图的最短路径算法就剩下几个了,Floyd-Warshall算法是利用动态规划来实现的,其可以用来统计图的任意点对之间的距离。不过复杂度显而易见,需要O(V^3)。
Wiki上有该算法的原理如下:
设 为从
为从 到
到 的只以
的只以 集合中的节点为中间节点的最短路径的长度。
集合中的节点为中间节点的最短路径的长度。
- 若最短路径经过点k,则
 ;
; - 若最短路径不经过点k,则
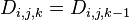 。
。
因此, 。
。
代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#define GRAPHSIZE 12
#define MAX_INT 0x7FFFFFFF
#define NO_PAHT -1
using namespace std;
class Graph
{
public:
long map[GRAPHSIZE][GRAPHSIZE];
void floydWarshall();
void getData();
void putResult();
private:
int vertexNum;
int path[GRAPHSIZE][GRAPHSIZE]; //path[i][j] means the last but one vertex in the shortest path from i to j.
long distance[GRAPHSIZE][GRAPHSIZE][GRAPHSIZE]; //distance[i][j][k] means the cost of the shortest path, which has no vertex more than k between.
void initialize();
void putPath(int source, int destination);
};
void Graph::getData()
{
cout << "Please input the vertex number, no more than " << GRAPHSIZE - 1 << ": ";
cin >> vertexNum;
cout << "Please input edge number: ";
int edgenum;
int source, destination,cost;
cin >> edgenum;
while (edgenum--)
{
cin >> source >> destination >> cost;
map[source][destination] = cost;
}
}
void Graph::putPath(int source, int destination)
{
if (source == destination)
{
cout << source;
}
else if (NO_PAHT == path[source][destination])
{
cout << source << " " << destination << " ";
}
else
{
putPath(source, path[source][destination]);
cout << destination << " ";
}
}
void Graph::putResult()
{
int shortest;
for (int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < vertexNum; j++)
{
cout << "From vertex_" << i << " to vertex_" << j << " is: ";
shortest = distance[i][j][0];
for (int k = 1; k <= vertexNum; k++)
{
if (shortest > distance[i][j][k])
{
shortest = distance[i][j][k];
}
}
if (shortest == MAX_INT)
{
cout << "+∞" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << shortest << " Path: ";
putPath(i, j);
cout << endl;
}
}
}
}
void Graph::initialize()
{
for (int i = 0; i < GRAPHSIZE; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < GRAPHSIZE; j++)
{
for (int k = 0; k < GRAPHSIZE; k++)
{
distance[i][j][k] = MAX_INT;
}
map[i][j] = MAX_INT;
if (i == j)
{
map[i][j] = 0;
}
path[i][j] = NO_PAHT;
}
}
getData();
for (int i = 0; i < GRAPHSIZE; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < GRAPHSIZE; j++)
{
distance[i][j][0] = map[i][j];
}
}
}
void Graph::floydWarshall()
{
initialize();
int k, i, j;
for (k = 1; k < vertexNum; k++)
{
for (i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < vertexNum; j++)
{
distance[i][j][k] = distance[i][j][k - 1];
if (distance[i][k][k - 1] != MAX_INT && distance[k][j][k - 1] != MAX_INT && distance[i][j][k] > distance[i][k][k - 1] + distance[k][j][k - 1])
{
distance[i][j][k] = distance[i][k][k - 1] + distance[k][j][k - 1];
path[i][j] = k;
}
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
Graph test;
test.floydWarshall();
test.putResult();
return 0;
}其实,也说到了,可以进行优化,空间上的优化。既是在原来的空间上进行迭代,将空间优化为二维,如下:

代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#define GRAPHSIZE 12
#define MAX_INT 0x7FFFFFFF
#define NO_PAHT -1
using namespace std;
class Graph
{
public:
long map[GRAPHSIZE][GRAPHSIZE];
void floydWarshall();
void getData();
void putResult();
private:
int vertexNum;
int path[GRAPHSIZE][GRAPHSIZE]; //path[i][j] means the last but one vertex in the shortest path from i to j.
long distance[GRAPHSIZE][GRAPHSIZE]; //distance[i][j] means the cost of the shortest path from i to j.
void initialize();
void putPath(int source, int destination);
};
void Graph::getData()
{
cout << "Please input the vertex number, no more than " << GRAPHSIZE - 1 << ": ";
cin >> vertexNum;
cout << "Please input edge number: ";
int edgenum;
int source, destination,cost;
cin >> edgenum;
while (edgenum--)
{
cin >> source >> destination >> cost;
map[source][destination] = cost;
}
}
void Graph::putPath(int source, int destination)
{
if (source == destination)
{
cout << source;
}
else if (NO_PAHT == path[source][destination])
{
cout << source << " " << destination << " ";
}
else
{
putPath(source, path[source][destination]);
cout << destination << " ";
}
}
void Graph::putResult()
{
int shortest;
for (int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < vertexNum; j++)
{
cout << "From vertex_" << i << " to vertex_" << j << " is: ";
shortest = distance[i][j];
if (shortest == MAX_INT)
{
cout << "+∞" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << shortest << " Path: ";
putPath(i, j);
cout << endl;
}
}
}
}
void Graph::initialize()
{
for (int i = 0; i < GRAPHSIZE; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < GRAPHSIZE; j++)
{
distance[i][j] = MAX_INT;
map[i][j] = MAX_INT;
if (i == j)
{
map[i][j] = 0;
}
path[i][j] = NO_PAHT;
}
}
getData();
for (int i = 0; i < GRAPHSIZE; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < GRAPHSIZE; j++)
{
distance[i][j] = map[i][j];
}
}
}
void Graph::floydWarshall()
{
initialize();
int k, i, j;
for (k = 1; k < vertexNum; k++)
{
for (i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < vertexNum; j++)
{
if (distance[i][k] != MAX_INT && distance[k][j] != MAX_INT && distance[i][j] > distance[i][k] + distance[k][j])
{
distance[i][j] = distance[i][k] + distance[k][j];
path[i][j] = k;
}
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
Graph test;
test.floydWarshall();
test.putResult();
return 0;
}





















 848
848

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








