a virtual server impose processing requirements that exceed the virtual server’s capacity, the performance and reliability of the hosted IT resources and the virtual server itself may be compromised.Solution
An elastic provisioning system is established to dynamically allocate and reclaim CPUs and RAM for a virtual server in response to the fluctuating processing requirements of its hosted IT resources.Application
Resource pools are utilized by scaling technology that interacts with the hypervisor and/or VIM to retrieve and return CPU and RAM resources at runtime, as per necessary processing capacity.Mechanisms
Automated Scaling Listener, Cloud Usage Monitor, Hypervisor, Live VM Migration, Pay-Per-Use Monitor, Resource Replication, Virtual CPU, Virtual Infrastructure Manager, Virtual RAM, Virtual ServerCompound Patterns
Burst In, Burst Out to Private Cloud, Burst Out to Public Cloud, Cloud Authentication, Cloud Balancing, Elastic Environment, Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Isolated Trust Boundary, Multitenant Environment, Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), Private Cloud, Public Cloud, Resilient Environment, Resource Workload Management, Secure Burst Out to Private Cloud/Public Cloud, Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)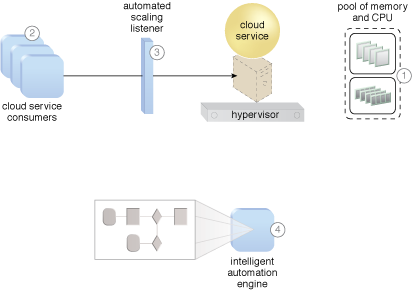
The application of the Elastic Resource Capacity pattern on a sample cloud architecture (Part I).
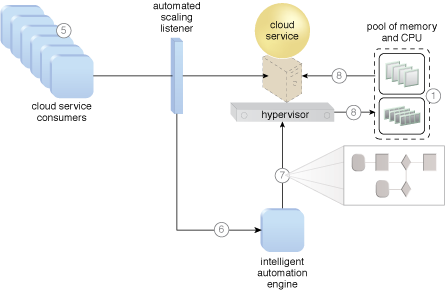
The application of the Elastic Resource Capacity pattern on a sample cloud architecture (Part II).
NIST Reference Architecture Mapping
This pattern relates to the highlighted parts of the NIST reference architecture, as follows:
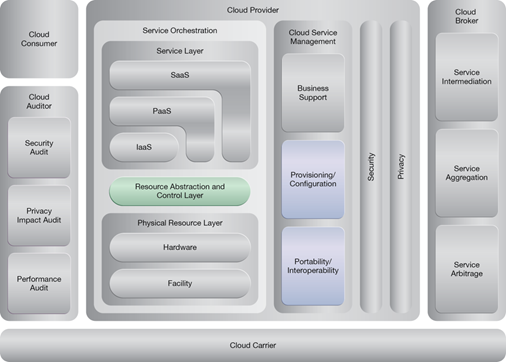
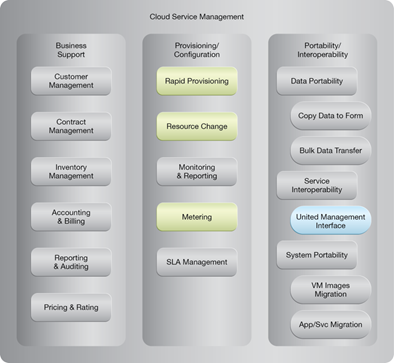






















 2913
2913

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








