1、综述
这里尝试探究一下属性动画的运行原理及各种魔性的动画如何自定义出来(前提是我们已经对系统提供的属性动画的基本调用流程已经了然)。
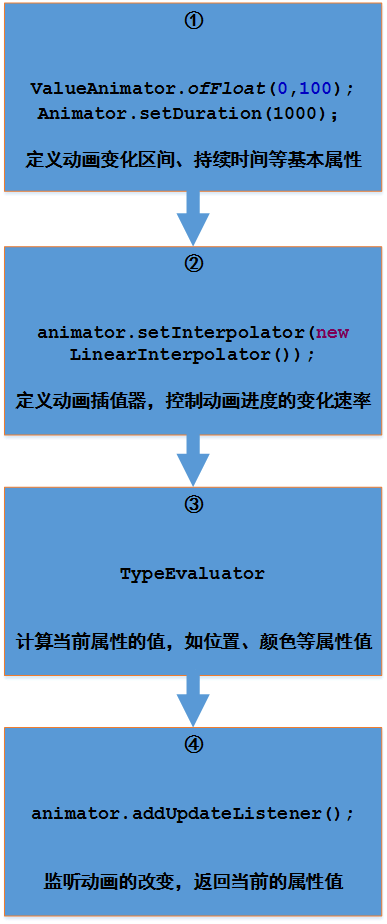
整体流程:
以上流程中①、④按需要调用系统相对应方法即可,这里主要看②、③步,其中简单的使用系统动画的话②、③均可以省略,因为系统已经默认做了默认实现。本篇重点探究第②步,记录一下自己对Interpolator的理解。
2、Interpolator?
扒出Interpolator源码看看先:
public interface Interpolator extends TimeInterpolator {
// A new interface, TimeInterpolator, was introduced for the new android.animation
// package. This older Interpolator interface extends TimeInterpolator so that users of
// the new Animator-based animations can use either the old Interpolator implementations or
// new classes that implement TimeInterpolator directly.
}
再看看TimeInterpolator:
/**
* A time interpolator defines the rate of change of an animation. This allows animations
* to have non-linear motion, such as acceleration and deceleration.
*/
public interface TimeInterpolator {
/**
* Maps a value representing the elapsed fraction of an animation to a value that represents
* the interpolated fraction. This interpolated value is then multiplied by the change in
* value of an animation to derive the animated value at the current elapsed animation time.
*
* @param input A value between 0 and 1.0 indicating our current point
* in the animation where 0 represents the start and 1.0 represents
* the end
* @return The interpolation value. This value can be more than 1.0 for
* interpolators which overshoot their targets, or less than 0 for
* interpolators that undershoot their targets.
*/
float getInterpolation(float input);
}可见插值器的作用是用来定义动画的改变速率的,可以用来定义非线性的变化,如加速、减速。
有一个待实现的方法 floatgetInterpolation(float input);
输入:input,这个参数的取值范围是[0,1],可以理解为所设置的动画时间(setDuration(1000))的一个线性映射,即0代表动画开始执行0ms,1代表动画结束1000ms。
输出:此方法是有返回值的,返回值的返回没有限定,但一般需要保证返回值的范围也是[0,1],如果返回<0或>1的数值,那么动画将跳出你所设定的范围,即步骤①中ValueAnimator.ofFloat(0,100)所设定的 [0,100]的变化范围,如果是设置动画平移等运动的话可能跑出屏幕。这里的返回值是经过处理后的动画进度,可以理解为加快或减慢了单次动画的执行时间,如直接return 1f,那么动画直接进入到结束的状态(那就不是动画了,一开始就已经进度为1了 ,开始就结束了,Oh ,god)。
3、解析系统提供的Interpolator
系统已经为我们实现的Interpolator如下:
为了演示效果,这里绘制一个小球,动画控制其下落。
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
width = getWidth();
height = getHeight();
mPaint.setStyle(Style.FILL);
mPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
mPaint.setColor(Color.MAGENTA);
if (cy == -1) {
startAnimationMotion();// 执行动画
}
canvas.drawCircle(width / 2, cy, 30, mPaint);
} private void startAnimationMotion() {
ValueAnimator animator = ValueAnimator.ofFloat(mRadius, height
- mRadius);
animator.setDuration(3000).setRepeatCount(3);
animator.addUpdateListener(new AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator animation) {
cy = (Float) animation.getAnimatedValue();
invalidate();
}
});
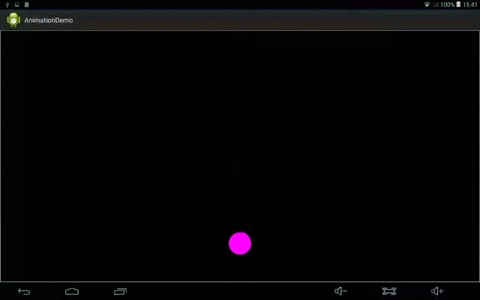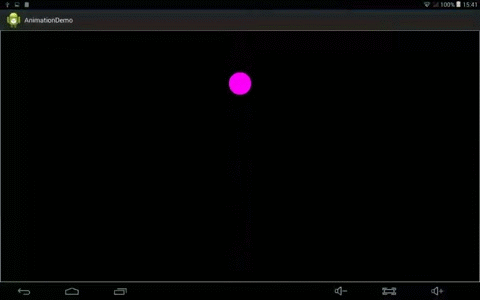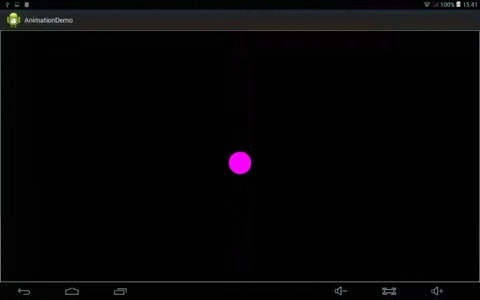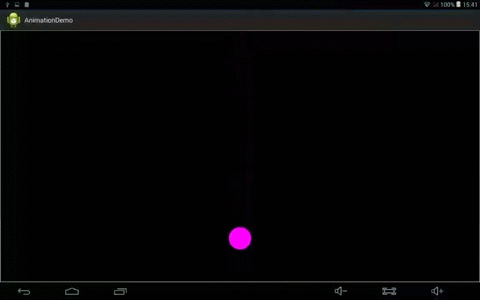
animator.setInterpolator(new LinearInterpolator());//设置插值器
animator.start();
}1、 LinearInterpolator
先看一下系统实现的插值器LinearInterpolator源码:
/**
* An interpolator where the rate of change is constant
*
*/
public class LinearInterpolator implements Interpolator {
public LinearInterpolator() {
}
public LinearInterpolator(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
}
public float getInterpolation(float input) {
return input;
}
}
函数图像:
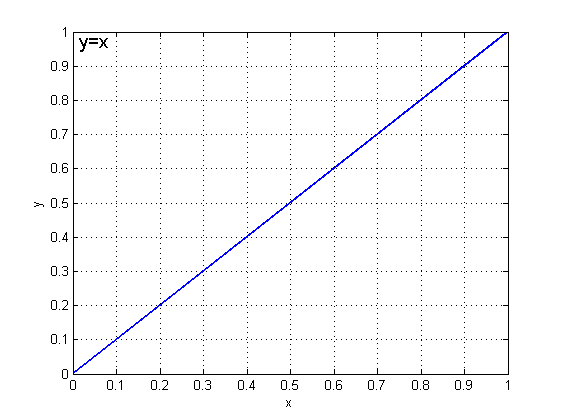
效果:
2 、AccelerateDecelerateInterpolator
先加速后减速插值器,即中间变化最快。
**
* An interpolator where the rate of change starts and ends slowly but
* accelerates through the middle.
*
*/
public class AccelerateDecelerateInterpolator implements Interpolator {
public AccelerateDecelerateInterpolator() {
}
@SuppressWarnings({"UnusedDeclaration"})
public AccelerateDecelerateInterpolator(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
}
public float getInterpolation(float input) {
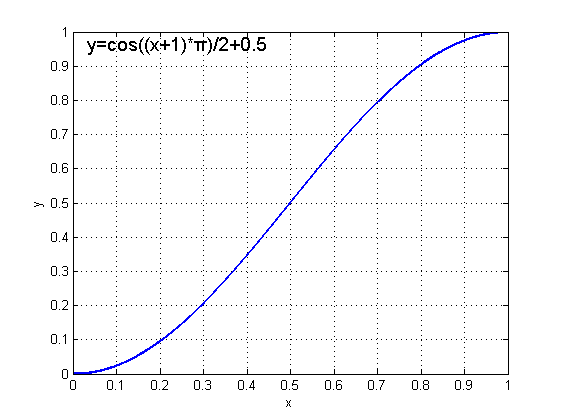
return (float)(Math.cos((input + 1) * Math.PI) / 2.0f) + 0.5f;
}
}图像:
效果:
3 、BounceInterpolator
这是一个模拟弹跳效果的插值器。
/**
* An interpolator where the change bounces at the end.
*/
public class BounceInterpolator implements Interpolator {
public BounceInterpolator() {
}
@SuppressWarnings({"UnusedDeclaration"})
public BounceInterpolator(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
}
private static float bounce(float t) {
return t * t * 8.0f;
}
public float getInterpolation(float t) {
// _b(t) = t * t * 8
// bs(t) = _b(t) for t < 0.3535
// bs(t) = _b(t - 0.54719) + 0.7 for t < 0.7408
// bs(t) = _b(t - 0.8526) + 0.9 for t < 0.9644
// bs(t) = _b(t - 1.0435) + 0.95 for t <= 1.0
// b(t) = bs(t * 1.1226)
t *= 1.1226f;
if (t < 0.3535f) return bounce(t);
else if (t < 0.7408f) return bounce(t - 0.54719f) + 0.7f;
else if (t < 0.9644f) return bounce(t - 0.8526f) + 0.9f;
else return bounce(t - 1.0435f) + 0.95f;
}
}
matlab绘图:
x=0:0.0000001:1;
t=x *1.1226;
y=(t.^2* 8).*(0<t&t<0.3535)+((t - 0.54719).^2* 8+0.7).*(t>=0.3535&t<0.7408)+((t - 0.8526).^2* 8 + 0.9)
.*(t>=0.7408&t<0.9644)+((t - 1.0435).^2* 8 + 0.95).*(t>=0.9644); %整个表达式需同一行
plot(x,y,'LineWidth',2)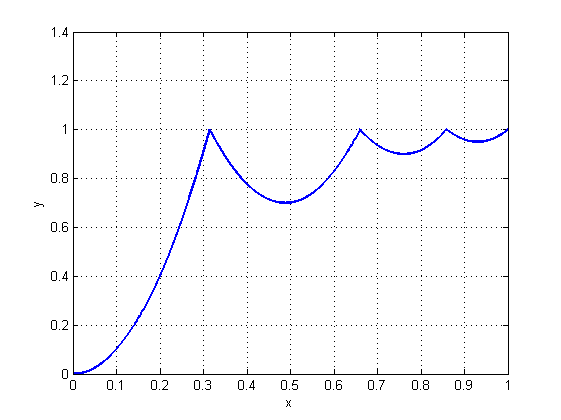
效果:
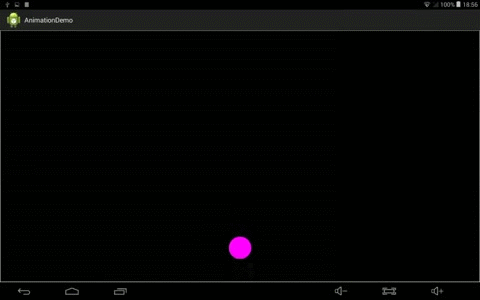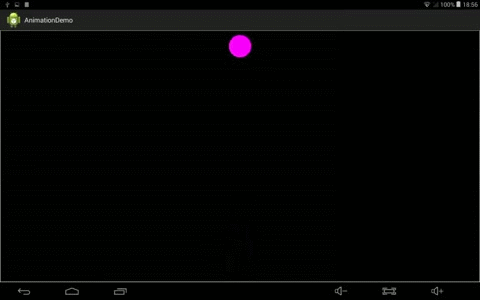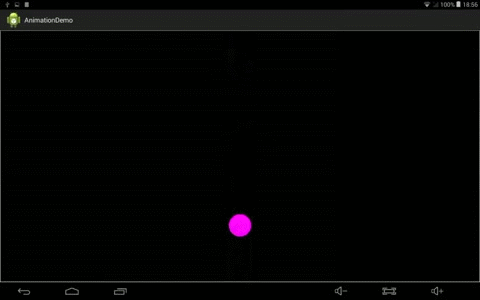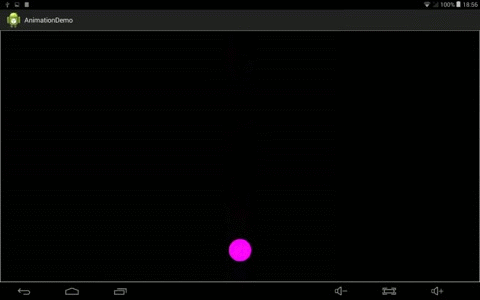
4、自己实现Interpolator
通过以上观察系统的的实现过程,我们可以自己根据需求定义Interpolator了。
1、定义OvershootInterPolator
这是一个一直加速的插值器返回值范围[0,2],这里验证一下当返回值的变化范围超过[0,1]时将会出现什么情况。
/**
*一直加速,返回值范围超出0-1
*/
class OvershootInterPolator implements TimeInterpolator {
@Override
public float getInterpolation(float input) {
return (float) (2 * Math.pow(input, 3));
}
}
图像:
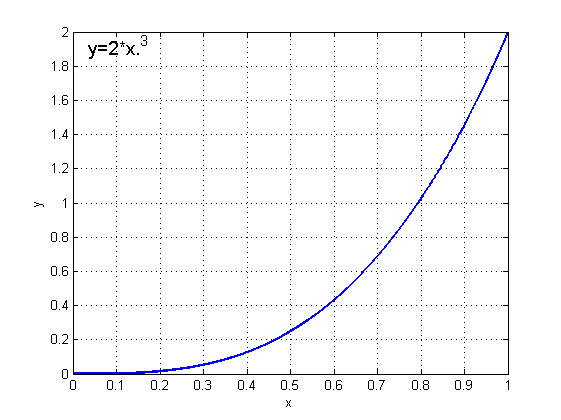
效果:

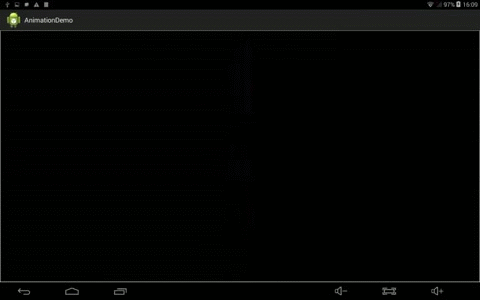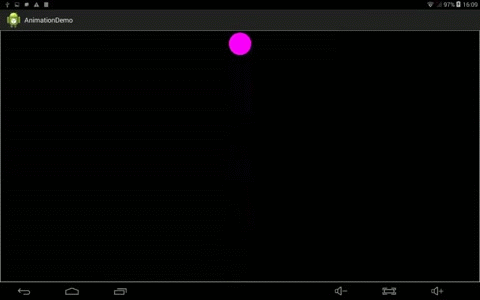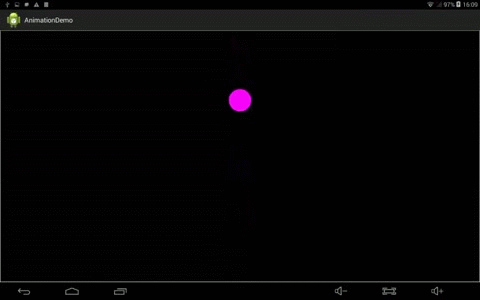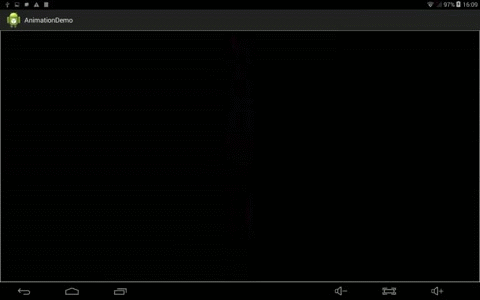
2、定义OscillationInterPolator
这里模拟定义一个衰减振荡的效果
/**
* 衰减振荡
*/
class OscillationInterPolator implements TimeInterpolator {
@Override
public float getInterpolation(float input) {
float output = (float) (Math.exp(-3 * input) * Math.sin(10 * Math.PI * input));
return Math.abs(output);
}
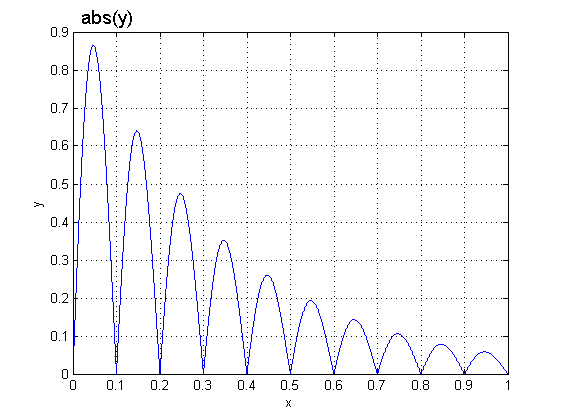
}y=|exp(-3*t).*sin(10*pi*t)|;
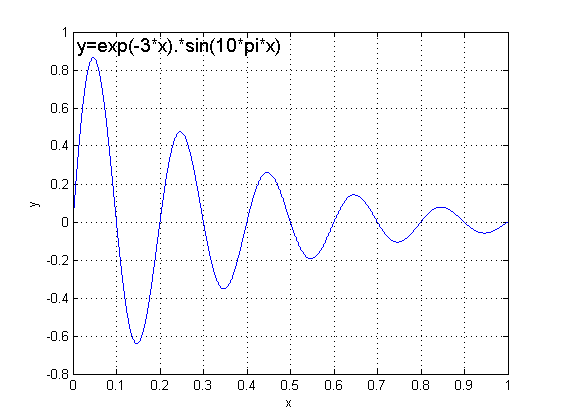
不让返回值超出[0,1],这里取y的绝对值
这里动画时间改长一点
animator.setDuration(6000);
好了,这里是对文章综述中步骤2关于插值器的详细介绍,先到这里,关与步骤3
TypeEvaluator,参见: Android 属性动画探究(二)——TypeEvaluator解析与自定义。
























 616
616

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








