---------------------- ASP.Net+Android+IO开发S、.Net培训、期待与您交流! ----------------------
 死锁
死锁
死锁(开发过程中要避免死锁)
同步中嵌套同步。
为了透彻了解死锁,下面写一个死锁程序:
class Test implements Runnable{
private boolean flag;
Test(boolean flag){
this.flag = flag;
}
public void run(){
if(flag==true){
synchronized(MyLock.lockA){
System.out.println("if lockA");
synchronized(MyLock.lockB){
System.out.println("if lockB");
}
}
}else{
synchronized(MyLock.lockB){
System.out.println("else lockB");
synchronized(MyLock.lockA){
System.out.println("else lockA");
}
}
}
}
}
class MyLock{
public static Object lockA = new Object();
public static Object lockB = new Object();
}
class DeadLockDemo{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Thread t1 = new Thread(new Test(true));
Thread t2 = new Thread(new Test(false));
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
 线程间通信
线程间通信
线程之间的通讯:
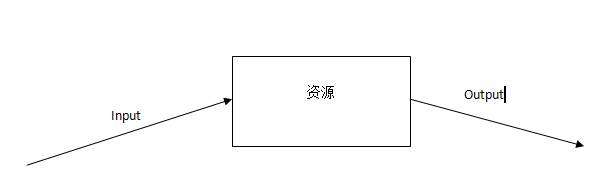
其实就是多个线程在操作同一个资源,但是操作的动作不同。
class Res{
String name;
String sex;
}
class Input implements Runnable{
private Res r;
Input(Res r){
this.r = r;
}
public void run(){
int x = 0;
while (true)
{
if(x==0){
r.name = "Tom";
r.sex = "man";
}else
{
r.name = "春丽";
r.sex = "女";
}
x = (x+1)%2;
}
}
}
class Output implements Runnable{
private Res r;
Output(Res r){
this.r = r;
}
public void run(){
while (true)
{
System.out.println(r.name+"----"+r.sex);
System.out.println(r.name+"----"+r.sex);
}
}
}
class InputOutputDemo{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Res res = new Res();
Input in = new Input(res);
Output out = new Output(res);
Thread t1 = new Thread(in);
Thread t2 = new Thread(out);
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
 这该怎么办吖.
这该怎么办吖.
class Res{
String name;
String sex;
}
class Input implements Runnable{
private Res r;
Input(Res r){
this.r = r;
}
public void run(){
int x = 0;
while (true)
{
synchronized(r){
if(x==0){
r.name = "Tom";
r.sex = "man";
}else
{
r.name = "春丽";
r.sex = "女";
}
}
x = (x+1)%2;
}
}
}
class Output implements Runnable{
private Res r;
Output(Res r){
this.r = r;
}
public void run(){
while (true)
{
synchronized(r){
System.out.println(r.name+"----"+r.sex);
}
}
}
}
class InputOutputDemo{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Res res = new Res();
Input in = new Input(res);
Output out = new Output(res);
Thread t1 = new Thread(in);
Thread t2 = new Thread(out);
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
虽然正常了,但是打印不爽。要是存一个打印一个就好。。。
wait();
notify();
notifyAll();
都使用在同步中:
因为要对持有监视器(锁)的线程操作;所以要使用在同步中,因为只有同步才具有锁。
为什么这些操作线程的方法要定义Object类中呢?
1.因为这些方法在操作同步中线程时,都必须要标识它们所操作线程只有锁。
2.只有同一个锁上的被等待线程,可以被同一个锁上notify唤醒。
3.不可以对不同锁中的线程进行唤醒。
也就是说,等待和唤醒必须是同一个锁。
而锁可以是任意对象,所以可以被任意对象调用的方法定义Object类中。
class Res{
private String name;
private String sex;
boolean flag = false;
public synchronized void set(String name,String sex){
if(flag)
try{this.wait();}catch(Exception e){}
this.name = name;
this.sex = sex;
flag = true;
this.notify();
}
public synchronized void out(){
if(!flag)
try{this.wait();}catch(Exception e){}
System.out.println("name:"+name+"----sex:"+sex);
flag = false;
this.notify();
}
}
class Input implements Runnable{
private Res r;
Input(Res r){
this.r = r;
}
public void run(){
int x = 0;
while(true){
if(x==0)
r.set("Tom","Man");
else
r.set("春丽","女");
x=(x+1)%2;
}
}
}
class Output implements Runnable{
private Res r;
Output(Res r){
this.r = r;
}
public void run(){
while(true){
r.out();
}
}
}
class InputOutputDemo{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Res res = new Res();
new Thread(new Input(res)).start();
new Thread(new Output(res)).start();
}
}
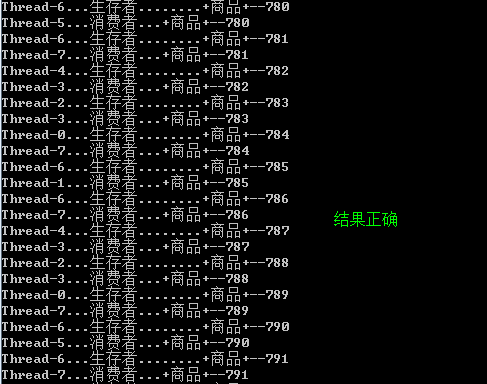
消费者,生产者问题小程序:
class Resourse{
private String name;
private int count = 1;
private boolean flag = false;
public synchronized void set(String name){
while(flag)
try
{
this.wait();
}
catch (Exception e){}
this.name = name+"--"+count++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"...生存者........"+this.name);
flag = true;
this.notifyAll();
}
public synchronized void out(){
while(!flag)
try
{
this.wait();
}
catch (Exception e){}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"...消费者..."+this.name);
flag = false;
this.notifyAll();
}
}
class Producer implements Runnable{
Producer(Resourse res){
this.res = res;
}
private Resourse res ;
public void run(){
while(true){
res.set("+商品+");
}
}
}
class Consumer implements Runnable{
Consumer(Resourse res){
this.res = res;
}
private Resourse res;
public void run(){
while(true){
res.out();
}
}
}
class ProducerConsumerDemo{
public static void main(String[] args){
Resourse res = new Resourse();
new Thread(new Producer(res)).start();
new Thread(new Consumer(res)).start();
new Thread(new Producer(res)).start();
new Thread(new Consumer(res)).start();
new Thread(new Producer(res)).start();
new Thread(new Consumer(res)).start();
new Thread(new Producer(res)).start();
new Thread(new Consumer(res)).start();
}
}
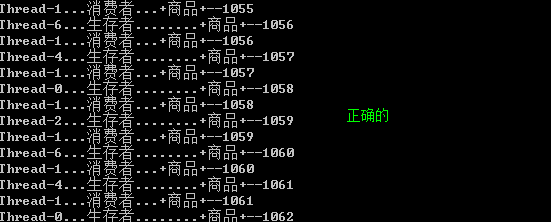
JDK 1.5中提供了多线程升级解决方案。
将同步synchronized替换成现实Lock操作。
将Object中的wait,notify,notifyAll,替换了Condition对象。
该对象可以Lock锁 进行获取。
该示例中,实现了本方只唤醒对方操作。
import java.util.concurrent.locks.*;
class Resourse {
private String name;
private int count = 1;
private boolean flag = false;
private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
private Condition condition_pro = lock.newCondition();
private Condition condition_con = lock.newCondition();
public void set(String name) throws InterruptedException {
lock.lock();
try {
while (flag)
condition_pro.await();
this.name = name + "--" + count++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ "...生存者........" + this.name);
flag = true;
condition_con.signal();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public synchronized void out() throws InterruptedException {
lock.lock();
try {
while (!flag)
condition_con.await();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "...消费者..."
+ this.name);
flag = false;
condition_pro.signal();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
class Producer implements Runnable {
Producer(Resourse res) {
this.res = res;
}
private Resourse res;
public void run() {
while (true) {
try {
res.set("+商品+");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
}
}
class Consumer implements Runnable {
Consumer(Resourse res) {
this.res = res;
}
private Resourse res;
public void run() {
while (true) {
try {
res.out();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
}
}
class ProducerConsumerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Resourse res = new Resourse();
new Thread(new Producer(res)).start();
new Thread(new Consumer(res)).start();
new Thread(new Producer(res)).start();
new Thread(new Consumer(res)).start();
new Thread(new Producer(res)).start();
new Thread(new Consumer(res)).start();
new Thread(new Producer(res)).start();
new Thread(new Consumer(res)).start();
}
}---------------------- ASP.Net+Android+IOS开发、.Net培训、期待与您交流! ----------------------
详情请查看:http://edu.csdn.net























 371
371











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








