系列文章目录
第一章 java JUC并发编程 Future: link
第二章 java JUC并发编程 多线程锁: link
第三章 java JUC并发编程 中断机制: link
第四章 java JUC并发编程 java内存模型JMM: link
第五章 java JUC并发编程 volatile与JMM: link
第六章 java JUC并发编程 CAS: link
第七章 java JUC并发编程 原子操作类增强: link
第八章 java JUC并发编程 ThreadLocal: link
第九章 java JUC并发编程 对象内存布局与对象头: link
第十章 java JUC并发编程 Synchronized与锁升级: link
第十一章 java JUC并发编程 AbstractQueuedSynchronizer之AQS: link
1 AQS理论知识
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer 抽象的队列同步器,前置知识在前面的公平锁和非公平锁、可重入锁、自旋思想、LockSupport、数据结构之双向链表、设计模式之模板设计模式。
1.1 理论知识
源码位置:并发包的锁包下面
是用来实现锁或者其他同步器组件的公共基础部分的抽象实现,是重量级基础框架及整个JUC体系的基石,主要用于解决锁分配给谁的问题
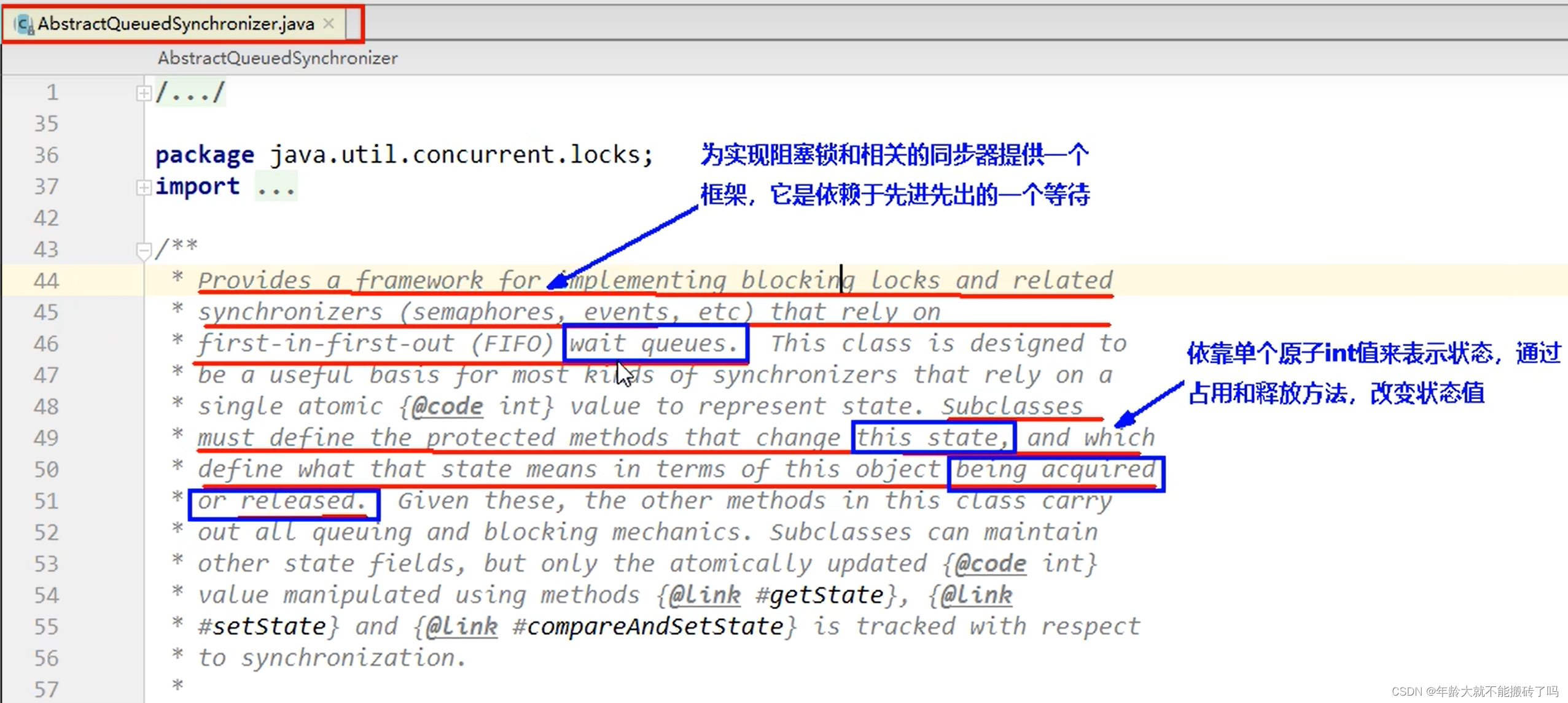
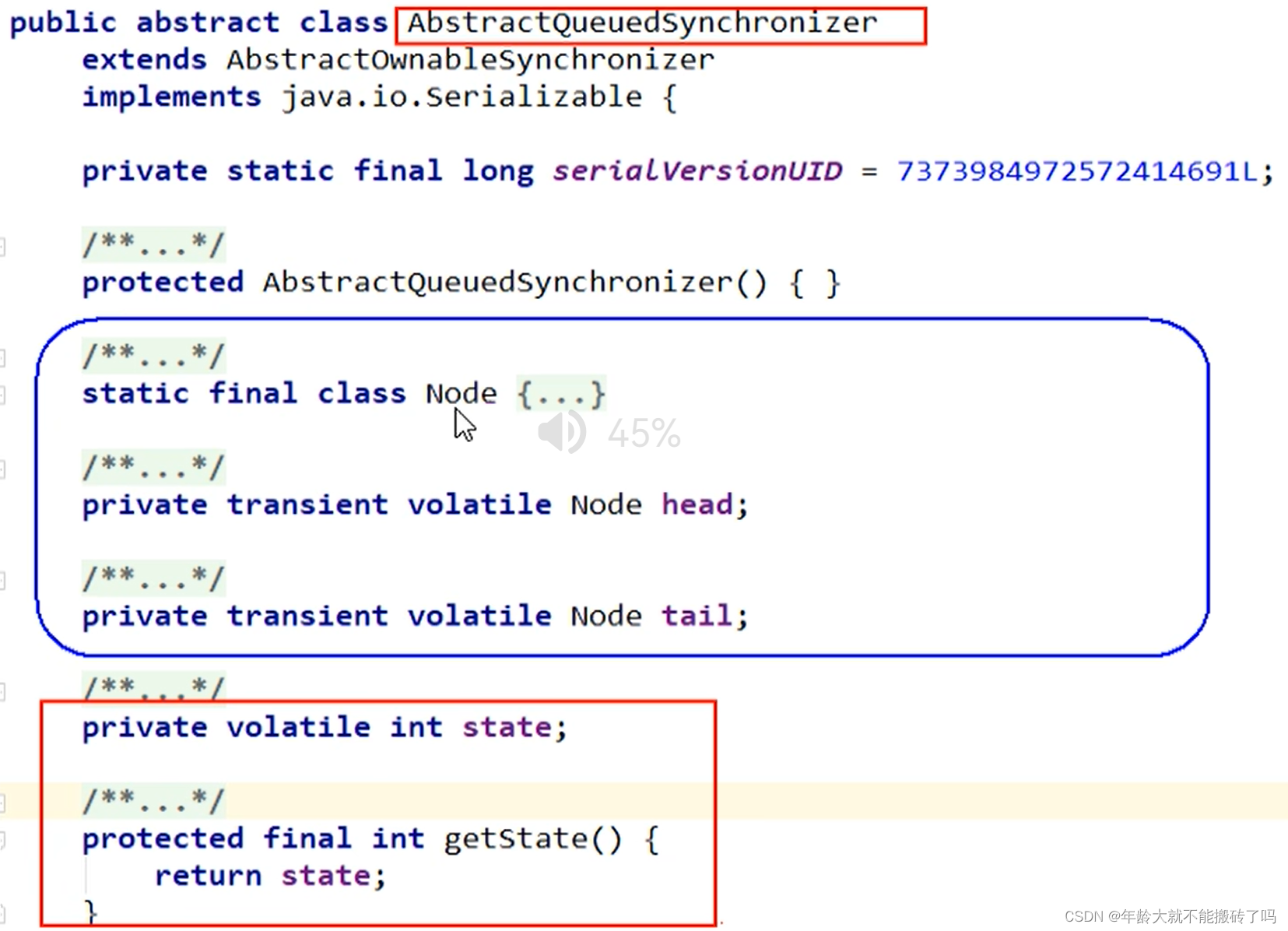
整体就是一个抽象的FIFO队列来完成资源获取线程的排队工作,并通过一个int类变量表示持有锁的状态。
和AQS有关的:
ReentrantLock靠sync的变量继承了AbstractQueuedSynchronizer里面有一个抽象的lock方法
规矩都放在父类
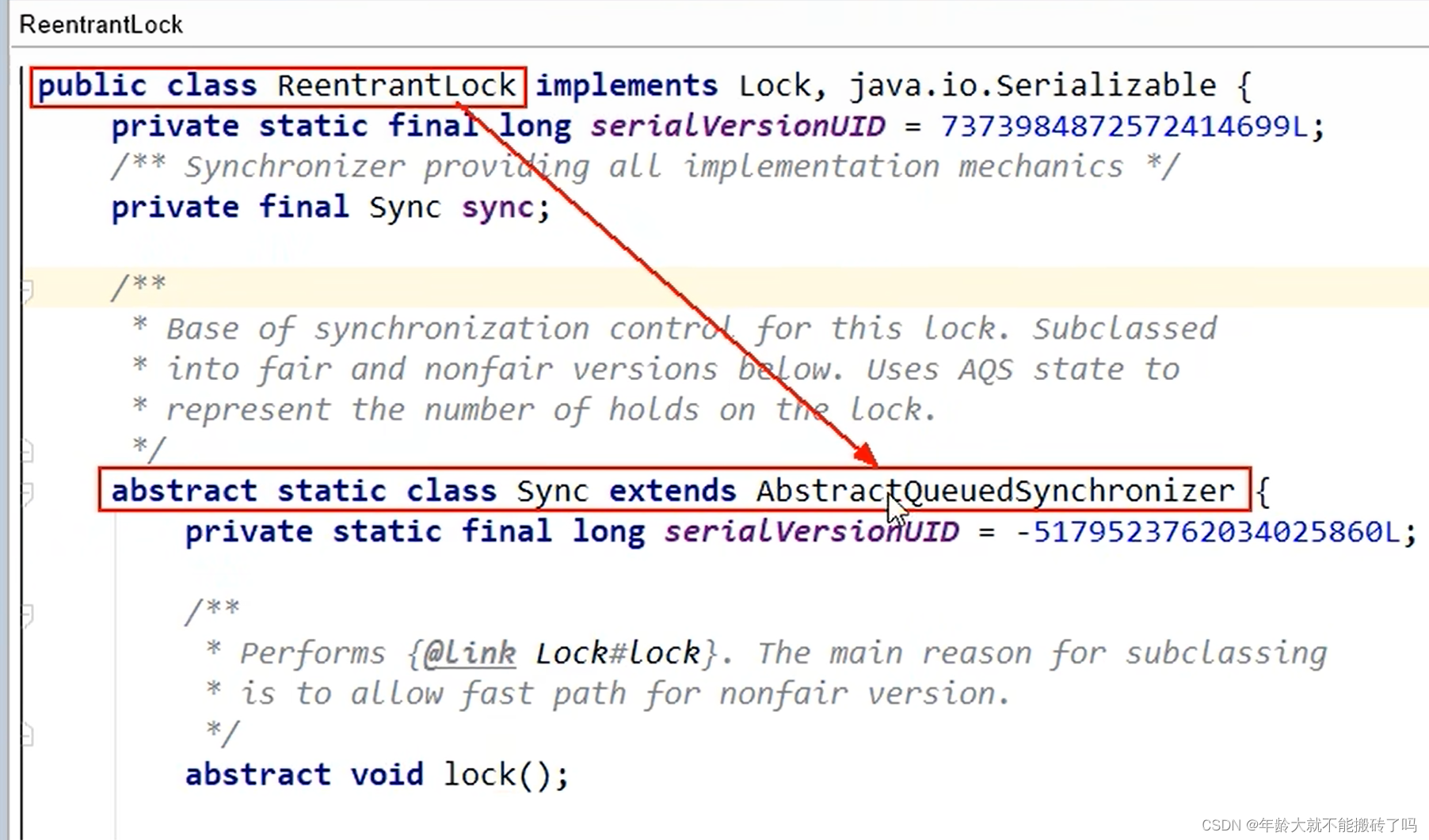
CountDownLatch
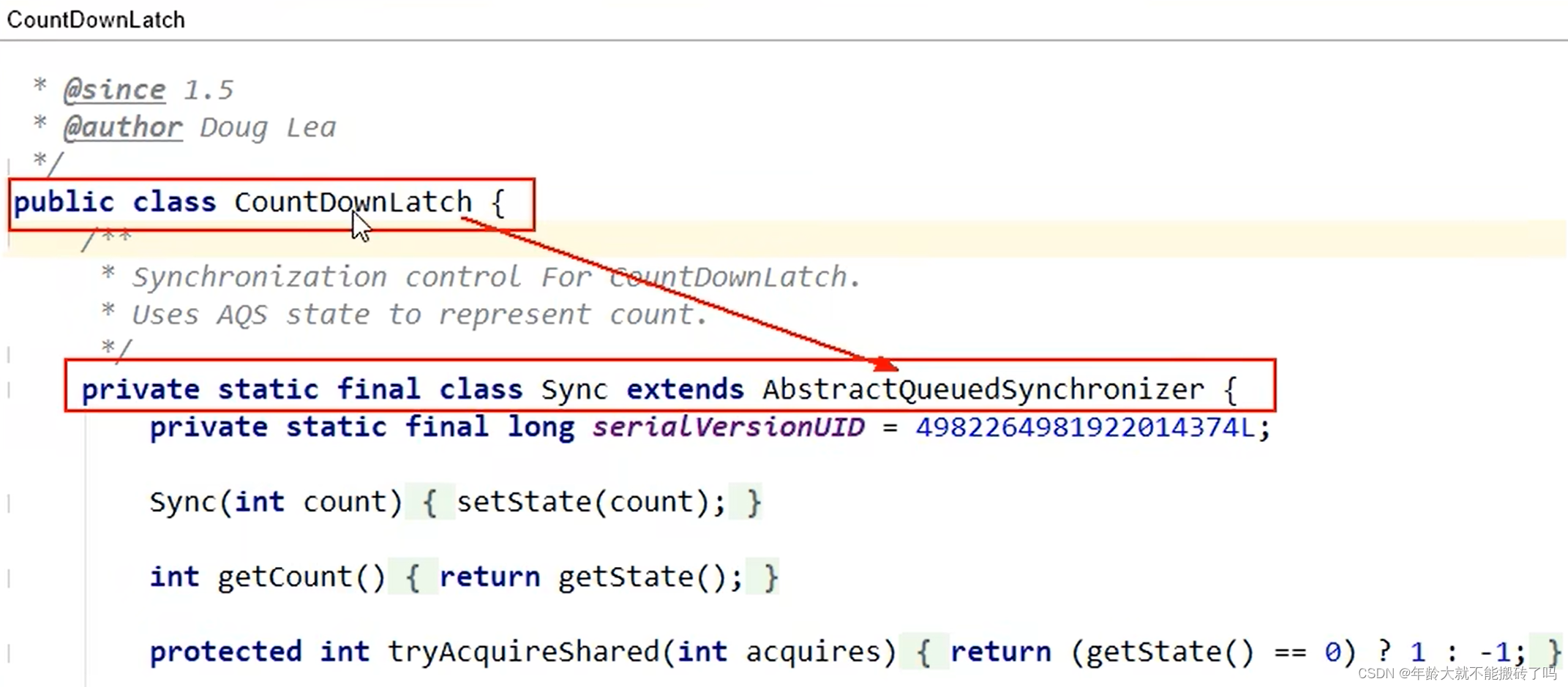
ReentrantReadWriteLock
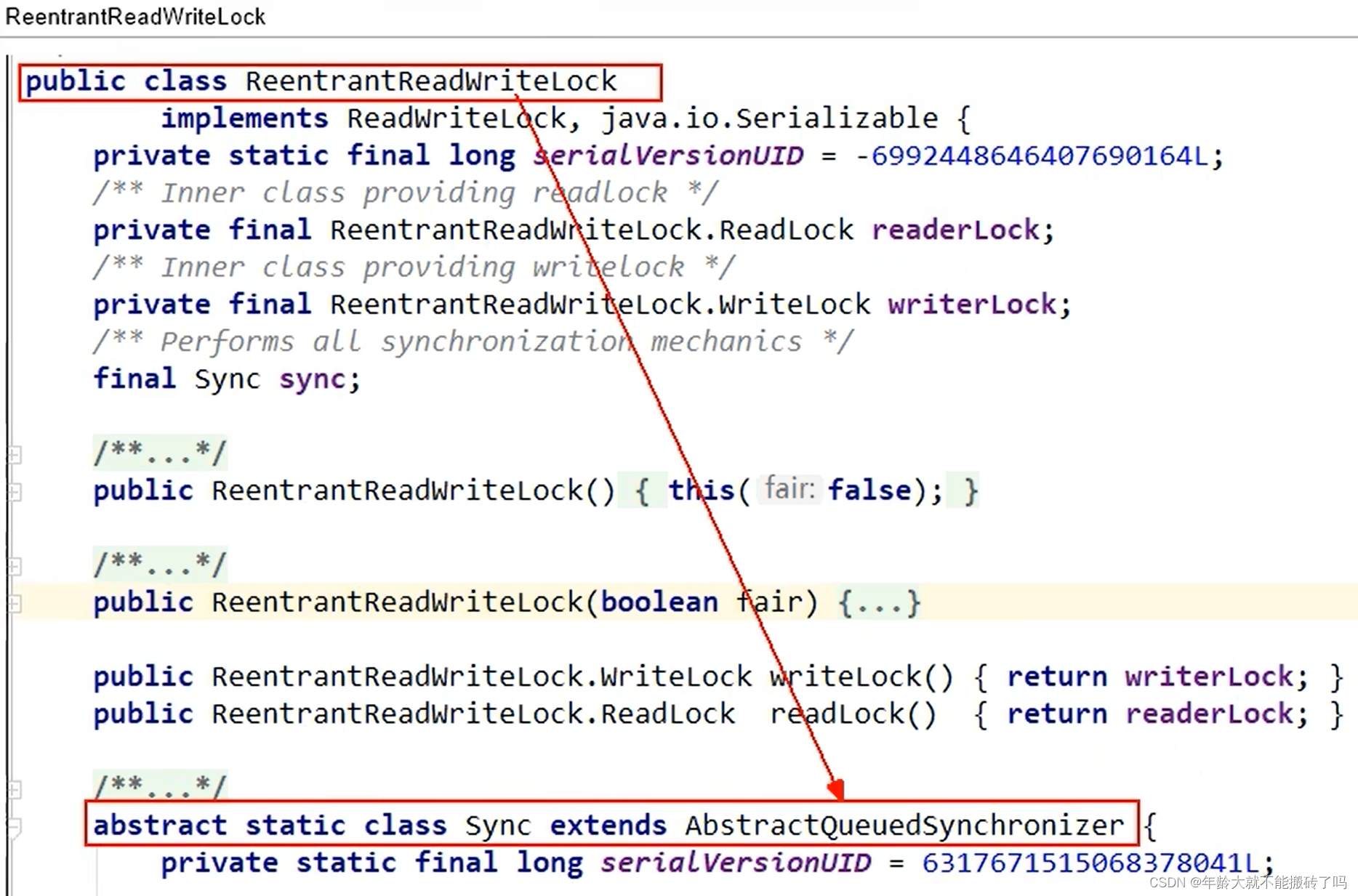
Semaphore
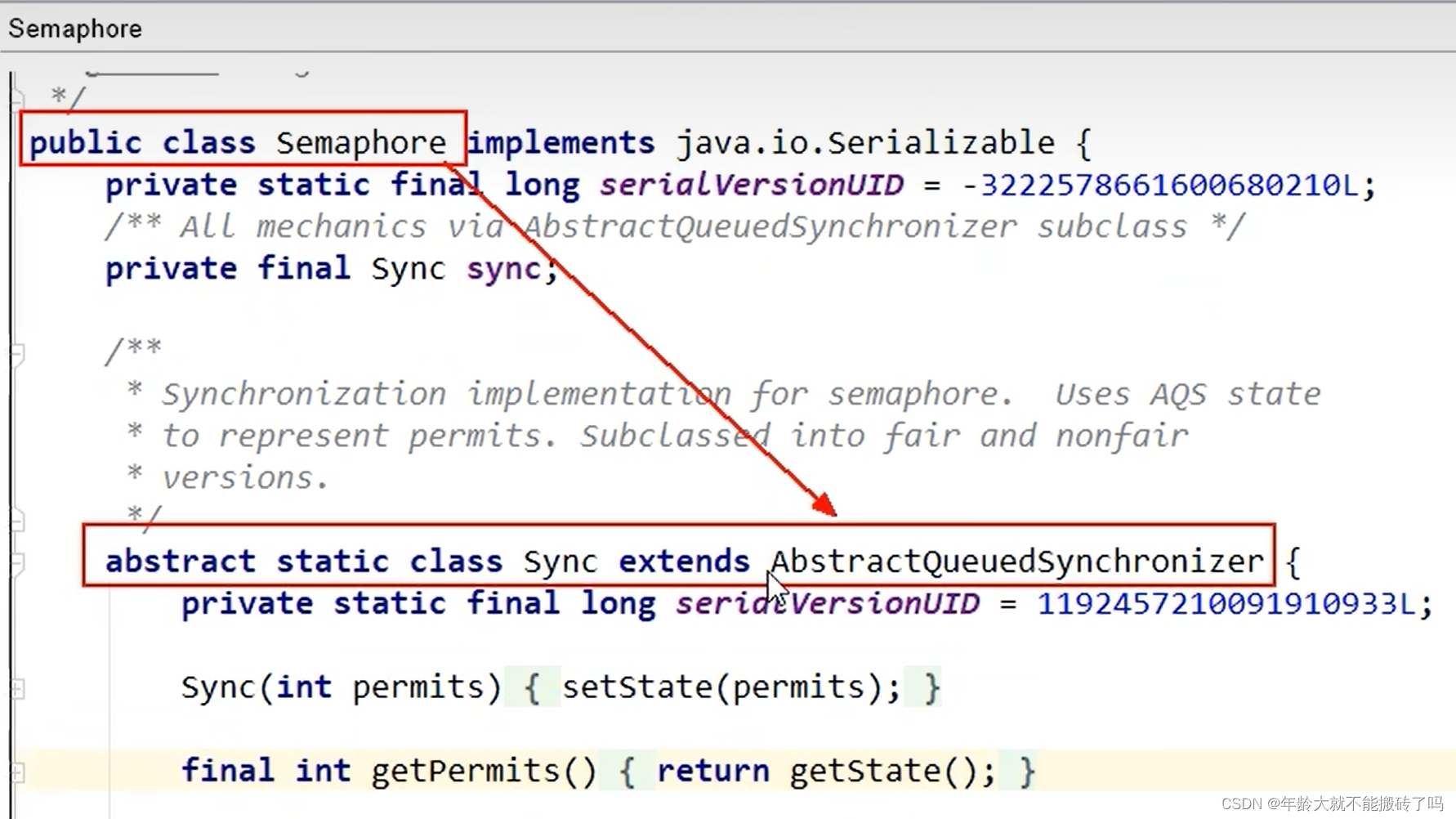
1.2 锁和同步器的关系
锁,面向锁的使用者:
定义了程序员和锁交互的使用层API,隐藏了实现细节,调用即可。
同步器,面向锁的实现者:
java并发大神DougLee,提出统一规范化简化了锁的实现,将其抽象出来屏蔽了同步状态管理、同步队列的管理和维护、阻塞线程排队和通知、唤醒机制等,是一切锁和同步组实现的公共基础部分。
1.3 解决了什么问题
加锁会导致阻塞,有阻塞就需要排队,实现排队必然需要队列。
解释说明:

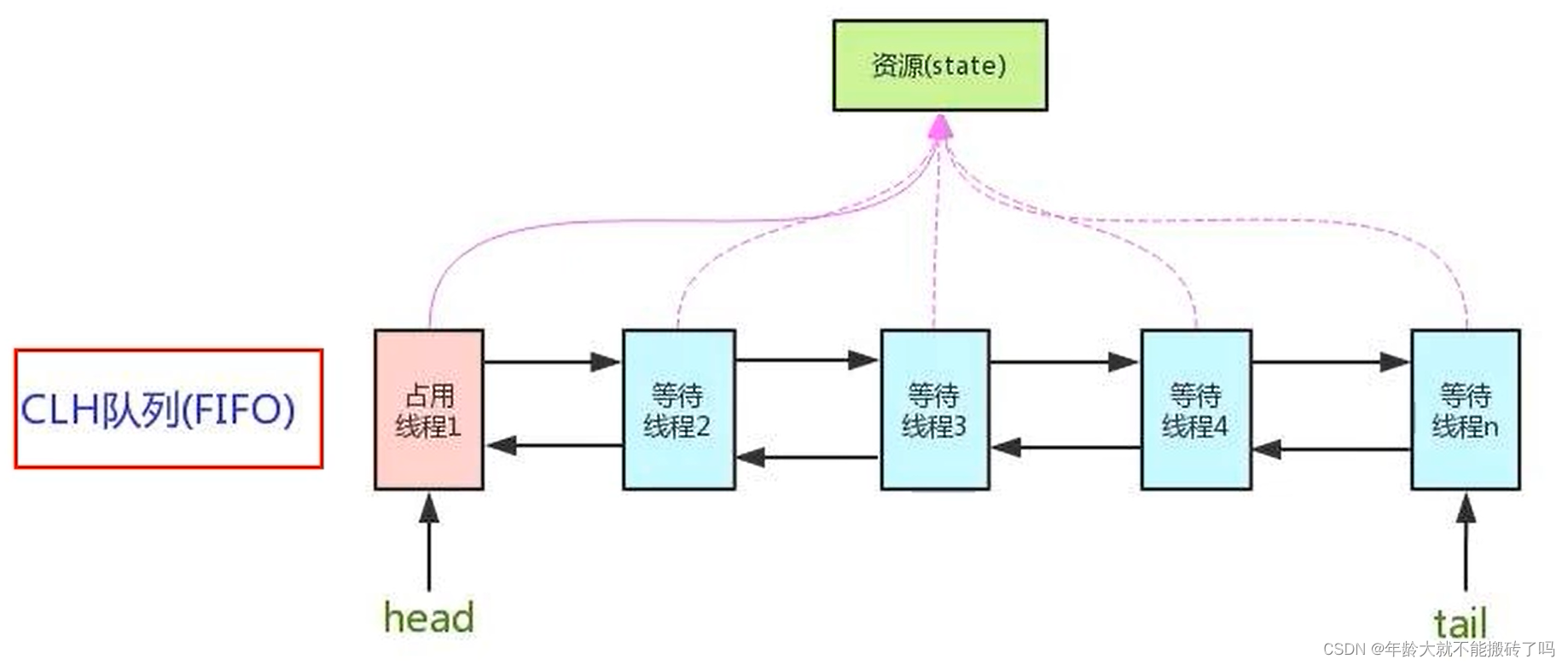
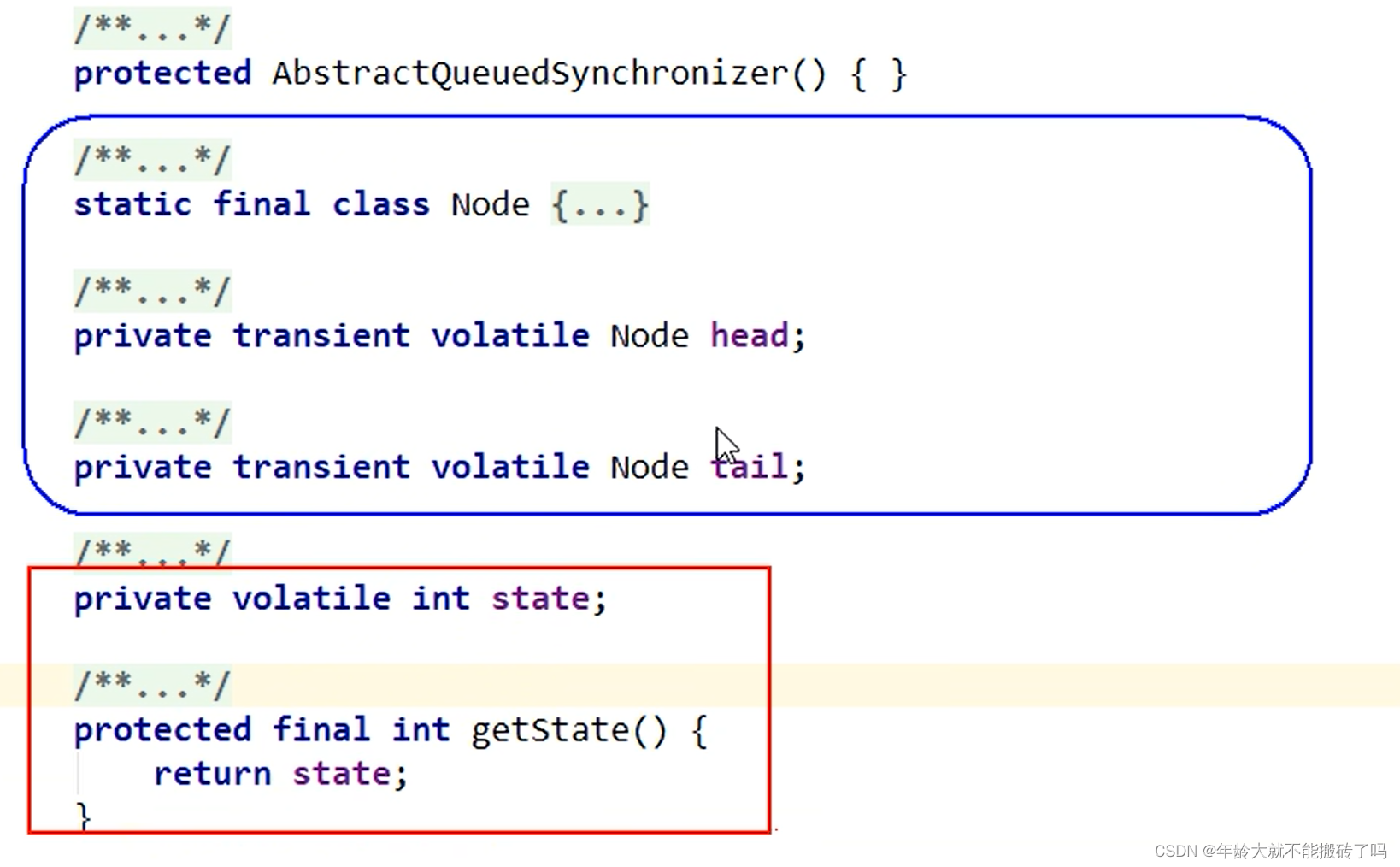
Node:node节点
head:头指针
tail:尾指针
state:状态位
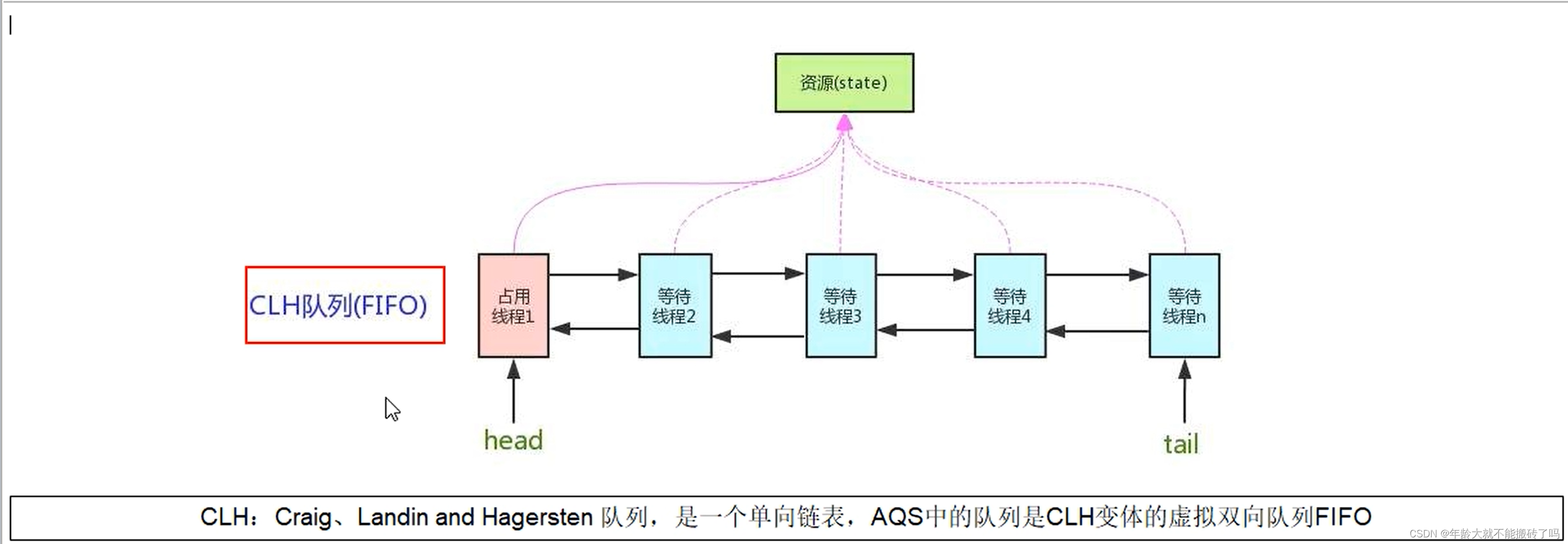
AQS使用一个volatile的int类型的成员变量来表示同步状态,通过内置的FIFO队列来完成资源获取的排队工作将每条要抢占资源的线程封装成一个Node节点来实现锁的分配,通过CAS完成对state值的修改。
AQS同步队列的基本结构:
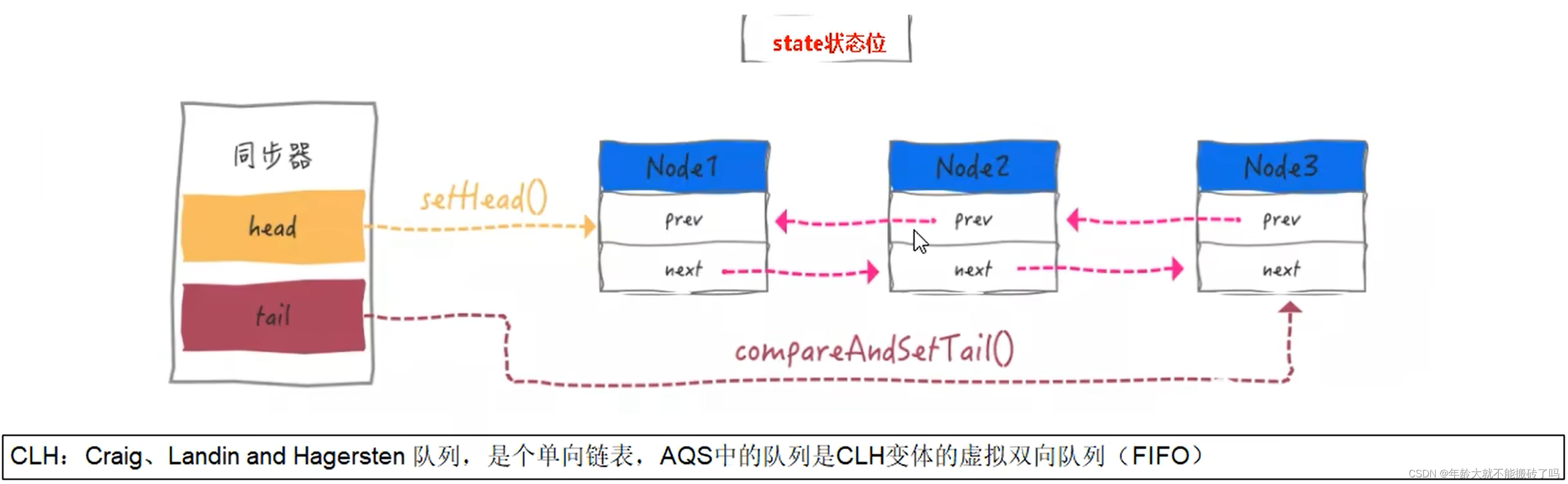
头尾前后4个维度形成的node节点组织起来形成的队列
2 AQS源码分析
2.1 AQS内部体系架构
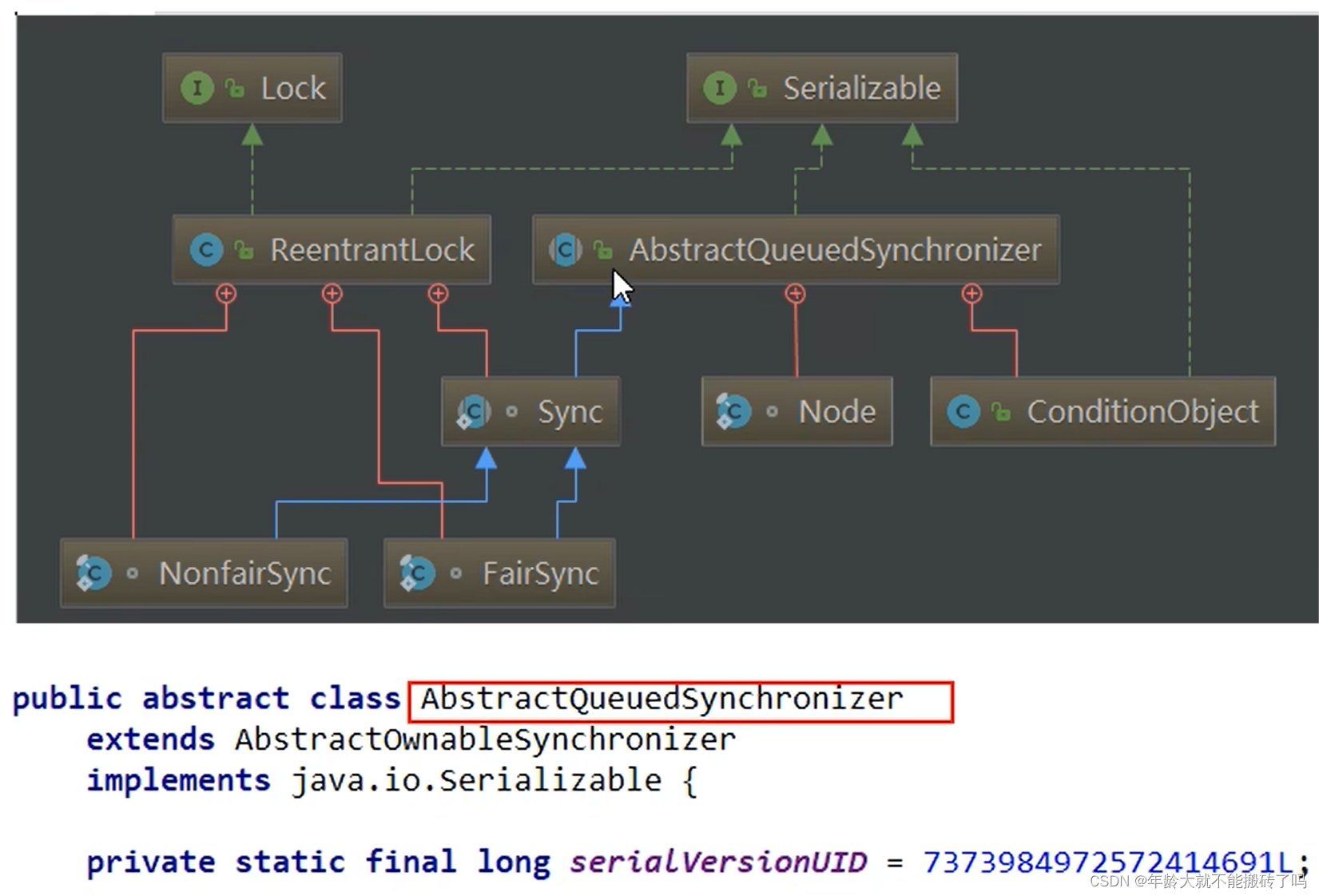
AQS的int变量,AQS的同步状态state成员变量如果等于0就是没有线程占用,如果大于1就是有线程在占用
CLH队列(三个大牛的名字组成)成为一个双向队列
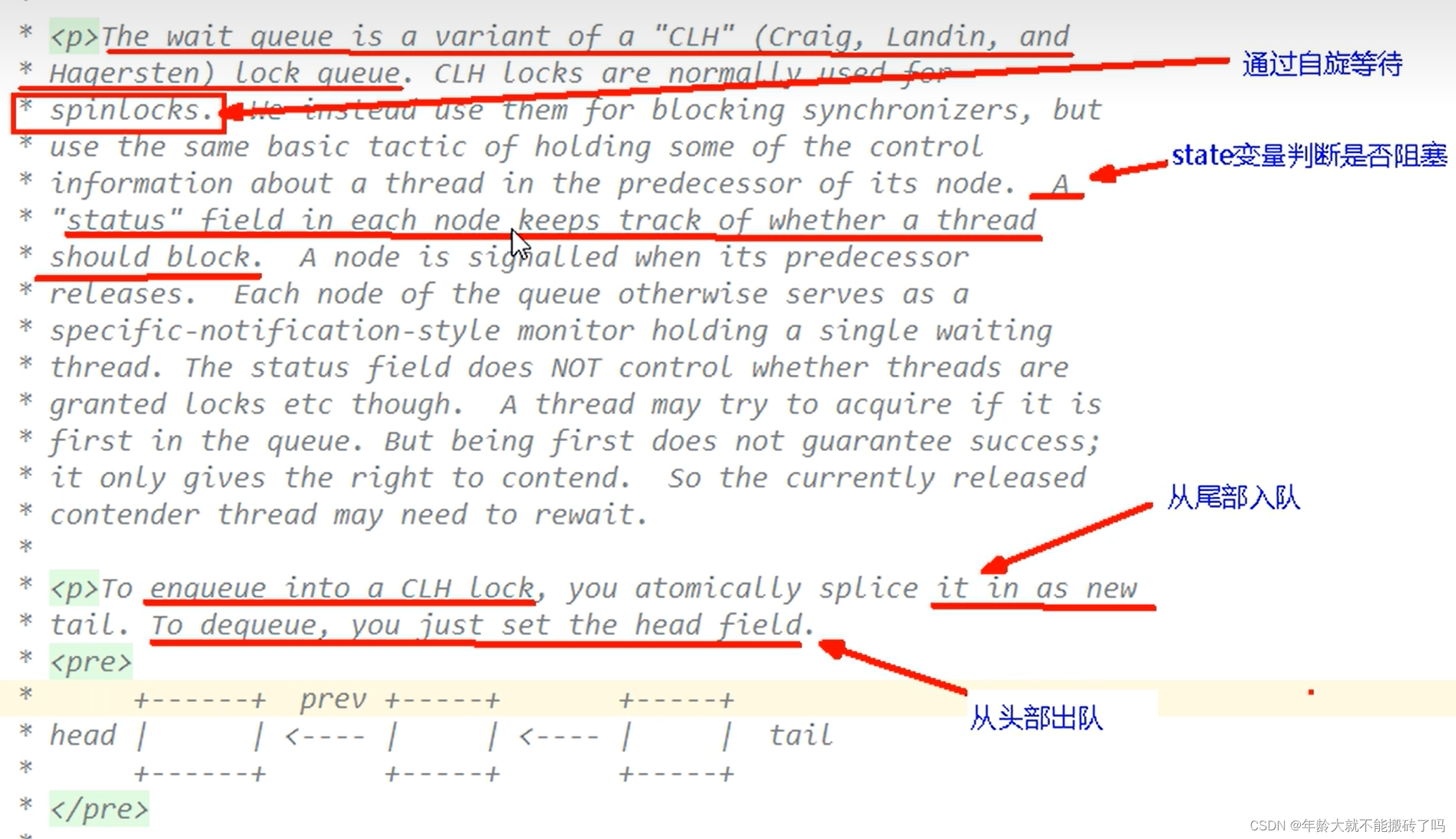
有阻塞就需要排队,实现排队必然需要队列
state变量+CLH双端队列
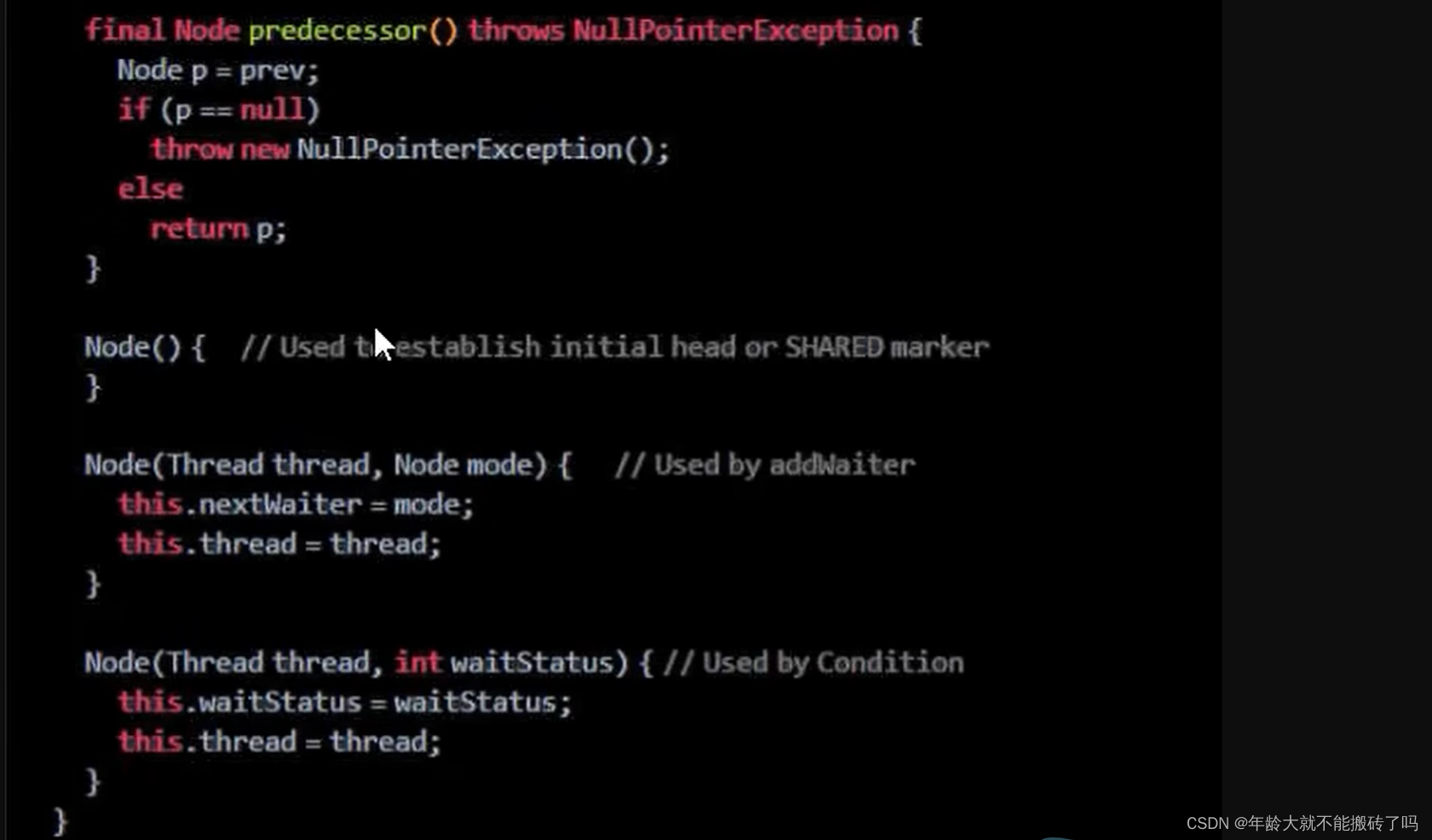
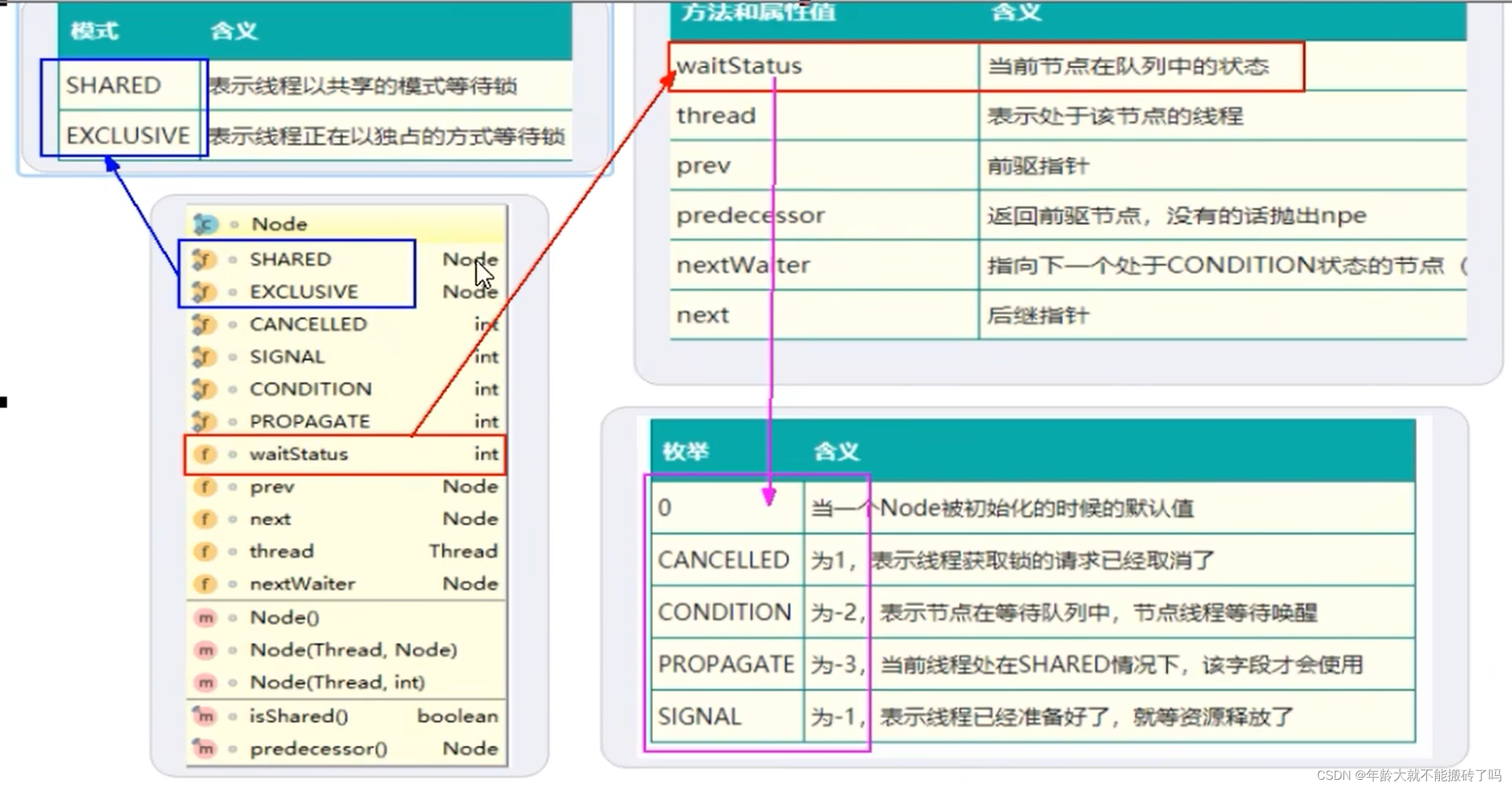
2.2 内部类Node(Node类在AQS类内部)
Node的int变量:Node的等待状态waitState成员变量

就是等候区中其他线程的等待状态
队列中每个排队的个体就是一个node
2.2.1 内部结构:
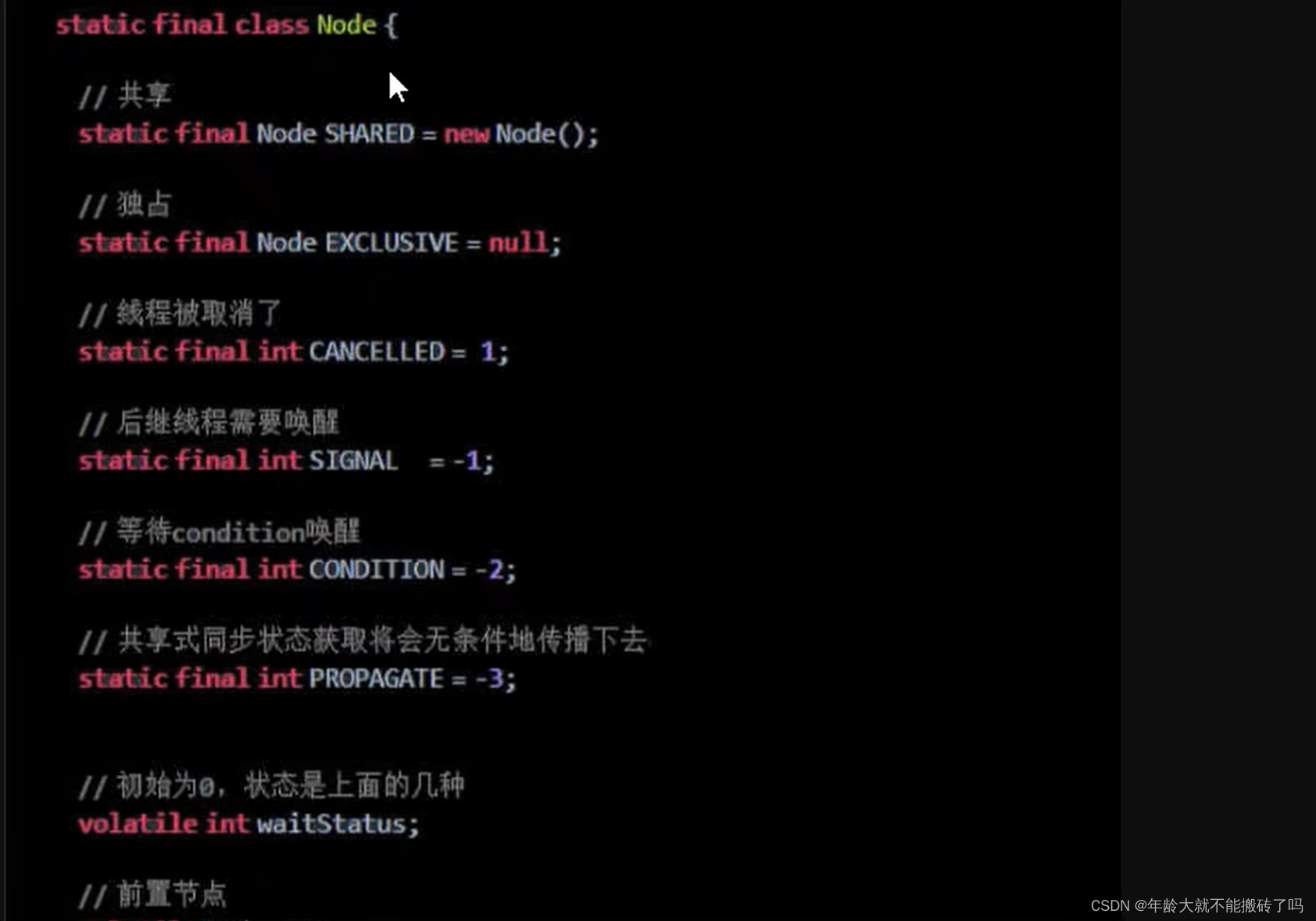
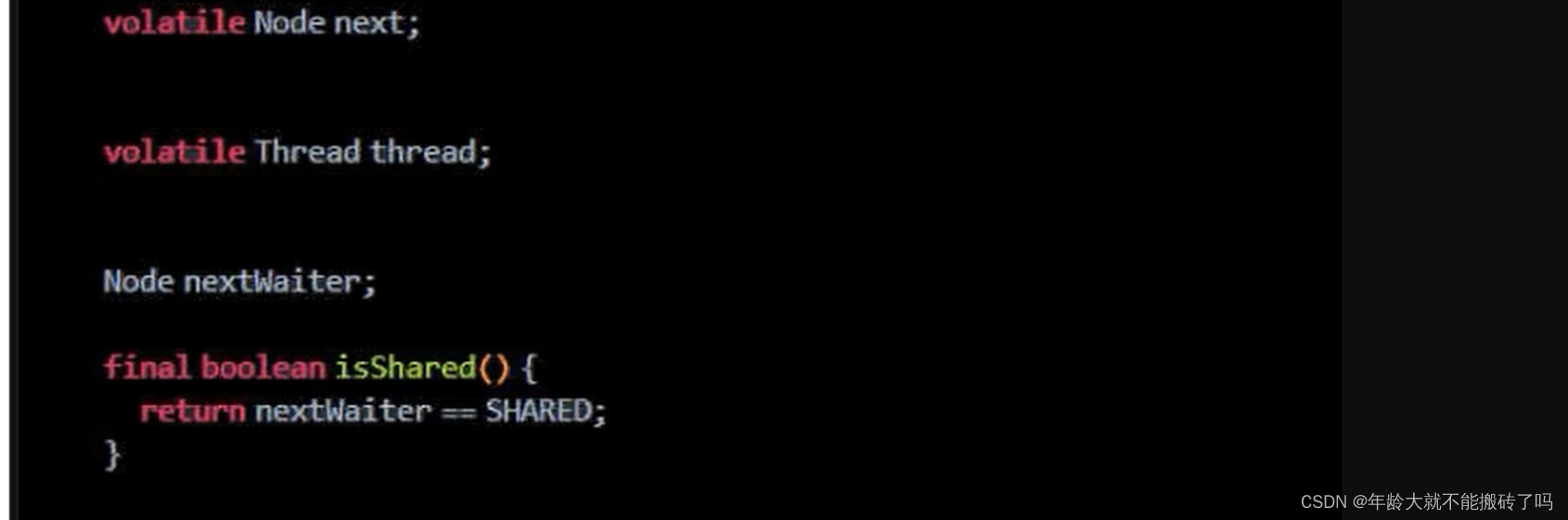
2.2.2 属性说明
3 AQS源码深度分析
解决的问题:
1.锁的使用,谁先抢到了把state状态位标记为1
2.锁的占用,抢到的去使用,抢不到的去排队后续去使用或者放弃由AQS统一调配
Lock接口的实现类,基本都是通过聚合了一个队列同步器的子类完成线程访问控制的
3.1 ReentrantLock的原理
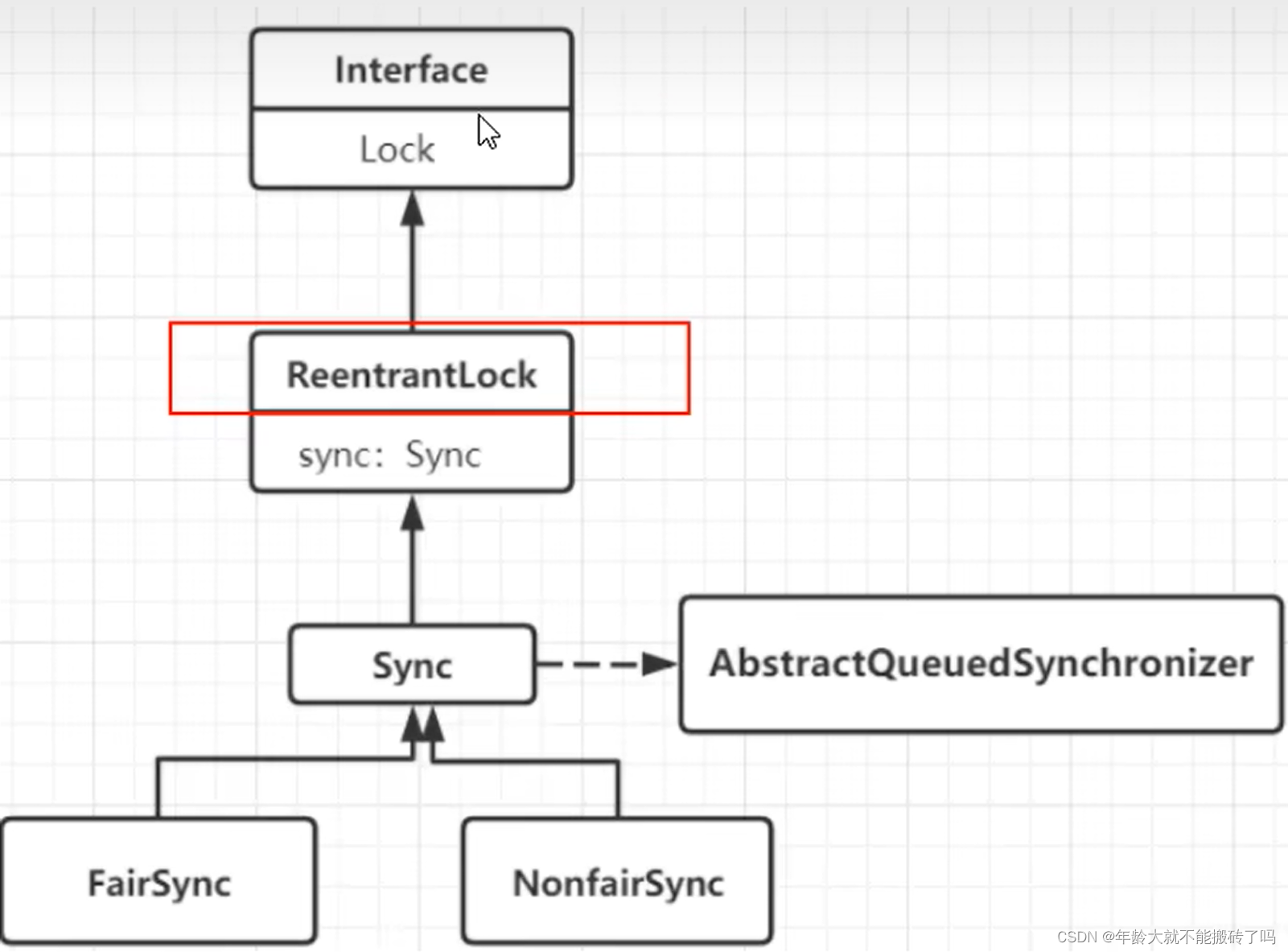
3.2 用最简单的的lock方法开始看看公平锁和非公平锁
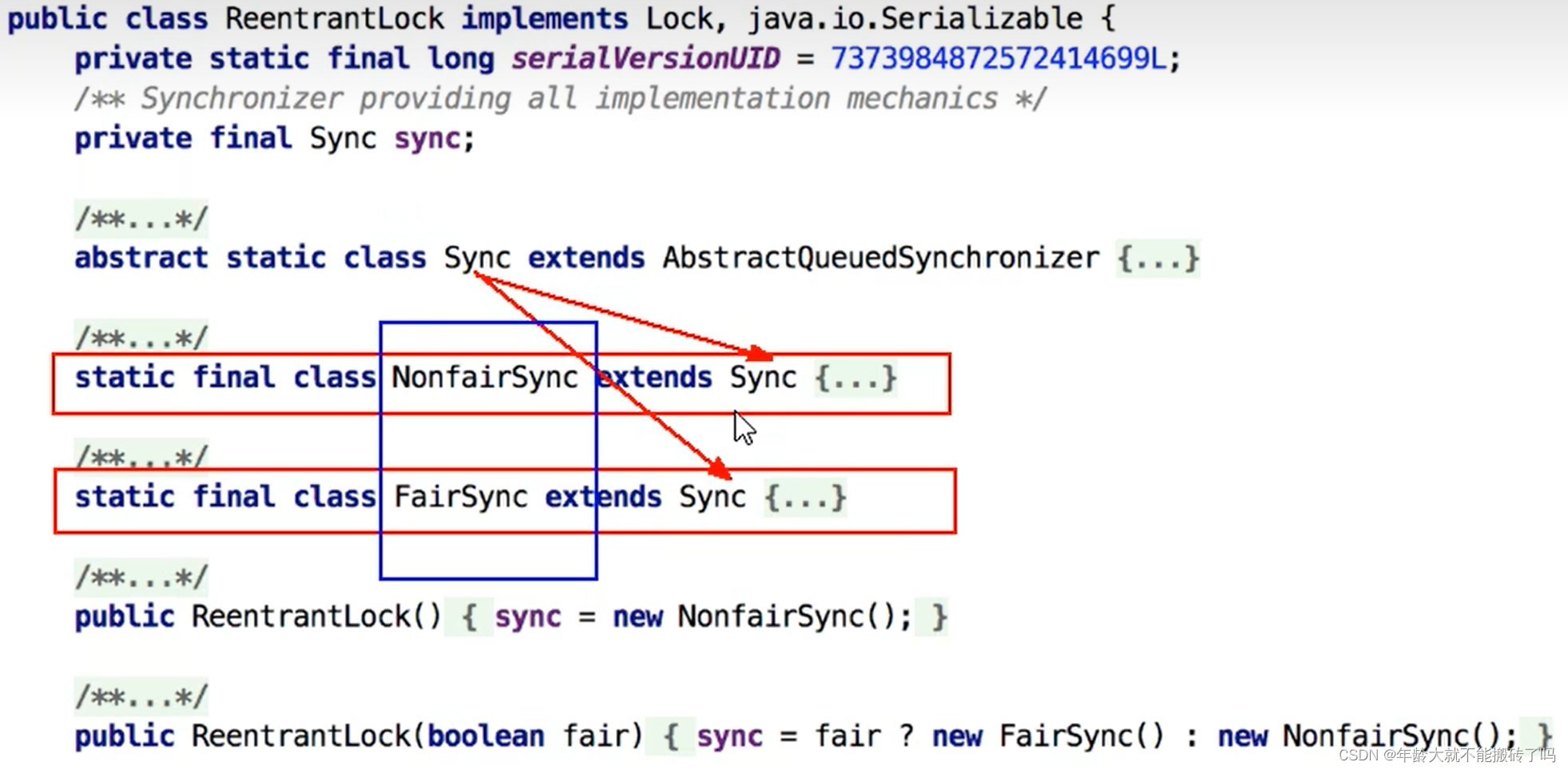



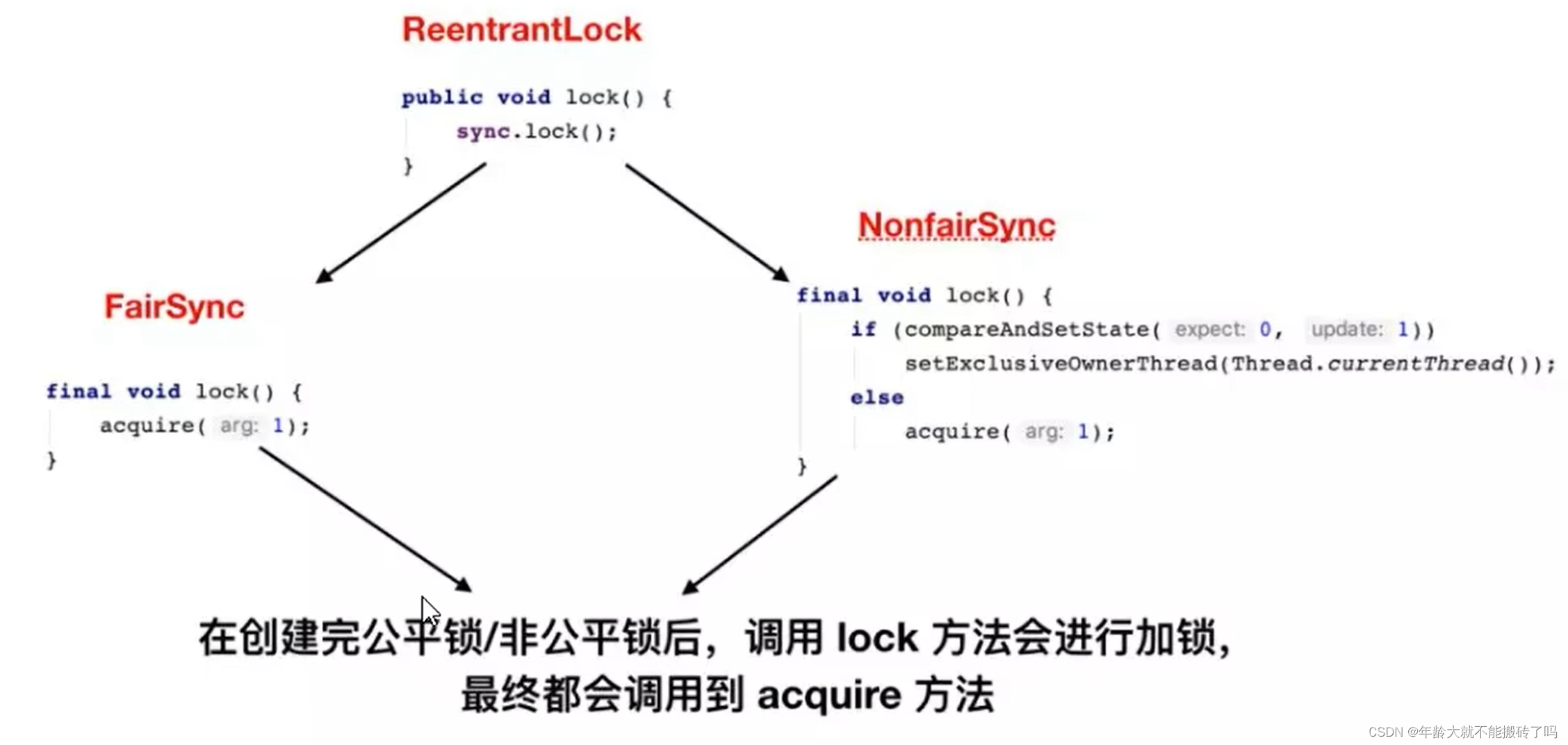
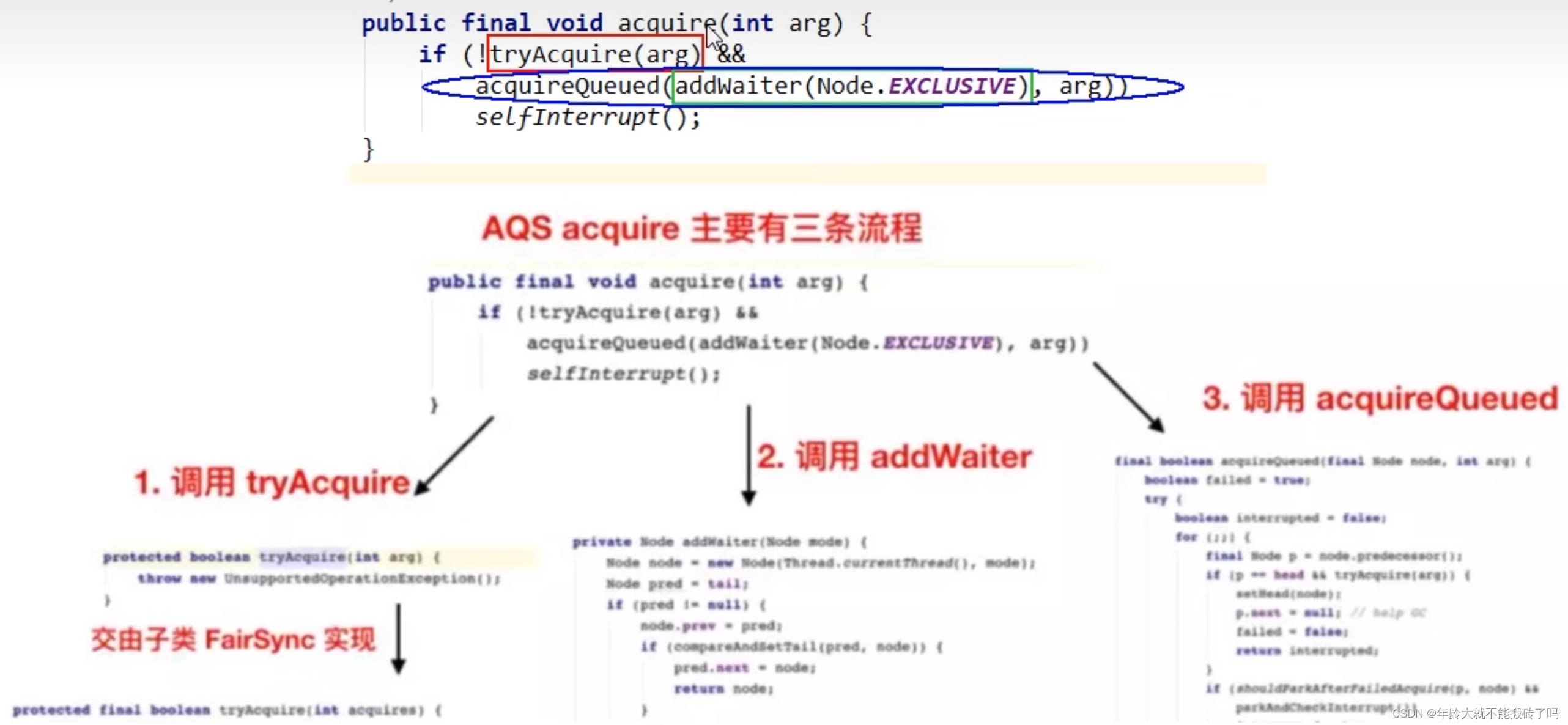
3.2.1 tryAcquire(arg)
lock()
code
package com.atguigu.springcloud.util.interrup;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
public class AQSDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ReentrantLock reentrantLock = new ReentrantLock();//非公平
//A B C 三个线程执行业务A先到,此时没有竞争
//A严重超时,长期占用线程资源
new Thread(()->{
reentrantLock.lock();
try {
System.out.println("----come in A");
try {
TimeUnit.MINUTES.sleep(20);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}
} finally {
reentrantLock.unlock();
}
},"A").start();
//B是第二个线程,看到A一直占用,只能去队列中等待,等到A办理完成,尝试去抢占
new Thread(()->{
reentrantLock.lock();
try {
System.out.println("----come in B");
} finally {
reentrantLock.unlock();
}
},"B").start();
//C是第三个线程,看到被A占用,只能去等待队列进入AQS队列,等待A办理完成尝试抢占锁前面是B FIFO
new Thread(()->{
reentrantLock.lock();
try {
System.out.println("----come in C");
} finally {
reentrantLock.unlock();
}
},"C").start();
//DEFG以此类推
}
}
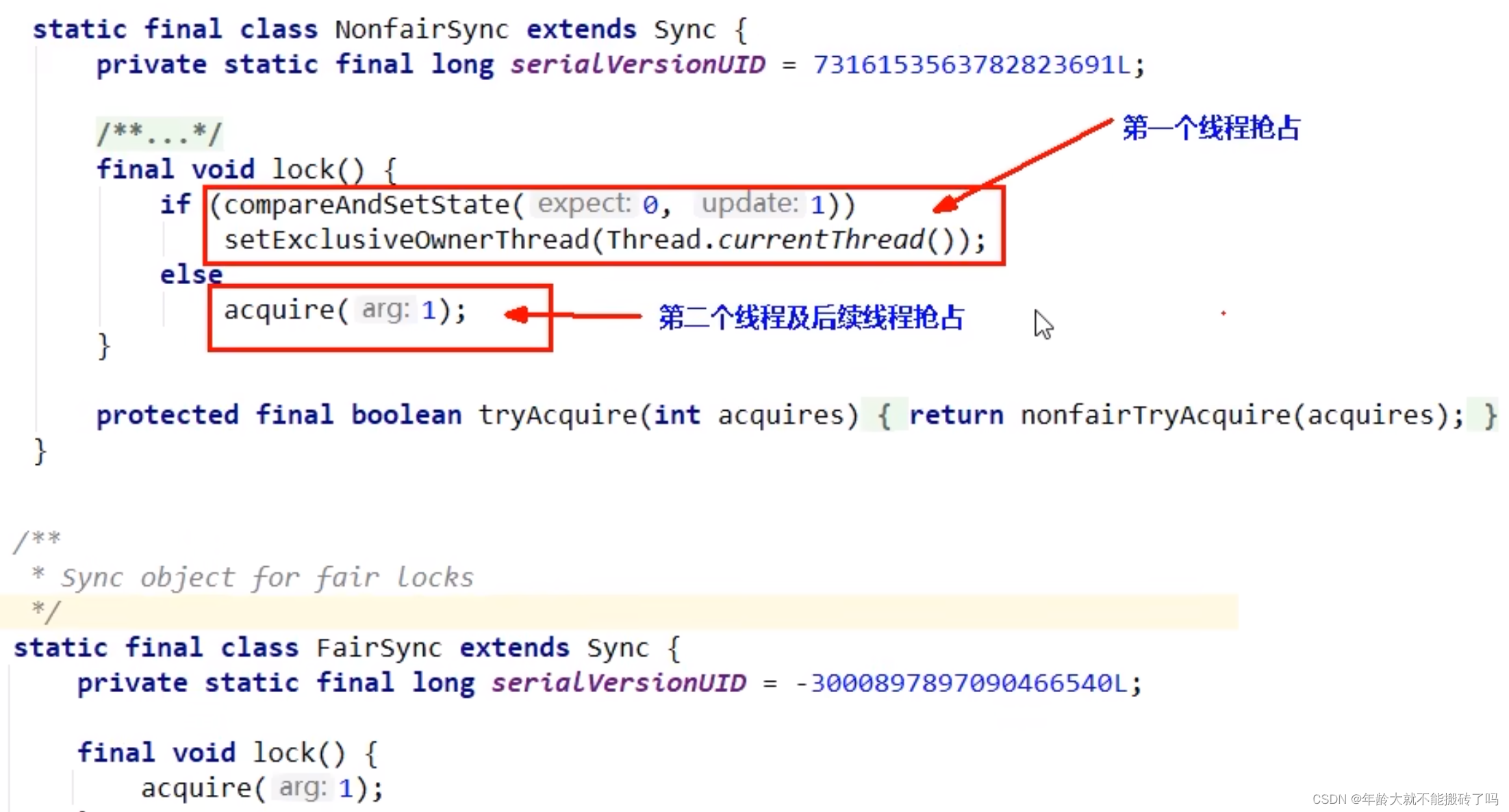
非公平锁在ReentrantLock里面

如果getState方法为0马上上位又把状态改为1,说明抢占成功(A正好释放锁,B马上尝试抢锁)
else if 判断当前线程和当前抢占到的线程是否是同一个
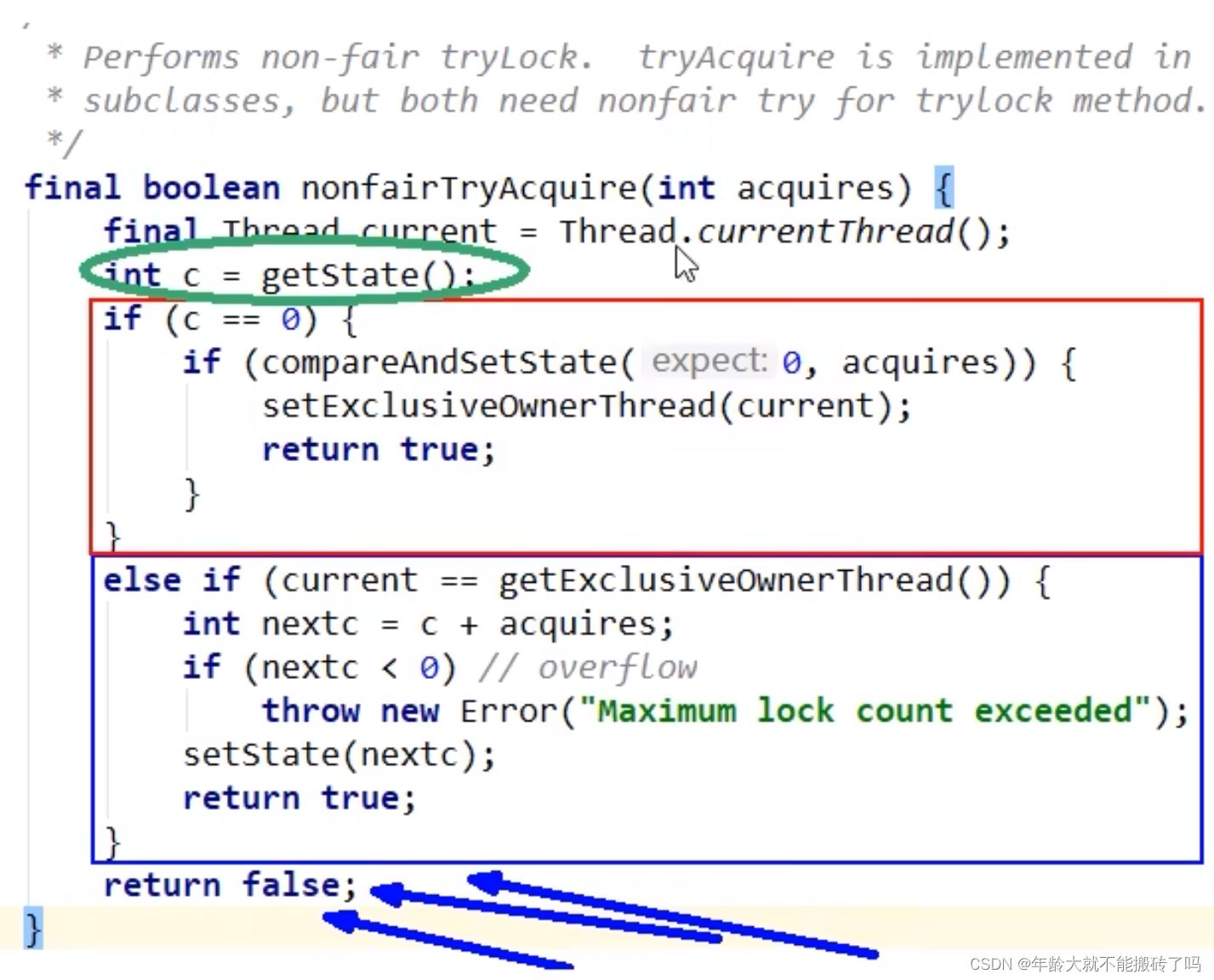
return false后取反->继续推进条件,走下一个方法
return true 结束(抢锁成功)
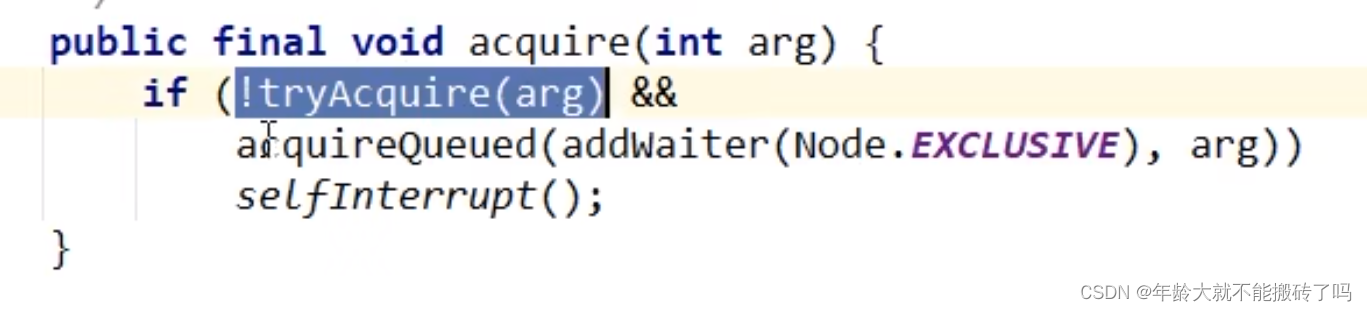
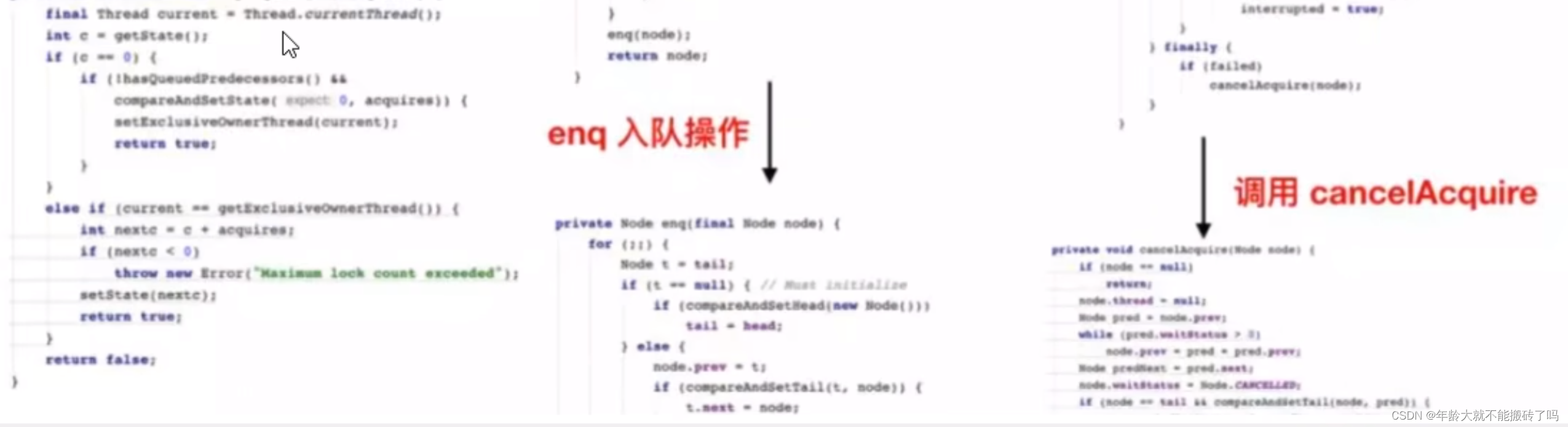
3.2.2 addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE)
addWaiter(Node mode)
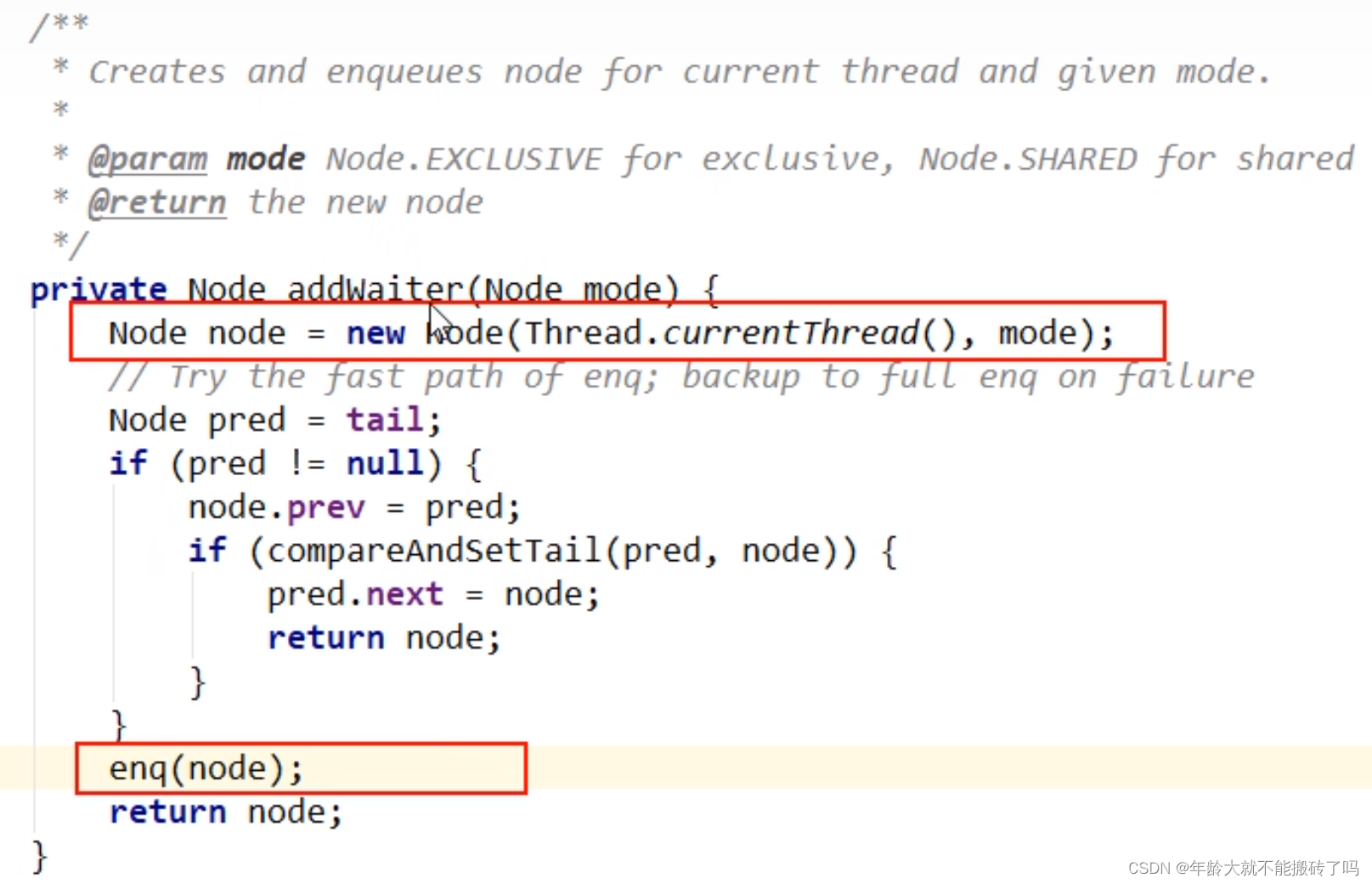
第一次进入enq的红色代码区域new了一个虚拟的节点(哨兵节点)完成的初始化
然后第二次循环的时候b挂在了哨兵节点的后面(蓝色代码块)
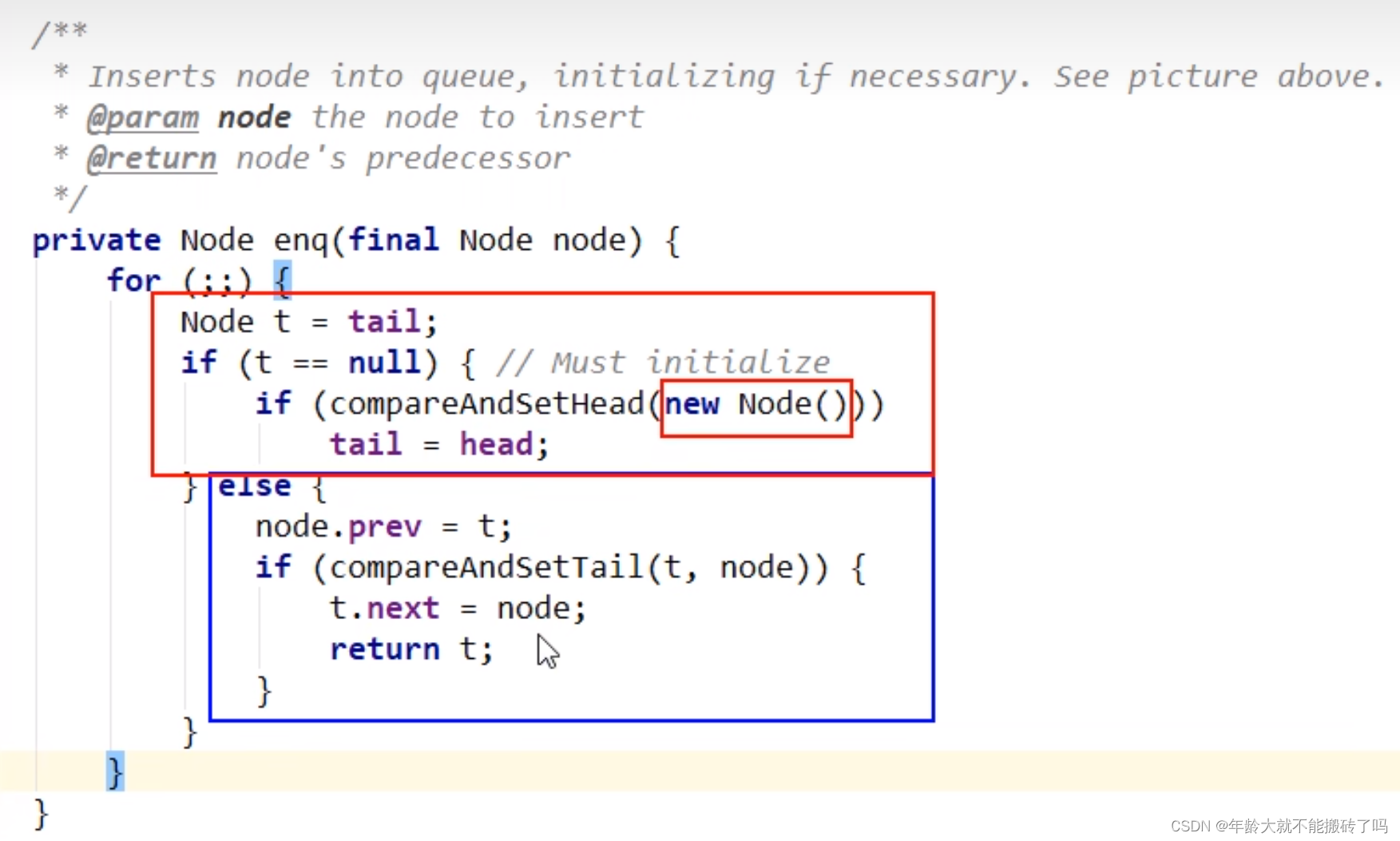
3号线程进来
prev指向B
compareAndSetTail 指向新的尾指针
next 把B的下一个节点指向c
3.2.3 acquireQueued(AddWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE),arg)
B线程代码调用逻辑
/**
* Acquires in exclusive uninterruptible mode for thread already in
* queue. Used by condition wait methods as well as acquire.
*
* @param node the node
* @param arg the acquire argument
* @return {@code true} if interrupted while waiting
*/
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
//目前node是b线程
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) {
//predecessor():获得当前节点的前置节点,目前是头节点(虚拟节点)。第二次循环的node就是b节点,它的前一个节点就是p,
//不会进入第一个if
final Node p = node.predecessor();
//头节点=p(true) 尝试执行tryAcquire尝试抢夺资源,当前会返回false,不执行if
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return interrupted;
}
//P:B节点的前置节点 shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire()返回了false跳出了当前循环执行下一个循环
//第二次循环的时候node P是虚拟节点 node是B, 第二次循环到方法里面的时候第一个if判断成立,所以第二次进来返回了true
//之后调用parkAndCheckInterrupt()
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
/**
* Checks and updates status for a node that failed to acquire.
* Returns true if thread should block. This is the main signal
* control in all acquire loops. Requires that pred == node.prev.
*
* @param pred node's predecessor holding status
* @param node the node
* @return {@code true} if thread should block
*/
private static boolean shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(Node pred, Node node) {
//前置节点的位置 ws:0(当一个node被初始化的默认值) waitStatus:当前节点在队列中的状态 具体的看前面的状态图
int ws = pred.waitStatus;
//Node.SIGNAL=-1 不进
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL)
/*
* This node has already set status asking a release
* to signal it, so it can safely park.
*/
return true;
// 条件也不成立
if (ws > 0) {
/*
* Predecessor was cancelled. Skip over predecessors and
* indicate retry.
*/
do {
node.prev = pred = pred.prev;
} while (pred.waitStatus > 0);
pred.next = node;
} else {
/*
* waitStatus must be 0 or PROPAGATE. Indicate that we
* need a signal, but don't park yet. Caller will need to
* retry to make sure it cannot acquire before parking.
*/
//pred:头结点 的ws(0)状态改为Node.SIGNAL(-1)
compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL);
}
return false;
}
/**
* Convenience method to park and then check if interrupted
*
* @return {@code true} if interrupted
*/
private final boolean parkAndCheckInterrupt() {
//park()方法使得B停在这里了,等待后面的通知唤醒机制
LockSupport.park(this);
return Thread.interrupted();
}
C线程代码调用逻辑
/**
* Acquires in exclusive uninterruptible mode for thread already in
* queue. Used by condition wait methods as well as acquire.
*
* @param node the node
* @param arg the acquire argument
* @return {@code true} if interrupted while waiting
*/
//node:C
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) {
//首次循环c节点的前置节点(B)是P
final Node p = node.predecessor();
//P是head?false 不执行代码
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return interrupted;
}
//P:B node:C
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
/**
* Checks and updates status for a node that failed to acquire.
* Returns true if thread should block. This is the main signal
* control in all acquire loops. Requires that pred == node.prev.
*
* @param pred node's predecessor holding status
* @param node the node
* @return {@code true} if thread should block
*/
private static boolean shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(Node pred, Node node) {
//B节点的waitStatus=0
int ws = pred.waitStatus;
//不进判断
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL)
/*
* This node has already set status asking a release
* to signal it, so it can safely park.
*/
return true;
//不进判断
if (ws > 0) {
/*
* Predecessor was cancelled. Skip over predecessors and
* indicate retry.
*/
do {
node.prev = pred = pred.prev;
} while (pred.waitStatus > 0);
pred.next = node;
} else {
/*
* waitStatus must be 0 or PROPAGATE. Indicate that we
* need a signal, but don't park yet. Caller will need to
* retry to make sure it cannot acquire before parking.
*/
//把前置节点(B )的状态由0设置为-1
compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL);
}
return false;
}
3.3.4 unlock
sync.release(1);释放
tryRelease(arg) 尝试释放
unparkSuccessor 唤醒
/**
* Releases in exclusive mode. Implemented by unblocking one or
* more threads if {@link #tryRelease} returns true.
* This method can be used to implement method {@link Lock#unlock}.
*
* @param arg the release argument. This value is conveyed to
* {@link #tryRelease} but is otherwise uninterpreted and
* can represent anything you like.
* @return the value returned from {@link #tryRelease}
*/
public final boolean release(int arg) {
//true
if (tryRelease(arg)) {
Node h = head;//获取头节点
//头节点不为null?true waitStatus=-1!=0?true
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0)
unparkSuccessor(h);//unpark(h)
return true;
}
return false;
}
/*
* Note that tryRelease and tryAcquire can be called by
* Conditions. So it is possible that their arguments contain
* both read and write holds that are all released during a
* condition wait and re-established in tryAcquire.
*/
protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {
if (!isHeldExclusively())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
// nextc = 1-1 =0
int nextc = getState() - releases;
boolean free = exclusiveCount(nextc) == 0;
if (free)
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);//A要出去了
setState(nextc);//设置状态为0
return free;
}
/**
* Wakes up node's successor, if one exists.
*
* @param node the node
*/
private void unparkSuccessor(Node node) {
/*
* If status is negative (i.e., possibly needing signal) try
* to clear in anticipation of signalling. It is OK if this
* fails or if status is changed by waiting thread.
*/
//ws=-1 进入if
int ws = node.waitStatus;
if (ws < 0)
compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, ws, 0);//比较ws重新设置为0
/*
* Thread to unpark is held in successor, which is normally
* just the next node. But if cancelled or apparently null,
* traverse backwards from tail to find the actual
* non-cancelled successor.
*/
//头节点的下一个值是B
Node s = node.next;
//条件不成立
if (s == null || s.waitStatus > 0) {
s = null;
for (Node t = tail; t != null && t != node; t = t.prev)
if (t.waitStatus <= 0)
s = t;
}
//B节点不为null进入代码块 让Bunpark
if (s != null)
LockSupport.unpark(s.thread);
}
/**
* Convenience method to park and then check if interrupted
*
* @return {@code true} if interrupted
*/
private final boolean parkAndCheckInterrupt() {
LockSupport.park(this);
//B被唤醒之后interrupted()返回false
return Thread.interrupted();
}
/**
* Acquires in exclusive uninterruptible mode for thread already in
* queue. Used by condition wait methods as well as acquire.
*
* @param node the node
* @param arg the acquire argument
* @return {@code true} if interrupted while waiting
*/
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) {
//2.获取B的头节点
final Node p = node.predecessor();
//B线程执行tryAcquire时抢到锁返回了true
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
//1.设置头节点为节点B
//2.node.thread=null
//3.设置B的前置节点为null
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return interrupted;
}
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
//1.B线程unpark之后下面返回了false 进入下个循环
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
3.3.5 cancelAcquire(node)
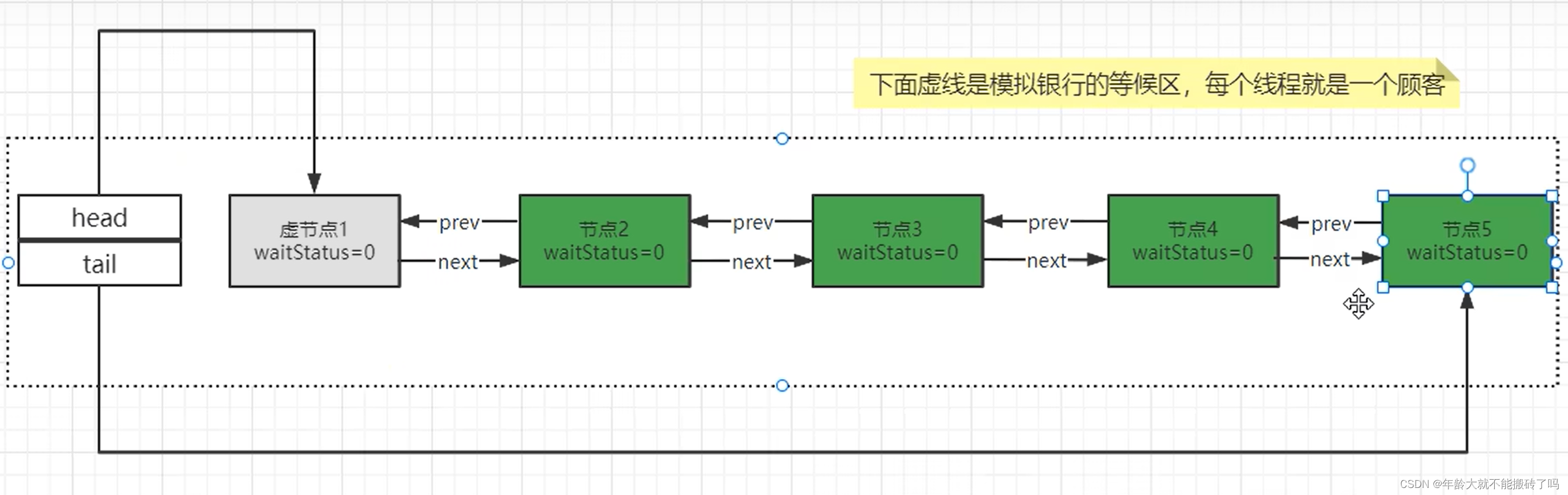
5号节点模拟取消code走向:
/**
* Cancels an ongoing attempt to acquire.
*
* @param node the node
*/
private void cancelAcquire(Node node) {
// Ignore if node doesn't exist
if (node == null)
return;
node.thread = null;
// Skip cancelled predecessors
//1.获取5号的前一个节点(4号)
Node pred = node.prev;
//2.判断4号节点的waitStatus是否大于0,目前不进
while (pred.waitStatus > 0)
node.prev = pred = pred.prev;
// predNext is the apparent node to unsplice. CASes below will
// fail if not, in which case, we lost race vs another cancel
// or signal, so no further action is necessary.
//3.获取4号节点的下个节点也就是5号
Node predNext = pred.next;
// Can use unconditional write instead of CAS here.
// After this atomic step, other Nodes can skip past us.
// Before, we are free of interference from other threads.
//4.把5号节点的waitStatus改为CANCELLED
node.waitStatus = Node.CANCELLED;
// If we are the tail, remove ourselves.
//5.5号节点的前置节点4号设置为尾节点
if (node == tail && compareAndSetTail(node, pred)) {
//6.把5号节点的前置节点的下一个设置为null
compareAndSetNext(pred, predNext, null);
} else {
// If successor needs signal, try to set pred's next-link
// so it will get one. Otherwise wake it up to propagate.
int ws;
if (pred != head &&
((ws = pred.waitStatus) == Node.SIGNAL ||
(ws <= 0 && compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL))) &&
pred.thread != null) {
Node next = node.next;
if (next != null && next.waitStatus <= 0)
compareAndSetNext(pred, predNext, next);
} else {
unparkSuccessor(node);
}
node.next = node; // help GC
}
}
4号节点模拟取消code走向:
/**
* Cancels an ongoing attempt to acquire.
*
* @param node the node
*/
private void cancelAcquire(Node node) {
// Ignore if node doesn't exist
if (node == null)
return;
node.thread = null;
// Skip cancelled predecessors
//1.获取4号的前一个3号节点
Node pred = node.prev;
//2.如果4号节点的前一个3号节点也要出队的情况
while (pred.waitStatus > 0)
//3.把3号节点的前一个2号赋值给4号节点的前一个(最终找到前节点不取消的那个节点)
node.prev = pred = pred.prev;
// predNext is the apparent node to unsplice. CASes below will
// fail if not, in which case, we lost race vs another cancel
// or signal, so no further action is necessary.
//获取3号节点的下一个4号
Node predNext = pred.next;
// Can use unconditional write instead of CAS here.
// After this atomic step, other Nodes can skip past us.
// Before, we are free of interference from other threads.
//4.4号节点的状态改为CANCELLED
node.waitStatus = Node.CANCELLED;
// If we are the tail, remove ourselves.
if (node == tail && compareAndSetTail(node, pred)) {
compareAndSetNext(pred, predNext, null);
} else {
// If successor needs signal, try to set pred's next-link
// so it will get one. Otherwise wake it up to propagate.
int ws;
if (pred != head &&
((ws = pred.waitStatus) == Node.SIGNAL ||
(ws <= 0 && compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL))) &&
pred.thread != null) {
//5.4号节点的next就是5
Node next = node.next;
//6.5号节点不为Null
if (next != null && next.waitStatus <= 0)
//7.3号节点的下一个(4)设置为next(5)
compareAndSetNext(pred, predNext, next);
} else {
unparkSuccessor(node);
}
node.next = node; // help GC
}
}






















 1277
1277











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








