博客地址:http://blog.csdn.net/ikerpeng/article/details/20523679
首先补充以下:7种颜色 r g b y m c k (红,绿,蓝,黄,品红,青,黑)
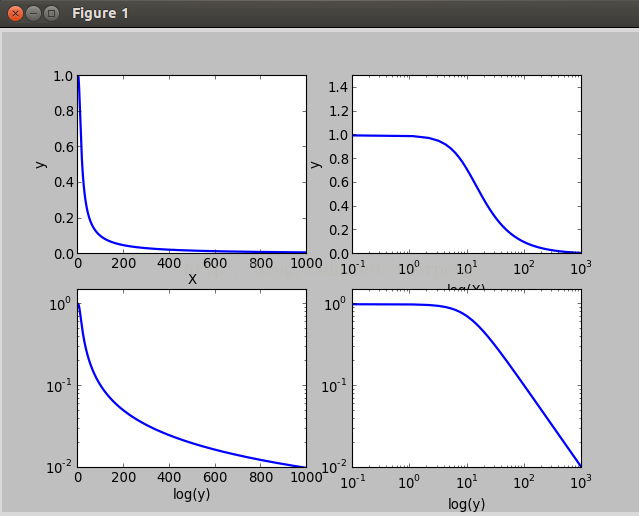
在科研的过程中,坐标系中的XY不一定就是等尺度的。例如在声波中对Y轴取对数。肆意我们也必须知道这种坐标系如何画出来的。
1,对数坐标图
有3个函数可以实现这种功能,分别是:semilogx(),semilogy(),loglog()。它们分别表示对X轴,Y轴,XY轴取对数。下面在一个2*2的figure里面来比较这四个子图(还有plot())。
1 import numpy as np
2 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
3 w=np.linspace(0.1,1000,1000)
4 p=np.abs(1/(1+0.1j*w))
5
6 plt.subplot(221)
7 plt.plot(w,p,lw=2)
8 plt.xlabel('X')
9 plt.ylabel('y')
10
11
12 plt.subplot(222)
13 plt.semilogx(w,p,lw=2)
14 plt.ylim(0,1.5)
15 plt.xlabel('log(X)')
16 plt.ylabel('y')
17
18 plt.subplot(223)
19 plt.semilogy(w,p,lw=2)
20 plt.ylim(0,1.5)
21 plt.xlabel('x')
22 plt.xlabel('log(y)')
23
24 plt.subplot(224)
25 plt.loglog(w,p,lw=2)
26 plt.ylim(0,1.5)
27 plt.xlabel('log(x)')
28 plt.xlabel('log(y)')
29 plt.show()
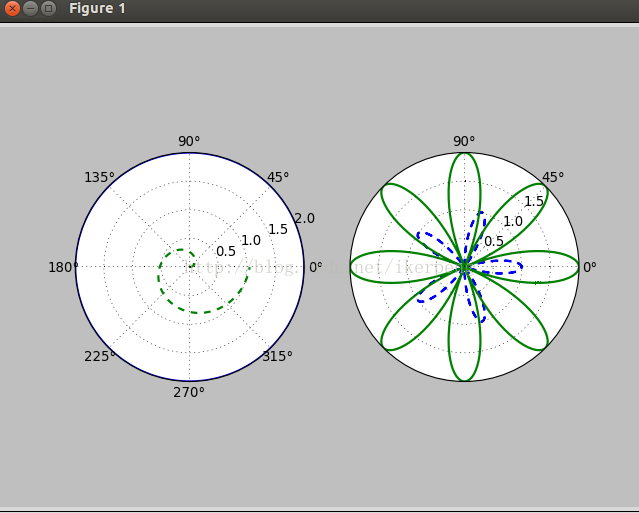
2,极坐标图像
极坐标系中的点由一个夹角和一段相对于中心位置的距离来表示。其实在plot()函数里面本来就有一个polar的属性,让他为True就行了。下面绘制一个极坐标图像:
1 import numpy as np
2 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
3
4 theta=np.arange(0,2*np.pi,0.02)
5
6 plt.subplot(121,polar=True)
7 plt.plot(theta,2*np.ones_like(theta),lw=2)
8 plt.plot(theta,theta/6,'--',lw=2)
9
10 plt.subplot(122,polar=True)
11 plt.plot(theta,np.cos(5*theta),'--',lw=2)
12 plt.plot(theta,2*np.cos(4*theta),lw=2)
13 plt.rgrids(np.arange(0.5,2,0.5),angle=45)
14 plt.thetagrids([0,45,90])
15
16 plt.show()
~ 整个代码很好理解,在后面的13,14行没见过。第一个plt.rgrids(np.arange(0.5,2,0.5),angle=45) 表示绘制半径为0.5 1.0 1.5的三个同心圆,同时将这些半径的值标记在45度位置的那个直径上面。plt.thetagrids([0,45,90]) 表示的是在theta为0,45,90度的位置上标记上度数。得到的图像是:








 本文详细介绍了使用matplotlib进行科学计算中的绘图技巧,包括对数坐标图的创建、极坐标图像绘制、柱状图、散点图以及3D图像的生成。通过实例代码,展示了matplotlib在科研绘图中的应用,帮助读者掌握matplotlib的基本操作。
本文详细介绍了使用matplotlib进行科学计算中的绘图技巧,包括对数坐标图的创建、极坐标图像绘制、柱状图、散点图以及3D图像的生成。通过实例代码,展示了matplotlib在科研绘图中的应用,帮助读者掌握matplotlib的基本操作。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章















 1113
1113

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








