参考:http://blog.csdn.net/ikerpeng/article/details/20523679
首先补充以下:7种颜色 r g b y m c k (红,绿,蓝,黄,品红,青,黑)
在科研的过程中,坐标系中的XY不一定就是等尺度的。例如在声波中对Y轴取对数。肆意我们也必须知道这种坐标系如何画出来的。
1,对数坐标图
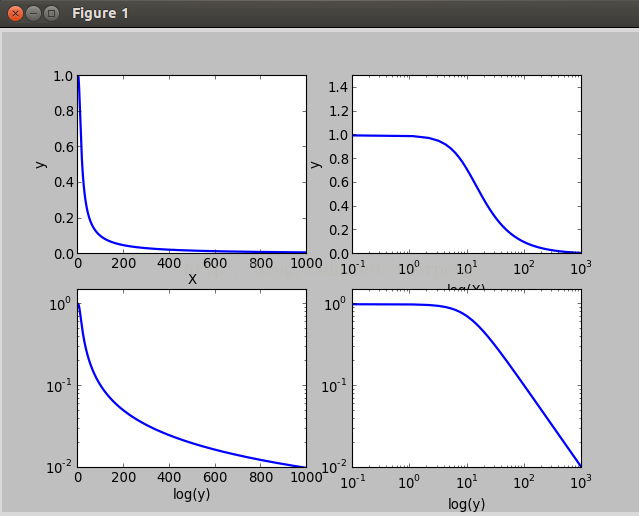
有3个函数可以实现这种功能,分别是:semilogx(),semilogy(),loglog()。它们分别表示对X轴,Y轴,XY轴取对数。下面在一个2*2的figure里面来比较这四个子图(还有plot())。
- <span style="font-size:14px;"> 1 import numpy as np
- 2 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
- 3 w=np.linspace(0.1,1000,1000)
- 4 p=np.abs(1/(1+0.1j*w))
- 5
- 6 plt.subplot(221)
- 7 plt.plot(w,p,lw=2)
- 8 plt.xlabel('X')
- 9 plt.ylabel('y')
- 10
- 11
- 12 plt.subplot(222)
- 13 plt.semilogx(w,p,lw=2)
- 14 plt.ylim(0,1.5)
- 15 plt.xlabel('log(X)')
- 16 plt.ylabel('y')
- 17
- 18 plt.subplot(223)
- 19 plt.semilogy(w,p,lw=2)
- 20 plt.ylim(0,1.5)
- 21 plt.xlabel('x')
- 22 plt.xlabel('log(y)')
- 23
- 24 plt.subplot(224)
- 25 plt.loglog(w,p,lw=2)
- 26 plt.ylim(0,1.5)
- 27 plt.xlabel('log(x)')
- 28 plt.xlabel('log(y)')
- 29 plt.show()
- </span>
如上面的代码所示,对一个低通滤波器函数绘图。得到四个不同坐标尺度的图像。如下图所示:
2,极坐标图像
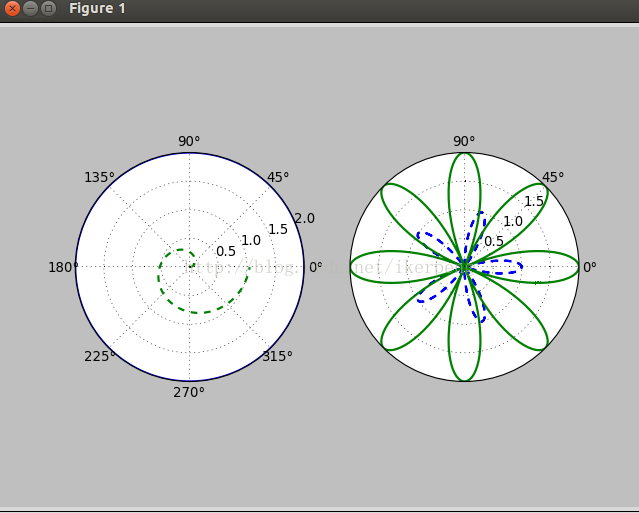
极坐标系中的点由一个夹角和一段相对于中心位置的距离来表示。其实在plot()函数里面本来就有一个polar的属性,让他为True就行了。下面绘制一个极坐标图像:
- 1 import numpy as np
- 2 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
- 3
- 4 theta=np.arange(0,2*np.pi,0.02)
- 5
- 6 plt.subplot(121,polar=True)
- 7 plt.plot(theta,2*np.ones_like(theta),lw=2)
- 8 plt.plot(theta,theta/6,'--',lw=2)
- 9
- 10 plt.subplot(122,polar=True)
- 11 plt.plot(theta,np.cos(5*theta),'--',lw=2)
- 12 plt.plot(theta,2*np.cos(4*theta),lw=2)
- 13 plt.rgrids(np.arange(0.5,2,0.5),angle=45)
- 14 plt.thetagrids([0,45,90])
- 15
- 16 plt.show()
- ~
整个代码很好理解,在后面的13,14行没见过。第一个plt.rgrids(np.arange(0.5,2,0.5),angle=45) 表示绘制半径为0.5 1.0 1.5的三个同心圆,同时将这些半径的值标记在45度位置的那个直径上面。plt.thetagrids([0,45,90]) 表示的是在theta为0,45,90度的位置上标记上度数。得到的图像是:
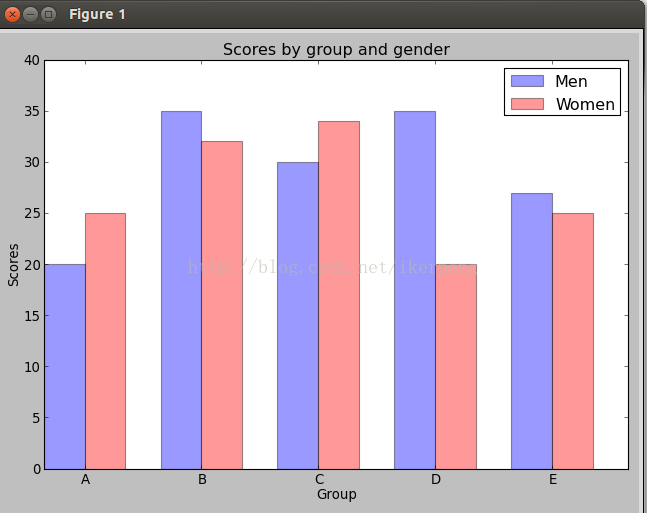
3,柱状图:核心代码matplotlib.pyplot.bar(left, height, width=0.8, bottom=None, hold=None, **kwargs)里面重要的参数是左边起点,高度,宽度。下面例子:
- 1 import numpy as np
- 2 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
- 3
- 4
- 5 n_groups = 5
- 6
- 7 means_men = (20, 35, 30, 35, 27)
- 8 means_women = (25, 32, 34, 20, 25)
- 9
- 10 fig, ax = plt.subplots()
- 11 index = np.arange(n_groups)
- 12 bar_width = 0.35
- 13
- 14 opacity = 0.4
- 15 rects1 = plt.bar(index, means_men, bar_width,alpha=opacity, color='b',label= 'Men')
- 16 rects2 = plt.bar(index + bar_width, means_women, bar_width,alpha=opacity,col or='r',label='Women')
- 17
- 18 plt.xlabel('Group')
- 19 plt.ylabel('Scores')
- 20 plt.title('Scores by group and gender')
- 21 plt.xticks(index + bar_width, ('A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E'))
- 22 plt.ylim(0,40)
- 23 plt.legend()
- 24
- 25 plt.tight_layout()
- 26 plt.show()
得到的图像是:
4,散列图,有离散的点构成的。函数是:matplotlib.pyplot.scatter(x, y, s=20, c='b', marker='o', cmap=None, norm=None, vmin=None, vmax=None, alpha=None, linewidths=None, verts=None, hold=None,**kwargs),其中,xy是点的坐标,s点的大小,maker是形状可以maker=(5,1)5表示形状是5边型,1表示是星型(0表示多边形,2放射型,3圆形);alpha表示透明度;facecolor=‘none’表示不填充。例子如下:
- 1 import numpy as np
- 2 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
- 3
- 4 plt.figure(figsize=(8,4))
- 5 x=np.random.random(100)
- 6 y=np.random.random(100)
- 7 plt.scatter(x,y,s=x*1000,c='y',marker=(5,1),alpha=0.5,lw=2,facecolors='none')
- 8 plt.xlim(0,1)
- 9 plt.ylim(0,1)
- 10
- 11 plt.show()
上面代码的facecolors参数使得前面的c=‘y’不起作用了。图像:

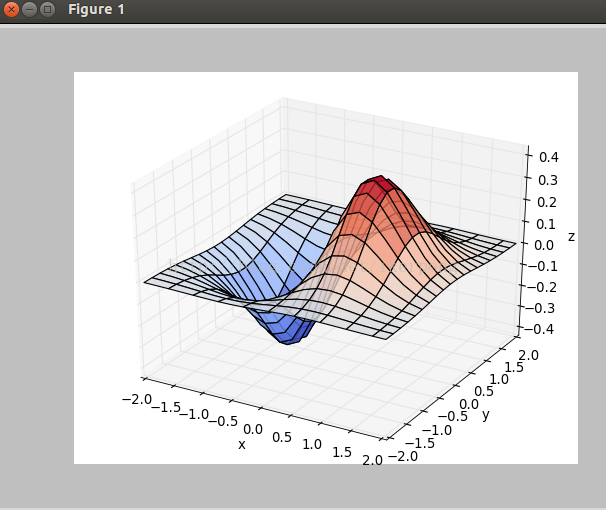
5,3D图像,主要是调用3D图像库。看下面的例子:
- 1 import numpy as np
- 2 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
- 3 import mpl_toolkits.mplot3d
- 4
- 5 x,y=np.mgrid[-2:2:20j,-2:2:20j]
- 6 z=x*np.exp(-x**2-y**2)
- 7
- 8 ax=plt.subplot(111,projection='3d')
- 9 ax.plot_surface(x,y,z,rstride=2,cstride=1,cmap=plt.cm.coolwarm,alpha=0.8)
- 10 ax.set_xlabel('x')
- 11 ax.set_ylabel('y')
- 12 ax.set_zlabel('z')
- 13
- 14 plt.show()
得到的图像如下图所示:
到此,matplotlib基本操作的学习结束了,相信大家也可以基本完成自己的科研任务了。下面将继续学习Python的相关课程,请继续关注。
参考书目:
《python科学计算》
《matplotlib手册》



























 122
122

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








