内容概要
* 这是我的第二篇博客,但为什么是android学习(3)呢,因为我的第二篇博客的代码不在这里,只好先来写这一篇了。
* 今天上午把android英文文档的Fragment部分阅读完毕,那是相当的吃力,还好有个中文的可以对照着看,这篇主要来记录我学习Android Fragment时所经历的一些代码与疑惑等;
基本概念
Fragment 表示 Activity 中的行为或用户界面部分。您可以将多个片段组合在一个 Activity 中来构建多窗格 UI,以及在多个 Activity 中重复使用某个片段。您可以将片段视为 Activity 的模块化组成部分,它具有自己的生命周期,能接收自己的输入事件,并且您可以在 Activity 运行时添加或删除片段(有点像您可以在不同 Activity 中重复使用的“子 Activity”)。
其原理图,一目了然:

按照我的理解这也是模块化的一种多样性的展现,就像造零件,一个零件可以作为一个东西,这一个零件和其他零件组合到一起,又成为一个大的零件,我这么说好粗鄙啊,,,我隐隐中觉得这个和material design有些许的联系,但是又觉得相去甚远,还需学习下material design才能再做打算;
主要知识点
(1)Fragment子类
- DialogFragment
- ListFragment
- PreferenceFragment
(2)使用的基本流程
- 添加用户界面
public static class ExampleFragment extends Fragment {
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// Inflate the layout for this fragment
return inflater.inflate(R.layout.example_fragment, container, false);
}
}为了给fragment提供一个布局,你必须实现onCreateView()回调函数,在绘制fragment布局时Android系统会调用它。实现这个函数时需要返回fragment所属的根View。
注意:如果你的fragment时ListFragment的子类,默认实现从onCreateView()返回一个ListView,所以你不需要实现它。
为了从onCreateView()返回一个布局,你可以从layout resource定义的XML文件inflate它。为了便于你这样做,onCreateView()提供一个LayoutInflater对象。inflate()函数需要以下三个参数:
要inflate的布局的资源ID。
被inflate的布局的父ViewGroup。传入container很重要,这是为了让系统将布局参数应用到被inflate的布局的根view中去,由其将要嵌入的父view指定。
一个布尔值,表明在inflate期间被infalte的布局是否应该附上ViewGroup(第二个参数)。(在这个例子中传入的是false,因为系统已经将被inflate的布局插入到容器中(container)——传入true会在最终的布局里创建一个多余的ViewGroup。)
- 将fragment添加到activity之中
两种方法:
1.布局文件声明,主要属性:name、id;
2.通过编码将fragment添加到已存在的ViewGroup中;
FragmentManager fragmentManager = getFragmentManager();
FragmentTransaction fragmentTransaction = fragmentManager.beginTransaction();
ExampleFragment fragment = new ExampleFragment();
fragmentTransaction.add(R.id.fragment_container, fragment);
fragmentTransaction.commit();Fragment事务管理
想要管理activity中的fragment,可以使用FragmentManager。可以通过在activity中调用getFragmentManager()获得。
使用FragmentManager 可以做如下事情,包括:
使用findFragmentById()(用于在activity布局中提供有界面的fragment)或者findFragmentByTag()获取activity中存在的fragment(用于有界面或者没有界面的fragment)。
使用popBackStack()(模仿用户的BACK命令)从后台栈弹出fragment。
使用addOnBackStackChangedListener()注册一个监听后台栈变化的监听器。addToBackStack
在调用commit()之前,为了将事务添加到fragment事务后台栈中,你可能会想调用addToBackStatck()。这个后台栈由activity管理,并且允许用户通过按BACK键回退到前一个fragment状态。
代码示例:
// Create new fragment and transaction
Fragment newFragment = new ExampleFragment();
FragmentTransaction transaction = getFragmentManager().beginTransaction();
// Replace whatever is in the fragment_container view with this fragment,
// and add the transaction to the back stack
transaction.replace(R.id.fragment_container, newFragment);
transaction.addToBackStack(null);
// Commit the transaction
transaction.commit();- 与Activity交互
(1)fragment访问activity:
View listView = getActivity().findViewById(R.id.list);(2)activity访问fragment:
ExampleFragment fragment = (ExampleFragment) getFragmentManager().findFragmentById(R.id.example_fragment);(3)fragment与activity共享事件
在一些情况下,你可能需要fragment与activity共享事件。这样做的一个好方法是在fragment内部定义一个回调接口,并需要宿主activity实现它。当activity通过接口接收到回调时,可以在必要时与布局中的其它fragment共享信息。
举个例子,如果新闻应用的actvity中有两个fragment——一个显示文章列表(fragment A),另一个显示一篇文章(fragment B)——然后fragment A 必须要告诉activity列表项何时被选种,这样,activity可以通知fragment B显示这篇文章。这种情况下,在fragment A内部声明接口OnArticleSelectedListener:
public static class FragmentA extends ListFragment {
...
// Container Activity must implement this interface
public interface OnArticleSelectedListener {
public void onArticleSelected(Uri articleUri);
}
...
}然后fragment的宿主activity实现了OnArticleSelectedListener接口,并且重写onArticleSelected()以通知fragment B来自于fragment A的事件。为了确保宿主activity实现了这个接口,fragment A的onAttach()回调函数(当添加fragment到activity中时系统会调用它)通过作为参数传入onAttach()的activity的类型转换来实例化一个OnArticleSelectedListener实例。
public static class FragmentA extends ListFragment {
OnArticleSelectedListener mListener;
...
@Override
public void onAttach(Activity activity) {
super.onAttach(activity);
try {
mListener = (OnArticleSelectedListener) activity;
} catch (ClassCastException e) {
throw new ClassCastException(activity.toString() + " must implement OnArticleSelectedListener");
}
}
...
}如果activity没有实现这个接口,那么fragment会抛出一个ClassCaseException异常。一旦成功,mListener成员会保留一个activity的OnArticleSelectedListener实现的引用,由此fragment A可以通过调用由OnArticleSelectedListener接口定义的方法与activity共享事件。例如,如果fragment A是ListFragment的子类,每次用户点击列表项时,系统都会调用fragment的onListItemClick()事件,然后fragment调用onArticleSelected()来与activity共享事件。
public static class FragmentA extends ListFragment {
OnArticleSelectedListener mListener;
...
@Override
public void onListItemClick(ListView l, View v, int position, long id) {
// Append the clicked item's row ID with the content provider Uri
Uri noteUri = ContentUris.withAppendedId(ArticleColumns.CONTENT_URI, id);
// Send the event and Uri to the host activity
mListener.onArticleSelected(noteUri);
}
...
}传递给onListItemClick()的参数id是点击的列表项行id,activity(或者其它fragment)用以从应用的ContentProvider获取文章。
以上具体参见:android文档-fragment
DEMO
这个demo是按照文档的最后一个例子来的,这个例子的源码我找了好久,就是找不到,然后在StackOverFlow上搜到了一个问题,他也找不到,哈哈哈:
android-fragment-source-code-for-fragmentlayout-java
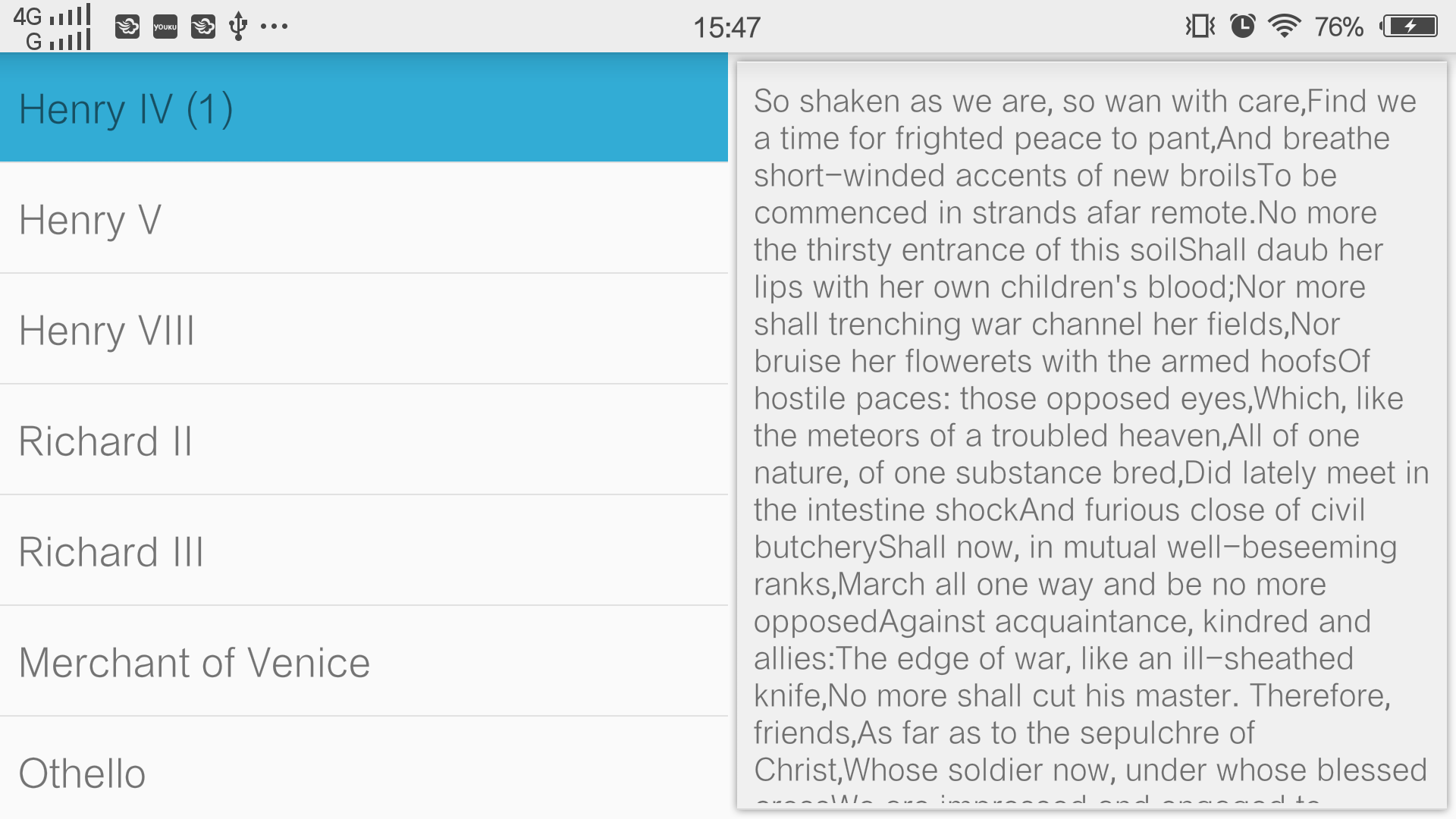
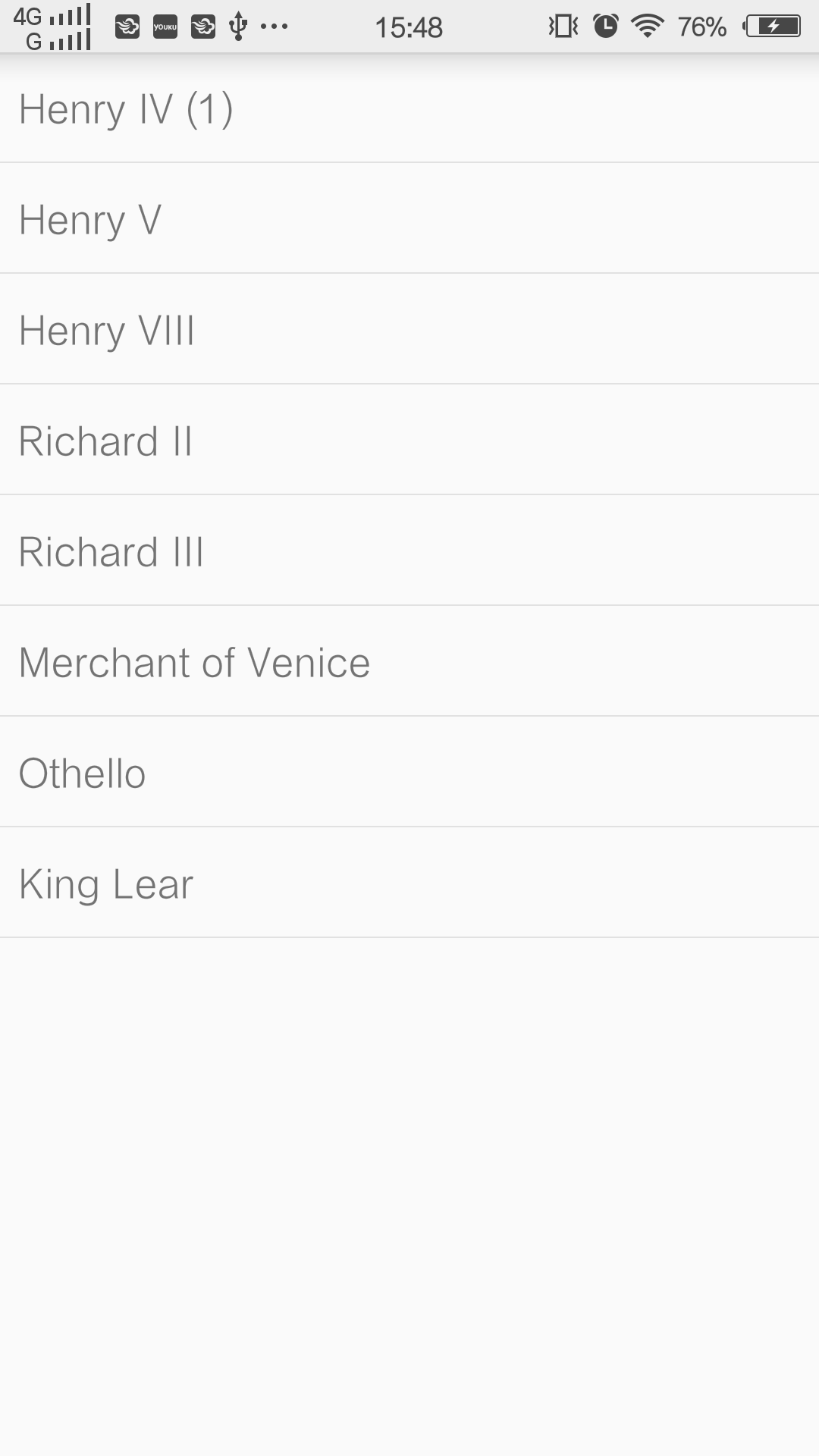
然后下载了Level18的Sample,在里面找到了相应的源码,提取出来在Android Studio中复原了这个莎士比亚的戏剧阅读小程序:
这个小程序主要是根据手机的横竖屏来判断Layout文件的加载,横屏加载两个Fragment,竖屏只加载一个,具体的见源码吧,我还没有完全的理解透彻,感觉官网给的代码要严谨好多;
源码如下:
百度网盘-FragmentDemo
最后上几张图吧,无图无真相:























 4389
4389

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








