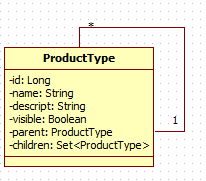
一、实体类图及属性如下:
二、代码
ProductType.java
package com.charlie.shop.domain.product;
/**
* 这是产品类别的实体
* @author charlie
* 1、创建属性
* 2、生成setter/getter方法
* 3、重写hashCode和equals方法
* 4、对id添加JPA映射
* 5、对基本属性添加JPA映射
* 6、对parent、children添加多对一双向映射
* 7、在hibernate.cfg.xml的mapping结点添加映射配置
*
*/
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
import javax.persistence.CascadeType;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.FetchType;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.JoinColumn;
import javax.persistence.ManyToOne;
import javax.persistence.OneToMany;
@Entity
public class ProductType implements Serializable{
/**产品类别id**/
private Long id;
/**产品类别名称**/
private String name;
/**备注,用于google搜索页面描述**/
private String descript;
/**可见性,默认为可见,用于删除操作,删除并不是真正删除,只是设为不可见**/
private Boolean visible = true;
/**直接上级分类**/
private ProductType parent;
/**下级分类**/
private Set<ProductType> children = new HashSet<ProductType>();
//----------------构造方法---------------
public ProductType(){
}
public ProductType(String name, String descript) {
this.name = name;
this.descript = descript;
}
//--------重写hashCode()和equals()-----------
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + ((id == null) ? 0 : id.hashCode());
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
ProductType other = (ProductType) obj;
if (id == null) {
if (other.id != null)
return false;
} else if (!id.equals(other.id))
return false;
return true;
}
//--------下面是getter/setter方法-----------------------
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy=GenerationType.AUTO)
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
@Column(length=36,nullable=false)
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
//要去掉形参前后的空格
this.name = name.trim();
}
@Column(length=200)
public String getDescript() {
return descript;
}
public void setDescript(String descript) {
//要去掉形参前后的空格
this.descript = descript.trim();
}
@Column(nullable=false)
public Boolean getVisible() {
return visible;
}
public void setVisible(Boolean visible) {
this.visible = visible;
}
@ManyToOne(cascade=CascadeType.REFRESH,fetch=FetchType.EAGER)
@JoinColumn(name="parentid")
public ProductType getParent() {
return parent;
}
public void setParent(ProductType parent) {
this.parent = parent;
}
@OneToMany(cascade={CascadeType.REFRESH,CascadeType.REMOVE},mappedBy="parent")
//设置为级联删除,当删除当前类别时,连同他所有的下级分类也一起删除
public Set<ProductType> getChildren() {
return children;
}
public void setChildren(Set<ProductType> children) {
this.children = children;
}
}
说明:因为在页面传过来的字符串,其前后可能包含有用户输入的空格,我们一般是要去掉字符串前后的空格,如果放在业务方法或action类中才去前后空格的话,那么在每次遇到字符串时都得要去前后空格,相当麻烦。为了避免手动去前后空格,我们可以对实体类的setter方法进行改造,对String类型的属性的setter方法都进行改造,比如,当前实体类我们对name和descript属性进行了改造。如下:
public void setName(String name) {
//要去掉形参前后的空格
this.name = name.trim();
}
public void setDescript(String descript) {
//要去掉形参前后的空格
this.descript = descript.trim();
}





















 9448
9448

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








