Due to the challenging problems, some of the contestants decide to escape from this contest. However, to prevent this from happening, the EVIL problem setters made a labyrinth at the stadium's exit. The labyrinth is made of an n×m grid, on which lie the entrance and the exit, and k black holes. Contestants who accidentally step into any black hole will fall into it and thus can never escape from the contest.
What's worse, the problem setters may also adjust the coordinates of the entrance and the exit. You, a poor contestant, who start from the entrance and wish to reach the exit without stepping into any of the black holes, can only move to one of the four adjacent cells in each step. You want to know, after each time the problem setters change the coordinates of the entrance and the exit, what's the minimum number of steps needed to reach the exit starting from the entrance?
Input Specification:
The first line of the input contains four integers n,m,k,q (1≤n,m≤200000,nm≤200000,0≤k≤42, 1≤q≤100000), denoting the number of rows, the number of columns, the number of black holes in the labyrinth, and the number of queries, respectively.
The following k lines contain the description of the black holes. Each of these lines contains two integers x,y (1≤x≤n,1≤y≤m), denoting the coordinates of a black hole. No two black holes are located at the same position.
The last q lines contain the description of the queries. Each of the q lines contains four integers xs,ys,xt,yt (1≤xs,xt≤n,1≤ys,yt≤m), where (xs,ys) is the coordinates of the entrace and (xt,yt) is the exit.
Output Specification:
For each query, output a number in a line, denoting the minimum number of steps needed to reach the exit starting from the entrance. If it is impossible to reach the exit, output -1 instead. It should be considered impossible when the entrace or the exit coincides with a black hole.
Sample Input 1:
5 5 4 7
2 2
2 3
3 2
3 3
2 1 3 4
1 1 1 1
2 2 2 2
1 1 1 5
2 2 5 5
2 1 2 4
1 1 3 3
Sample Output 1:
6
0
-1
4
-1
5
-1
Sample Input 2:
2 3 2 1
1 2
2 1
1 1 2 3
Sample Output 2:
-1
Notes:
The plots for the labyrinth and the first query of the first sample data are shown below.
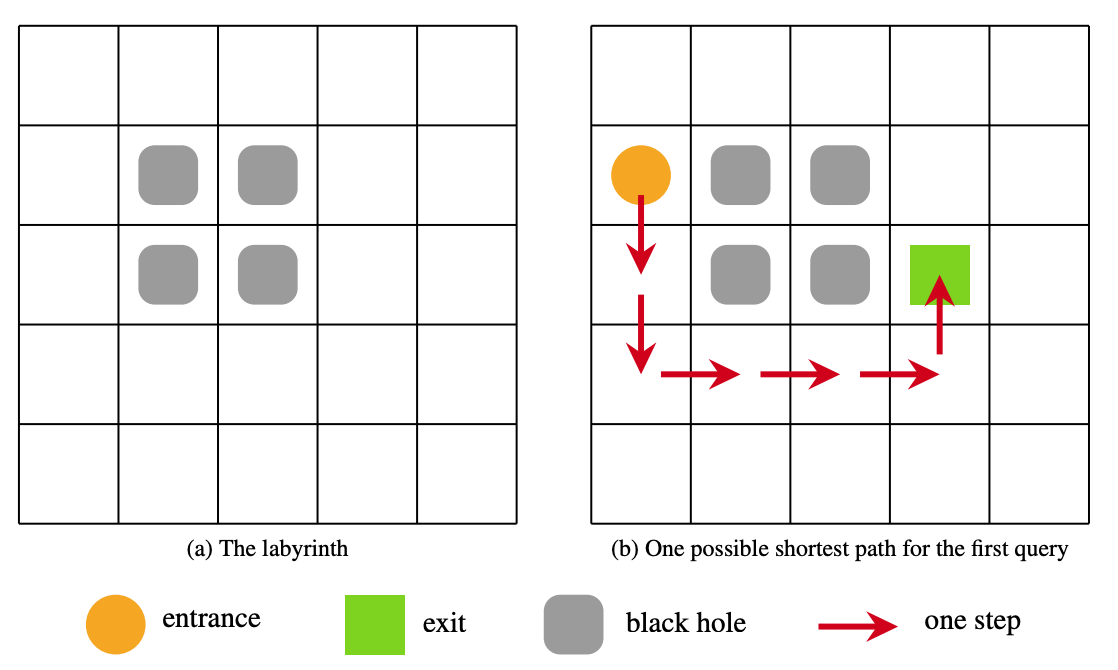
题意:图上有黑洞没法走,多次询问,求出两点之间的最短距离。
思路:
题目很关键的给了这么小的k,肯定从k出发
1.如果两个点之间没有黑洞,那么就是两点之间的曼哈顿距离。
2.如果有黑洞,那么最短路的路径经过过其中一个黑洞{上,下,左,右}的一个方向点。
那么预处理每个黑洞到图上所有点的最短距离,保存下来。询问的时候枚举所有黑洞的以各自四周为起点的到达给出两点的距离和,求最小值。
同时这个题卡空间,代码上用dis距离是否更新过来代替vis数组,dis数组也是动态分配的,用到再开。
注意一个黑洞的隔壁如果还是黑洞,这个dis空间是要开出来的,但不必bfs,不然的话在最后枚举最小值的时候是全范围枚举而没有空间就会段错误。
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#define debug(a) cout<<#a<<"="<<a<<endl;
using namespace std;
const int maxn=2e5+100;
typedef int LL;
const int inf =0x3f3f3f3f;
set<pair<LL,LL>>st;
LL n,m,k,q;
int dx[4]={1,-1,0,0};
int dy[4]={0,0,-1,1};
int *dis[50][4][maxn];///dis[id][pos][x][y];
///为了节省空间,用dis是否更新过来代替标记矩阵
vector<pair<LL,LL> >node;
struct Node{
LL x,y,step;
};
void bfs()
{
for(LL id=0;id<node.size();id++)///枚举所有黑洞作为起点
{
LL x,y;
x=node[id].first;y=node[id].second;
for(LL pos=0;pos<4;pos++)///枚举该黑洞的四周
{
LL xx=x+dx[pos];
LL yy=y+dy[pos];
if(xx<1||xx>n||yy<1||yy>m) continue;
///if(st.count({xx,yy})) continue;不能在这里判断
for(LL p=1;p<=n;p++){
dis[id][pos][p]=new int [m+5];
for(LL o=1;o<=m;o++){
dis[id][pos][p][o]=inf;
}
}
if(st.count({xx,yy})) continue;
queue<Node>que;
que.push({xx,yy,0});
dis[id][pos][xx][yy]=0;
while(!que.empty())
{
Node now=que.front();que.pop();
for(LL p=0;p<4;p++){
LL tx=now.x+dx[p];LL ty=now.y+dy[p];LL tstep=now.step+1;
if(tx<1||tx>n||ty<1||ty>m) continue;
if(st.count({tx,ty})) continue;
if(dis[id][pos][tx][ty]!=inf) continue;
dis[id][pos][tx][ty]=tstep;
que.push({tx,ty,tstep});
}
}
}
}
}
bool check(LL x1,LL y1,LL x2,LL y2)
{
if(x1>x2) swap(x1,x2);
if(y1>y2) swap(y1,y2);
for(LL i=0;i<k;i++){
LL xx=node[i].first;
LL yy=node[i].second;
if(xx>=x1&&xx<=x2&&yy>=y1&&yy<=y2){
return 1;
}
}
return 0;
}
int main(void)
{
cin.tie(0);std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin>>n>>m>>k>>q;
for(LL i=1;i<=k;i++){
LL x,y;cin>>x>>y;
node.push_back({x,y});
st.insert({x,y});
}
bfs();
///cout<<"fuck"<<endl;
while(q--)
{
LL x1,y1,x2,y2;
cin>>x1>>y1>>x2>>y2;
if(check(x1,y1,x2,y2)==0){
cout<<abs(x2-x1)+abs(y2-y1)<<endl;
}
else{
LL ans=0x3f3f3f3f;
for(LL i=0;i<k;i++){
for(int j=0;j<4;j++){
int xx=node[i].first+dx[j];
int yy=node[i].second+dy[j];
if(xx<1||xx>n||yy<1||yy>m) continue;
ans=min(ans,dis[i][j][x1][y1]+dis[i][j][x2][y2]);
}
}
if(ans==inf)cout<<"-1"<<endl;
else cout<<ans<<endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
























 333
333











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








