写这篇文章的起因是看到何登成博士发的一个微博问题,如下:

自己想不太明白,顺下找了他以前分享的一些资料和其他人的博客阅读,在这里做个笔记,内容主要来自何博的ppt。关于微博问题的讨论最后再说。
实际上问题所涉及到的知识点非常多,我也有很多还没理解,这里尽量省去细枝末节,更详细的内容请参考附录链接。
一. Cache Coherence
1. What is a cache? cache line ?
cache : Small, fast storage used to improve average access time to slow memory.
cache line : The minimum amount of cache which can be loaded or stored to memory
2. Cache Write Policy
– Write Back
•脏数据,写出到Cache;
– Write Through
•脏数据,写穿到Memory;
– Write Invalidate(大部分系统采用)
Write时,同时发出Invalidate消息,使得所有其他CPU L1/L2 Cache中同一Cache Line失效
– Write Update
•Write时,同时更新其他CPU L1/L2 Cache中同一Cache Line;
3.
Cache Coherence
在多核处理器上,由于每个核都有自己的cache,如果有多层cache,如L3往往是多核共享的。所以会存在Cache Coherence 问题,
False cache line sharing:When one processor modifies a value in its cache, other processors cannot use the old value anymore.
That memory location will be invalidated in all of the caches. Furthermore, since caches operate on the granularity of cache lines and
not individual bytes, the entire cache line will be invalidated in all caches!
Cache Coherence Protocol (MESI, MOESI),作用于CPU Cache与Memory层面,若操作的数据在Register,或者是Register与L1
Cache之间(下面会提到的Store Buffer,Load Buffer),则这些数据不会参与Cache Coherence协议。
二、Atomic Operation
•An operation acting on shared memory is atomic if it completes in a single step relative to other threads. When an atomic store is performed on a shared variable, no other thread can observe the modification half-complete. When an atomic load is performed on a shared variable, it reads the entire value as it appeared at a single moment in time.
1. 高级语言与汇编指令的映射
高级语言(如:C/C++),被编译为汇编语言,才能够被执行。因此,高级语言与汇编语言之间,存在着几种简单的映射关系。
•Simple Write
– Write to Memory

– Atomic
•Simple Read
–Read from Memory

–Atomic (
注:实际上这里是指将a 读取到寄存器eax是atomic的,赋值语句b=a 包括两条汇编命令,不是atomic的)
•Read-Modify-Write(RMW)
– Read from Memory
– Modify

– Write to Memory
– Non-Atomic
•Read/Write 64 Bits on 32 Bits Systems
– Write:Non-Atomic
– Read:Non-Atomic
2. Non-Atomic 的危害(在32位机上读写64位数如上图)
•Half Write
– mov dword ptr [c], 2 执行后,会短暂出现c的half write现象;
•Half Read
–若c 出现half write,则读取c 会出现half read现象;
•Composite Write
– 两个线程同时write c,一个完成,一个half write,则c的值,来自线程1,2两个write操作的组合;
•危害
– 出现Half Read,会导致程序判断逻辑出错;出现Composite Write,会导致数据出错
3. 如何消除Non-Atomic Read/Write?
•Intel/AMD CPU 平台方面 (参考各CPU白皮书)
– Aligned 2-,4-Byte Simple Read/Write -> Atomic
– Aligned 8-Byte,CPU型号判断-> 一般为Atomic
– Unaligned 2-, 4-, 8-Byte,CPU型号判断 -> 尽量少用
•RMW Operation
尽量使用系统自带的,或者是提供的原子操作函数;这些函数,对不同CPU类型,做了较好的封装,更加易用;
4. Atomic Instructions and Lock
•Atomic Instructions
– 常见指令:CMPXCHG,XCHG,XADD,...
– CMPXCHG(compare-and-exchange)

•将Operand1(Reg/Mem)中的内容与EAX比较,若相等,则拷贝Operand2(Reg)中的内容至Operand1;若不等,
则将Operand2中的数据写入EAX;
•一个Atomic RMW操作,若Operand1为Memory,则CMPXCHG指令还需要Lock指令配合 (Lock prefix);
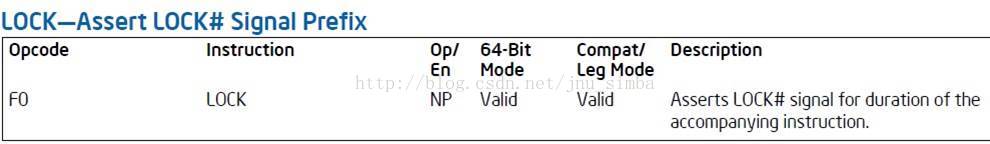
•Lock Instruction
– Lock指令是一个前缀,可以用在很多指令之前,代表当前指令
所操作的内存(Memory),在指令执行期间,只能被当前CPU所用;
– Intel’s Description about Lock Instruction
– Lock with CMPXCHG

- x++可以用汇编来写 : __asm LOCK inc dword ptr[x]
三、Memory Ordering(Reordering)
1.Reordering
Reads and writes do not always happen in the order that you have written them in your code.
用户程序,无论是在编译期间,还是在执行期间,都会产生Reordering;
•Why Reordering
– Performance
•Reordering Principle
– In single threaded programs from the programmer'












 本文从缓存一致性问题开始,探讨了多核处理器中的Cache Write Policy和Cache Coherence Protocol。接着,介绍了原子操作的重要性,特别是在32位系统中处理64位数据的场景。接着,讲解了内存排序(Reordering)和CPU Memory Barrier的使用。对于volatile关键字,对比了C/C++和Java中的行为,并指出在多线程环境中,volatile无法确保指令执行顺序,可能需要额外的内存屏障。最后,通过一个测试代码案例讨论了内存屏障在多核处理器上的影响。
本文从缓存一致性问题开始,探讨了多核处理器中的Cache Write Policy和Cache Coherence Protocol。接着,介绍了原子操作的重要性,特别是在32位系统中处理64位数据的场景。接着,讲解了内存排序(Reordering)和CPU Memory Barrier的使用。对于volatile关键字,对比了C/C++和Java中的行为,并指出在多线程环境中,volatile无法确保指令执行顺序,可能需要额外的内存屏障。最后,通过一个测试代码案例讨论了内存屏障在多核处理器上的影响。

 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
















 1597
1597

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








