最近在做人头统计方面的研究,尝试了多种办法,其中包括Adaboost+Haar特征、HOG特征+线性SVM两大模型。SVM+HOG的模型之前多数被应用于行人检测,我在做人头统计的过程中考虑到人头的边缘形状比较明显,图像梯度比较容易提取,所以将该方法搬到人头统计上来,效果还不错。不足之处是多尺度的HOG计算太慢了,难以达到实时性要求,所以我采用的多数是单尺度检测(64*64的固定窗口大小)。
我现在的工作只是做了个入门,本文意在抛砖引玉,希望感兴趣的小伙伴能够一起研究。
1、预处理
从视频中采集了1416个人头正样本,以及1957个负样本。正样本主要就是人头部(头发)的图像,负样本是不包括人头目标的图像。然后将它们统一归一化到64*64的大小(我这里为了简化训练过程,将人头图像的大小设置为和窗口大小一致)。
2、人头训练
开发环境是winxp+vs2008+opencv2.3.1。训练代码主要包括MySVM.h,global.h和global.cpp三个文件。其中MySVM.h是SVM类定义文件,global.h和global.cpp分别是全局函数声明和定义文件。
(1)MySVM.h如下:
#pragma once
#ifndef _MYSVM_H_
#define _MYSVM_H_
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/ml/ml.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
using namespace cv;
class MySVM: public CvSVM
{
public:
int get_alpha_count()
{
return this->sv_total;
}
int get_sv_dim()
{
return this->var_all;
}
int get_sv_count()
{
return this->decision_func->sv_count;
}
double* get_alpha()
{
return this->decision_func->alpha;
}
float** get_sv()
{
return this->sv;
}
float get_rho()
{
return this->decision_func->rho;
}
};
#endif#include "MySVM.h"
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
using namespace std;
//函数名:Train
//函数功能:SVM训练每张图片的HOG特征
//参数说明:
//const char* positivePath:正样本路径
//int pCount:正样本个数
//const char* negativePath:负样本路径
//int nCount:负样本个数
//const char* classifierSavePath:分类器保存路径
//const char* detectorSavePath:检测器保存路径
//返回bool:训练是否成功(true:成功,false:失败)
bool Train(const char* positivePath, int pCount, const char* negativePath, int nCount,
const char* classifierSavePath, const char* detectorSavePath);
//函数名:CalDimension
//函数功能:计算每张图片的HOG特征维度
//参数说明:
//CvSize winSize:窗口大小
//CvSize blockSize:块大小
//CvSize blockStride:块位移大小
//CvSize cellSize:胞元大小
//int nbins:bin数
//返回int:HOG特征维度
//参考计算方式详细:http://blog.csdn.net/carson2005/article/details/7782726
//参考参数说明详细:http://blog.csdn.net/raodotcong/article/details/6239431
int CalDimension(CvSize winSize, CvSize blockSize, CvSize blockStride, CvSize cellSize, int nbins);
//函数名:DetectMulti
//函数功能:用SVM+HOG分类器对图片做多尺度检测
//参数说明:
//const char* detectorSavePath:检测器保存路径
//const char* testPath:测试视频路径
//返回bool:检测是否成功(true:成功,false:失败)
bool DetectMulti(const char* detectorSavePath, const char* testPath);
//函数名:DetectSingle
//函数功能:用SVM+HOG分类器对图片做单尺度检测
//参数说明:
//const char* detectorSavePath:检测器保存路径
//const char* testPath:测试视频路径
//返回bool:检测是否成功(true:成功,false:失败)
bool DetectSingle(const char* classifierSavePath, const char* testPath);#include "global.h"
///参数设置///
CvSize winSize = cvSize(64, 64); //等于训练样本图像大小
CvSize blockSize = cvSize(16, 16); //block size
CvSize blockStride = cvSize(8, 8); //block stride
CvSize winStride = cvSize(8, 8); //window stride
CvSize cellSize = cvSize(8, 8); //cell size
int nbins = 9; //一般取9个梯度方向
函数定义//
int CalDimension(CvSize winSize, CvSize blockSize, CvSize blockStride, CvSize cellSize, int nbins)
{
//一个窗口(winSize)内宽和高方向分别有多少个块(blockSize)
//int hBlockNum = (winSize.height - 1) / cellSize.height;
//int wBlockNum = (winSize.width - 1) / cellSize.width;
int hBlockNum = (winSize.height - blockSize.height) / blockStride.height + 1;
int wBlockNum = (winSize.width - blockSize.width) / blockStride.width + 1;
//一个块(blockSize)里面有多少个单元(cellSize)
int hCellNum = blockSize.height / cellSize.height;
int wCellNum = blockSize.width / cellSize.width;
//一个单元(cellSize)里面有多少HOG特征维度
int hogNum = nbins;
//计算一个窗口的HOG特征维度:block的个数 * block内部cell的个数 * 每个cell的HOG特征维度
int totalHogNum = (hBlockNum * wBlockNum) * (hCellNum * wCellNum) * hogNum;
return totalHogNum;
}
bool Train(const char* positivePath, int pCount, const char* negativePath, int nCount,
const char* classifierSavePath, const char* detectorSavePath)
{
cout<<"******************** Train ********************"<<endl;
//首先计算图像的HOG特征维度
int dim = CalDimension(winSize, blockSize, blockStride, cellSize, nbins);
int totalCount = pCount + nCount;
cout<<"1: Start trainning for SVM:"<<endl;
cout<<"total samples: "<<totalCount<<endl;
cout<<"positive samples: "<<pCount<<endl;
cout<<"negative samples: "<<nCount<<endl;
cout<<"feature dimension is: "<<dim<<endl<<endl;
//训练正样本
cout<<"2: Start to train positive samples:"<<endl;
CvMat *sampleFeaturesMat = cvCreateMat(totalCount , dim, CV_32FC1);
//64*128的训练样本,该矩阵将是totalSample*3780
//64*64的训练样本,该矩阵将是totalSample*1764
cvSetZero(sampleFeaturesMat);
CvMat *sampleLabelMat = cvCreateMat(totalCount, 1, CV_32FC1);//样本标识
cvSetZero(sampleLabelMat);
char positiveImgPath[256];
for(int i=0; i<pCount; i++)
{
//载入图像
sprintf(positiveImgPath, "%s%d.bmp", positivePath, i);
string strPosPath(positiveImgPath);
cv::Mat img = cv::imread(strPosPath);
if( img.data == NULL )
{
cout<<"positive image sample load error: "<<i<<" "<<strPosPath<<endl;
//return false;
//system("pause");
continue;
}
cv::HOGDescriptor hog(winSize, blockSize, blockStride, cellSize, nbins);
vector<float> featureVec;
hog.compute(img, featureVec, winStride); //计算HOG特征向量
int featureVecSize = featureVec.size();
//加上类标,转化为CvMat
for (int j=0; j<featureVecSize; j++)
{
CV_MAT_ELEM( *sampleFeaturesMat, float, i, j ) = featureVec[j];
}
sampleLabelMat->data.fl[i] = 1;
}
cout<<"End of training for positive samples."<<endl<<endl;
//训练负样本
cout<<"3: Start to train negative samples: "<<endl;
char negativeImgPath[256];
for (int i=0; i<nCount; i++)
{
//载入图像
sprintf(negativeImgPath, "%s%d.bmp", negativePath, i);
string strNegPath(negativeImgPath);
cv::Mat img = cv::imread(strNegPath);
if(img.data == NULL)
{
cout<<"negative image sample load error: "<<strNegPath<<endl;
//return false;
//system("pause");
continue;
}
cv::HOGDescriptor hog(winSize, blockSize, blockStride, cellSize, nbins);
vector<float> featureVec;
hog.compute(img,featureVec, winStride);//计算HOG特征向量
int featureVecSize = featureVec.size();
for ( int j=0; j<featureVecSize; j ++)
{
CV_MAT_ELEM( *sampleFeaturesMat, float, i + pCount, j ) = featureVec[ j ];
}
sampleLabelMat->data.fl[ i + pCount ] = -1;
}
cout<<"End of training for negative samples."<<endl<<endl;
//SVM训练
cout<<"4: Start to train SVM classifier: "<<endl;
//设置SVM参数
CvSVMParams params;
int iteration = 1000;
double penaltyFactor = 0.01;
params.svm_type = CvSVM::C_SVC;
params.kernel_type = CvSVM::LINEAR;
params.term_crit = cvTermCriteria(CV_TERMCRIT_ITER, iteration, FLT_EPSILON);
params.C = penaltyFactor;
//print
cout<<"svm_type: C_SVC\nkernel_type: LINEAR\ntermination type: CV_TERMCRIT_ITER"
<<"\ntermination iteration: "<<iteration<<"\ntermination epsilon: "<<FLT_EPSILON
<<"\npenalty factor: "<<penaltyFactor<<endl;
MySVM svm;
svm.train( sampleFeaturesMat, sampleLabelMat, NULL, NULL, params ); //用线性SVM分类器训练
svm.save(classifierSavePath); //将SVM训练完的数据保存到指定的文件中
cvReleaseMat(&sampleFeaturesMat);
cvReleaseMat(&sampleLabelMat);
int supportVectorSize = svm.get_support_vector_count();
cout<<"\nsupport vector size of SVM:"<<supportVectorSize<<endl;
cout<<"End of training SVM classifier."<<endl<<endl;
//保存用于检测的HOG特征
cout<<"5. Save SVM detector file: "<<endl;
CvMat *sv,*alp,*re;//所有样本特征向量
sv = cvCreateMat(supportVectorSize , dim, CV_32FC1);
alp = cvCreateMat(1 , supportVectorSize, CV_32FC1);
re = cvCreateMat(1 , dim, CV_32FC1);
CvMat *res = cvCreateMat(1 , 1, CV_32FC1);
cvSetZero(sv);
cvSetZero(re);
for(int i=0; i<supportVectorSize; i++)
{
memcpy( (float*)(sv->data.fl+i*dim), svm.get_support_vector(i), dim*sizeof(float));
}
double* alphaArr = svm.get_alpha();
int alphaCount = svm.get_alpha_count();
for(int i=0; i<supportVectorSize; i++)
{
alp->data.fl[i] = alphaArr[i];
}
cvMatMul(alp, sv, re);
int posCount = 0;
for (int i=0; i<dim; i++)
{
re->data.fl[i] *= -1;
}
//保存为文本文件
FILE* fp = fopen(detectorSavePath,"wb");
if( NULL == fp )
{
return false;
}
for(int i=0; i<dim; i++)
{
fprintf(fp,"%f \n",re->data.fl[i]);
}
float rho = svm.get_rho();
fprintf(fp, "%f", rho);
fclose(fp);
cout<<"Save "<<detectorSavePath<<" OK!"<<endl;
return true;
}
//使用detectMultiScale检测
bool DetectMulti(const char* detectorSavePath, const char* testPath)
{
cout<<"\n******************** Detection Multi********************"<<endl;
CvCapture* cap = cvCreateFileCapture(testPath);
if (!cap)
{
cout<<"avi file load error..."<<endl;
return false;
}
vector<float> x;
ifstream fileIn(detectorSavePath, ios::in);
float val = 0.0f;
while(!fileIn.eof())
{
fileIn>>val;
x.push_back(val);
}
fileIn.close();
vector<cv::Rect> found;
cv::HOGDescriptor hog(winSize, blockSize, blockStride, cellSize, nbins);
hog.setSVMDetector(x);
IplImage* img = NULL;
cvNamedWindow("img", 0);
cvNamedWindow("video", 0);
int frameCount = 0;
double timeSum = 0.0;
while(img=cvQueryFrame(cap))
{
cvShowImage("video", img);
frameCount++;
double begin = clock();
hog.detectMultiScale(img, found, 0, winStride, cv::Size(0,0), 1.05, 2);
double end = clock();
double diff = (end-begin)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC*1000;
timeSum += diff;
cout<< "Detection time is: "<<diff<<"ms"<<endl;
if (found.size() > 0)
{
for (int i=0; i<found.size(); i++)
{
CvRect tempRect = cvRect(found[i].x, found[i].y, found[i].width, found[i].height);
cvRectangle(img, cvPoint(tempRect.x,tempRect.y),
cvPoint(tempRect.x+tempRect.width,tempRect.y+tempRect.height),CV_RGB(255,0,0), 2);
}
}
cvShowImage("img", img);
if (cvWaitKey(1) == 27)
{
break;
}
}
cvReleaseCapture(&cap);
cout<< "Average detection time is: "<<timeSum / frameCount<<"ms"<<endl;
return true;
}
//使用detect检测
bool DetectSingle(const char* detectorSavePath, const char* testPath)
{
cout<<"\n******************** Detection Single********************"<<endl;
CvCapture* cap = cvCreateFileCapture(testPath);
if (!cap)
{
cout<<"avi file load error..."<<endl;
return false;
}
vector<float> x;
ifstream fileIn(detectorSavePath, ios::in);
float val = 0.0f;
while(!fileIn.eof())
{
fileIn>>val;
x.push_back(val);
}
fileIn.close();
vector<cv::Point> found;
cv::HOGDescriptor hog(winSize, blockSize, blockStride, cellSize, nbins);
hog.setSVMDetector(x);
IplImage* img = NULL;
cvNamedWindow("img", 0);
cvNamedWindow("video", 0);
int frameCount = 0;
double timeSum = 0.0;
while(img=cvQueryFrame(cap))
{
cvShowImage("video", img);
frameCount++;
double begin = clock();
//检测:found为检测目标的左上角坐标点
hog.detect(img, found, 0, winStride, cvSize(0,0));
double end = clock();
double diff = (end-begin)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC*1000;
timeSum += diff;
cout<< "Detection time is: "<<diff<<"ms"<<endl;
if (found.size() > 0)
{
for (int i=0; i<found.size(); i++)
{
CvRect tempRect = cvRect(found[i].x, found[i].y, winSize.width, winSize.height);
cvRectangle(img, cvPoint(tempRect.x,tempRect.y),
cvPoint(tempRect.x+tempRect.width,tempRect.y+tempRect.height),CV_RGB(255,0,0), 2);
}
}
cvShowImage("img", img);
if (cvWaitKey(1) == 27)
{
break;
}
}
cvReleaseCapture(&cap);
cout<< "Average detection time is: "<<timeSum / frameCount<<"ms"<<endl;
return true;
}主文件main.cpp如下:
#include "global.h"
//SVM分类器文件
const char* classifierSavePath = ".\\HOG_SVM.xml";
//HOG检测器文件
const char* detectorSavePath = ".\\HogDetector.txt";
//正负样本存储路径
const char* positivePath = ".\\pos_64_64\\";
const char* negativePath = ".\\neg_64_64\\";
//正负样本数目
const int pCount = 1416;
const int nCount = 1957;
//测试视频文件路径
const char* testVideoPath = ".\\test.avi";
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
bool flag;
训练
flag = Train(positivePath, pCount, negativePath, nCount, classifierSavePath, detectorSavePath);
if (!flag)
{
cout<<"Train error!\n";
return -1;
}
检测-单尺度///
flag = DetectSingle(detectorSavePath, testVideoPath);
if (!flag)
{
cout<<"Detection error!\n";
return -1;
}
检测-多尺度///
//flag = DetectMulti(detectorSavePath, testVideoPath);
//if (!flag)
//{
// cout<<"Detection error!\n";
// return -1;
//}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
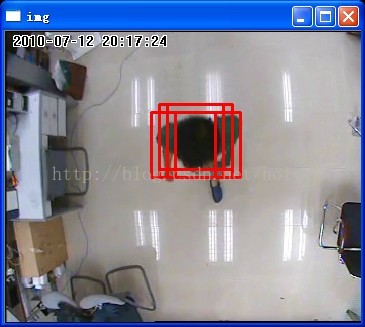
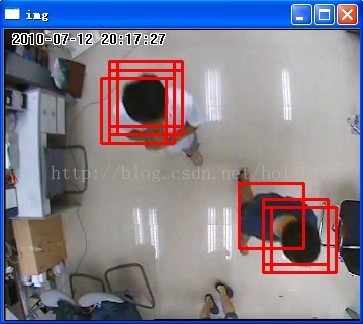
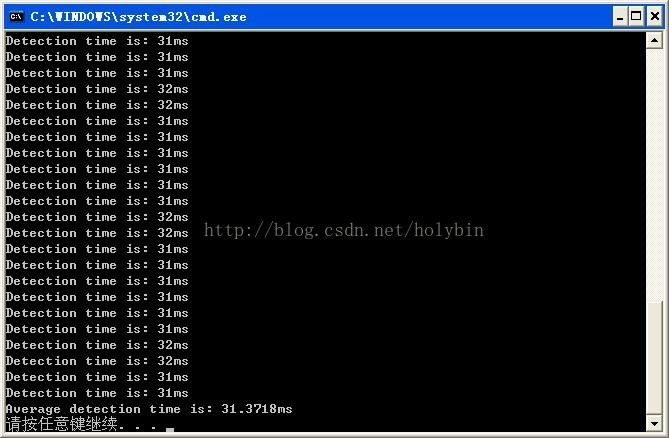
采集528幅图像使用xml分类器文件进行分类,一般识别准确率在99%左右;但是在对视频(CIF)做检测的时候,由于是滑动窗口的检测机制,准确率达不到这么高,大概有95%上下,每帧时间大概是31ms上下。除此之外,对于高分辨率视频的检测速度以及误检是个问题:误检主要是将静止物体识别为人头,或者是阴影的干扰,将非人头的运动物体识别为人头的情况比较少。下一步打算使用别的特征采取特征的融合,或者是结合背景建模去除静止物体等方法进行尝试,此外阴影消除算法也在考虑之列。
运行时间截图:
说明:
1、在training的时候一般把sample大小设置成窗口大小一样,开始可能需要resize sample(为了处理多尺度问题,可以使用multi-scale hog feature,然后用PCA降维)。
2、最后对检测出来的目标矩形框可能有多个,要采用一些方法如矩形合并法来处理,比如说多个目标框嵌套着,如果其中一个矩形框的中心在另一个矩形框中,则将这两个矩形框合并起来,直到最后合并到一个矩形框。这里的校正系数group_threshold(参考groupRectangles()函数)也能起到辅助找最合适的目标矩形框的作用。
3、因为hog检测出的矩形框比实际人体框要稍微大些,所以需要对这些矩形框大小尺寸做一些调整,比如更改参数scale0的值。























 1688
1688

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








