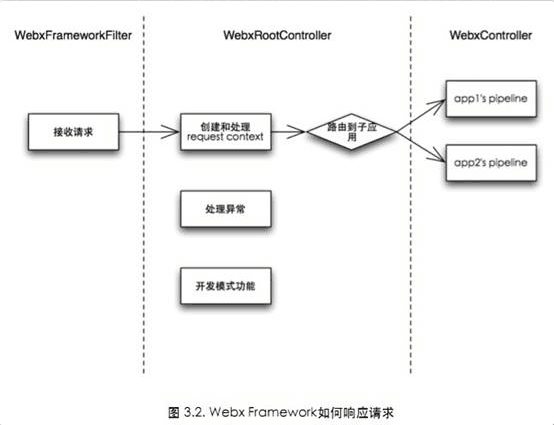
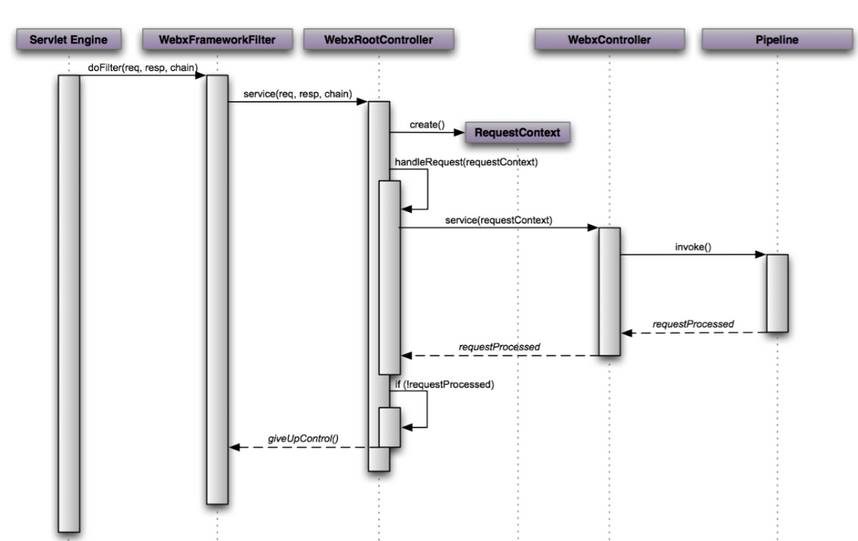
1.整体流程
更为具体的流程为:
在web.xml中可以看到如下配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<web-app version="2.4" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee/web-app_2_4.xsd
">
<!-- 初始化日志系统 -->
<listener>
<listener-class>com.alibaba.citrus.logconfig.LogConfiguratorListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<!-- 装载/WEB-INF/webx.xml, /WEB-INF/webx-*.xml -->
<listener>
<listener-class>com.alibaba.citrus.webx.context.WebxContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<filter>
<filter-name>mdc</filter-name>
<filter-class>com.alibaba.citrus.webx.servlet.SetLoggingContextFilter</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter>
<filter-name>webx</filter-name>
<filter-class>com.alibaba.citrus.webx.servlet.WebxFrameworkFilter</filter-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>excludes</param-name>
<param-value><!-- 需要被“排除”的URL路径,以逗号分隔,如/static, *.jpg。适合于映射静态页面、图片。 --></param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>passthru</param-name>
<param-value><!-- 需要被“略过”的URL路径,以逗号分隔,如/myservlet, *.jsp。适用于映射servlet、filter。
对于passthru请求,webx的request-contexts服务、错误处理、开发模式等服务仍然可用。 --></param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>mdc</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>webx</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
</web-app>2.WebxContextLoaderListener
从上面的webx.ml可以看到里面配置了Listener,所以 先看一下WebxContextLoaderListener
public class WebxContextLoaderListener extends ContextLoaderListener {
@Override
protected final ContextLoader createContextLoader() {
return new WebxComponentsLoader() {
@Override
protected Class<? extends WebxComponentsContext> getDefaultContextClass() {
Class<? extends WebxComponentsContext> defaultContextClass = WebxContextLoaderListener.this
.getDefaultContextClass();
if (defaultContextClass == null) {
defaultContextClass = super.getDefaultContextClass();
}
return defaultContextClass;
}
};
}public class ContextLoaderListener extends ContextLoader implements ServletContextListener {
private ContextLoader contextLoader;
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
this.contextLoader = createContextLoader();
if (this.contextLoader == null) {
this.contextLoader = this;
}
this.contextLoader.initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
}
@Deprecated
protected ContextLoader createContextLoader() {
return null;
}
.......
}1) ContextLoaderListener实现了ServletContextListener接口,并且实现了其中的contextInitialized方法,所以当 ServletContext被创建的时候该方法就会被调用
2)WebxContextLoaderListener重写了createContextLoader方法,生成了WebxComponentsLoader,所以在 ServletContext被创建的时候会调用这个实例的initWebApplicationContext方法
WebxComponentsLoader实际上就是读取bean的配置文件,并实例化相关的bean。(这里由webx框架给我们实例化ApplicationContext,就不用自己再实例化了)
3.WebxFrameworkFilter
webx.ml中配置了这个filter,它的url-mapping对应的是/*,表示任何request都会进入该filter,看下这个filter
@Override
protected void doFilter(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
// 如果指定了excludes,并且当前requestURI匹配任何一个exclude pattern,
// 则立即放弃控制,将控制还给servlet engine。
if (excludeFilter != null && excludeFilter.matches(request)) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
return;
}
try {
getWebxComponents().getWebxRootController().service(request, response, chain);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw e;
} catch (ServletException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new ServletException(e);
}
} 如果当前请求的uri正好匹配,filter就不用处理这个请求那么就直接跳过这个filter(也就是不经过webx了),把控制权交给servlet 引擎
如果当前filter需要处理这个请求,就进入WebxRootController的service方法
4.WebxRootController
public final void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain)
throws Exception {
RequestContext requestContext = null;
try {
requestContext = assertNotNull(getRequestContext(request, response), "could not get requestContext");
if (checkRequest(requestContext)) {
request = requestContext.getRequest();
response = requestContext.getResponse();
RequestHandlerContext ctx = internalHandlerMapping.getRequestHandler(request, response);
if (ctx == null) {
// 如果定义了passthru filter,则判断request是否被passthru,
// 对于需要被passthru的request不执行handleRequest,而直接返回。
// 该功能适用于仅将webx视作普通的filter,而filter chain的接下来的部分将可使用webx所提供的request contexts。
boolean requestProcessed = false;
if (passthruFilter == null || !passthruFilter.matches(request)) {
requestProcessed = handleRequest(requestContext);
}
if (!requestProcessed) {
giveUpControl(requestContext, chain);
}
} else {
ctx.getRequestHandler().handleRequest(ctx);
}
}
}
.....
}requestContext = assertNotNull(getRequestContext(request, response), "could not get requestContext"); if (passthruFilter == null || !passthruFilter.matches(request)) {
requestProcessed = handleRequest(requestContext);
} 看一下这个方法:
protected boolean handleRequest(RequestContext requestContext) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest request = requestContext.getRequest();
String path = ServletUtil.getResourcePath(request);
// 根据path查找component
WebxComponent component = getComponents().findMatchedComponent(path);
boolean served = false;
if (component != null) {
try {
WebxUtil.setCurrentComponent(request, component);
served = component.getWebxController().service(requestContext);
} finally {
WebxUtil.setCurrentComponent(request, null);
}
}
return served;
}
}5.WebxController
public boolean service(RequestContext requestContext) throws Exception {
PipelineInvocationHandle handle = pipeline.newInvocation();
handle.invoke();
// 假如pipeline被中断,则视作请求未被处理。filter将转入chain中继续处理请求。
return !handle.isBroken();
}
6.Pipeline(PipelineImpl)
public class PipelineImpl extends AbstractService<Pipeline> implements Pipeline {
private Valve[] valves;
private String label;
public PipelineInvocationHandle newInvocation() {
return new PipelineContextImpl(null);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return new ToStringBuilder().append(getBeanDescription()).append(valves).toString();
}
/**
* 实现<code>PipelineContext</code>。
*/
private final class PipelineContextImpl implements PipelineContext, PipelineInvocationHandle {
private int executedIndex = -1;
private int executingIndex = -1;
private boolean broken;
public void invokeNext() {
assertInitialized();
if (broken) {
return;
}
try {
executingIndex++;
if (executingIndex <= executedIndex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(descCurrentValve() + " has already been invoked: "
+ valves[executingIndex]);
}
executedIndex++;
if (executingIndex < valves.length) {
Valve valve = valves[executingIndex];
try {
if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {
log.trace("Entering {}: {}", descCurrentValve(), valve);
}
valve.invoke(this);
} catch (PipelineException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new PipelineException("Failed to invoke " + descCurrentValve() + ": " + valve, e);
} finally {
if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {
log.trace("...Exited {}: {}", descCurrentValve(), valve);
}
}
if (executedIndex < valves.length && executedIndex == executingIndex) {
if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {
log.trace("{} execution was interrupted by {}: {}", new Object[] { descCurrentPipeline(),
descCurrentValve(), valve });
}
}
} else {
if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {
log.trace("{} reaches its end.", descCurrentPipeline());
}
}
} finally {
executingIndex--;
}
} private final class PipelineContextImpl implements PipelineContext, PipelineInvocationHandle这里看一下我们如何在代码中调用Pipeline的
@Autowired
private Pipeline myPipeline;
public void invokePipeline() {
PipelineInvocationHandle invocation = myPipeline.newInvocation();
invocation.invoke();
System.out.println(invocation.isFinished());
System.out.println(invocation.isBroken());
} public void invoke() throws IllegalStateException {
assertTrue(!isBroken(), ILLEGAL_STATE, "cannot reinvoke a broken pipeline");
executingIndex = executedIndex = -1;
invokeNext();
} valve.invoke(this);现在有一个问题:一个valve执行完之后,如何执行下一个valve呢?
可以看一个自定的valve怎么实现:
public class MyValve implements Valve {
public void invoke(PipelineContext pipelineContext) throws Exception {
System.out.println("valve started.");
pipelineContext.invokeNext(); // 调用后序valves
System.out.println("valve ended.");
}
}注:
1)PipelineInvocationHandler 表示的是一个valve的执行
2)PipelineImpl 维护了一个valve数组,保存了所有的valve
3)PipelineContext 就是PipelineContextImpl的实现接口之一,代表的是一个valve的执行情况
7.几个重要的Pipeline
(1) 由子应用根据自己的pipeline配置文件(如果有的话,没有就用common子文件夹中的)对请求进行处理
上面是WEB-INF\common目录下的pipeline.xml目录中的pipeline定义。
其中每一个valve都有具体的类与之对应,核心是他们的invoke方法
(2)PrepareForTuibineValve
对应的元素是prepareForTuibine。它用于预备turbine运行时所需要的一些内容,根据request创建并初始化turbine 润达他,并放入pipelineContext,以便valve获得
/**
* 预备turbine运行所需要的一些内容。
*/
public class PrepareForTurbineValve extends AbstractValve {
@Autowired
private HttpServletRequest request;
public void invoke(PipelineContext pipelineContext) throws Exception {
TurbineRunData rundata = getTurbineRunData(request, true);
boolean contextSaved = false;
try {
pipelineContext.setAttribute("rundata", rundata);
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : Utils.getUtils().entrySet()) {
pipelineContext.setAttribute(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
pipelineContext.invokeNext();
} catch (Throwable e) {
saveTurbineRunDataContext(rundata);
contextSaved = true;
if (e instanceof Exception) {
throw (Exception) e;
} else if (e instanceof Error) {
throw (Error) e;
}
} finally {
cleanupTurbineRunData(request, !contextSaved);
}
}
public static class DefinitionParser extends AbstractValveDefinitionParser<PrepareForTurbineValve> {
}
}可以看到这里Valve实现类中的invoke方法中有一个参数PipelineContext,这是在PipelineContextImpl中的invokeNext方法中调用valve.invoke(this)传入的
valve.invoke(this); (3)AnalyzeURLValve
作用是对请求url和参数进行分析,为接下来的screen和action提供基础数据target等
/**
* 根据URL的内容来设置rundata。根据以下规则:
* <ol>
* <li>取得servletPath + pathInfo - componentPath作为target。</li>
* <li>使用MappingRuleService,将target的后缀转换成统一的内部后缀。例如:将jhtml转换成jsp。</li>
* </ol>
*/
public class AnalyzeURLValve extends AbstractValve {
private static final String DEFAULT_ACTION_PARAM_NAME = "action";
public void invoke(PipelineContext pipelineContext) throws Exception {
TurbineRunDataInternal rundata = (TurbineRunDataInternal) getTurbineRunData(request);
String target = null;
// 取得target,并转换成统一的内部后缀名。
String pathInfo = ServletUtil.getResourcePath(rundata.getRequest()).substring(
component.getComponentPath().length());
if ("/".equals(pathInfo)) {
pathInfo = getHomepage();
}
// 注意,必须将pathInfo转换成camelCase。
int lastSlashIndex = pathInfo.lastIndexOf("/");
if (lastSlashIndex >= 0) {
pathInfo = pathInfo.substring(0, lastSlashIndex) + "/"
+ StringUtil.toCamelCase(pathInfo.substring(lastSlashIndex + 1));
} else {
pathInfo = StringUtil.toCamelCase(pathInfo);
}
target = mappingRuleService.getMappedName(EXTENSION_INPUT, pathInfo);
rundata.setTarget(target);
// 取得action
String action = StringUtil.toCamelCase(trimToNull(rundata.getParameters().getString(actionParam)));
action = mappingRuleService.getMappedName(ACTION_MODULE, action);
rundata.setAction(action);
// 取得actionEvent
String actionEvent = ActionEventUtil.getEventName(rundata.getRequest());
rundata.setActionEvent(actionEvent);
pipelineContext.invokeNext();
}
public static class DefinitionParser extends AbstractValveDefinitionParser<AnalyzeURLValve> {
@Override
protected void doParse(Element element, ParserContext parserContext, BeanDefinitionBuilder builder) {
attributesToProperties(element, builder, "homepage", "actionParam");
}
}
}在这之后AnalyURLValve做了3件事
1)rundata.setTarget(target):向rundata中设置target,target作为screen的选择依据
2)rundata.setAction(action):向rundata中设置action,action标识了表单提交的处理类
3)rundata.setActionEvent(actionEvent):向rundata中设置actionEvent,actionEvent标识了表单处理类的方法名称
target和action的确定是mappingRuleService根据mappingRule从url和请求参数中获取并对应得到的。事实上,这些都是配置好的,mappingRuleService是webx内置的AbstractService,名称查找规则的配置通过SpringExt加载。
看一个配置webx-componet-and-root.xml:
<!-- 名称查找规则。 -->
<services:mapping-rules>
<!-- External target name => Internal target name -->
<mapping-rules:extension-rule id="extension.input">
<!-- 默认后缀 -->
<mapping extension="" to="" />
<!-- JSP -->
<mapping extension="jhtml" to="" />
<mapping extension="jsp" to="" />
<mapping extension="jspx" to="" />
<mapping extension="php" to="" />
<!-- Velocity -->
<mapping extension="htm" to="" />
<mapping extension="vhtml" to="" />
<mapping extension="vm" to="" />
</mapping-rules:extension-rule>
<!-- Internal target name => External target name -->
<mapping-rules:extension-rule id="extension.output">
<!-- 默认后缀 -->
<mapping extension="" to="htm" />
<!-- JSP -->
<mapping extension="jhtml" to="jhtml" />
<mapping extension="jsp" to="jhtml" />
<mapping extension="jspx" to="jhtml" />
<mapping extension="php" to="jhtml" />
<!-- Velocity -->
<mapping extension="htm" to="htm" />
<mapping extension="vhtml" to="htm" />
<mapping extension="vm" to="htm" />
</mapping-rules:extension-rule>
<!-- Target name => Action module name -->
<mapping-rules:direct-module-rule id="action" />
<!-- Target name => Screen module name (*.do) -->
<mapping-rules:direct-module-rule id="screen.notemplate" />
<!-- Target name => Screen module name (*.jsp, *.vm) -->
<mapping-rules:fallback-module-rule id="screen" moduleType="screen" />
<!-- Target name => Screen template name -->
<mapping-rules:direct-template-rule id="screen.template" templatePrefix="screen" />
<!-- Target name => Layout template name -->
<mapping-rules:fallback-template-rule id="layout.template" templatePrefix="layout" />
<!-- Target name => Control module name (setControl method) -->
<mapping-rules:direct-module-rule id="control.notemplate" />
<!-- Target name => Control module name (setTemplate method) -->
<mapping-rules:fallback-module-rule id="control" moduleType="control" />
<!-- Target name => Control template name -->
<mapping-rules:direct-template-rule id="control.template" templatePrefix="control" />
</services:mapping-rules> <direct-module-rule>标签对应的处理类是DirectModuleMappingRule,规则是对传入的String中的"/"替换为".",并且将action的名称规范化。例如传入supplier/supplierAuditAction,返回supplier.SupplierAuditAction
actionEvent的提取在ActionEventUtil.getEventName(HttpServletRequest)工具类中是吸纳,它会对event_submit_do开头的请求参数进行截断,取出后面的字符串作为actionEvent。例如请求参数中有event_submit_do_first_audit,那么返回的actionEvent是FirstAudit
(4)CheckCsrfTokenValve
用于检查csrf token,防止csrf攻击和重复提交。假如request和session中的token不匹配,则出错,或显示expired页面
(5)LoopValve
用于反复执行同一个Pipeline。LoopValve是一个带有子流程的valve(持有一个Pipeline引用),并且内部的valve可以循环调用。只要调用过程中没有中断handle.isBroken()判断,就会一直调用直到超过最大循环次数:10,抛出异常
/**
* 用来反复执行同一个子pipeline。
*
* @author Michael Zhou
*/
public class LoopValve extends AbstractValve {
private final static int DEFAULT_MAX_LOOP = 10;
private final static String DEFAULT_LOOP_COUNTER_NAME = "loopCount";
private Pipeline loopBody;
private Integer maxLoopCount;
private String loopCounterName;
public void invoke(PipelineContext pipelineContext) throws Exception {
assertInitialized();
PipelineInvocationHandle handle = initLoop(pipelineContext);
do {
invokeBody(handle);
} while (!handle.isBroken());
pipelineContext.invokeNext();
}
protected void invokeBody(PipelineInvocationHandle handle) {
String loopCounterName = getLoopCounterName();
int loopCount = (Integer) handle.getAttribute(loopCounterName);
int maxLoopCount = getMaxLoopCount();
// maxLoopCount<=0,意味着没有循环次数的限制。
if (maxLoopCount > 0 && loopCount >= maxLoopCount) {
throw new TooManyLoopsException("Too many loops: exceeds the maximum count: " + maxLoopCount);
}
handle.invoke();
handle.setAttribute(loopCounterName, ++loopCount);
}
}
(6)BreakUnlessTargetRedirectedValve
这是LoopValve中最后一个valve,用于在内部重定向页面时是否退出循环
public class BreakUnlessTargetRedirectedValve extends BreakValve {
@Autowired
private HttpServletRequest request;
@Override
public void invoke(PipelineContext pipelineContext) throws Exception {
TurbineRunDataInternal rundata = (TurbineRunDataInternal) getTurbineRunData(request);
String target = rundata.getTarget();
String redirectTarget = rundata.getRedirectTarget();
if (!isEmpty(redirectTarget) && !isEquals(target, redirectTarget)) {
rundata.setTarget(redirectTarget);
rundata.setRedirectTarget(null);
pipelineContext.invokeNext();
} else {
super.invoke(pipelineContext);
}
}
} (7)PerformActionValve
执行action modult,通常用来处理用户提交的表单
public class PerformActionValve extends AbstractValve {
@Autowired
private HttpServletRequest request;
@Autowired
private ModuleLoaderService moduleLoaderService;
public void invoke(PipelineContext pipelineContext) throws Exception {
TurbineRunData rundata = getTurbineRunData(request);
// 检查重定向标志,如果是重定向,则不需要将页面输出。
if (!rundata.isRedirected()) {
String action = rundata.getAction();
// 如果找到action,则执行之。
if (!StringUtil.isEmpty(action)) {
String actionKey = "_action_" + action;
// 防止重复执行同一个action。
if (rundata.getRequest().getAttribute(actionKey) == null) {
rundata.getRequest().setAttribute(actionKey, "executed");
try {
moduleLoaderService.getModule(ACTION_MODULE, action).execute();
} catch (ModuleLoaderException e) {
throw new PipelineException("Could not load action module: " + action, e);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new PipelineException("Failed to execute action module", e);
}
}
}
}
pipelineContext.invokeNext();
}
}ModuleLoaderServiceImpl通过ModuleFactory来实际加载module,而ModuleFactory是通过spring初始化时注入的各个模块,所以我们需要在webx.xml中配置模块的路径
ModuleLoaderServiceImpl对web层的action/screen/control等包进行扫描,自动加载到ioc中。要搜索的包名(可以用*通配符)在xml中配置。然后建立module key和module之间的关系。
(8)PerformTemplateScreenValve
用于执行screen的渲染类。invoke()的实现在其父类PerformScreenValve中。先取出rundata,如果重定向了,则不执行screen类,否则设置content-type为text/html,通过randata获取target,getScreenModule()通过target找到对应的screen module,调用execute()执行它
























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








