这一篇开始编写sql执行的过程,首先要先说下这两个组件,也可以说是执行的源头开始
SqlSessionFactory
看名字就可以确定这是用于获取 SqlSession 对象的工厂类,主要是说一下他的格式和创建方式,这是线程安全的,一般一个应用就只有一个factory对象
格式
public interface SqlSessionFactory {
/**
* 打开一个SqlSession接口
* @return
*/
SqlSession openSession();
/**
* 其他的都是重载方法
* @param autoCommit
* @return
*/
SqlSession openSession(boolean autoCommit);
SqlSession openSession(Connection connection);
SqlSession openSession(TransactionIsolationLevel level);
SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType execType);
SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType execType, boolean autoCommit);
SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level);
SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType execType, Connection connection);
/**
* 获取配置类信息
* @return
*/
Configuration getConfiguration();
}
获取
public static SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory(Properties properties) {
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = null;
try {
inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream, properties);
}
通过SqlSessionFactoryBuilder对象进行构建即可
如果是直接自己new DefaultSqlSessionFactory对象的话,xml里面的信息不会被加载,等于配置信息都要通过代码进行设置,所以一般推荐使用SqlSessionFactoryBuilder进行创建SqlSession
SqlSession对象,一个核心接口,包含了所有跟数据库的交互,比如select、update、delete与事务相关的操作,commit、rollback、获取数据库连接等,这个对象是线程不安全的,因为每次在跟数据库的时候都需要获取连接,而每个SqlSession对象获取连接的时候都是同一条,如果SqlSession对象在多线程环境运行的过程中,自然就会有一个连接被不同事务获取到进行执行的情况,那么也就会失去了事务的保证行了
定义
public interface SqlSession extends Closeable {
/**
* Retrieve a single row mapped from the statement key
* @param <T> the returned object type
* @param statement
* @return Mapped object
*/
<T> T selectOne(String statement);
/**
* Retrieve a single row mapped from the statement key and parameter.
* @param <T> the returned object type
* @param statement Unique identifier matching the statement to use.
* @param parameter A parameter object to pass to the statement.
* @return Mapped object
*/
<T> T selectOne(String statement, Object parameter);
/**
* Retrieve a list of mapped objects from the statement key and parameter.
* @param <E> the returned list element type
* @param statement Unique identifier matching the statement to use.
* @return List of mapped object
*/
<E> List<E> selectList(String statement);
/**
* Retrieve a list of mapped objects from the statement key and parameter.
* @param <E> the returned list element type
* @param statement Unique identifier matching the statement to use.
* @param parameter A parameter object to pass to the statement.
* @return List of mapped object
*/
<E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter);
/**
* Retrieve a list of mapped objects from the statement key and parameter,
* within the specified row bounds.
* @param <E> the returned list element type
* @param statement Unique identifier matching the statement to use.
* @param parameter A parameter object to pass to the statement.
* @param rowBounds Bounds to limit object retrieval
* @return List of mapped object
*/
<E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds);
/**
* The selectMap is a special case in that it is designed to convert a list
* of results into a Map based on one of the properties in the resulting
* objects.
* Eg. Return a of Map[Integer,Author] for selectMap("selectAuthors","id")
* @param <K> the returned Map keys type
* @param <V> the returned Map values type
* @param statement Unique identifier matching the statement to use.
* @param mapKey The property to use as key for each value in the list.
* @return Map containing key pair data.
*/
<K, V> Map<K, V> selectMap(String statement, String mapKey);
/**
* The selectMap is a special case in that it is designed to convert a list
* of results into a Map based on one of the properties in the resulting
* objects.
* @param <K> the returned Map keys type
* @param <V> the returned Map values type
* @param statement Unique identifier matching the statement to use.
* @param parameter A parameter object to pass to the statement.
* @param mapKey The property to use as key for each value in the list.
* @return Map containing key pair data.
*/
<K, V> Map<K, V> selectMap(String statement, Object parameter, String mapKey);
/**
* The selectMap is a special case in that it is designed to convert a list
* of results into a Map based on one of the properties in the resulting
* objects.
* @param <K> the returned Map keys type
* @param <V> the returned Map values type
* @param statement Unique identifier matching the statement to use.
* @param parameter A parameter object to pass to the statement.
* @param mapKey The property to use as key for each value in the list.
* @param rowBounds Bounds to limit object retrieval
* @return Map containing key pair data.
*/
<K, V> Map<K, V> selectMap(String statement, Object parameter, String mapKey, RowBounds rowBounds);
/**
* A Cursor offers the same results as a List, except it fetches data lazily using an Iterator.
* @param <T> the returned cursor element type.
* @param statement Unique identifier matching the statement to use.
* @return Cursor of mapped objects
*/
<T> Cursor<T> selectCursor(String statement);
/**
* A Cursor offers the same results as a List, except it fetches data lazily using an Iterator.
* @param <T> the returned cursor element type.
* @param statement Unique identifier matching the statement to use.
* @param parameter A parameter object to pass to the statement.
* @return Cursor of mapped objects
*/
<T> Cursor<T> selectCursor(String statement, Object parameter);
/**
* A Cursor offers the same results as a List, except it fetches data lazily using an Iterator.
* @param <T> the returned cursor element type.
* @param statement Unique identifier matching the statement to use.
* @param parameter A parameter object to pass to the statement.
* @param rowBounds Bounds to limit object retrieval
* @return Cursor of mapped objects
*/
<T> Cursor<T> selectCursor(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds);
/**
* Retrieve a single row mapped from the statement key and parameter
* using a {@code ResultHandler}.
* @param statement Unique identifier matching the statement to use.
* @param parameter A parameter object to pass to the statement.
* @param handler ResultHandler that will handle each retrieved row
*/
void select(String statement, Object parameter, ResultHandler handler);
/**
* Retrieve a single row mapped from the statement
* using a {@code ResultHandler}.
* @param statement Unique identifier matching the statement to use.
* @param handler ResultHandler that will handle each retrieved row
*/
void select(String statement, ResultHandler handler);
/**
* Retrieve a single row mapped from the statement key and parameter
* using a {@code ResultHandler} and {@code RowBounds}
* @param statement Unique identifier matching the statement to use.
* @param rowBounds RowBound instance to limit the query results
* @param handler ResultHandler that will handle each retrieved row
*/
void select(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler handler);
/**
* Execute an insert statement.
* @param statement Unique identifier matching the statement to execute.
* @return int The number of rows affected by the insert.
*/
int insert(String statement);
/**
* Execute an insert statement with the given parameter object. Any generated
* autoincrement values or selectKey entries will modify the given parameter
* object properties. Only the number of rows affected will be returned.
* @param statement Unique identifier matching the statement to execute.
* @param parameter A parameter object to pass to the statement.
* @return int The number of rows affected by the insert.
*/
int insert(String statement, Object parameter);
/**
* Execute an update statement. The number of rows affected will be returned.
* @param statement Unique identifier matching the statement to execute.
* @return int The number of rows affected by the update.
*/
int update(String statement);
/**
* Execute an update statement. The number of rows affected will be returned.
* @param statement Unique identifier matching the statement to execute.
* @param parameter A parameter object to pass to the statement.
* @return int The number of rows affected by the update.
*/
int update(String statement, Object parameter);
/**
* Execute a delete statement. The number of rows affected will be returned.
* @param statement Unique identifier matching the statement to execute.
* @return int The number of rows affected by the delete.
*/
int delete(String statement);
/**
* Execute a delete statement. The number of rows affected will be returned.
* @param statement Unique identifier matching the statement to execute.
* @param parameter A parameter object to pass to the statement.
* @return int The number of rows affected by the delete.
*/
int delete(String statement, Object parameter);
/**
* Flushes batch statements and commits database connection.
* Note that database connection will not be committed if no updates/deletes/inserts were called.
* To force the commit call {@link SqlSession#commit(boolean)}
*/
void commit();
/**
* Flushes batch statements and commits database connection.
* @param force forces connection commit
*/
void commit(boolean force);
/**
* Discards pending batch statements and rolls database connection back.
* Note that database connection will not be rolled back if no updates/deletes/inserts were called.
* To force the rollback call {@link SqlSession#rollback(boolean)}
*/
void rollback();
/**
* Discards pending batch statements and rolls database connection back.
* Note that database connection will not be rolled back if no updates/deletes/inserts were called.
* @param force forces connection rollback
*/
void rollback(boolean force);
/**
* Flushes batch statements.
* @return BatchResult list of updated records
* @since 3.0.6
*/
List<BatchResult> flushStatements();
/**
* Closes the session
*/
@Override
void close();
/**
* Clears local session cache
*/
void clearCache();
/**
* Retrieves current configuration
* @return Configuration
*/
Configuration getConfiguration();
/**
* Retrieves a mapper.
* @param <T> the mapper type
* @param type Mapper interface class
* @return a mapper bound to this SqlSession
*/
<T> T getMapper(Class<T> type);
/**
* Retrieves inner database connection
* @return Connection
*/
Connection getConnection();
}获取
入口在 org.apache.ibatis.session.defaults.DefaultSqlSessionFactory#openSessionFromDataSource
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
//从配置中心获取环境对象接口
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
//再从环境中获取事务工厂接口
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
//从工厂中获取事务接口
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
//创建执行器对象,这也是核心的操作,用来跟数据库真正打交道的
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
//把执行器传递给SqlSession,因为Executor包含了事务对象,事务对象包含了连接,那么SqlSession自然就包含了这些数据
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close()
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
里面比较核心的是获取Executor对象,再稍微看下这个逻辑
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
//如果不传,默认是使用ExecutorType.SIMPLE
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
//进行判断,默认就是SimpleExecutor类型的
Executor executor;
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
//如果是可缓存的,那么会再包装一层,这里也是使用了装饰者模式
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
//mybatis提供的插件,这里是封装了一遍增强这个对象的最终调用,多层代理
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}Executor
Executor是底层用来跟数据库进行打交道的接口,也是核心的另一个接口,跟数据库的查询交互都发生在这个接口中
格式
public interface Executor {
ResultHandler NO_RESULT_HANDLER = null;
/**
* 更新方法
*/
int update(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException;
/**
* 查询方法
*/
<E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey cacheKey, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException;
/**
* 查询方法
*/
<E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException;
<E> Cursor<E> queryCursor(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) throws SQLException;
List<BatchResult> flushStatements() throws SQLException;
/**
* 提交事务
*/
void commit(boolean required) throws SQLException;
/**
* 回滚事务
*/
void rollback(boolean required) throws SQLException;
CacheKey createCacheKey(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, BoundSql boundSql);
boolean isCached(MappedStatement ms, CacheKey key);
void clearLocalCache();
void deferLoad(MappedStatement ms, MetaObject resultObject, String property, CacheKey key, Class<?> targetType);
/**
* 获取事务管理对象
*/
Transaction getTransaction();
void close(boolean forceRollback);
boolean isClosed();
void setExecutorWrapper(Executor executor);
}几大实现
Executor的设计中采用了模板设计模式,这也是很多框架都会用的,主要有以下的实现
BaseExecutor: 体现了模板模式的地方,把一些公用的抽象出来了
BatchExecutor:进行批量操作的执行器,继承了BaseExecutor
ReuseExecutor:重用的执行器,继承了BaseExecutor
SimpleExecutor:简单执行器,也是我们最常用的,继承了BaseExecutor
CachingExecutor:缓存执行器,它属于装饰者模式,对基础的执行器再包装了一层缓存功能
至于获取上面已经讲过了,也并不是很复杂,内部处理逻辑可能才比较复杂
最后再把这几个的关系的UML图放在这里,一目了然
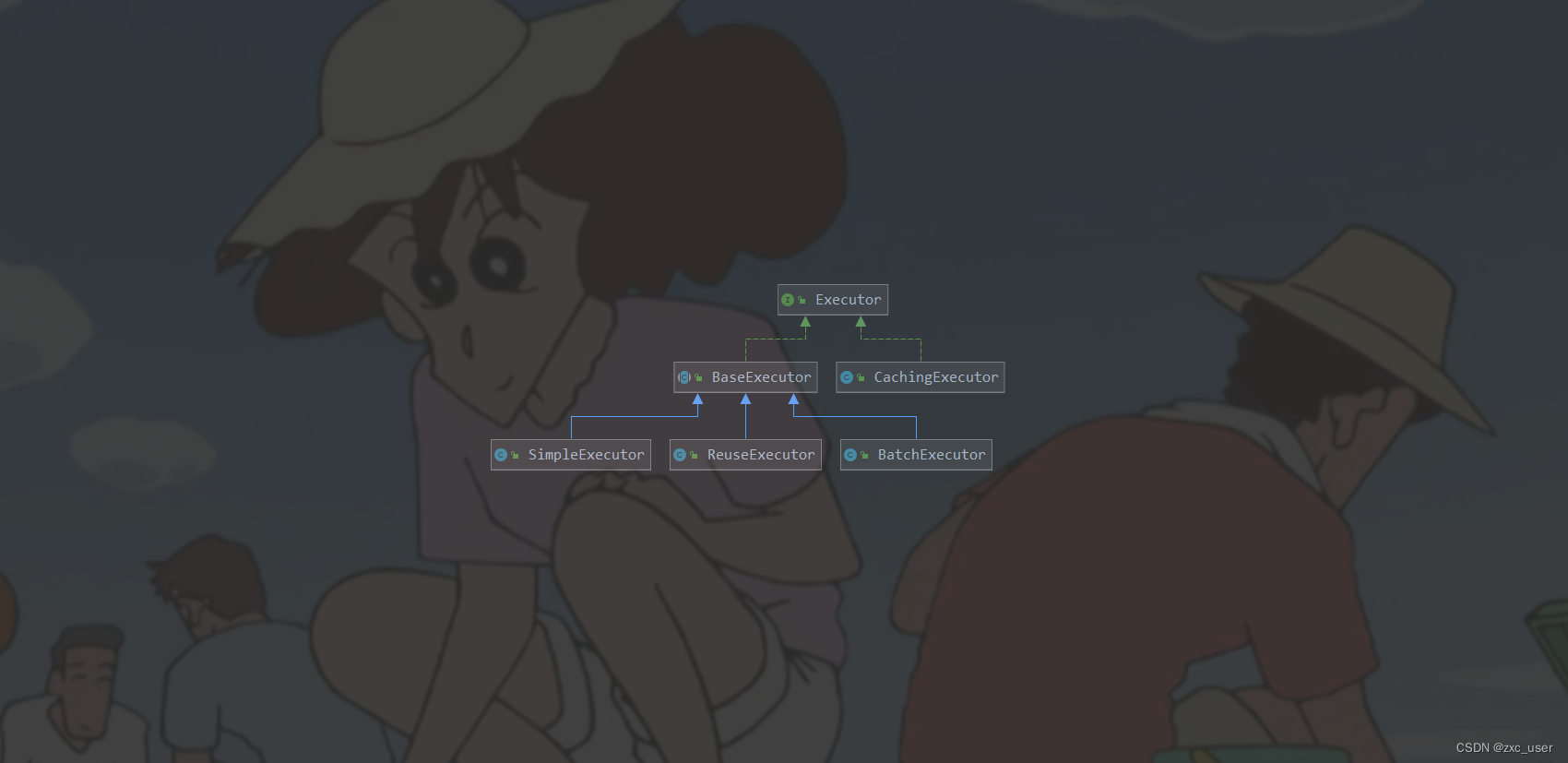
好了,这篇主要就是讲了一下这几个组件的获取和基本样式






















 4134
4134











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








