目录:
1.I/O流基础概念
按照流的方向分为输入流(InputStream)与输出流(OuputStream):
- 输入流:只能读取数据,不能写入数据。
- 输出流:只能写入数据,不能读取数据。
因为程序是运行在内存中,以内存角度来理解输入输出概念,如下:

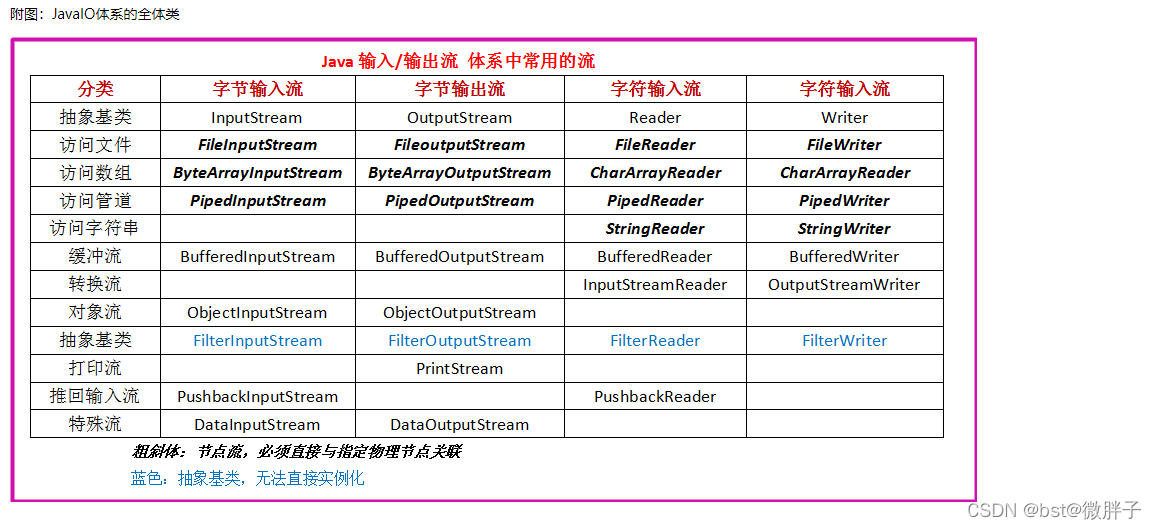
按照处理的数据单位分为字节流和字符流
- 字节流:操作的数据单元是8位的字节。InputStream、OutputStream作为抽象基类。
- 字符流:操作的数据单元是字符。以Writer、Reader作为抽象基类。
- 字节流可以处理所有数据文件,若处理的是纯文本数据,建议使用字符流。
IO流中的三类数据源
- 基于磁盘文件:FileInputStream、FileOutputSteam、FileReader、FileWriter
- 基于内存:ByteArrayInputStream ByteArrayOutputStream(ps:字节数组都是在内存中产生)
- 基于网络:SocketInputStream、SocketOutputStream(ps:网络通信时传输数据)
- PrintStream :打印输出字节数据。
- PrintWriter : 打印输出文本数据。
2.功能使用
(一)使用字节流读取本地文件
//File对象定位数据源
public static void getContent(File file) throws IOException {
//创建文件缓冲输入流
file BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(file));
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];//创建字节数组,存储临时读取的数据
int len = 0;//记录数据读取的长度
//循环读取数据
while((len = bis.read(buf)) != -1) { //长度为-1则读取完毕
System.out.println(new String(buf,0,len));
}
bis.close(); //关闭流
}
【技巧】如果数据源是纯文本数据,使用字符流效率更高。
(二)使用字符处理流读取本地文件内容
public static void getContent(String path) throws IOException {
File f = new File(path);
if (f.exists()) { // 判断文件或目录是否存在
if (f.isFile()) {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(path));//该缓冲流有一个readLine()独有方法
String s = null;
while ((s = br.readLine()) != null) {//readLine()每次读取一行
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}
}
该方法比上一个增加了文件判断,提高了程序的健壮性。使用了BufferedReader处理流来处理纯文本数据,比字节流更加简洁方便。
(三)使用字符流写入数据到指定文件:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//以标准输入作为扫描来源
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
File f = new File("D:\\reviewIO\\WRITERTest.txt");
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(f));
if(!f.exists()) {
f.createNewFile();
}
while(true) {
String s = sc.nextLine();
bw.write(s);
bw.flush();
if(s.equals("结束") || s.equals("")) {
System.out.println("写入数据结束!");
return;
}
}
}
四)使用转换流(InputStreamReader/OutputStreamWriter),对写入数据进行改进:
public static void testConvert(File f) throws IOException {
if(!f.exists()) {
f.createNewFile();
}
//以System.in作为读取的数据源,即从键盘读取
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(f,true)); //允许添加内容,不会清除原有数据源
String s = null;
while(!(s = br.readLine()).equals("")) {
bw.write(s);
bw.newLine();//空一行
}
bw.flush();
bw.close();
br.close();
}
(五)使用字节流完成文件复制
//字节流实现文件拷贝
public static String copyFile(String src, String dest) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
File srcFile = new File(src);//源文件数据源
File desFile = new File(dest);//写入到目标数据源
//数据源不存在
if(!srcFile.exists() || !desFile.exists()) {
throw new ClassNotFoundException("源文件或者拷贝目标文件地址不存在!");
}
//非文件类型
if(!srcFile.isFile() || !desFile.isFile()) {
return "源文件或者目标文件不是文件类型!";
}
InputStream is = null;
OutputStream os = null;
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];//缓存区
int len = 0;//读取长度
try {
is = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(srcFile));//读取数据源
os = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(desFile));//写入到数据源
while((len = is.read(buf)) != -1) { //读取长度不为-1,继续读取
os.write(buf); //读取内容之后马上写入目标数据源
}
os.flush();//输出
return "文件拷贝成功!查看拷贝文件路径:" + desFile.getPath();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(is != null)
is.close();
if(os != null)
os.close();
}
return "文件拷贝失败";
}
一般情况下,若是输出文本数据,建议使用打印流。PrintWriter还可以指定输出文本使用何种字符集、在构造参数中指定是否自动刷新。如果不想覆盖原来的数据,使用该类的append()方法,就会在文件尾部添加内容。
(六)使用打印流来完成写入数据操作:
//输出内容的文件数据源
File f = new File("D:\\reviewIO\\PW.java");
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(f);
//把指定内容打印至数据源中
pw.println("AAAAAAAAA");
pw.println("BBBBBBBBB");
pw.println("CCCCCCCCC");
pw.flush();
System.out.println("使用PrintWriter写入数据完成");
System.out.println("==========读取写入的数据==========");
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(f));
String s = null;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();//一个可变字符串
while((s = br.readLine()) != null) {
sb.append(s); //把读取的字符串组合起来
}
System.out.println(sb);
br.close();
pw.close();
(七)使用打印流来完成文本拷贝:
// 使用打印流PrintStream来完成文件拷贝
public static void copyFile(File src, File dest) throws Exception {
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(src));
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(dest));
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(bos, true);
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
//循环读取数据,然后写入到目标文件
while ((len = bis.read(buf)) != -1) {
ps.write(buf);
}
ps.close();
bos.close();
}























 704
704











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










