4.消息存储
目前的MQ中间件从存储模型来看,分为需要持久化和不需要持久化的两种模型,现在大多数的M Q 都是支持持久化存储的,比如ActiveMQ、RabbitMQ、Kafka、RocketMQ ,而ZeroMQ 却不需要支持持久化存储。然而业务系统也大多需要MQ 有持久存储的能力,能大大增加系统的高可用性。从存储方式和效率来看,文件系统高于KV 存储, KV 存储又高于关系型数据库,直接操作文件系统肯定是最快的,但可靠性却是最低的,而关系型数据库的性能和可靠性与文件系统恰恰相反。
4.1.存储概要设计
RocketMQ主要存储的文件包括Comitlog 文件、ConsumeQueue 文件、IndexFile 文件。RocketMQ 将所有主题的消息存储在同一个文件中,确保消息发送时顺序写文件,尽最大的能力确保消息发送的高性能与高吞吐量。但由于消息中间件一般是基于消息主题的订阅机制,这样便给按照消息主题检索消息带来了极大的不便。为了提高消息消费的效率, RocketMQ 引入了ConsumeQueue 消息队列文件,每个消息主题包含多个消息消费队列,每一个消息队列有一个消息文件。IndexFile 索引文件,其主要设计理念就是为了加速消息的检索性能,根据消息的属性快速从Commitlog 文件中检索消息。RocketMQ 是一款高性能的消息中间件,存储部分的设计是核心,存储的核心是IO访问性能,本章也会重点剖析RocketMQ 是如何提高IO 访问性能的。进入RocketMQ 存储剖析之前,先看一下RocketMQ 数据流向,如图4-1 所示。

-
CommitLog :消息存储文件,所有消息主题的消息都存储在CommitLog 文件中。
-
ConsumeQueue :消息消费队列,消息到达CommitLog 文件后,将异步转发到消息消费队列,供消息消费者消费。
-
IndexFile :消息索引文件,主要存储消息Key 与Offset 的对应关系。
-
事务状态服务: 存储每条消息的事务状态。
-
定时消息服务:每一个延迟级别对应一个消息消费队列,存储延迟队列的消息拉取进度。
4.2.初识消息存储
消息存储实现类:org.apache.rocketmq.store.DefaultMessageStore ,它是存储模块里面最重要的一个类,包含了很多对存储文件操作的API , 其他模块对消息实体的操作都是通过DefaultMessageStore 进行操作,其类图如图4-2 所示。

让我们来一一介绍DefaultMessageStore 的核心属性。
-
MessageStoreConfig messageStoreConfig :消息存储配置属性。
-
CommitLog commitLog: CommitLog 文件的存储实现类。
-
ConcurrentMap<String/* topic */, ConcurrentMap <Integer/* queueld */, Consume Queue>>consumeQueueTable :消息队列存储缓存表,按消息主题分组。
-
FlushConsumeQueueService flushConsumeQueueService :消息队列文件ConsumeQueue刷盘线程。
-
CleanCommitLogService cleanCommitLogService :清除CommitLog 文件服务。
-
CleanConsumeQueueService cleanConsumeQueueService : 清除ConsumeQueue 文件服务。
-
IndexService indexService : 索引文件实现类。
-
AllocateMappedFileService allocateMappedFileService: MappedFile 分配服务。
-
ReputMessageService reputMessageService : CommitLog 消息分发,根据CommitLog文件构建ConsumeQueue 、IndexFile 文件。
-
HAService haService :存储HA 机制。
-
TransientStorePool transientStorePool :消息堆内存缓存。
-
MessageArrivingListener messageArrivingListener :消息拉取长轮询模式消息达到监听器。
-
BrokerConfig brokerConfig: Broker 配置属性。
-
StoreCheckpoint storeCheckpoint :文件刷盘检测点。
-
LinkedList<CommitLogDispatcher> dispatcher List: CommitLog 文件转发请求。
4.3.消息发送存储流程
本节将以消息发送存储为突破点,一点一点揭开RocketMQ 存储设计的神秘面纱。消息存储入口: org.apache.rocketmq.store.DefaultMessageStore#putMessage 。
Step1:如果当前Broker 停止工作或Broker 为SLAVE 角色或当前Rocket 不支持写入则拒绝消息写入;如果消息主题长度超过256 个字符、消息属性长度超过65536 个字符将拒绝该消息写人。
如果日志中包含“ message store is not writeable, so putMessage is forbidden ” ,出现这种日志最有可能是磁盘空间不足,在写ConsumeQueue 、IndexFile 文件出现错误时会拒绝消息再次写入。
Step2 :如果消息的延迟级别大于0 ,将消息的原主题名称与原消息队列ID 存入消息属性中,用延迟消息主题SCHEDULE_TOPIC 、消息队列ID 更新原先消息的主题与队列, 这是并发消息消费重试关键的一步,下一章会重点探讨消息重试机制与定时消息的实现原理。
MappedFile unlockMappedFile = null; MappedFile mappedFile = this.mappedFileQueue.getLastMappedFile();
Step3 :获取当前可以写入的Commitlog 文件, RocketMQ 物理文件的组织方式如图4-3所示。

Commitlog 文件存储目录为{ ROCKET_HOME }/store/commitlog 目录,每一个文件默认1G , 一个文件写满后再创建另外一个,以该文件中第一个偏移量为文件名,偏移量小于20 位用0 补齐。图4 -3 所示的第一个文件初始偏移量为0 ,第二个文件的1073741824 ,代表该文件中的第一条消息的物理偏移量为1073741824 ,这样根据物理偏移量能快速定位到消息。MappedFileQueue 可以看作是{ ROCKET_HOME }/store/commitlog 文件夹,而MappedFile 则对应该文件夹下一个个的文件。
Step4 :在写入CommitLog 之前,先申请putMessageLock,也就是将消息存储到CommitLog 文件中是串行的。
//org.apache.rocketmq.store.CommitLog#putMessage
public PutMessageResult putMessage(final MessageExtBrokerInner msg) {
// Set the storage time
msg.setStoreTimestamp(System.currentTimeMillis());
// Set the message body BODY CRC (consider the most appropriate setting
// on the client)
msg.setBodyCRC(UtilAll.crc32(msg.getBody()));
// Back to Results
AppendMessageResult result = null;
StoreStatsService storeStatsService = this.defaultMessageStore.getStoreStatsService();
String topic = msg.getTopic();
int queueId = msg.getQueueId();
final int tranType = MessageSysFlag.getTransactionValue(msg.getSysFlag());
if (tranType == MessageSysFlag.TRANSACTION_NOT_TYPE
|| tranType == MessageSysFlag.TRANSACTION_COMMIT_TYPE) {
// Delay Delivery
if (msg.getDelayTimeLevel() > 0) {
if (msg.getDelayTimeLevel() > this.defaultMessageStore.getScheduleMessageService().getMaxDelayLevel()) {
msg.setDelayTimeLevel(this.defaultMessageStore.getScheduleMessageService().getMaxDelayLevel());
}
topic = ScheduleMessageService.SCHEDULE_TOPIC;
queueId = ScheduleMessageService.delayLevel2QueueId(msg.getDelayTimeLevel());
// Backup real topic, queueId
MessageAccessor.putProperty(msg, MessageConst.PROPERTY_REAL_TOPIC, msg.getTopic());
MessageAccessor.putProperty(msg, MessageConst.PROPERTY_REAL_QUEUE_ID, String.valueOf(msg.getQueueId()));
msg.setPropertiesString(MessageDecoder.messageProperties2String(msg.getProperties()));
msg.setTopic(topic);
msg.setQueueId(queueId);
}
}
long eclipseTimeInLock = 0;
MappedFile unlockMappedFile = null;
MappedFile mappedFile = this.mappedFileQueue.getLastMappedFile();
putMessageLock.lock(); //spin or ReentrantLock ,depending on store config
try {
long beginLockTimestamp = this.defaultMessageStore.getSystemClock().now();
this.beginTimeInLock = beginLockTimestamp;
// Here settings are stored timestamp, in order to ensure an orderly
// global
msg.setStoreTimestamp(beginLockTimestamp);
if (null == mappedFile || mappedFile.isFull()) {
mappedFile = this.mappedFileQueue.getLastMappedFile(0); // Mark: NewFile may be cause noise
}
if (null == mappedFile) {
log.error("create mapped file1 error, topic: " + msg.getTopic() + " clientAddr: " + msg.getBornHostString());
beginTimeInLock = 0;
return new PutMessageResult(PutMessageStatus.CREATE_MAPEDFILE_FAILED, null);
}
result = mappedFile.appendMessage(msg, this.appendMessageCallback);
switch (result.getStatus()) {
case PUT_OK:
break;
case END_OF_FILE:
unlockMappedFile = mappedFile;
// Create a new file, re-write the message
mappedFile = this.mappedFileQueue.getLastMappedFile(0);
if (null == mappedFile) {
// XXX: warn and notify me
log.error("create mapped file2 error, topic: " + msg.getTopic() + " clientAddr: " + msg.getBornHostString());
beginTimeInLock = 0;
return new PutMessageResult(PutMessageStatus.CREATE_MAPEDFILE_FAILED, result);
}
result = mappedFile.appendMessage(msg, this.appendMessageCallback);
break;
case MESSAGE_SIZE_EXCEEDED:
case PROPERTIES_SIZE_EXCEEDED:
beginTimeInLock = 0;
return new PutMessageResult(PutMessageStatus.MESSAGE_ILLEGAL, result);
case UNKNOWN_ERROR:
beginTimeInLock = 0;
return new PutMessageResult(PutMessageStatus.UNKNOWN_ERROR, result);
default:
beginTimeInLock = 0;
return new PutMessageResult(PutMessageStatus.UNKNOWN_ERROR, result);
}
eclipseTimeInLock = this.defaultMessageStore.getSystemClock().now() - beginLockTimestamp;
beginTimeInLock = 0;
} finally {
putMessageLock.unlock();
}
if (eclipseTimeInLock > 500) {
log.warn("[NOTIFYME]putMessage in lock cost time(ms)={}, bodyLength={} AppendMessageResult={}", eclipseTimeInLock, msg.getBody().length, result);
}
if (null != unlockMappedFile && this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().isWarmMapedFileEnable()) {
this.defaultMessageStore.unlockMappedFile(unlockMappedFile);
}
PutMessageResult putMessageResult = new PutMessageResult(PutMessageStatus.PUT_OK, result);
// Statistics
storeStatsService.getSinglePutMessageTopicTimesTotal(msg.getTopic()).incrementAndGet();
storeStatsService.getSinglePutMessageTopicSizeTotal(topic).addAndGet(result.getWroteBytes());
handleDiskFlush(result, putMessageResult, msg);
handleHA(result, putMessageResult, msg);
return putMessageResult;
}
Step5:设置消息的存储时间,如果mappedFile 为空,表明$ {ROCKET_HOME}/store/commitlog 目录下不存在任何文件,说明本次消息是第一次消息发送,用偏移量0 创建第一个commit 文件,文件为00000000000000000000 ,如果文件创建失败,抛出CREATE_MAPEDFILE_FAILED ,很有可能是磁盘空间不足或权限不够。
//org.apache.rocketmq.store.MappedFile#appendMessagesInner
public AppendMessageResult appendMessagesInner(final MessageExt messageExt, final AppendMessageCallback cb) {
assert messageExt != null;
assert cb != null;
int currentPos = this.wrotePosition.get();
if (currentPos < this.fileSize) {
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = writeBuffer != null ? writeBuffer.slice() : this.mappedByteBuffer.slice();
byteBuffer.position(currentPos);
AppendMessageResult result = null;
if (messageExt instanceof MessageExtBrokerInner) {
result = cb.doAppend(this.getFileFromOffset(), byteBuffer, this.fileSize - currentPos, (MessageExtBrokerInner) messageExt);
} else if (messageExt instanceof MessageExtBatch) {
result = cb.doAppend(this.getFileFromOffset(), byteBuffer, this.fileSize - currentPos, (MessageExtBatch) messageExt);
} else {
return new AppendMessageResult(AppendMessageStatus.UNKNOWN_ERROR);
}
this.wrotePosition.addAndGet(result.getWroteBytes());
this.storeTimestamp = result.getStoreTimestamp();
return result;
}
log.error("MappedFile.appendMessage return null, wrotePosition: {} fileSize: {}", currentPos, this.fileSize);
return new AppendMessageResult(AppendMessageStatus.UNKNOWN_ERROR);
}
Step6:将消息追加到MappedFile 中。首先先获取MappedFile 当前写指针,如果currentPos 大于或等于文件大小则表明文件已写满,抛出AppendMessageStatus.UNKNOWN_ERROR。如果currentPos 小于文件大小,通过slice()方法创建一个与MappedFile 的共享内存区,并设置position 为当前指针。
//Commitlog$DefaultAppendMessageCallback#doAppend // PHY OFFSET long wroteOffset = fileFromOffset + byteBuffer.position(); this.resetByteBuffer(hostHolder, 8); String msgId = MessageDecoder.createMessageId(this.msgIdMemory, msgInner.getStoreHostBytes(hostHolder), wroteOffset);
Step7 :创建全局唯一消息ID ,消息ID 有16 字节,消息ID 组成如图4-4 所示。

但为了消息ID可读性,返回给应用程序的msgId 为字符类型,可以通过UtilAll.bytes2string 方法将msgId 字节数组转换成字符串,通过Uti1All.string2bytes 方法将msgId字符串还原成16 个字节的字节数组,从而根据提取消息偏移量,可以快速通过msgId 找到消息内容。
//Commitlog$DefaultAppendMessageCallback#doAppend
// Record ConsumeQueue information
keyBuilder.setLength(0);
keyBuilder.append(msgInner.getTopic());
keyBuilder.append('-');
keyBuilder.append(msgInner.getQueueId());
String key = keyBuilder.toString();
Long queueOffset = CommitLog.this.topicQueueTable.get(key);
if (null == queueOffset) {
queueOffset = 0L;
CommitLog.this.topicQueueTable.put(key, queueOffset);
}
Step8 : 获取该消息在消息队列的偏移量。CommitLog 中保存了当前所有消息队列的当前待写入偏移量。
//Commitlog$DefaultAppendMessageCallback#doAppend
private static int calMsgLength(int bodyLength, int topicLength, int propertiesLength) {
final int msgLen = 4 //TOTALSIZE
+ 4 //MAGICCODE
+ 4 //BODYCRC
+ 4 //QUEUEID
+ 4 //FLAG
+ 8 //QUEUEOFFSET
+ 8 //PHYSICALOFFSET
+ 4 //SYSFLAG
+ 8 //BORNTIMESTAMP
+ 8 //BORNHOST
+ 8 //STORETIMESTAMP
+ 8 //STOREHOSTADDRESS
+ 4 //RECONSUMETIMES
+ 8 //Prepared Transaction Offset
+ 4 + (bodyLength > 0 ? bodyLength : 0) //BODY
+ 1 + topicLength //TOPIC
+ 2 + (propertiesLength > 0 ? propertiesLength : 0) //propertiesLength
+ 0;
return msgLen;
}
Step9 : 根据消息、体的长度、主题的长度、属性的长度结合消息存储格式计算消息的总长度。
RocketMQ 消息存储格式如下。
-
TOTALSIZE : 该消息条目总长度,4 字节。
-
MAGICCODE : 魔数, 4 字节。固定值0xdaa320a7 。
-
BODYCRC : 消息体crc校验码, 4 字节。
-
QUEUEID : 消息消费队列ID , 4 字节。
-
FLAG : 消息FLAG , RocketMQ 不做处理, 供应用程序使用,默认4 字节。
-
QUEUEOFFSET :消息在消息消费队列的偏移量, 8 字节。
-
PHYSICALOFFSET : 消息在CommitLog 文件中的偏移量, 8 字节。
-
SYSFLAG : 消息系统Flag ,例如是否压缩、是否是事务消息等, 4 字节。
-
BORNTIMESTAMP : 消息生产者调用消息发送API 的时间戳, 8 字节。
-
BORNHOST :消息发送者IP 、端口号, 8 字节。
-
STORETIMESTAMP : 消息存储时间戳, 8 字节。
-
STOREHOSTADDRESS: Broker 服务器IP+端口号, 8 字节。
-
RECONSUMETIMES : 消息重试次数, 4 字节。
-
Prepared Transaction Offset : 事务消息物理偏移量, 8 字节。
-
BodyLength :消息体长度, 4 字节。
-
Body : 消息体内容,长度为bodyLen th 中存储的值。
-
TopieLength : 主题存储长度, 1 字节,表示主题名称不能超过255 个字符。
-
Topic : 主题,长度为TopieL e n g th 中存储的值。
-
PropertiesLength : 消息属性长度, 2 字节, 表示消息属性长度不能超过6 553 6 个字符。
-
Properties : 消息属性,长度为PropertiesLength 中存储的值。
上述表示CommitLog 条目是不定长的,每一个条目的长度存储在前4 个字节中。
//Commitlog$DefaultAppendMessageCallback#doAppend
// Determines whether there is sufficient free space
if ((msgLen + END_FILE_MIN_BLANK_LENGTH) > maxBlank) {
this.resetByteBuffer(this.msgStoreItemMemory, maxBlank);
// 1 TOTALSIZE
this.msgStoreItemMemory.putInt(maxBlank);
// 2 MAGICCODE
this.msgStoreItemMemory.putInt(CommitLog.BLANK_MAGIC_CODE);
// 3 The remaining space may be any value
// Here the length of the specially set maxBlank
final long beginTimeMills = CommitLog.this.defaultMessageStore.now();
byteBuffer.put(this.msgStoreItemMemory.array(), 0, maxBlank);
return new AppendMessageResult(AppendMessageStatus.END_OF_FILE, wroteOffset, maxBlank, msgId, msgInner.getStoreTimestamp(),
queueOffset, CommitLog.this.defaultMessageStore.now() - beginTimeMills);
}
Step10:如果消息长度+END_FILE_MIN_BLANK_LENGTH 大于CommitLog 文件的空闲空间,则返回AppendMessageStatus.END_OF_FILE, Broker 会重新创建一个新的CommitLog 文件来存储该消息。从这里可以看出,每个CommitLog 文件最少会空闲8个字节,高4 字节存储当前文件剩余空间,低4 字节存储魔数: CommitLog.BLANK_MAGIC_CODE 。
//Commitlog$DefaultAppendMessageCallback#doAppend
final long beginTimeMills = CommitLog.this.defaultMessageStore.now();
// Write messages to the queue buffer
byteBuffer.put(this.msgStoreItemMemory.array(), 0, msgLen);
AppendMessageResult result = new AppendMessageResult(AppendMessageStatus.PUT_OK, wroteOffset, msgLen, msgId,
msgInner.getStoreTimestamp(), queueOffset, CommitLog.this.defaultMessageStore.now() - beginTimeMills);
Step11 :将消息内容存储到ByteBuffer 中,然后创建AppendMessageResult 。这里只是将消息存储在MappedFile 对应的内存映射Buffer 中,并没有刷写到磁盘,追加结果如图4-5 所示。

下面我们来一一介绍下AppendMessageResult 的属性。
-
AppendMessageStatus status :消息追加结果,取值PUT_OK : 追加成功; END_OF_FILE: 超过文件大小; MESSAGE_SIZE_EXCEEDED :消息长度超过最大允许长度:PROPERTIES_SIZE_EXCEEDED :消息、属性超过最大允许长度; UNKNOWN_ERROR :未知异常。
-
long wroteOffset :消息的物理偏移量。
-
String msgld :消息ID 。
-
long storeTimestamp :消息存储时间戳。
-
long logicsOffset :消息消费队列逻辑偏移量,类似于数组下标。
-
long pagecacheRT = 0 :当前未使用。
-
int msgNum = 1 :消息条数,批量消息发送时消息条数。
//Commitlog$DefaultAppendMessageCallback#doAppend
switch (tranType) {
case MessageSysFlag.TRANSACTION_PREPARED_TYPE:
case MessageSysFlag.TRANSACTION_ROLLBACK_TYPE:
break;
case MessageSysFlag.TRANSACTION_NOT_TYPE:
case MessageSysFlag.TRANSACTION_COMMIT_TYPE:
// The next update ConsumeQueue information
CommitLog.this.topicQueueTable.put(key, ++queueOffset);
break;
default:
break;
}
Step12 :更新消息队列逻辑偏移量。 Step13 :处理完消息追加逻辑后将释放putMessageLock 锁。
//Commitlog#putMessage handleDiskFlush(result, putMessageResult, msg); handleHA(result, putMessageResult, msg); return putMessageResult;
Step14 : DefaultAppendMessageCallback#doAppend 只是将消息追加在内存中, 需要根据是同步刷盘还是异步刷盘方式,将内存中的数据持久化到磁盘,关于刷盘操作后面会详细介绍。然后执行HA 主从同步复制,主从同步将在第7 章详细介绍。消息发送的基本流程就介绍到这里,下一节开始详细剖析RocketMQ 消息存储机制的各个方面。
4.4.存储文件组织与内存映射
RocketMQ 通过使用内存映射文件来提高IO 访问性能,无论是CommitLog 、ConsumeQueue 还是IndexFile ,单个文件都被设计为固定长度,如果一个文件写满以后再创建一个新文件,文件名就为该文件第一条消息对应的全局物理偏移量。例如CommitLog文件的组织方式如图4-6 所示。
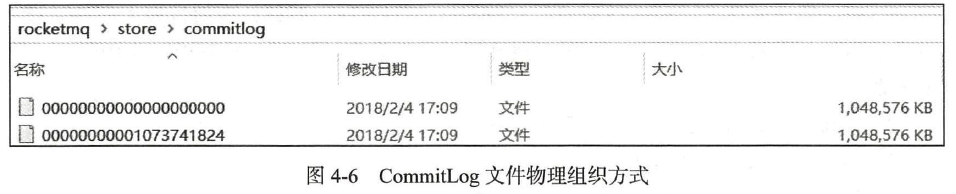
RocketMQ 使用MappedFile 、MappedFileQueue 来封装存储文件,其关系如图4-7 所示。

4.4.1.MappedFileQueue 映射文件队列
MappedFileQueue是MappedFile 的管理容器, MappedFileQueue 是对存储目录的封装,例如CommitLog 文件的存储路径{ ROCKET_HOME} /store/commitlog/ ,该目录下会存在多个内存映射文件(MappedFile) 。MappedFileQueue 类图如图4-8 所示。

下面让我们一一来介绍MappedFileQueue 的核心属性。
-
String storePath :存储目录。
-
int mappedFileSize : 单个文件的存储大小。
-
CopyOnWriteArrayList<MappedFile> mappedFiles: MappedFile 文件集合。
-
AllocateMappedFileService allocateMappedFileService :创建MappedFile 服务类。
-
long flushedWhere = 0 : 当前刷盘指针, 表示该指针之前的所有数据全部持久化到磁盘。
-
long committedWhere = 0 : 当前数据提交指针,内存中ByteBuffer 当前的写指针,该值大于等于flushedWhere 。
接下来重点分析一下根据不同查询维度查找MappedFile 。
public MappedFile getMappedFileByTime(final long timestamp) {
Object[] mfs = this.copyMappedFiles(0);
if (null == mfs)
return null;
for (int i = 0; i < mfs.length; i++) {
MappedFile mappedFile = (MappedFile) mfs[i];
if (mappedFile.getLastModifiedTimestamp() >= timestamp) {
return mappedFile;
}
}
return (MappedFile) mfs[mfs.length - 1];
}
根据消息存储时间戳来查找MappdFile 。从MappedFile 列表中第一个文件开始查找,找到第一个最后一次更新时间大于待查找时间戳的文件,如果不存在,则返回最后一个MappedFile 文件。
public MappedFile findMappedFileByOffset(final long offset, final boolean returnFirstOnNotFound) {
try {
MappedFile firstMappedFile = this.getFirstMappedFile();
MappedFile lastMappedFile = this.getLastMappedFile();
if (firstMappedFile != null && lastMappedFile != null) {
if (offset < firstMappedFile.getFileFromOffset() || offset >= lastMappedFile.getFileFromOffset() + this.mappedFileSize) {
LOG_ERROR.warn("Offset not matched. Request offset: {}, firstOffset: {}, lastOffset: {}, mappedFileSize: {}, mappedFiles count: {}",
offset,
firstMappedFile.getFileFromOffset(),
lastMappedFile.getFileFromOffset() + this.mappedFileSize,
this.mappedFileSize,
this.mappedFiles.size());
} else {
int index = (int) ((offset / this.mappedFileSize) - (firstMappedFile.getFileFromOffset() / this.mappedFileSize));
MappedFile targetFile = null;
try {
targetFile = this.mappedFiles.get(index);
} catch (Exception ignored) {
}
if (targetFile != null && offset >= targetFile.getFileFromOffset()
&& offset < targetFile.getFileFromOffset() + this.mappedFileSize) {
return targetFile;
}
for (MappedFile tmpMappedFile : this.mappedFiles) {
if (offset >= tmpMappedFile.getFileFromOffset()
&& offset < tmpMappedFile.getFileFromOffset() + this.mappedFileSize) {
return tmpMappedFile;
}
}
}
if (returnFirstOnNotFound) {
return firstMappedFile;
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("findMappedFileByOffset Exception", e);
}
return null;
}
根据消息偏移量offset 查找MappedFile 。根据offet 查找MappedFile 直接使用offset%mappedFileSize是否可行?答案是否定的,由于使用了内存映射,只要存在于存储目录下的文件,都需要对应创建内存映射文件,如果不定时将已消费的消息从存储文件中删除,会造成极大的内存压力与资源浪费,所有RocketMQ 采取定时删除存储文件的策略,也就是说在存储文件中, 第一个文件不一定是00000000000000000000 ,因为该文件在某一时刻会被删除,故根据offset 定位MappedFile 的算法为int index = (int) ((offset / this.mappedFileSize) - (firstMappedFile.getFileFromOffset() / this.mappedFileSize)); 。
这是一个很重要的点:因为使用了内存映射技术commitLog不能长期保存
public long getMinOffset() {
if (!this.mappedFiles.isEmpty()) {
try {
return this.mappedFiles.get(0).getFileFromOffset();
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
//continue;
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("getMinOffset has exception.", e);
}
}
return -1;
}
获取存储文件最小偏移量,从这里也可以看出,并不是直接返回0 ,而是返回MappedFile的getFileFromOffset() 。
public long getMaxOffset() {
MappedFile mappedFile = getLastMappedFile();
if (mappedFile != null) {
return mappedFile.getFileFromOffset() + mappedFile.getReadPosition();
}
return 0;
}
获取存储文件的最大偏移量。返回最后一个Mapp巳dFile 文件的fileFromOffset 加上MappedFile 文件当前的写指针。
public long getMaxWrotePosition() {
MappedFile mappedFile = getLastMappedFile();
if (mappedFile != null) {
return mappedFile.getFileFromOffset() + mappedFile.getWrotePosition();
}
return 0;
}
返回存储文件当前的写指针。返回最后一个文件的fil eF rom Offset 加上当前写指针位置。MappedFileQueue 的相关业务方法在具体使用到时再去剖析。
4.4.2.MappedFile内存映射文件
MappedFile 是RocketMQ 内存映射文件的具体实现,如图4-9 所示。

下面让我们一一来介绍MappedFile 的核心属性。
-
int OS_PAGE_SIZE :操作系统每页大小,默认4k 。
-
AtomicLong TOTAL_MAPPED_VIRTUAL_MEMORY : 当前JVM 实例中MappedFile虚拟内存。
-
Atomiclnteger TOTAL_MAPPED_FILES :当前JVM 实例中MappedFile 对象个数。
-
Atomiclnteger wrotePosition : 当前该文件的写指针,从0 开始(内存映射文件中的写指针)
-
Atomiclnteger committedPosition :当前文件的提交指针,如果开启transientStore PoolEnable, 则数据会存储在TransientStorePool 中, 然后提交到内存映射ByteBuffer 中, 再刷写到磁盘。
-
Atomiclnteger flushedPosition :刷写到磁盘指针,该指针之前的数据持久化到磁盘中。
-
int fileSize :文件大小。
-
FileChannel fileChannel : 文件通道。
-
ByteBuffer writeBuffer :堆内存ByteBuffer , 如果不为空,数据首先将存储在该Buffer 中, 然后提交到MappedFile 对应的内存映射文件Buffer 。transientStorePoolEnable为true 时不为空。
-
TransientStorePool transientStorePool :堆内存池, transientStorePoolEnable 为true时启用。
-
String fileName :文件名称。
-
long fileFromOffset :该文件的初始偏移量。
-
File file :物理文件。
-
MappedByteBuffer mappedByteBuffer :物理文件对应的内存映射Buffer 。
-
volatile long storeTimestamp = 0 :文件最后一次内容写入时间。
-
boolean firstCreatelnQueue :是否是MappedFileQueue 队列中第一个文件。
MappedFile 初始化
根据是否开启transientStorePoolEnable 存在两种初始化情况。transientStorePoolEnable为true 表示内容先存储在堆外内存,然后通过Commit 线程将数据提交到内存映射Buffer中,再通过Flush 线程将内存映射Buffer 中的数据持久化到磁盘中。
//MappedFile#init(final St 「ing filer、Jame , final int fileSize)
private void init(final String fileName, final int fileSize) throws IOException {
this.fileName = fileName;
this.fileSize = fileSize;
this.file = new File(fileName);
this.fileFromOffset = Long.parseLong(this.file.getName());
boolean ok = false;
ensureDirOK(this.file.getParent());
try {
this.fileChannel = new RandomAccessFile(this.file, "rw").getChannel();
this.mappedByteBuffer = this.fileChannel.map(MapMode.READ_WRITE, 0, fileSize);
TOTAL_MAPPED_VIRTUAL_MEMORY.addAndGet(fileSize);
TOTAL_MAPPED_FILES.incrementAndGet();
ok = true;
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
log.error("create file channel " + this.fileName + " Failed. ", e);
throw e;
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("map file " + this.fileName + " Failed. ", e);
throw e;
} finally {
if (!ok && this.fileChannel != null) {
this.fileChannel.close();
}
}
}
初始化fileFromOffset 为文件名,也就是文件名代表该文件的起始偏移量,通过RandomAccessFile 创建读写文件通道,并将文件内容使用NIO 的内存映射Buffer 将文件映射到内存中。
public void init(final String fileName, final int fileSize,
final TransientStorePool transientStorePool) throws IOException {
init(fileName, fileSize);
this.writeBuffer = transientStorePool.borrowBuffer();
this.transientStorePool = transientStorePool;
}
如果transientStorePoolEnable为true ,则初始化MappedFile 的writeBuffer , 该buffer从transientStorePool ,下一节重点分析一下TransientStorePool 。
MappedFile 提交(commit)
内存映射文件的提交动作由MappedFile 的commit 方法实现,如代码清单4-18 所示。
public int commit(final int commitLeastPages) {
if (writeBuffer == null) {
//no need to commit data to file channel, so just regard wrotePosition as committedPosition.
return this.wrotePosition.get();
}
if (this.isAbleToCommit(commitLeastPages)) {
if (this.hold()) {
commit0(commitLeastPages);
this.release();
} else {
log.warn("in commit, hold failed, commit offset = " + this.committedPosition.get());
}
}
// All dirty data has been committed to FileChannel.
if (writeBuffer != null && this.transientStorePool != null && this.fileSize == this.committedPosition.get()) {
this.transientStorePool.returnBuffer(writeBuffer);
this.writeBuffer = null;
}
return this.committedPosition.get();
}
执行提交操作, commitLeastPages 为本次提交最小的页数,如果待提交数据不满commitLeastPages ,则不执行本次提交操作,待下次提交。writeBuffer 如果为空,直接返回wrotePosition 指针,无须执行commit操作, 表明commit 操作主体是writeBuffer。
protected boolean isAbleToCommit(final int commitLeastPages) {
int flush = this.committedPosition.get();
int write = this.wrotePosition.get();
if (this.isFull()) {
return true;
}
if (commitLeastPages > 0) {
return ((write / OS_PAGE_SIZE) - (flush / OS_PAGE_SIZE)) >= commitLeastPages;
}
return write > flush;
}
判断是否执行commit 操作。如果文件己满返回true ;如果commitLeastPages 大于0,则比较wrotePosition ( 当前writeBuffe 的写指针)与上一次提交的指针(committedPosition)的差值,除以OS_PAGE_SIZE 得到当前脏页的数量,如果大于commitLeastPages 则返回 true ;如果commitLeastPages 小于0 表示只要存在脏页就提交。
protected void commit0(final int commitLeastPages) {
int writePos = this.wrotePosition.get();
int lastCommittedPosition = this.committedPosition.get();
if (writePos - this.committedPosition.get() > 0) {
try {
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = writeBuffer.slice();
byteBuffer.position(lastCommittedPosition);
byteBuffer.limit(writePos);
this.fileChannel.position(lastCommittedPosition);
this.fileChannel.write(byteBuffer);
this.committedPosition.set(writePos);
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("Error occurred when commit data to FileChannel.", e);
}
}
}
具体的提交实现。首先创建writeBuffer 的共享缓存区,然后将新创建的position 回退到上一次提交的位置( committedPosition ) , 设置limit 为wrotePosition (当前最大有效数据指针),然后把commitedPosition 到wrotePosition 的数据复制(写入)到FileChannel中, 然后更新committedPosition 指针为wrotePosition。commit 的作用就是将MappedFile#writeBuffer中的数据提交到文件通道FileChannel 中。
ByteBuffer 使用技巧: slice() 方法创建一个共享缓存区, 与原先的ByteBuffer 共享内存但维护一套独立的指针( position 、mark 、limit) 。
MappedFile刷盘(flush)
刷盘指的是将内存中的数据刷写到磁盘,永久存储在磁盘中,其具体实现由MappedFile 的flush 方法实现,如代码清单4-21 所示。
public int flush(final int flushLeastPages) {
if (this.isAbleToFlush(flushLeastPages)) {
if (this.hold()) {
int value = getReadPosition();
try {
//We only append data to fileChannel or mappedByteBuffer, never both.
if (writeBuffer != null || this.fileChannel.position() != 0) {
this.fileChannel.force(false);
} else {
this.mappedByteBuffer.force();
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("Error occurred when force data to disk.", e);
}
this.flushedPosition.set(value);
this.release();
} else {
log.warn("in flush, hold failed, flush offset = " + this.flushedPosition.get());
this.flushedPosition.set(getReadPosition());
}
}
return this.getFlushedPosition();
}
刷写磁盘,直接调用mappedByteBuffer 或fileChannel 的force 方法将内存中的数据持久化到磁盘,那么flushedPosition 应该等于MappedByteBuffer 中的写指针;如果writeBuffer不为空, 则flushedPosition 应等于上一次commit 指针;因为上一次提交的数据就是进入到MappedByteBuffer 中的数据;如果writeBuffer 为空,数据是直接进入到MappedByteBuffer的,wrotePosition 代表的是MappedByteBuffer 中的指针,故设置flushedPosition 为wrotePosition 。
获取MappedFile 最大读指针(getReadPosition)
RocketMQ 文件的一个组织方式是内存映射文件,预先申请一块连续的固定大小的内存, 需要一套指针标识当前最大有效数据的位置,获取最大有效数据偏移量的方法由MappedFile 的getReadPosition 方法实现,如代码清单4-22 所示。
//MappedFile#getReadPosition
public int getReadPosition() {
return this.writeBuffer == null ? this.wrotePosition.get() : this.committedPosition.get();
}
获取当前文件最大的可读指针。如果writeBuffer 为空, 则直接返回当前的写指针;如果writeBuffer 不为空, 则返回上一次提交的指针。在MappedFile 设计中,只有提交了的数据(写入到MappedByteBuffer 或FileChannel 中的数据)才是安全的数据。
//MappedFile#selectMappedBuffe
public SelectMappedBufferResult selectMappedBuffer(int pos, int size) {
int readPosition = getReadPosition();
if ((pos + size) <= readPosition) {
if (this.hold()) {
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = this.mappedByteBuffer.slice();
byteBuffer.position(pos);
ByteBuffer byteBufferNew = byteBuffer.slice();
byteBufferNew.limit(size);
return new SelectMappedBufferResult(this.fileFromOffset + pos, byteBufferNew, size, this);
} else {
log.warn("matched, but hold failed, request pos: " + pos + ", fileFromOffset: "
+ this.fileFromOffset);
}
} else {
log.warn("selectMappedBuffer request pos invalid, request pos: " + pos + ", size: " + size
+ ", fileFromOffset: " + this.fileFromOffset);
}
return null;
}
public SelectMappedBufferResult selectMappedBuffer(int pos) {
int readPosition = getReadPosition();
if (pos < readPosition && pos >= 0) {
if (this.hold()) {
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = this.mappedByteBuffer.slice();
byteBuffer.position(pos);
int size = readPosition - pos;
ByteBuffer byteBufferNew = byteBuffer.slice();
byteBufferNew.limit(size);
return new SelectMappedBufferResult(this.fileFromOffset + pos, byteBufferNew, size, this);
}
}
return null;
}
查找pos 到当前最大可读之间的数据,由于在整个写入期间都未曾改变MappedByteBuffer的指针,所以mappedByteBuffer.slice()方法返回的共享缓存区空间为整个MappedFile,然后通过设置byteBuffer 的position 为待查找的值,读取字节为当前可读字节长度,最终返回的ByteBuffer 的limit ( 可读最大长度)为size 。整个共享缓存区的容量为( MappedFile#fileSize -pos ) ,故在操作SelectMappedBufferResult 不能对包含在里面的 ByteBuffer 调用flip 方法。
操作ByteBuffer 时如果使用了slice () 方法,对其ByteBuffer 进行读取时一般手动指定position 与limit 指针,而不是调用flip 方法来切换读写状态。
MappedFile 销毁( destory)
MappedFile 文件销毁的实现方法为public boolean destroy(final long intervalForcibly),intervalForcibly 表示拒绝被销毁的最大存活时间。
public boolean destroy(final long intervalForcibly) {
this.shutdown(intervalForcibly);
if (this.isCleanupOver()) {
try {
this.fileChannel.close();
log.info("close file channel " + this.fileName + " OK");
long beginTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
boolean result = this.file.delete();
log.info("delete file[REF:" + this.getRefCount() + "] " + this.fileName
+ (result ? " OK, " : " Failed, ") + "W:" + this.getWrotePosition() + " M:"
+ this.getFlushedPosition() + ", "
+ UtilAll.computeEclipseTimeMilliseconds(beginTime));
} catch (Exception e) {
log.warn("close file channel " + this.fileName + " Failed. ", e);
}
return true;
} else {
log.warn("destroy mapped file[REF:" + this.getRefCount() + "] " + this.fileName
+ " Failed. cleanupOver: " + this.cleanupOver);
}
return false;
}
public void shutdown(final long intervalForcibly) {
if (this.available) {
this.available = false;
this.firstShutdownTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
this.release();
} else if (this.getRefCount() > 0) {
if ((System.currentTimeMillis() - this.firstShutdownTimestamp) >= intervalForcibly) {
this.refCount.set(-1000 - this.getRefCount());
this.release();
}
}
}
Step1:关闭MappedFile 。初次调用时this.available 为true ,设置available 为false ,并设置初次关闭的时间戳( firstShutdownTimestamp )为当前时间戳, 然后调用release() 方法尝试释放资源, release 只有在引用次数小于1 的情况下才会释放资源;如果引用次数大于0 ,对比当前时间与firstShutdownTimestamp ,如果已经超过了其最大拒绝存活期,每执行一次,将引用数减少1000 ,直到引用数小于0 时通过执行realse 方法释放资源。
public boolean isCleanupOver() {
return this.refCount.get() <= 0 && this.cleanupOver;
}
Step2 : 判断是否清理完成,判断标准是引用次数小于等于0 并且cleanupOver 为true,cleanupOver 为true 的触发条件是release 成功将MappedByteBuffer 资源释放。稍后详细分析release 方法。
this.fileChannel.close();
log.info("close file channel " + this.fileName + " OK");
long beginTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
boolean result = this.file.delete();
Step3 : 关闭文件通道, 删除物理文件。
在整个MappedFile 销毁过程,首先需要释放资源,释放资源的前提条件是该MappedFile的引用小于等于0 ,接下来重点看一下release 方法的实现原理。
public void release() {
long value = this.refCount.decrementAndGet();
if (value > 0)
return;
synchronized (this) {
this.cleanupOver = this.cleanup(value);
}
}
将引用次数减1,如果引用数小于等于0 ,则执行cleanup 方法,接下来重点分析一下cleanup 方法的实现。
@Override
public boolean cleanup(final long currentRef) {
if (this.isAvailable()) {
log.error("this file[REF:" + currentRef + "] " + this.fileName
+ " have not shutdown, stop unmapping.");
return false;
}
if (this.isCleanupOver()) {
log.error("this file[REF:" + currentRef + "] " + this.fileName
+ " have cleanup, do not do it again.");
return true;
}
clean(this.mappedByteBuffer);
TOTAL_MAPPED_VIRTUAL_MEMORY.addAndGet(this.fileSize * (-1));
TOTAL_MAPPED_FILES.decrementAndGet();
log.info("unmap file[REF:" + currentRef + "] " + this.fileName + " OK");
return true;
}
如果available 为true ,表示MappedFile 当前可用,无须清理,返回false ;如果资源已经被清除,返回true ;如果是堆外内存,调用堆外内存的cleanup 方法清除,维护MappedFile 类变量TOTAL_MAPPED_VIRTUAL_MEMORY 、TOTAL_MAPPED_FILES 并返回true,表示cleanupOver 为true 。
4.4.3.TransientStorePool
TransientStorePool : 短暂的存储池。RocketMQ 单独创建一个MappedByteBuffer 内存缓存池,用来临时存储数据,数据先写人该内存映射中,然后由commit 线程定时将数据从该内存复制到与目的物理文件对应的内存映射中。RokcetMQ 引人该机制主要的原因是仅供提供一种内存锁定,将当前堆外内存一直锁定在内存中,避免被进程将内存交换到磁盘。
TransientStorePool 类图如图4-10 所示。

下面让我们一一介绍Trans i entStorePool 的核心属性。
-
int poolSize: avaliableBuffers 个数,可通过在broker 中配置文件中设置transientStorePoolSize, 默认为5 。
-
int fileSize: 每个ByteBuffer 大小, 默认为mapedFileSizeCommitLog ,表明TransientStorePool 为commitlog 文件服务。
-
Deque< ByteBuffer> availableBuffers: ByteBuffer 容器,双端队列。
public void init() {
for (int i = 0; i < poolSize; i++) {
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(fileSize);
final long address = ((DirectBuffer) byteBuffer).address();
Pointer pointer = new Pointer(address);
LibC.INSTANCE.mlock(pointer, new NativeLong(fileSize));
availableBuffers.offer(byteBuffer);
}
}
创建poolSize 个堆外内存, 并利用com.sun.jna.Library 类库将该批内存锁定,避免被置换到交换区,提高存储性能。
4.5.RocketMQ存储文件
RocketMQ 存储路径为${ROCKET_HOME}/store ,主要存储文件如图4-11 所示。下面让我们一一介绍一下RocketMQ 主要的存储文件夹。
joyren@localhost ~/rocketmq/store tree . ├── abort ├── checkpoint ├── commitLog │ ├── 00000000000000000000 │ └── 00000000001073741824 ├── config │ ├── consumerFilter.json │ ├── consumerFilter.json.bak │ ├── consumerOffset.json │ ├── consumerOffset.json.bak │ ├── delayOffset.json │ ├── delayOffset.json.bak │ ├── subscriptionGroup.json │ ├── topics.json │ └── topics.json.bak ├── consumequeue │ ├── OFFSET_MOVED_EVENT │ │ └── 0 │ │ └── 00000000000000000000 │ └── TopicTest │ ├── 0 │ │ └── 00000000000000000000 │ ├── 1 │ │ └── 00000000000000000000 │ ├── 2 │ │ └── 00000000000000000000 │ └── 3 │ └── 00000000000000000000 ├── index │ └── 20190729015534442 └── lock
-
commitlog :消息存储目录。
-
config :运行期间一些配置信息,主要包括下列信息。
-
consumerFilter.json : 主题消息过滤信息。
-
consumerOffset.json : 集群消费模式消息消费进度。
-
delayOffset.json :延时消息队列拉取进度。
-
subscriptionGroup.json : 消息消费组配置信息。
-
topics.json: topic 配置属性。
-
-
consumequeue :消息消费队列存储目录。
-
index :消息索引文件存储目录。
-
abort :如果存在abort 文件说明Broker 非正常关闭,该文件默认启动时创建,正常退出之前删除。
-
checkpoint :文件检测点,存储commitlog 文件最后一次刷盘时间戳、consumequeue最后一次刷盘时间、index 索引文件最后一次刷盘时间戳。
4.5.1.Commitlog 文件
commitlog 目录的组织方式在4.4 节中已经详细介绍过了,该目录下的文件主要存储消息,其特点是每一条消息长度不相同,消息存储协议已在4.3 节中详细描述, Commitlog 文件存储的逻辑视图如图4-12 所示,每条消息的前面4 个字节存储该条消息的总长度。

Commitlog 文件的存储目录默认为${ROCKET_HOME} /store/commitlog ,可以通过在broker 配置文件中设置storePathRootDir 属性来改变默认路径。commitlog 文件默认大小为1G ,可通过在broker 配置文件中设置mapedFileSizeCommitLog 属性来改变默认大小。本节将基于上述存储结构重点分析消息的查找实现,其他诸如文件刷盘、文件恢复机制等将在下文中详细介绍。
//Commitlog#getMinO仔set
public long getMinOffset() {
MappedFile mappedFile = this.mappedFileQueue.getFirstMappedFile();
if (mappedFile != null) {
if (mappedFile.isAvailable()) {
return mappedFile.getFileFromOffset();
} else {
return this.rollNextFile(mappedFile.getFileFromOffset());
}
}
return -1;
}
获取当前Commitlog 目录最小偏移量,首先获取目录下的第一个文件,如果该文件可用, 则返回该文件的起始偏移量,否则返回下一个文件的起始偏移量。
//Commitlog#rollNextFile
public long rollNextFile(final long offset) {
int mappedFileSize = this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getMapedFileSizeCommitLog();
return offset + mappedFileSize - offset % mappedFileSize;
}
根据该offset 返回下一个文件的起始偏移量。首先获取一个文件的大小, 减去(offset%mappedFileSize)其目的是回到下一文件的起始偏移量。
public SelectMappedBufferResult getMessage(final long offset, final int size) {
int mappedFileSize = this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getMapedFileSizeCommitLog();
MappedFile mappedFile = this.mappedFileQueue.findMappedFileByOffset(offset, offset == 0);
if (mappedFile != null) {
int pos = (int) (offset % mappedFileSize);
return mappedFile.selectMappedBuffer(pos, size);
}
return null;
}
根据偏移量与消息长度查找消息。首先根据偏移找到所在的物理偏移量,然后用offset与文件长度取余得到在文件内的偏移量,从该偏移量读取size 长度的内容返回即可。如果只根据消息偏移查找消息, 则首先找到文件内的偏移量,然后尝试读取4个字节获取消息的实际长度, 最后读取指定字节即可。
4.5.2.ConsumeQueue文件
RocketMQ 基于主题订阅模式实现消息消费,消费者关心的是一个主题下的所有消息,但由于同一主题的消息不连续地存储在commitlog 文件中,试想一下如果消息消费者直接从消息存储文件(commitlog)中去遍历查找订阅主题下的消息,效率将极其低下,RocketMQ 为了适应消息消费的检索需求,设计了消息消费队列文件(Consumequeue),该文件可以看成是Commitlog 关于消息消费的“索引”文件, consumequeue 的第一级目录为消息主题,第二级目录为主题的消息队列,如图所示。
joyren@localhost ~/rocketmq/store tree . ├── abort ├── checkpoint ├── commitLog │ ├── 00000000000000000000 │ └── 00000000001073741824 ├── config │ ├── consumerFilter.json │ ├── consumerFilter.json.bak │ ├── consumerOffset.json │ ├── consumerOffset.json.bak │ ├── delayOffset.json │ ├── delayOffset.json.bak │ ├── subscriptionGroup.json │ ├── topics.json │ └── topics.json.bak ├── consumequeue │ ├── OFFSET_MOVED_EVENT │ │ └── 0 │ │ └── 00000000000000000000 │ └── TopicTest │ ├── 0 │ │ └── 00000000000000000000 │ ├── 1 │ │ └── 00000000000000000000 │ ├── 2 │ │ └── 00000000000000000000 │ └── 3 │ └── 00000000000000000000 ├── index │ └── 20190729015534442 └── lock
为了加速ConsumeQueue 消息条目的检索速度与节省磁盘空间,每一个Consumequeue条目不会存储消息的全量信息,其存储格式如图4-14 所示。

单个ConsumeQueue 文件中默认包含30 万个条目,单个文件的长度为30w × 20 字节,单个ConsumeQueue 文件可以看出是一个ConsumeQueue 条目的数组,其下标为ConsumeQueue的逻辑偏移量,消息消费进度存储的偏移量即逻辑偏移量。ConsumeQueue 即为Commitlog 文件的索引文件, 其构建机制是当消息到达Commitlog 文件后, 由专门的线程产生消息转发任务,从而构建消息消费队列文件与下文提到的索引文件。
本节只分析如何根据消息逻辑偏移量、时间戳查找消息的实现,下一节将重点讨论消息消费队列的构建、恢复等。
public SelectMappedBufferResult getIndexBuffer(final long startIndex) {
int mappedFileSize = this.mappedFileSize;
long offset = startIndex * CQ_STORE_UNIT_SIZE;
if (offset >= this.getMinLogicOffset()) {
MappedFile mappedFile = this.mappedFileQueue.findMappedFileByOffset(offset);
if (mappedFile != null) {
SelectMappedBufferResult result = mappedFile.selectMappedBuffer((int) (offset % mappedFileSize));
return result;
}
}
return null;
}
根据startIndex 获取消息消费队列条目。首先startIndex*20 得到在consumequeue 中的物理偏移量,如果该offset 小于minLogicOffset ,则返回null ,说明该消息已被删除;如果大于minLogicOffset ,则根据偏移量定位到具体的物理文件,然后通过offset 与物理文大小取模获取在该文件的偏移量,从而从偏移量开始连续读取20个字节即可。
ConsumeQueue 提供了根据消息存储时间来查找具体实现的算法getOffsetInQueueByTime(final long timestamp) , 其具体实现如下。
public long getOffsetInQueueByTime(final long timestamp) {
MappedFile mappedFile = this.mappedFileQueue.getMappedFileByTime(timestamp);
if (mappedFile != null) {
long offset = 0;
int low = minLogicOffset > mappedFile.getFileFromOffset() ? (int) (minLogicOffset - mappedFile.getFileFromOffset()) : 0;
int high = 0;
int midOffset = -1, targetOffset = -1, leftOffset = -1, rightOffset = -1;
long leftIndexValue = -1L, rightIndexValue = -1L;
long minPhysicOffset = this.defaultMessageStore.getMinPhyOffset();
SelectMappedBufferResult sbr = mappedFile.selectMappedBuffer(0);
if (null != sbr) {
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = sbr.getByteBuffer();
high = byteBuffer.limit() - CQ_STORE_UNIT_SIZE;
try {
while (high >= low) {
midOffset = (low + high) / (2 * CQ_STORE_UNIT_SIZE) * CQ_STORE_UNIT_SIZE;
byteBuffer.position(midOffset);
long phyOffset = byteBuffer.getLong();
int size = byteBuffer.getInt();
if (phyOffset < minPhysicOffset) {
low = midOffset + CQ_STORE_UNIT_SIZE;
leftOffset = midOffset;
continue;
}
long storeTime =
this.defaultMessageStore.getCommitLog().pickupStoreTimestamp(phyOffset, size);
if (storeTime < 0) {
return 0;
} else if (storeTime == timestamp) {
targetOffset = midOffset;
break;
} else if (storeTime > timestamp) {
high = midOffset - CQ_STORE_UNIT_SIZE;
rightOffset = midOffset;
rightIndexValue = storeTime;
} else {
low = midOffset + CQ_STORE_UNIT_SIZE;
leftOffset = midOffset;
leftIndexValue = storeTime;
}
}
if (targetOffset != -1) {
offset = targetOffset;
} else {
if (leftIndexValue == -1) {
offset = rightOffset;
} else if (rightIndexValue == -1) {
offset = leftOffset;
} else {
offset =
Math.abs(timestamp - leftIndexValue) > Math.abs(timestamp
- rightIndexValue) ? rightOffset : leftOffset;
}
}
return (mappedFile.getFileFromOffset() + offset) / CQ_STORE_UNIT_SIZE;
} finally {
sbr.release();
}
}
}
return 0;
}
Step1 :首先根据时间戳定位到物理文件,其具体实现在前面有详细介绍,就是从第一个文件开始找到第一个文件更新时间大于该时间戳的文件。
int high = 0;
int midOffset = -1, targetOffset = -1, leftOffset = -1, rightOffset = -1;
long leftIndexValue = -1L, rightIndexValue = -1L;
long minPhysicOffset = this.defaultMessageStore.getMinPhyOffset();
SelectMappedBufferResult sbr = mappedFile.selectMappedBuffer(0);
if (null != sbr) {
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = sbr.getByteBuffer();
high = byteBuffer.limit() - CQ_STORE_UNIT_SIZE;
Step2 : 采用二分查找来加速检索。首先计算最低查找偏移量,取消息队列最小偏移量与该文件最小偏移量二者中的最小偏移量为low 。获取当前存储文件中有效的最小消息物理偏移量minPhysicOffset ,如果查找到消息偏移量小于该物理偏移量, 则结束该查找过程。
while (high >= low) {
midOffset = (low + high) / (2 * CQ_STORE_UNIT_SIZE) * CQ_STORE_UNIT_SIZE;
byteBuffer.position(midOffset);
long phyOffset = byteBuffer.getLong();
int size = byteBuffer.getInt();
if (phyOffset < minPhysicOffset) {
low = midOffset + CQ_STORE_UNIT_SIZE;
leftOffset = midOffset;
continue;
}
long storeTime =
this.defaultMessageStore.getCommitLog().pickupStoreTimestamp(phyOffset, size);
if (storeTime < 0) {
return 0;
} else if (storeTime == timestamp) {
targetOffset = midOffset;
break;
} else if (storeTime > timestamp) {
high = midOffset - CQ_STORE_UNIT_SIZE;
rightOffset = midOffset;
rightIndexValue = storeTime;
} else {
low = midOffset + CQ_STORE_UNIT_SIZE;
leftOffset = midOffset;
leftIndexValue = storeTime;
}
}
二分查找的常规退出循环为( low>high ), 首先查找中间的偏移量midOffset ,将整个Consume Queue 文件对应的ByteBuffer 定位到midOffset ,然后读取4 个字节获取该消息的物理偏移量offset 。
-
如果得到的物理偏移量小于当前的最小物理偏移量,说明待查找的物理偏移量肯定大于midOffset,所以将low 设置为midOffset ,然后继续折半查找。
-
如果offset 大于最小物理偏移量,说明该消息是有效消息,则根据消息偏移量和消息长度获取消息的存储时间戳。
-
如果存储时间小于0 ,消息为无效消息,直接返回0 。
-
如果存储时间戳等于待查找时间戳,说明查找到匹配消息,设置targetOffset 并跳出循环。
-
如果存储时间戳大于待查找时间戳,说明待查找信息小于mi dOffset ,则设置high为midOffset , 并设置rightIndexValue 等于midOffset 。
-
如果存储时间小于待查找时间戳,说明待查找消息在大于midOffset ,则设置low为midOffset ,并设置leftIndexValue巳等于midOffset。
if (targetOffset != -1) {
offset = targetOffset;
} else {
if (leftIndexValue == -1) {
offset = rightOffset;
} else if (rightIndexValue == -1) {
offset = leftOffset;
} else {
offset =
Math.abs(timestamp - leftIndexValue) > Math.abs(timestamp
- rightIndexValue) ? rightOffset : leftOffset;
}
}
Step3 : 如果targetOffset 不等于-1 表示找到了存储时间戳等于待查找时间戳的消息;如果leftIndexValue等于-1 , 表示返回当前时间戳大并且最接近待查找的偏移量;如果rightIndexValue 等于-1 , 表示返回的消息比待查找时间戳小并且最接近查找的偏移量。
public long rollNextFile(final long index) {
int mappedFileSize = this.mappedFileSize;
int totalUnitsInFile = mappedFileSize / CQ_STORE_UNIT_SIZE;
return index + totalUnitsInFile - index % totalUnitsInFile;
}
根据当前偏移量获取下一个文件的起始偏移量。首先获取一个文件包含多少个消息消费队列条目,减去index%totalUnitslnF ile 的目的是选中下一个文件的起始偏移量。
4.5.3.Index索引文件
消息消费队列是RocketMQ 专门为消息订阅构建的索引文件,提高根据主题与消息队列检索消息的速度,另外RocketMQ 引入了Hash 索引机制为消息建立索引, HashMap 的设计包含两个基本点: Hash 槽与Hash 冲突的链表结构。RocketMQ 索引文件布局如图4-15所示。
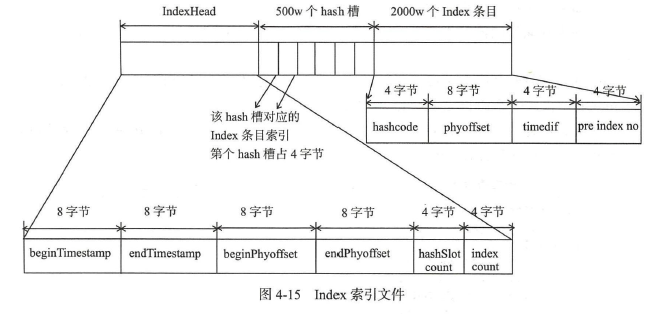
从图中可以看出, IndexFile 总共包含IndexHeader 、Hash 槽、Hash 条目(数据) 。
-
IndexHeader 头部,包含40 个字节,记录该IndexFile 的统计信息,其结构如下。
-
beginTimestamp : 该索引文件中包含消息的最小存储时间。
-
end Times tamp : 该索引文件中包含消息的最大存储时间。
-
beginPhyoffset : 该索引文件中包含消息的最小物理偏移量( c ommitlog 文件偏移量) 。
-
endPhyoffset :该索引文件中包含消息的最大物理偏移量( commitlog 文件偏移量) 。
-
hashslotCount: hashslot 个数,并不是hash 槽使用的个数,在这里意义不大。
-
indexCount: Index 条目列表当前已使用的个数, Index 条目在Index 条目列表中按顺序存储。
-
-
Hash 槽, 一个IndexFile 默认包含500 万个Hash 槽,每个Hash 槽存储的是落在该Hash 槽的hashcode 最新的Index 的索引。
-
Index 条目列表,默认一个索引文件包含2000 万个条目,每一个Index 条目结构如下。
-
hashcode: key 的hashcode 。
-
phyoffset : 消息对应的物理偏移量。
-
timedif:该消息存储时间与第一条消息的时间戳的差值,小于0 该消息无效。
-
preIndexNo :该条目的前一条记录的Index 索引, 当出现hash 冲突时, 构建的链表结构
-
接下来将重点分析如何将Map<String/*消息索引key*/,long phyOffset/*消息物理偏移量*/>存入索引文件,以及如何根据消息索引key 快速查找消息。
RocketMQ 将消息索引键与消息偏移量映射关系写入到IndexFile 的实现方法为: public boolean putKey (final String key, final long phyOffset, final long storeTimestamp ),参数含义分别为消息索引、消息物理偏移量、消息存储时间。
public boolean putKey(final String key, final long phyOffset, final long storeTimestamp) {
if (this.indexHeader.getIndexCount() < this.indexNum) {
int keyHash = indexKeyHashMethod(key);
int slotPos = keyHash % this.hashSlotNum;
int absSlotPos = IndexHeader.INDEX_HEADER_SIZE + slotPos * hashSlotSize;
FileLock fileLock = null;
try {
// fileLock = this.fileChannel.lock(absSlotPos, hashSlotSize,
// false);
int slotValue = this.mappedByteBuffer.getInt(absSlotPos);
if (slotValue <= invalidIndex || slotValue > this.indexHeader.getIndexCount()) {
slotValue = invalidIndex;
}
long timeDiff = storeTimestamp - this.indexHeader.getBeginTimestamp();
timeDiff = timeDiff / 1000;
if (this.indexHeader.getBeginTimestamp() <= 0) {
timeDiff = 0;
} else if (timeDiff > Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
timeDiff = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
} else if (timeDiff < 0) {
timeDiff = 0;
}
int absIndexPos =
IndexHeader.INDEX_HEADER_SIZE + this.hashSlotNum * hashSlotSize
+ this.indexHeader.getIndexCount() * indexSize;
this.mappedByteBuffer.putInt(absIndexPos, keyHash);
this.mappedByteBuffer.putLong(absIndexPos + 4, phyOffset);
this.mappedByteBuffer.putInt(absIndexPos + 4 + 8, (int) timeDiff);
this.mappedByteBuffer.putInt(absIndexPos + 4 + 8 + 4, slotValue);
this.mappedByteBuffer.putInt(absSlotPos, this.indexHeader.getIndexCount());
if (this.indexHeader.getIndexCount() <= 1) {
this.indexHeader.setBeginPhyOffset(phyOffset);
this.indexHeader.setBeginTimestamp(storeTimestamp);
}
this.indexHeader.incHashSlotCount();
this.indexHeader.incIndexCount();
this.indexHeader.setEndPhyOffset(phyOffset);
this.indexHeader.setEndTimestamp(storeTimestamp);
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("putKey exception, Key: " + key + " KeyHashCode: " + key.hashCode(), e);
} finally {
if (fileLock != null) {
try {
fileLock.release();
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("Failed to release the lock", e);
}
}
}
} else {
log.warn("Over index file capacity: index count = " + this.indexHeader.getIndexCount()
+ "; index max num = " + this.indexNum);
}
return false;
}
if (this.indexHeader.getIndexCount() < this.indexNum) {
int keyHash = indexKeyHashMethod(key);
int slotPos = keyHash % this.hashSlotNum;
int absSlotPos = IndexHeader.INDEX_HEADER_SIZE + slotPos * hashSlotSize;
Step1:如果当前已使用条目大于等于允许最大条目数时,则返回fas le ,表示当前索引文件已写满。如果当前索引文件未写满则根据key 算出key 的hash code ,然后keyHash 对hash 槽数量取余定位到hasbcode对应的hash 槽下标, hashcode 对应的hash 槽的物理地址为IndexHeader 头部(40 字节)加上下标乘以每个hash 槽的大小(4 字节) 。
根据定位hash 槽算法, 如果不同key 的hash code 值相同或不同的key 不同的? 叫hash code 但对hash 槽数量取余后结果相同都将引发Hash 冲突, 那IndxFile 如何解决这个问题呢?
// fileLock = this.fileChannel.lock(absSlotPos, hashSlotSize,
// false);
int slotValue = this.mappedByteBuffer.getInt(absSlotPos);
if (slotValue <= invalidIndex || slotValue > this.indexHeader.getIndexCount()) {
slotValue = invalidIndex;
}
Step2 : 读取hash 槽中存储的数据,如果hash 槽存储的数据小于0 或大于当前索引文件中的索引条目格式, 则将slotValue 设置为0 。
long timeDiff = storeTimestamp - this.indexHeader.getBeginTimestamp();
timeDiff = timeDiff / 1000;
if (this.indexHeader.getBeginTimestamp() <= 0) {
timeDiff = 0;
} else if (timeDiff > Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
timeDiff = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
} else if (timeDiff < 0) {
timeDiff = 0;
}
Step3 :计算待存储消息的时间戳与第一条消息时间戳的差值,并转换成秒。
int absIndexPos =
IndexHeader.INDEX_HEADER_SIZE + this.hashSlotNum * hashSlotSize
+ this.indexHeader.getIndexCount() * indexSize;
this.mappedByteBuffer.putInt(absIndexPos, keyHash);
this.mappedByteBuffer.putLong(absIndexPos + 4, phyOffset);
this.mappedByteBuffer.putInt(absIndexPos + 4 + 8, (int) timeDiff);
this.mappedByteBuffer.putInt(absIndexPos + 4 + 8 + 4, slotValue);
this.mappedByteBuffer.putInt(absSlotPos, this.indexHeader.getIndexCount());
Step4 :将条目信息存储在IndexFile 中。
-
计算新添加条目的起始物理偏移量, 等于头部字节长度+ hash 槽数量* 单个hash槽大小(4 个字节)+当前Index 条目个数*单个Index 条目大小(20 个字节) 。
-
依次将hash code、消息物理偏移量、消息存储时间戳与索引文件时间戳、当前Hash 槽的值存入MappedByteBuffer 中。
-
将当前Index 中包含的条目数量存入Hash 槽中,将覆盖原先Hash 槽的值。
这里是Hash 冲突链式解决方案的关键实现, Hash 槽中存储的是该HashCode 所对应的最新的Index 条目的下标,新的Index 条目的最后4 个字节存储该HashCode 上一个条目的Index 下标。如果Hash 槽中存储的值为0 或大于当前lndexFile 最大条目数或小于- 1 , 表示该Hash 槽当前并没有与之对应的Index 条目。值得关注的是, IndexFile 条目中存储的不是消息索引key 而是消息属性key 的HashCode ,在根据key 查找时需要根据消息物理偏移量找到消息进而再验证消息key 的值,之所以只存储Hash Code 而不存储具体的key , 是为了将Index 条目设计为定长结构,才能方便地检索与定位条目。
if (this.indexHeader.getIndexCount() <= 1) {
this.indexHeader.setBeginPhyOffset(phyOffset);
this.indexHeader.setBeginTimestamp(storeTimestamp);
}
this.indexHeader.incHashSlotCount();
this.indexHeader.incIndexCount();
this.indexHeader.setEndPhyOffset(phyOffset);
this.indexHeader.setEndTimestamp(storeTimestamp);
Step5 : 更新文件索引头信息。如果当前文件只包含一个条目,更新beginPhyOffset 与 beginTimestamp 、更新endPyhOffset 、endTimestamp 、当前文件使用索引条目等信息。
RocketMQ 根据索引key 查找消息的实现方法为: selectPhyOffset(List<Long> phyOffs, String key, int maxNum, long begin, long end),其参数说如下。
-
List<Long> phyOffsets : 查找到的消息物理偏移量。
-
String key : 索引key 。
-
int maxNum : 本次查找最大消息条数。
-
long begin : 开始时间戳。
-
long end :结束时间戳。
//org.apache.rocketmq.store.index.IndexFile#selectPhyOffset int keyHash = indexKeyHashMethod(key); int slotPos = keyHash % this.hashSlotNum; int absSlotPos = IndexHeader.INDEX_HEADER_SIZE + slotPos * hashSlotSize;
Step1:根据key 算出key 的hashcode ,然后keyHash 对hash 槽数量取余定位到hashcode 对应的hash 槽下标, hashcode 对应的hash 槽的物理地址为IndexHeader 头部( 40字节)加上下标乘以每个hash 槽的大小( 4字节) 。
//org.apache.rocketmq.store.index.IndexFile#selectPhyOffset
if (slotValue <= invalidIndex || slotValue > this.indexHeader.getIndexCount()
|| this.indexHeader.getIndexCount() <= 1) {
} else {
for (int nextIndexToRead = slotValue; ; ) {
if (phyOffsets.size() >= maxNum) {
break;
}
int absIndexPos =
IndexHeader.INDEX_HEADER_SIZE + this.hashSlotNum * hashSlotSize
+ nextIndexToRead * indexSize;
int keyHashRead = this.mappedByteBuffer.getInt(absIndexPos);
long phyOffsetRead = this.mappedByteBuffer.getLong(absIndexPos + 4);
long timeDiff = (long) this.mappedByteBuffer.getInt(absIndexPos + 4 + 8);
int prevIndexRead = this.mappedByteBuffer.getInt(absIndexPos + 4 + 8 + 4);
if (timeDiff < 0) {
break;
}
timeDiff *= 1000L;
long timeRead = this.indexHeader.getBeginTimestamp() + timeDiff;
boolean timeMatched = (timeRead >= begin) && (timeRead <= end);
if (keyHash == keyHashRead && timeMatched) {
phyOffsets.add(phyOffsetRead);
}
if (prevIndexRead <= invalidIndex
|| prevIndexRead > this.indexHeader.getIndexCount()
|| prevIndexRead == nextIndexToRead || timeRead < begin) {
break;
}
nextIndexToRead = prevIndexRead;
}
}
Step2 :如果对应的Hash 槽中存储的数据小于1 或大于当前索引条目个数则表示该HashCode 没有对应的条目, 直接返回。
Step3 :由于会存在hash 冲突,根据slotValue 定位该hash 槽最新的一个Item 条目, 将仅供存储的物理偏移加入到phyOffsets 中,然后继续验证Item 条目中存储的上一个Index 下标,如果大于等于l 并且小于最大条目数, 则继续查找, 否则结束查找。
int absIndexPos =
IndexHeader.INDEX_HEADER_SIZE + this.hashSlotNum * hashSlotSize
+ nextIndexToRead * indexSize;
int keyHashRead = this.mappedByteBuffer.getInt(absIndexPos);
long phyOffsetRead = this.mappedByteBuffer.getLong(absIndexPos + 4);
long timeDiff = (long) this.mappedByteBuffer.getInt(absIndexPos + 4 + 8);
int prevIndexRead = this.mappedByteBuffer.getInt(absIndexPos + 4 + 8 + 4);
Step4 :根据Index 下标定位到条目的起始物理偏移量,然后依次读取hashcode 、物理偏移量、时间差、上一个条目的Index 下标。
if (timeDiff < 0) {
break;
}
timeDiff *= 1000L;
long timeRead = this.indexHeader.getBeginTimestamp() + timeDiff;
boolean timeMatched = (timeRead >= begin) && (timeRead <= end);
if (keyHash == keyHashRead && timeMatched) {
phyOffsets.add(phyOffsetRead);
}
if (prevIndexRead <= invalidIndex
|| prevIndexRead > this.indexHeader.getIndexCount()
|| prevIndexRead == nextIndexToRead || timeRead < begin) {
break;
}
nextIndexToRead = prevIndexRead;
Step5 :如果存储的时间差小于0 ,则直接结束;如果hashcode 匹配并且消息存储时间介于待查找时间start 、end 之间则将消息物理偏移量加入到phyOffsets , 并验证条目的前一个Index 索引,如果索引大于等于l 并且小于Index 条目数, 则继续查找,否则结束整个查找。
4.5.4.checkpoint文件
checkpoint 的作用是记录Comitlog 、ConsumeQueue 、Index 文件的刷盘时间点, 文件固定长度为4k ,其中只用该文件的前面24 个字节, 其存储格式如图4-16 所示。
-
physicMsgTimestamp: commitlog 文件刷盘时间点。
-
logicsMsgTimestamp : 消息消费队列文件刷盘时间点。
-
indexMsgTimestamp : 索引文件刷盘时间点。
4.6.实时更新消息消费队列与索引文件
消息消费队列文件、消息属性索引文件都是基于CommitLog文件构建的, 当消息生产者提交的消息存储在C ommitlog 文件中, ConsumeQueue 、IndexFile 需要及时更新,否则消息无法及时被消费,根据消息属性查找消息也会出现较大延迟。RocketMQ 通过开启一个线程ReputMessageServcie 来准实时转发CommitLog 文件更新事件, 相应的任务处理器根据转发的消息及时更新ConsumeQueue 、IndexFile 文件。
if (this.getMessageStoreConfig().isDuplicationEnable()) {
this.reputMessageService.setReputFromOffset(this.commitLog.getConfirmOffset());
} else {
this.reputMessageService.setReputFromOffset(this.commitLog.getMaxOffset());
}
this.reputMessageService.start();
Broker 服务器在启动时会启动ReputMessageService 线程,并初始化一个非常关键的参数reputFromOffset , 该参数的含义是ReputMessageService 从哪个物理偏移量开始转发消息给ConsumeQueue和IndexFile 。如果允许重复转发, reputFromOffset 设置为CommitLog 的提交指针;如果不允许重复转发, reputFromOffset 设置为Commitlog 的内存中最大偏移量。
//org.apache.rocketmq.store.DefaultMessageStore.ReputMessageService#run
@Override
public void run() {
DefaultMessageStore.log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service started");
while (!this.isStopped()) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1);
this.doReput();
} catch (Exception e) {
DefaultMessageStore.log.warn(this.getServiceName() + " service has exception. ", e);
}
}
DefaultMessageStore.log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service end");
}
ReputMessageService 线程每执行一次任务推送休息1 毫秒就继续尝试推送消息到消息消费队列和索引文件,消息消费转发的核心实现在doReput 方法中实现。
private void doReput() {
for (boolean doNext = true; this.isCommitLogAvailable() && doNext; ) {
if (DefaultMessageStore.this.getMessageStoreConfig().isDuplicationEnable()
&& this.reputFromOffset >= DefaultMessageStore.this.getConfirmOffset()) {
break;
}
SelectMappedBufferResult result = DefaultMessageStore.this.commitLog.getData(reputFromOffset);
if (result != null) {
try {
this.reputFromOffset = result.getStartOffset();
for (int readSize = 0; readSize < result.getSize() && doNext; ) {
DispatchRequest dispatchRequest =
DefaultMessageStore.this.commitLog.checkMessageAndReturnSize(result.getByteBuffer(), false, false);
int size = dispatchRequest.getMsgSize();
if (dispatchRequest.isSuccess()) {
if (size > 0) {
DefaultMessageStore.this.doDispatch(dispatchRequest);
if (BrokerRole.SLAVE != DefaultMessageStore.this.getMessageStoreConfig().getBrokerRole()
&& DefaultMessageStore.this.brokerConfig.isLongPollingEnable()) {
DefaultMessageStore.this.messageArrivingListener.arriving(dispatchRequest.getTopic(),
dispatchRequest.getQueueId(), dispatchRequest.getConsumeQueueOffset() + 1,
dispatchRequest.getTagsCode(), dispatchRequest.getStoreTimestamp(),
dispatchRequest.getBitMap(), dispatchRequest.getPropertiesMap());
}
this.reputFromOffset += size;
readSize += size;
if (DefaultMessageStore.this.getMessageStoreConfig().getBrokerRole() == BrokerRole.SLAVE) {
DefaultMessageStore.this.storeStatsService
.getSinglePutMessageTopicTimesTotal(dispatchRequest.getTopic()).incrementAndGet();
DefaultMessageStore.this.storeStatsService
.getSinglePutMessageTopicSizeTotal(dispatchRequest.getTopic())
.addAndGet(dispatchRequest.getMsgSize());
}
} else if (size == 0) {
this.reputFromOffset = DefaultMessageStore.this.commitLog.rollNextFile(this.reputFromOffset);
readSize = result.getSize();
}
} else if (!dispatchRequest.isSuccess()) {
if (size > 0) {
log.error("[BUG]read total count not equals msg total size. reputFromOffset={}", reputFromOffset);
this.reputFromOffset += size;
} else {
doNext = false;
if (DefaultMessageStore.this.brokerConfig.getBrokerId() == MixAll.MASTER_ID) {
log.error("[BUG]the master dispatch message to consume queue error, COMMITLOG OFFSET: {}",
this.reputFromOffset);
this.reputFromOffset += result.getSize() - readSize;
}
}
}
}
} finally {
result.release();
}
} else {
doNext = false;
}
}
}
SelectMappedBufferResult result = DefaultMessageStore.this.commitLog.getData(reputFromOffset);
Step1:返回reputFromOffset 偏移量开始的全部有效数据(commitlog 文件) 。然后循环读取每一条消息。
DispatchRequest dispatchRequest =
DefaultMessageStore.this.commitLog.checkMessageAndReturnSize(result.getByteBuffer(), false, false);
int size = dispatchRequest.getMsgSize();
if (dispatchRequest.isSuccess()) {
if (size > 0) {
DefaultMessageStore.this.doDispatch(dispatchRequest);
Step2: 从result 返回的ByteBuffer 中循环读取消息,一次读取一条,创建DispatchRequest对象。DispatchR巳quest 类图如图4-17 所示, 如果消息长度大于0 ,则调用doDispatch方法。最终将分别调用CommitLogDispatcherBuildConsumeQueue (构建消息消费队列)、CommitLogDispatcherBuildlndex (构建索引文件) 。

下面让我们一一介绍DispatchRequest 的核心属性。
-
String topic :消息主题名称。
-
int queueld :消息队列ID 。
-
long commitLogOffset : 消息物理偏移量。
-
int msgSize : 消息长度。
-
long tagsCode : 消息过滤tag hashcode 。
-
long storeTimestamp :消息存储时间戳。
-
long consumeQueueOffset :消息队列偏移量。
-
String keys : 消息索引key 。多个索引key 用空格隔开,例如“ key! key2 ” 。
-
boolean success :是否成功解析到完整的消息。
-
String uniqKey : 消息唯一键。
-
int sysFlag : 消息系统标记。
-
long preparedTransactionOffset : 消息预处理事务偏移量。
-
Map< String, String> propertiesMap : 消息属性。
-
byte[] bitMap : 位图。
4.6.1.根据消息更新ConumeQueue
消息消费队列转发任务实现类为: CommitLogDispatcherBuildConsumeQueue ,内部最终将调用putMessagePositioninfo 方法。
//org.apache.rocketmq.store.DefaultMessageStore#putMessagePositionInfo
public void putMessagePositionInfo(DispatchRequest dispatchRequest) {
ConsumeQueue cq = this.findConsumeQueue(dispatchRequest.getTopic(), dispatchRequest.getQueueId());
cq.putMessagePositionInfoWrapper(dispatchRequest);
}
Step1:根据消息主题与队列ID ,先获取对应的ConumeQueue 文件,其逻辑比较简单,因为每一个消息主题对应一个消息消费队列目录然后主题下每一个消息队列对应一个文件夹,然后取出该文件夹最后的ConsumeQueue 文件即可。
public void putMessagePositionInfoWrapper(DispatchRequest request) {
final int maxRetries = 30;
boolean canWrite = this.defaultMessageStore.getRunningFlags().isCQWriteable();
for (int i = 0; i < maxRetries && canWrite; i++) {
long tagsCode = request.getTagsCode();
if (isExtWriteEnable()) {
ConsumeQueueExt.CqExtUnit cqExtUnit = new ConsumeQueueExt.CqExtUnit();
cqExtUnit.setFilterBitMap(request.getBitMap());
cqExtUnit.setMsgStoreTime(request.getStoreTimestamp());
cqExtUnit.setTagsCode(request.getTagsCode());
long extAddr = this.consumeQueueExt.put(cqExtUnit);
if (isExtAddr(extAddr)) {
tagsCode = extAddr;
} else {
log.warn("Save consume queue extend fail, So just save tagsCode! {}, topic:{}, queueId:{}, offset:{}", cqExtUnit,
topic, queueId, request.getCommitLogOffset());
}
}
boolean result = this.putMessagePositionInfo(request.getCommitLogOffset(),
request.getMsgSize(), tagsCode, request.getConsumeQueueOffset());
if (result) {
this.defaultMessageStore.getStoreCheckpoint().setLogicsMsgTimestamp(request.getStoreTimestamp());
return;
} else {
// XXX: warn and notify me
log.warn("[BUG]put commit log position info to " + topic + ":" + queueId + " " + request.getCommitLogOffset()
+ " failed, retry " + i + " times");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.warn("", e);
}
}
}
// XXX: warn and notify me
log.error("[BUG]consume queue can not write, {} {}", this.topic, this.queueId);
this.defaultMessageStore.getRunningFlags().makeLogicsQueueError();
}
private boolean putMessagePositionInfo(final long offset, final int size, final long tagsCode,
final long cqOffset) {
if (offset <= this.maxPhysicOffset) {
return true;
}
this.byteBufferIndex.flip();
this.byteBufferIndex.limit(CQ_STORE_UNIT_SIZE);
this.byteBufferIndex.putLong(offset);
this.byteBufferIndex.putInt(size);
this.byteBufferIndex.putLong(tagsCode);
final long expectLogicOffset = cqOffset * CQ_STORE_UNIT_SIZE;
MappedFile mappedFile = this.mappedFileQueue.getLastMappedFile(expectLogicOffset);
if (mappedFile != null) {
if (mappedFile.isFirstCreateInQueue() && cqOffset != 0 && mappedFile.getWrotePosition() == 0) {
this.minLogicOffset = expectLogicOffset;
this.mappedFileQueue.setFlushedWhere(expectLogicOffset);
this.mappedFileQueue.setCommittedWhere(expectLogicOffset);
this.fillPreBlank(mappedFile, expectLogicOffset);
log.info("fill pre blank space " + mappedFile.getFileName() + " " + expectLogicOffset + " "
+ mappedFile.getWrotePosition());
}
if (cqOffset != 0) {
long currentLogicOffset = mappedFile.getWrotePosition() + mappedFile.getFileFromOffset();
if (expectLogicOffset < currentLogicOffset) {
log.warn("Build consume queue repeatedly, expectLogicOffset: {} currentLogicOffset: {} Topic: {} QID: {} Diff: {}",
expectLogicOffset, currentLogicOffset, this.topic, this.queueId, expectLogicOffset - currentLogicOffset);
return true;
}
if (expectLogicOffset != currentLogicOffset) {
LOG_ERROR.warn(
"[BUG]logic queue order maybe wrong, expectLogicOffset: {} currentLogicOffset: {} Topic: {} QID: {} Diff: {}",
expectLogicOffset,
currentLogicOffset,
this.topic,
this.queueId,
expectLogicOffset - currentLogicOffset
);
}
}
this.maxPhysicOffset = offset;
return mappedFile.appendMessage(this.byteBufferIndex.array());
}
return false;
}
this.byteBufferIndex.flip();
this.byteBufferIndex.limit(CQ_STORE_UNIT_SIZE);
this.byteBufferIndex.putLong(offset);
this.byteBufferIndex.putInt(size);
this.byteBufferIndex.putLong(tagsCode);
final long expectLogicOffset = cqOffset * CQ_STORE_UNIT_SIZE;
MappedFile mappedFile = this.mappedFileQueue.getLastMappedFile(expectLogicOffset);
if (mappedFile != null) {
return mappedFile.appendMessage(this.byteBufferIndex.array());
}
Step2 :依次将消息偏移量、消息长度、tag hashcode 写入到ByteBuffer 中,并根据consumeQueueOffset 计算ConumeQueue 中的物理地址,将内容追加到ConsumeQueue 的内存映射文件中(本操作只追击并不刷盘), ConumeQueue 的刷盘方式固定为异步刷盘模式。
4.6.2.根据消息更新Index 索引文件
Hash 索引文件转发任务实现类: CommitLogDispatcherBuildIndex 。
@Override
public void dispatch(DispatchRequest request) {
if (DefaultMessageStore.this.messageStoreConfig.isMessageIndexEnable()) {
DefaultMessageStore.this.indexService.buildIndex(request);
}
}
如果messsageIndexEnable 设置为true ,则调用IndexService#buildIndex 构建Hash索引,否则忽略本次转发任务。
//org.apache.rocketmq.store.index.IndexService#buildIndex
public void buildIndex(DispatchRequest req) {
IndexFile indexFile = retryGetAndCreateIndexFile();
if (indexFile != null) {
long endPhyOffset = indexFile.getEndPhyOffset();
DispatchRequest msg = req;
String topic = msg.getTopic();
String keys = msg.getKeys();
if (msg.getCommitLogOffset() < endPhyOffset) {
return;
}
final int tranType = MessageSysFlag.getTransactionValue(msg.getSysFlag());
switch (tranType) {
case MessageSysFlag.TRANSACTION_NOT_TYPE:
case MessageSysFlag.TRANSACTION_PREPARED_TYPE:
case MessageSysFlag.TRANSACTION_COMMIT_TYPE:
break;
case MessageSysFlag.TRANSACTION_ROLLBACK_TYPE:
return;
}
if (req.getUniqKey() != null) {
indexFile = putKey(indexFile, msg, buildKey(topic, req.getUniqKey()));
if (indexFile == null) {
log.error("putKey error commitlog {} uniqkey {}", req.getCommitLogOffset(), req.getUniqKey());
return;
}
}
if (keys != null && keys.length() > 0) {
String[] keyset = keys.split(MessageConst.KEY_SEPARATOR);
for (int i = 0; i < keyset.length; i++) {
String key = keyset[i];
if (key.length() > 0) {
indexFile = putKey(indexFile, msg, buildKey(topic, key));
if (indexFile == null) {
log.error("putKey error commitlog {} uniqkey {}", req.getCommitLogOffset(), req.getUniqKey());
return;
}
}
}
}
} else {
log.error("build index error, stop building index");
}
}
Step1:获取或创建IndexFile 文件并获取所有文件最大的物理偏移量。如果该消息的物理偏移量小于索引文件中的物理偏移,则说明是重复数据,忽略本次索引构建。
Step2 :如果消息的唯一键不为空,则添加到Hash 索引中,以便加速根据唯一键检索消息。
Step3 :构建索引键, RocketMQ 支持为同一个消息建立多个索引,多个索引键空格分开。具体如何构建Hash 索引在4.5 节中已做了详细分析。
4.7.消息队列与索引文件恢复
由于RocketMQ 存储首先将消息全量存储在Commitlog 文件中,然后异步生成转发任务更新ConsumeQueue 、Index 文件。如果消息成功存储到Commitlog 文件中,转发任务未成功执行,此时消息服务器Broker 由于某个原因看机,导致Commitlog 、ConsumeQueue 、IndexFile 文件数据不一致。如果不加以人工修复的话,会有一部分消息即便在Commitlog文件中存在,但由于并没有转发到Consum巳queue ,这部分消息将永远不会被消费者消费。那RocketMQ 是如何使Commitlog 、消息消费队列( ConsumeQueue )达到最终一致性的呢? 下面详细分析一下RocketMQ 关于存储文件的加载流程来一窥端倪。
//org.apache.rocketmq.store.DefaultMessageStore#load
public boolean load() {
boolean result = true;
try {
boolean lastExitOK = !this.isTempFileExist();
log.info("last shutdown {}", lastExitOK ? "normally" : "abnormally");
if (null != scheduleMessageService) {
result = result && this.scheduleMessageService.load();
}
// load Commit Log
result = result && this.commitLog.load();
// load Consume Queue
result = result && this.loadConsumeQueue();
if (result) {
this.storeCheckpoint =
new StoreCheckpoint(StorePathConfigHelper.getStoreCheckpoint(this.messageStoreConfig.getStorePathRootDir()));
this.indexService.load(lastExitOK);
this.recover(lastExitOK);
log.info("load over, and the max phy offset = {}", this.getMaxPhyOffset());
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("load exception", e);
result = false;
}
if (!result) {
this.allocateMappedFileService.shutdown();
}
return result;
}
boolean lastExitOK = !this.isTempFileExist();
log.info("last shutdown {}", lastExitOK ? "normally" : "abnormally");
if (null != scheduleMessageService) {
result = result && this.scheduleMessageService.load();
}
Step1:判断上一次退出是否正常。其实现机制是Broker 在启动时创建${ ROCKET_HOME} /store/abort 文件,在退出时通过注册NM 钩子函数删除abort 文件。如果下一次启动时存在abort 文件。说明Broker 是异常退出的, Commitlog 与Consumequeue 数据有可能不一致,需要进行修复。
if (null != scheduleMessageService) {
result = result && this.scheduleMessageService.load();
}
Step2 :加载延迟队列, RocketMQ 定时消息相关, 该部分将在第5 章详细分析。
public boolean load() {
File dir = new File(this.storePath);
File[] files = dir.listFiles();
if (files != null) {
// ascending order
Arrays.sort(files);
for (File file : files) {
if (file.length() != this.mappedFileSize) {
log.warn(file + "\t" + file.length()
+ " length not matched message store config value, ignore it");
return true;
}
try {
MappedFile mappedFile = new MappedFile(file.getPath(), mappedFileSize);
mappedFile.setWrotePosition(this.mappedFileSize);
mappedFile.setFlushedPosition(this.mappedFileSize);
mappedFile.setCommittedPosition(this.mappedFileSize);
this.mappedFiles.add(mappedFile);
log.info("load " + file.getPath() + " OK");
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("load file " + file + " error", e);
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
Step3:加载Commitlog 文件, 加载$ { ROCKET_HOME }/store/commitlog 目录下所有文件并按照文件名排序。如果文件大小与配置文件的单个文件大小不一致,将忽略该目录下所有文件, 然后创建MappedFile 对象。注意load 方法将wrotePosition 、flushedPosition ,committedPosition 三个指针都设置为文件大小。
Step4 :加载消息消费队列, 调用DefaultMessageStore# loadConsumeQueue ,其思路与CommitLog 大体一致, 遍历消息消费队列根目录,获取该Broker 存储的所有主题, 然后遍历每个主题目录,获取该主题下的所有消息消费队列, 然后分别加载每个消息消费队列下的文件, 构建ConsumeQueue 对象,主要初始化ConsumeQueue 的topic 、queueld 、storePath 、mappedFileSize 属性。
this.storeCheckpoint =
new StoreCheckpoint(StorePathConfigHelper.getStoreCheckpoint(this.messageStoreConfig.getStorePathRootDir()));
Step5:加载存储检测点,检测点主要记录commitlog 文件、Consumequeue 文件、Index 索引文件的刷盘点,将在下文的文件刷盘机制中再次提交。
//org.apache.rocketmq.store.index.IndexService#load
public boolean load(final boolean lastExitOK) {
File dir = new File(this.storePath);
File[] files = dir.listFiles();
if (files != null) {
// ascending order
Arrays.sort(files);
for (File file : files) {
try {
IndexFile f = new IndexFile(file.getPath(), this.hashSlotNum, this.indexNum, 0, 0);
f.load();
if (!lastExitOK) {
if (f.getEndTimestamp() > this.defaultMessageStore.getStoreCheckpoint()
.getIndexMsgTimestamp()) {
f.destroy(0);
continue;
}
}
log.info("load index file OK, " + f.getFileName());
this.indexFileList.add(f);
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("load file {} error", file, e);
return false;
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
log.error("load file {} error", file, e);
}
}
}
return true;
}
Step6 :加载索引文件,如果上次异常退出,而且索引文件上次刷盘时间小于该索引文件最大的消息时间戳该文件将立即销毁。
//org.apache.rocketmq.store.DefaultMessageStore#recover
private void recover(final boolean lastExitOK) {
long maxPhyOffsetOfConsumeQueue = this.recoverConsumeQueue();
if (lastExitOK) {
this.commitLog.recoverNormally(maxPhyOffsetOfConsumeQueue);
} else {
this.commitLog.recoverAbnormally(maxPhyOffsetOfConsumeQueue);
}
this.recoverTopicQueueTable();
}
Step7 :根据Broker 是否是正常停止执行不同的恢复策略,下文将分别介绍异常停止、正常停止的文件恢复机制。
private void recoverTopicQueueTable() {
HashMap<String/* topic-queueid */, Long/* offset */> table = new HashMap<String, Long>(1024);
long minPhyOffset = this.commitLog.getMinOffset();
for (ConcurrentMap<Integer, ConsumeQueue> maps : this.consumeQueueTable.values()) {
for (ConsumeQueue logic : maps.values()) {
String key = logic.getTopic() + "-" + logic.getQueueId();
table.put(key, logic.getMaxOffsetInQueue());
logic.correctMinOffset(minPhyOffset);
}
}
this.commitLog.setTopicQueueTable(table);
}
Step8 :恢复ConsumeQueue 文件后,将在CommitLog 实例中保存每个消息消费队列当前的存储逻辑偏移量, 这也是消息中不仅存储主题、消息队列ID 还存储了消息队列偏移量的关键所在。
4.7.1.Broker 正常停止文件恢复
Broker 正常停止文件恢复的实现为CommitLog#recoverNormally 。
/**
* When the normal exit, data recovery, all memory data have been flush
*/
public void recoverNormally(long maxPhyOffsetOfConsumeQueue) {
boolean checkCRCOnRecover = this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().isCheckCRCOnRecover();
final List<MappedFile> mappedFiles = this.mappedFileQueue.getMappedFiles();
if (!mappedFiles.isEmpty()) {
// Began to recover from the last third file
int index = mappedFiles.size() - 3;
if (index < 0)
index = 0;
MappedFile mappedFile = mappedFiles.get(index);
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = mappedFile.sliceByteBuffer();
long processOffset = mappedFile.getFileFromOffset();
long mappedFileOffset = 0;
while (true) {
DispatchRequest dispatchRequest = this.checkMessageAndReturnSize(byteBuffer, checkCRCOnRecover);
int size = dispatchRequest.getMsgSize();
// Normal data
if (dispatchRequest.isSuccess() && size > 0) {
mappedFileOffset += size;
}
// Come the end of the file, switch to the next file Since the
// return 0 representatives met last hole,
// this can not be included in truncate offset
else if (dispatchRequest.isSuccess() && size == 0) {
index++;
if (index >= mappedFiles.size()) {
// Current branch can not happen
log.info("recover last 3 physics file over, last mapped file " + mappedFile.getFileName());
break;
} else {
mappedFile = mappedFiles.get(index);
byteBuffer = mappedFile.sliceByteBuffer();
processOffset = mappedFile.getFileFromOffset();
mappedFileOffset = 0;
log.info("recover next physics file, " + mappedFile.getFileName());
}
}
// Intermediate file read error
else if (!dispatchRequest.isSuccess()) {
log.info("recover physics file end, " + mappedFile.getFileName());
break;
}
}
processOffset += mappedFileOffset;
this.mappedFileQueue.setFlushedWhere(processOffset);
this.mappedFileQueue.setCommittedWhere(processOffset);
this.mappedFileQueue.truncateDirtyFiles(processOffset);
// Clear ConsumeQueue redundant data
if (maxPhyOffsetOfConsumeQueue >= processOffset) {
log.warn("maxPhyOffsetOfConsumeQueue({}) >= processOffset({}), truncate dirty logic files", maxPhyOffsetOfConsumeQueue, processOffset);
this.defaultMessageStore.truncateDirtyLogicFiles(processOffset);
}
}
}
boolean checkCRCOnRecover = this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().isCheckCRCOnRecover();
final List<MappedFile> mappedFiles = this.mappedFileQueue.getMappedFiles();
if (!mappedFiles.isEmpty()) {
// Began to recover from the last third file
int index = mappedFiles.size() - 3;
if (index < 0)
index = 0;
Step1 : Broker 正常停止再重启时,从倒数第三个文件开始进行恢复,如果不足3 个文件,则从第一个文件开始恢复。checkCRCOnRecover 参数设置在进行文件恢复时查找消息时是否验证CRC 。
MappedFile mappedFile = mappedFiles.get(index); ByteBuffer byteBuffer = mappedFile.sliceByteBuffer(); long processOffset = mappedFile.getFileFromOffset(); long mappedFileOffset = 0;
Step2 :解释一下两个局部变量, mappedFileOffset 为当前文件已校验通过的offset ,processOffset 为Commitlog 文件已确认的物理偏移量等于mappedFile.getFileFromOffset 加上mappedFileOffset 。
DispatchRequest dispatchRequest = this.checkMessageAndReturnSize(byteBuffer, checkCRCOnRecover);
int size = dispatchRequest.getMsgSize();
// Normal data
if (dispatchRequest.isSuccess() && size > 0) {
mappedFileOffset += size;
}
// Come the end of the file, switch to the next file Since the
// return 0 representatives met last hole,
// this can not be included in truncate offset
else if (dispatchRequest.isSuccess() && size == 0) {
index++;
if (index >= mappedFiles.size()) {
// Current branch can not happen
log.info("recover last 3 physics file over, last mapped file " + mappedFile.getFileName());
break;
} else {
mappedFile = mappedFiles.get(index);
byteBuffer = mappedFile.sliceByteBuffer();
processOffset = mappedFile.getFileFromOffset();
mappedFileOffset = 0;
log.info("recover next physics file, " + mappedFile.getFileName());
}
}
// Intermediate file read error
else if (!dispatchRequest.isSuccess()) {
log.info("recover physics file end, " + mappedFile.getFileName());
break;
}
Step3:遍历Commitlog 文件, 每次取出一条消息, 如果查找结果为true 并且消息的长度大于0 表示消息正确, mappedFileOffset 指针向前移动本条消息的长度; 如果查找结果为true 并且消息的长度等于0 , 表示已到该文件的末尾,如果还有下一个文件,则重置process Offset 、mappedFileOffset 重复步骤3 ,否则跳出循环; 如果查找结构为false ,表明该文件未填满所有消息,跳出循环,结束遍历文件。
processOffset += mappedFileOffset; this.mappedFileQueue.setFlushedWhere(processOffset); this.mappedFileQueue.setCommittedWhere(processOffset); this.mappedFileQueue.truncateDirtyFiles(processOffset);
Step4 : 更新MappedFileQueue 的flushedWhere 与commiteedWhere 指针。
public void truncateDirtyFiles(long offset) {
List<MappedFile> willRemoveFiles = new ArrayList<MappedFile>();
for (MappedFile file : this.mappedFiles) {
long fileTailOffset = file.getFileFromOffset() + this.mappedFileSize;
if (fileTailOffset > offset) {
if (offset >= file.getFileFromOffset()) {
file.setWrotePosition((int) (offset % this.mappedFileSize));
file.setCommittedPosition((int) (offset % this.mappedFileSize));
file.setFlushedPosition((int) (offset % this.mappedFileSize));
} else {
file.destroy(1000);
willRemoveFiles.add(file);
}
}
}
this.deleteExpiredFile(willRemoveFiles);
}
Step5:删除offset 之后的所有文件。遍历目录下的文件,如果文件的尾部偏移量小于offset 则跳过该文件,如果尾部的偏移量大于offset ,则进一步比较offset 与文件的开始偏移量, 如果offset 大于文件的起始偏移量, 说明当前文件包含了有效偏移量,设置MappedFile 的flushedPosition 和commitedPosition ;如果offset 小于文件的起始偏移量,说明该文件是有效文件后面创建的,调用MappedFile#destory 释放MappedFile 占用的内存资源(内存映射与内存通道等),然后加入到待删除文件列表中,最终调用deleteExpiredFile将文件从物理磁盘删除。过期文件的删除将在下文详细介绍。
4.7.2.Broker 异常停止文件恢复
Broker 异常停止文件恢复的实现为CommitLog#recoverAbnormally 。异常文件恢复的步骤与正常停止文件恢复的流程基本相同,其主要差别有两个。首先,正常停止默认从倒数第三个文件开始进行恢复, 而异常停止则需要从最后一个文件往前走, 找到第一个消息存储正常的文件。其次,如果commitlog 目录没有消息文件,如果在消息消费队列目录下存在文件,则需要销毁。
如何判断一个消息文件是一个正确的文件呢?
//org.apache.rocketmq.store.CommitLog#isMappedFileMatchedRecover
private boolean isMappedFileMatchedRecover(final MappedFile mappedFile) {
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = mappedFile.sliceByteBuffer();
int magicCode = byteBuffer.getInt(MessageDecoder.MESSAGE_MAGIC_CODE_POSTION);
if (magicCode != MESSAGE_MAGIC_CODE) {
return false;
}
long storeTimestamp = byteBuffer.getLong(MessageDecoder.MESSAGE_STORE_TIMESTAMP_POSTION);
if (0 == storeTimestamp) {
return false;
}
if (this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().isMessageIndexEnable()
&& this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().isMessageIndexSafe()) {
if (storeTimestamp <= this.defaultMessageStore.getStoreCheckpoint().getMinTimestampIndex()) {
log.info("find check timestamp, {} {}",
storeTimestamp,
UtilAll.timeMillisToHumanString(storeTimestamp));
return true;
}
} else {
if (storeTimestamp <= this.defaultMessageStore.getStoreCheckpoint().getMinTimestamp()) {
log.info("find check timestamp, {} {}",
storeTimestamp,
UtilAll.timeMillisToHumanString(storeTimestamp));
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
int magicCode = byteBuffer.getInt(MessageDecoder.MESSAGE_MAGIC_CODE_POSTION);
if (magicCode != MESSAGE_MAGIC_CODE) {
return false;
}
Step1:首先判断文件的魔数,如果不是MESSAGE_MAGIC_CODE ,返回false ,表示该文件不符合commitlog 消息文件的存储格式。
long storeTimestamp = byteBuffer.getLong(MessageDecoder.MESSAGE_STORE_TIMESTAMP_POSTION);
if (0 == storeTimestamp) {
return false;
}
Step2 :如果文件中第一条消息的存储时间等于0 , 返回false ,说明该消息存储文件中未存储任何消息。
if (this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().isMessageIndexEnable()
&& this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().isMessageIndexSafe()) {
if (storeTimestamp <= this.defaultMessageStore.getStoreCheckpoint().getMinTimestampIndex()) {
log.info("find check timestamp, {} {}",
storeTimestamp,
UtilAll.timeMillisToHumanString(storeTimestamp));
return true;
}
} else {
if (storeTimestamp <= this.defaultMessageStore.getStoreCheckpoint().getMinTimestamp()) {
log.info("find check timestamp, {} {}",
storeTimestamp,
UtilAll.timeMillisToHumanString(storeTimestamp));
return true;
}
}
Step3 :对比文件第一条消息的时间戳与检测点,文件第一条消息的时间戳小于文件检测点说明该文件部分消息是可靠的, 则从该文件开始恢复。文件检测点中保存了Commitlog 文件、消息消费队列( ConsumeQueue ) 、索引文件( IndexFile )的文件刷盘点,RocketMQ 默认选择这消息文件与消息消费队列这两个文件的时间刷盘点中最小值与消息文件第一消息的时间戳对比,如果messagelndexEnable 为true , 表示索引文件的刷盘时间点也参与计算。
Step4 :如果根据前3 步算法找到MappedFile ,则遍历MappedFile 中的消息,验证消息的合法性,并将消息重新转发到消息消费队列与索引文件,该步骤在4. 7. 1 节中已详细说明。
Step5 :如果未找到有效MappedFile , 则设置commitlog 目录的flushedWhere 、committedWhere指针都为0 ,并销毁消息消费队列文件。
public void destroy() {
this.maxPhysicOffset = -1;
this.minLogicOffset = 0;
this.mappedFileQueue.destroy();
if (isExtReadEnable()) {
this.consumeQueueExt.destroy();
}
}
重置ConsumeQueue 的maxPhysicOffset 与minLogicOffset , 然后调用Mapp巳dFileQueue的destory。可方法将消息消费队列目录下的所有文件全部删除。
存储启动时所谓的文件恢复主要完成flushedPosition, committed Where 指针的设置、消息消费队列最大偏移量加载到内存,并删除flushedPosition 之后所有的文件。如果Broker异常启动, 在文件恢复过程中, RocketMQ 会将最后一个有效文件中的所有消息重新转发到消息消费队列与索引文件,确保不丢失消息,但同时会带来消息重复的问题,纵观RocktMQ 的整体设计思想, RocketMQ 保证消息不丢失但不保证消息不会重复消费, 故消息消费业务方需要实现消息消费的幕等设计。
4.8.文件刷盘机制
RocketMQ 的存储与读写是基于JDKNIO 的内存映射机制( MappedByteBuffer )的,消息存储时首先将消息追加到内存,再根据配置的刷盘策略在不同时间进行刷写磁盘。如果是同步刷盘,消息追加到内存后,将同步调用MappedByteBuffer 的force ()方法;如果是异步刷盘,在消息追加到内存后立刻返回给消息发送端。RocketMQ 使用一个单独的线程按照某一个设定的频率执行刷盘操作。通过在broker 配置文件中配置flushDiskType 来设定刷盘方式,可选值为ASYNC_FLUSH (异步刷盘)、SYNC_FLUSH ( 同步刷盘) , 默认为异步刷盘。这里以消息存储文件Commitlog 文件刷盘机制为例来剖析RocketMQ 的刷盘机制, ConsumeQueue 、IndexFile 刷盘的实现原理与Commitlog 刷盘机制类似。RocketMQ 处理刷盘的实现方法为Commitlog#handleDiskFlush() 方法, 刷盘流程作为消息发送、消息存储的子流程,请先重点了解4.3 节中关于消息存储流程的相关知识。值得注意的是索引文件的刷盘并不是采取定时刷盘机制,而是每更新一次索引文件就会将上一次的改动刷写到磁盘。
4.8.1.Broker 同步刷盘
同步刷盘,指的是在消息追加到内存映射文件的内存中后,立即将数据从内存刷写到磁盘文件,由CommitLog 的handleDiskFlush 方法实现,如代码清单4-73 所示。
public void handleDiskFlush(AppendMessageResult result, PutMessageResult putMessageResult, MessageExt messageExt) {
// Synchronization flush
if (FlushDiskType.SYNC_FLUSH == this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getFlushDiskType()) {
final GroupCommitService service = (GroupCommitService) this.flushCommitLogService;
if (messageExt.isWaitStoreMsgOK()) {
GroupCommitRequest request = new GroupCommitRequest(result.getWroteOffset() + result.getWroteBytes());
service.putRequest(request);
boolean flushOK = request.waitForFlush(this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getSyncFlushTimeout());
if (!flushOK) {
log.error("do groupcommit, wait for flush failed, topic: " + messageExt.getTopic() + " tags: " + messageExt.getTags()
+ " client address: " + messageExt.getBornHostString());
putMessageResult.setPutMessageStatus(PutMessageStatus.FLUSH_DISK_TIMEOUT);
}
} else {
service.wakeup();
}
}
// Asynchronous flush
else {
if(!this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().isTransientStorePoolEnable()) {
flushCommitLogService.wakeup();
} else {
commitLogService.wakeup();
}
}
}
同步刷盘实现流程如下。
-
构建GroupCommitRequest 同步任务并提交到GroupCommitRequest 。
-
等待同步刷盘任务完成,如果超时则返回刷盘错误, 刷盘成功后正常返回给调用方。GroupCommitRequest 的类图如图4-18 所示。

下面让我们一一介绍GroupCommitRequest 的核心属性。
-
long nextOffset :刷盘点偏移量。
-
CountDownLatch countDownLatch :倒记数锁存器。
-
flushOk :刷盘结果, 初始为false 。
public boolean waitForFlush(long timeout) {
try {
this.countDownLatch.await(timeout, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
return this.flushOK;
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.error("Interrupted", e);
return false;
}
}
消费发送线程将消息追加到内存映射文件后,将同步任务GroupCommitRequest 提交到GroupCommitService 线程,然后调用阻塞等待刷盘结果,超时时间默认为5s 。
public void wakeupCustomer(final boolean flushOK) {
this.flushOK = flushOK;
this.countDownLatch.countDown();
}
GroupCommitService 线程处理GroupCommitRequest 对象后将调用wakeupCustomer 方法将消费发送线程唤醒,并将刷盘告知GroupCommitRequest 。
同步刷盘线程实现GroupCommitService 类图如图4-19 所示。
-
private volatile List<GroupCommitRequest> requestsWrite: 同步刷盘任务暂存容器。
-
private volatile List<GroupCommitRequest> requestsRead: GroupCommitService 线程每次处理的request 容器,这是一个设计亮点,避免了任务提交与任务执行的锁冲突。
public synchronized void putRequest(final GroupCommitRequest request) {
synchronized (this.requestsWrite) {
this.requestsWrite.add(request);
}
if (hasNotified.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
waitPoint.countDown(); // notify
}
}
客户端提交同步刷盘任务到GroupCommitService 线程,如果废线程处于等待状态则将仅供其唤醒。
private void swapRequests() {
List<GroupCommitRequest> tmp = this.requestsWrite;
this.requestsWrite = this.requestsRead;
this.requestsRead = tmp;
}
由于避免同步刷盘消费任务与其他消息生产者提交任务直接的锁竞争, GroupCommitService 提供读容器与写容器,这两个容器每执行完一次任务后,交换,继续消费任务。15850680911
//GroupCommitService#run
public void run() {
CommitLog.log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service started");
while (!this.isStopped()) {
try {
this.waitForRunning(10);
this.doCommit();
} catch (Exception e) {
CommitLog.log.warn(this.getServiceName() + " service has exception. ", e);
}
}
// Under normal circumstances shutdown, wait for the arrival of the
// request, and then flush
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
CommitLog.log.warn("GroupCommitService Exception, ", e);
}
synchronized (this) {
this.swapRequests();
}
this.doCommit();
CommitLog.log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service end");
}
GroupCommitService 每处理一批同步刷盘请求(requestsRead 容器中请求)后“休息” 10ms , 然后继续处理下一批,其任务的核心实现为doCommit方法。
private void doCommit() {
synchronized (this.requestsRead) {
if (!this.requestsRead.isEmpty()) {
for (GroupCommitRequest req : this.requestsRead) {
// There may be a message in the next file, so a maximum of
// two times the flush
boolean flushOK = false;
for (int i = 0; i < 2 && !flushOK; i++) {
flushOK = CommitLog.this.mappedFileQueue.getFlushedWhere() >= req.getNextOffset();
if (!flushOK) {
CommitLog.this.mappedFileQueue.flush(0);
}
}
req.wakeupCustomer(flushOK);
}
long storeTimestamp = CommitLog.this.mappedFileQueue.getStoreTimestamp();
if (storeTimestamp > 0) {
CommitLog.this.defaultMessageStore.getStoreCheckpoint().setPhysicMsgTimestamp(storeTimestamp);
}
this.requestsRead.clear();
} else {
// Because of individual messages is set to not sync flush, it
// will come to this process
CommitLog.this.mappedFileQueue.flush(0);
}
}
}
执行刷盘操作,即调用MappedByteBuffer#force 方法。
-
遍历同步刷盘任务列表,根据加入顺序逐一执行刷盘逻辑。
-
调用mappedFileQueue# flush 方法执行刷盘操作,最终会调用MappedByteBuffer#force()方法,其具体实现已在4.4 节中做了详细说明。如果已刷盘指针大于等于提交的刷盘点,表示刷盘成功, 每执行一次刷盘操作后,立即调用GroupCommitReques做wakeupCustomer唤醒消息发送线程并通知刷盘结果。
-
处理完所有同步刷盘任务后,更新刷盘检测点StoreCheckpoint 中的physicMsgTimestamp,但并没有执行检测点的刷盘操作,刷盘检测点的刷盘操作将在刷写消息队列文件时触发。
同步刷盘的简单描述就是,消息生产者在消息服务端将消息内容追加到内存映射文件中(内存)后,需要同步将内存的内容立刻刷写到磁盘。通过调用内存映射文件( MappedByteBuffer 的force 方法)可将内存中的数据写入磁盘。
4.8.2.Broker异步刷盘
public void handleDiskFlush(AppendMessageResult result, PutMessageResult putMessageResult, MessageExt messageExt) {
// Synchronization flush
if (FlushDiskType.SYNC_FLUSH == this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getFlushDiskType()) {
final GroupCommitService service = (GroupCommitService) this.flushCommitLogService;
if (messageExt.isWaitStoreMsgOK()) {
GroupCommitRequest request = new GroupCommitRequest(result.getWroteOffset() + result.getWroteBytes());
service.putRequest(request);
boolean flushOK = request.waitForFlush(this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getSyncFlushTimeout());
if (!flushOK) {
log.error("do groupcommit, wait for flush failed, topic: " + messageExt.getTopic() + " tags: " + messageExt.getTags()
+ " client address: " + messageExt.getBornHostString());
putMessageResult.setPutMessageStatus(PutMessageStatus.FLUSH_DISK_TIMEOUT);
}
} else {
service.wakeup();
}
}
// Asynchronous flush
else {
if (!this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().isTransientStorePoolEnable()) {
flushCommitLogService.wakeup();
} else {
commitLogService.wakeup();
}
}
}
// Asynchronous flush
else {
if (!this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().isTransientStorePoolEnable()) {
flushCommitLogService.wakeup();
} else {
commitLogService.wakeup();
}
}
异步刷盘根据是否开启transientStorePoolEnable机制,刷盘实现会有细微差别。如果transientStorePoolEnable 为true , RocketMQ 会单独申请一个与目标物理文件( commitlog)同样大小的堆外内存, 该堆外内存将使用内存锁定,确保不会被置换到虚拟内存中去,消息首先追加到堆外内存,然后提交到与物理文件的内存映射内存中,再flush 到磁盘。如果transientStorePoolEnable 为flalse ,消息直接追加到与物理文件直接映射的内存中,然后刷写到磁盘中。transientStorePoolEnable 为true 的磁盘刷写流程如图4-20 所示。
-
首先将消息直接追加到ByteBuffer (堆外内存DirectByteBuffer ), wrotePosition 随着消息的不断追加向后移动。
-
CommitRealTimeService 线程默认每200ms 将ByteBuffer 新追加的内容( wrotePosihon减去commitedPosition )的数据提交到Ma ppedB yte Buff1巳r 中。
-
MappedByt巳Buffer 在内存中追加提交的内容, wrotePosition 指针向前后移动, 然后返回。
-
commit 操作成功返回,将commitedPosition 向前后移动本次提交的内容长度,此时wrotePosition 指针依然可以向前推进。
-
FlushRealTimeService 线程默认每500ms 将MappedByteBuffer 中新追加的内存( wrotePosition 减去上一次刷写位置flushedPositiont )通过调用MappedByteBuffer#force()方法将数据刷写到磁盘。
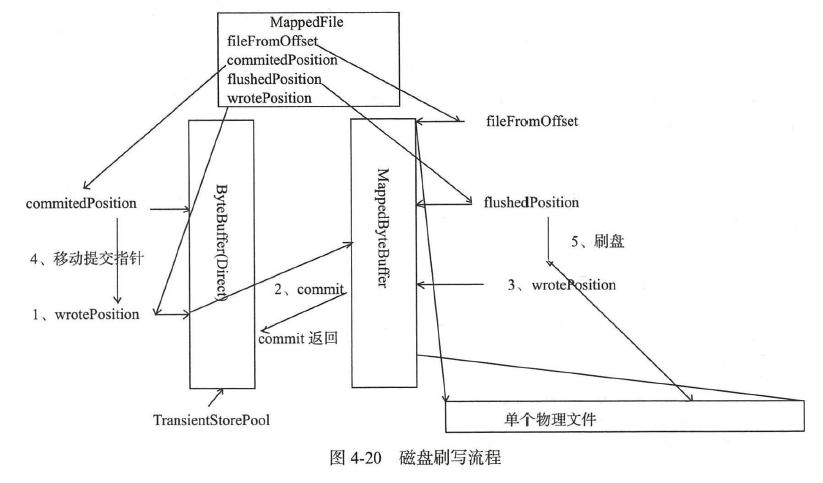
CommitRealTimeService 提交线程工作机制
@Override
public void run() {
CommitLog.log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service started");
while (!this.isStopped()) {
int interval = CommitLog.this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getCommitIntervalCommitLog();
int commitDataLeastPages = CommitLog.this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getCommitCommitLogLeastPages();
int commitDataThoroughInterval =
CommitLog.this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getCommitCommitLogThoroughInterval();
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
if (begin >= (this.lastCommitTimestamp + commitDataThoroughInterval)) {
this.lastCommitTimestamp = begin;
commitDataLeastPages = 0;
}
try {
boolean result = CommitLog.this.mappedFileQueue.commit(commitDataLeastPages);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
if (!result) {
this.lastCommitTimestamp = end; // result = false means some data committed.
//now wake up flush thread.
flushCommitLogService.wakeup();
}
if (end - begin > 500) {
log.info("Commit data to file costs {} ms", end - begin);
}
this.waitForRunning(interval);
} catch (Throwable e) {
CommitLog.log.error(this.getServiceName() + " service has exception. ", e);
}
}
boolean result = false;
for (int i = 0; i < RETRY_TIMES_OVER && !result; i++) {
result = CommitLog.this.mappedFileQueue.commit(0);
CommitLog.log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service shutdown, retry " + (i + 1) + " times " + (result ? "OK" : "Not OK"));
}
CommitLog.log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service end");
}
int interval = CommitLog.this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getCommitIntervalCommitLog();
int commitDataLeastPages = CommitLog.this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getCommitCommitLogLeastPages();
int commitDataThoroughInterval =
CommitLog.this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getCommitCommitLogThoroughInterval();
Step1: 首先解释三个配置参数的含义。
-
commitlnterva!CommitLog: CommitRea!TimeService 线程间隔时间,默认200ms 。
-
commitCommitLogLeastPages : 一次提交任务至少包含页数, 如果待提交数据不足,小于该参数配置的值,将忽略本次提交任务,默认4 页。
-
commitDataThoroughinterval :两次真实提交最大间隔,默认200ms 。
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
if (begin >= (this.lastCommitTimestamp + commitDataThoroughInterval)) {
this.lastCommitTimestamp = begin;
commitDataLeastPages = 0;
}
Step2 :如果距上次提交间隔超过commitDataThoroughInterval , 则本次提交忽略commitCommitLogLeastPages参数, 也就是如果待提交数据小于指定页数, 也执行提交操作。
boolean result = CommitLog.this.mappedFileQueue.commit(commitDataLeastPages);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
if (!result) {
this.lastCommitTimestamp = end; // result = false means some data committed.
//now wake up flush thread.
flushCommitLogService.wakeup();
}
if (end - begin > 500) {
log.info("Commit data to file costs {} ms", end - begin);
}
this.waitForRunning(interval);
Step3 :执行提交操作,将待提交数据提交到物理文件的内存映射内存区,如果返回false ,并不是代表提交失败,而是只提交了一部分数据,唤醒刷盘线程执行刷盘操作。该线程每完成一次提交动作,将等待2 00ms 再继续执行下一次提交任务。
FlushRealTimeService 刷盘线程工作机制
public void run() {
CommitLog.log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service started");
while (!this.isStopped()) {
boolean flushCommitLogTimed = CommitLog.this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().isFlushCommitLogTimed();
int interval = CommitLog.this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getFlushIntervalCommitLog();
int flushPhysicQueueLeastPages = CommitLog.this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getFlushCommitLogLeastPages();
int flushPhysicQueueThoroughInterval =
CommitLog.this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getFlushCommitLogThoroughInterval();
boolean printFlushProgress = false;
// Print flush progress
long currentTimeMillis = System.currentTimeMillis();
if (currentTimeMillis >= (this.lastFlushTimestamp + flushPhysicQueueThoroughInterval)) {
this.lastFlushTimestamp = currentTimeMillis;
flushPhysicQueueLeastPages = 0;
printFlushProgress = (printTimes++ % 10) == 0;
}
try {
if (flushCommitLogTimed) {
Thread.sleep(interval);
} else {
this.waitForRunning(interval);
}
if (printFlushProgress) {
this.printFlushProgress();
}
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
CommitLog.this.mappedFileQueue.flush(flushPhysicQueueLeastPages);
long storeTimestamp = CommitLog.this.mappedFileQueue.getStoreTimestamp();
if (storeTimestamp > 0) {
CommitLog.this.defaultMessageStore.getStoreCheckpoint().setPhysicMsgTimestamp(storeTimestamp);
}
long past = System.currentTimeMillis() - begin;
if (past > 500) {
log.info("Flush data to disk costs {} ms", past);
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
CommitLog.log.warn(this.getServiceName() + " service has exception. ", e);
this.printFlushProgress();
}
}
// Normal shutdown, to ensure that all the flush before exit
boolean result = false;
for (int i = 0; i < RETRY_TIMES_OVER && !result; i++) {
result = CommitLog.this.mappedFileQueue.flush(0);
CommitLog.log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service shutdown, retry " + (i + 1) + " times " + (result ? "OK" : "Not OK"));
}
this.printFlushProgress();
CommitLog.log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service end");
}
boolean flushCommitLogTimed = CommitLog.this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().isFlushCommitLogTimed();
int interval = CommitLog.this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getFlushIntervalCommitLog();
int flushPhysicQueueLeastPages = CommitLog.this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getFlushCommitLogLeastPages();
int flushPhysicQueueThoroughInterval =
CommitLog.this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getFlushCommitLogThoroughInterval();
Step1: 首先解释四个配置参数的含义。
-
flushCommitLogTimed : 默认为false , 表示await 方法等待;如果为true ,表示使用Thread.sleep 方法等待。
-
flushIntervalCommitLog: FlushRealTimeService 线程任务运行间隔。
-
flushPhysicQueueLeastPages : 一次刷写任务至少包含页数, 如果待刷写数据不足,小于该参数配置的值,将忽略本次刷写任务,默认4 页。
-
flushPhysicQueueThoroughInterval :两次真实刷写任务最大间隔, 默认10s 。
// Print flush progress
long currentTimeMillis = System.currentTimeMillis();
if (currentTimeMillis >= (this.lastFlushTimestamp + flushPhysicQueueThoroughInterval)) {
this.lastFlushTimestamp = currentTimeMillis;
flushPhysicQueueLeastPages = 0;
printFlushProgress = (printTimes++ % 10) == 0;
}
Step2 :如果距上次提交间隔超过flushPhysicQueueThoroughInterval ,则本次刷盘任务将忽略flushPhysicQueueLeastPages , 也就是如果待刷写数据小于指定页数也执行刷写磁盘操作。
if (flushCommitLogTimed) {
Thread.sleep(interval);
} else {
this.waitForRunning(interval);
}
Step3 :执行一次刷盘任务前先等待指定时间间隔, 然后再执行刷盘任务。
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
CommitLog.this.mappedFileQueue.flush(flushPhysicQueueLeastPages);
long storeTimestamp = CommitLog.this.mappedFileQueue.getStoreTimestamp();
if (storeTimestamp > 0) {
CommitLog.this.defaultMessageStore.getStoreCheckpoint().setPhysicMsgTimestamp(storeTimestamp);
}
Step4 :调用flush 方法将内存中数据刷写到磁盘,并且更新存储检测点文件的comm1tlog 文件的更新时间戳,文件检测点文件( checkpoint 文件)的刷盘动作在刷盘消息消费队列线程中执行, 其入口为DefaultMessageStore# FlushConsumeQueueS 巳rvice 。由于消息消费队列、索引文件的刷盘实现原理与Comm itlog 文件的刷盘机制类同,故本书不再做重复分析。
4.9.过期文件删除机制
由于RocketMQ 操作CommitLog 、ConsumeQueue 文件是基于内存映射机制并在启动的时候会加载commitlog 、ConsumeQueue 目录下的所有文件,为了避免内存与磁盘的浪费,不可能将消息永久存储在消息服务器上,所以需要引人一种机制来删除己过期的文件。RocketMQ 顺序写Commitlog 文件、Cons umeQueue 文件,所有写操作全部落在最后一个CommitLog 或Cons umeQueu e 文件上,之前的文件在下一个文件创建后将不会再被更新。RocketMQ 清除过期文件的方法是:如果非当前写文件在一定时间间隔内没有再次被更新,则认为是过期文件,可以被删除, RocketMQ 不会关注这个文件上的消息是否全部被消费。默认每个文件的过期时间为72 小时,通过在Broker 配置文件中设置fi leReservedTime 来改变过期时间,单位为小时· 。接下来详细分析RocketMQ 是如何设计与实现上述机制的。
private void addScheduleTask() {
this.scheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
DefaultMessageStore.this.cleanFilesPeriodically();
}
}, 1000 * 60, this.messageStoreConfig.getCleanResourceInterval(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
this.scheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
DefaultMessageStore.this.checkSelf();
}
}, 1, 10, TimeUnit.MINUTES);
this.scheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
if (DefaultMessageStore.this.getMessageStoreConfig().isDebugLockEnable()) {
try {
if (DefaultMessageStore.this.commitLog.getBeginTimeInLock() != 0) {
long lockTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - DefaultMessageStore.this.commitLog.getBeginTimeInLock();
if (lockTime > 1000 && lockTime < 10000000) {
String stack = UtilAll.jstack();
final String fileName = System.getProperty("user.home") + File.separator + "debug/lock/stack-"
+ DefaultMessageStore.this.commitLog.getBeginTimeInLock() + "-" + lockTime;
MixAll.string2FileNotSafe(stack, fileName);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
}
}, 1, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
// this.scheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() {
// @Override
// public void run() {
// DefaultMessageStore.this.cleanExpiredConsumerQueue();
// }
// }, 1, 1, TimeUnit.HOURS);
}
RocketMQ 会每隔10 s 调度一次cleanFilesPeriodically , 检测是否需要清除过期文件。执行频率可以通过设置cleanResourceInterval ,默认为10 s 。
private void cleanFilesPeriodically() {
this.cleanCommitLogService.run();
this.cleanConsumeQueueService.run();
}
分别执行清除消息存储文件( Commitlog 文件)与消息消费队列文件( ConsumeQueue文件) 。由于消息消费队列文件与消息存储文件( Commitlo g )共用一套过期文件删除机制,本书将重点讲解消息存储过期文件删除。实现方法: DefaultMessage Store$Clean CommitLogService#deleteExpiredFiles 。
private void deleteExpiredFiles() {
int deleteCount = 0;
long fileReservedTime = DefaultMessageStore.this.getMessageStoreConfig().getFileReservedTime();
int deletePhysicFilesInterval = DefaultMessageStore.this.getMessageStoreConfig().getDeleteCommitLogFilesInterval();
int destroyMapedFileIntervalForcibly = DefaultMessageStore.this.getMessageStoreConfig().getDestroyMapedFileIntervalForcibly();
boolean timeup = this.isTimeToDelete();
boolean spacefull = this.isSpaceToDelete();
boolean manualDelete = this.manualDeleteFileSeveralTimes > 0;
if (timeup || spacefull || manualDelete) {
if (manualDelete)
this.manualDeleteFileSeveralTimes--;
boolean cleanAtOnce = DefaultMessageStore.this.getMessageStoreConfig().isCleanFileForciblyEnable() && this.cleanImmediately;
log.info("begin to delete before {} hours file. timeup: {} spacefull: {} manualDeleteFileSeveralTimes: {} cleanAtOnce: {}",
fileReservedTime,
timeup,
spacefull,
manualDeleteFileSeveralTimes,
cleanAtOnce);
fileReservedTime *= 60 * 60 * 1000;
deleteCount = DefaultMessageStore.this.commitLog.deleteExpiredFile(fileReservedTime, deletePhysicFilesInterval,
destroyMapedFileIntervalForcibly, cleanAtOnce);
if (deleteCount > 0) {
} else if (spacefull) {
log.warn("disk space will be full soon, but delete file failed.");
}
}
}
Step1: 解释一下这个三个配置属性的含义。
int deleteCount = 0; long fileReservedTime = DefaultMessageStore.this.getMessageStoreConfig().getFileReservedTime(); int deletePhysicFilesInterval = DefaultMessageStore.this.getMessageStoreConfig().getDeleteCommitLogFilesInterval(); int destroyMapedFileIntervalForcibly = DefaultMessageStore.this.getMessageStoreConfig().getDestroyMapedFileIntervalForcibly();
-
fileReservedTime : 文件保留时间, 也就是从最后一次更新时间到现在, 如果超过了该时间, 则认为是过期文件, 可以被删除。
-
deletePhysicFilesInterval :删除物理文件的间隔,因为在一次清除过程中, 可能需要被删除的文件不止一个,该值指定两次删除文件的问隔时间。
-
destroyMapedFilelntervalForcibly : 在清除过期文件时, 如果该文件被其他线程所占用(引用次数大于0 ,比如读取消息), 此时会阻止此次删除任务, 同时在第一次试图删除该文件时记录当前时间戳, destroyMapedFile lntervalForcibly 表示第一次拒绝删除之后能保留的最大时间,在此时间内, 同样可以被拒绝删除, 同时会将引用减少1000 个,超过该时间间隔后,文件将被强制删除。
boolean timeup = this.isTimeToDelete();
boolean spacefull = this.isSpaceToDelete();
boolean manualDelete = this.manualDeleteFileSeveralTimes > 0;
if (timeup || spacefull || manualDelete) {
if (manualDelete)
this.manualDeleteFileSeveralTimes--;
boolean cleanAtOnce = DefaultMessageStore.this.getMessageStoreConfig().isCleanFileForciblyEnable() && this.cleanImmediately;
log.info("begin to delete before {} hours file. timeup: {} spacefull: {} manualDeleteFileSeveralTimes: {} cleanAtOnce: {}",
fileReservedTime,
timeup,
spacefull,
manualDeleteFileSeveralTimes,
cleanAtOnce);
fileReservedTime *= 60 * 60 * 1000;
deleteCount = DefaultMessageStore.this.commitLog.deleteExpiredFile(fileReservedTime, deletePhysicFilesInterval,
destroyMapedFileIntervalForcibly, cleanAtOnce);
if (deleteCount > 0) {
} else if (spacefull) {
log.warn("disk space will be full soon, but delete file failed.");
}
}
Step2: RocketMQ 在如下三种情况任意之一满足的情况下将继续执行删除文件操作。
-
指定删除文件的时间点, RocketMQ 通过delete When 设置一天的固定时间执行一次删除过期文件操作, 默认为凌晨4 点。
-
磁盘空间是否充足,如果磁盘空间不充足,则返回true ,表示应该触发过期文件删除操作。
-
预留,手工触发,可以通过调用excuteDeleteFilesManualy 方法手工触发过期文件删除,目前RocketMQ 暂未封装手工触发文件删除的命令。
本节重点分析一下磁盘空间是否充足的实现逻辑。
private boolean isSpaceToDelete() {
double ratio = DefaultMessageStore.this.getMessageStoreConfig().getDiskMaxUsedSpaceRatio() / 100.0;
cleanImmediately = false;
{
String storePathPhysic = DefaultMessageStore.this.getMessageStoreConfig().getStorePathCommitLog();
double physicRatio = UtilAll.getDiskPartitionSpaceUsedPercent(storePathPhysic);
if (physicRatio > diskSpaceWarningLevelRatio) {
boolean diskok = DefaultMessageStore.this.runningFlags.getAndMakeDiskFull();
if (diskok) {
DefaultMessageStore.log.error("physic disk maybe full soon " + physicRatio + ", so mark disk full");
}
cleanImmediately = true;
} else if (physicRatio > diskSpaceCleanForciblyRatio) {
cleanImmediately = true;
} else {
boolean diskok = DefaultMessageStore.this.runningFlags.getAndMakeDiskOK();
if (!diskok) {
DefaultMessageStore.log.info("physic disk space OK " + physicRatio + ", so mark disk ok");
}
}
if (physicRatio < 0 || physicRatio > ratio) {
DefaultMessageStore.log.info("physic disk maybe full soon, so reclaim space, " + physicRatio);
return true;
}
}
{
String storePathLogics = StorePathConfigHelper
.getStorePathConsumeQueue(DefaultMessageStore.this.getMessageStoreConfig().getStorePathRootDir());
double logicsRatio = UtilAll.getDiskPartitionSpaceUsedPercent(storePathLogics);
if (logicsRatio > diskSpaceWarningLevelRatio) {
boolean diskok = DefaultMessageStore.this.runningFlags.getAndMakeDiskFull();
if (diskok) {
DefaultMessageStore.log.error("logics disk maybe full soon " + logicsRatio + ", so mark disk full");
}
cleanImmediately = true;
} else if (logicsRatio > diskSpaceCleanForciblyRatio) {
cleanImmediately = true;
} else {
boolean diskok = DefaultMessageStore.this.runningFlags.getAndMakeDiskOK();
if (!diskok) {
DefaultMessageStore.log.info("logics disk space OK " + logicsRatio + ", so mark disk ok");
}
}
if (logicsRatio < 0 || logicsRatio > ratio) {
DefaultMessageStore.log.info("logics disk maybe full soon, so reclaim space, " + logicsRatio);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
1 )首先解释一下几个参数的含义。
-
diskMaxUsedSpaceRatio : 表示commitlog 、consumequeue 文件所在磁盘分区的最大使用量,如果超过该值, 则需要立即清除过期文件。
-
cleanImmediately : 表示是否需要立即执行清除过期文件操作。
-
physicRatio : 当前commitlog 目录所在的磁盘分区的磁盘使用率,通过File#getTotalSpace()获取文件所在磁盘分区的总容量,通过File#getFreeSpace() 获取文件所在磁盘分区剩余容量。
-
diskSpaceWarningLevelRatio : 通过系统参数-Drocketmq.broker.diskSpace WamingLevelRatio设置,默认0.90 。如果磁盘分区使用率超过该阔值,将设置磁盘不可写,此时会拒绝新消息的写人。
-
diskSpaceCleanForciblyRatio :通过系统参数-Drocketmq.broker.diskSpaceCleanF orciblyRatio设置, 默认0.85 。如果磁盘分区使用超过该阔值,建议立即执行过期文件清除,但不会拒绝新消息的写入。
2 ) 如果当前磁盘分区使用率大于diskSpace WarningLeve!Ratio ,设置磁盘不可写,应该立即启动过期文件删除操作;如果当前磁盘分区使用率大于diskSpaceCleanForciblyRatio,建议立即执行过期文件清除;如果磁盘使用率低于diskSpaceCl eanF orcibly Ratio 将恢复磁盘可写;如果当前磁盘使用率小于diskMax U sedSpaceRatio 则返回false ,表示磁盘使用率正常,否则返回true , 需要执行清除过期文件。
for (int i = 0; i < mfsLength; i++) {
MappedFile mappedFile = (MappedFile) mfs[i];
long liveMaxTimestamp = mappedFile.getLastModifiedTimestamp() + expiredTime;
if (System.currentTimeMillis() >= liveMaxTimestamp || cleanImmediately) {
if (mappedFile.destroy(intervalForcibly)) {
files.add(mappedFile);
deleteCount++;
if (files.size() >= DELETE_FILES_BATCH_MAX) {
break;
}
if (deleteFilesInterval > 0 && (i + 1) < mfsLength) {
try {
Thread.sleep(deleteFilesInterval);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
} else {
break;
}
} else {
//avoid deleting files in the middle
break;
}
}
执行文件销毁与删除。从倒数第二个文件开始遍历,计算文件的最大存活时间( = 文件的最后一次更新时间+文件存活时间(默认72 小时)) , 如果当前时间大于文件的最大存活时间或需要强制删除文件(当磁盘使用超过设定的阔值)时则执行MappedFile#destory 方法,清除MappedFile 占有的相关资源,如果执行成功,将该文件加入到待删除文件列表中,然后统一执行File#delete 方法将文件从物理磁盘中删除。
4.10.本章小节
RocketMQ 主要存储文件包含消息文件( commitlog )、消息消费队列文件(ConsumeQueue)、Hash 索引文件(indexFile)、检测点文件( checkpoint ) 、abort (关闭异常文件) 。单个消息存储文件、消息消费队列文件、Hash 索引文件长度固定以便使用内存映射机制进行文件的读写操作。RocketMQ 组织文件以文件的起始偏移量来命名文件,这样根据偏移量能快速定位到真实的物理文件。RocketMQ 基于内存映射文件机制提供了同步刷盘与异步刷盘两种机制,异步刷盘是指在消息存储时先追加到内存映射文件,然后启动专门的刷盘线程定时将内存中的数据刷写到磁盘。
Commitlog,消息存储文件, RocketMQ 为了保证消息发送的高吞吐量,采用单一文件存储所有主题的消息,保证消息存储是完全的顺序写,但这样给文件读取同样带来了不便,为此RocketMQ 为了方便消息消费构建了消息消费队列文件,基于主题与队列进行组织, 同时RocketMQ 为消息实现了Hash 索引,可以为消息设置索引键,根据索引能够快速从Commitog 文件中检索消息。
当消息到达Commitlog 文件后,会通过ReputMessageService 线程接近实时地将消息转发给消息消费队列文件与索引文件。为了安全起见, RocketMQ 引人abort 文件,记录Broker 的停机是正常关闭还是异常关闭,在重启Broker 时为了保证Commitlog 文件、消息消费队列文件与Hash 索引文件的正确性,分别采取不同的策略来恢复文件。
RocketMQ 不会永久存储消息文件、消息消费队列文件,而是启用文件过期机制并在磁盘空间不足或默认在凌晨4 点删除过期文件,文件默认保存72 小时并且在删除文件时并不会判断该消息文件上的消息是否被消费。下面一章我们将重点分析有关消息、消费的实现机制。


























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










